【Redis源码剖析】 - Redis内置数据结构之字典dict
今天我们来讲讲Redis中的哈希表。哈希表在C++中对应的是map数据结构,但在redis中称作dict(字典)。Redis只是用了几个简单的结构体和几种常见的哈希算法就实现了一个简单的类似高级语言中的map结构。下面我们来具体分析一下dict的实现。
在学习数据结构的时候,我们接触过一种称作“散列表”的结构,可以根据关键字而直接访问记录。说的具体一点就是通过把key值映射到表中的一个位置来访问,从而加快查找速度。Redis中的dict数据结构和我们之前学过的“散列表”大同小异。总结如下:
1、dict的结构
Redis定义了dictEntry、dictType、dictht和dict四个结构体来实现散列表的功能。它们具体定义如下:
(1)dictEntry结构体
/* 保存键值(key - value)对的结构体,类似于STL的pair。*/
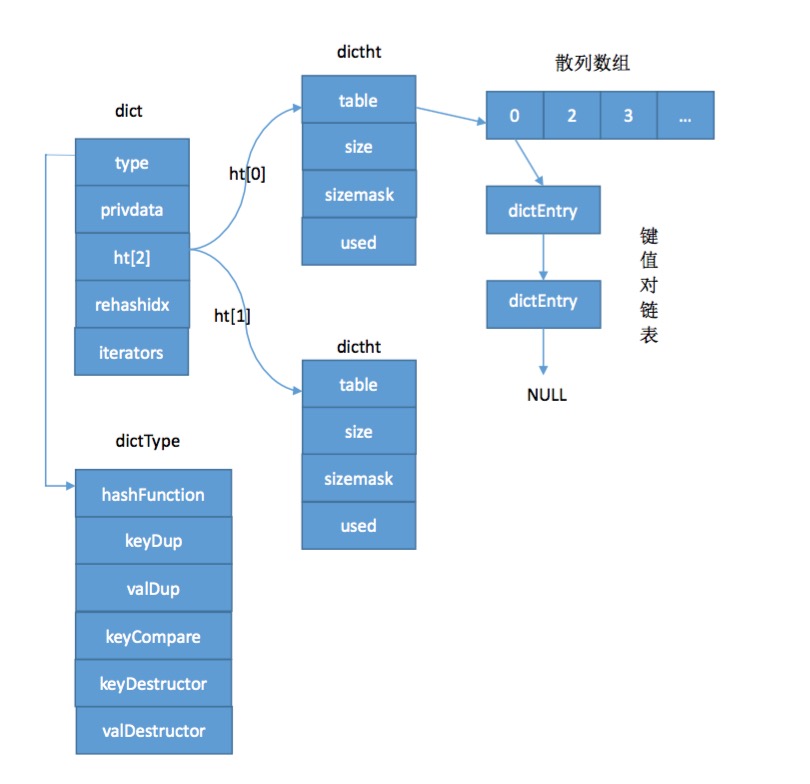
typedef struct dictEntry {// 关键字key定义void *key; // 值value定义,只能存放一个被选中的成员union {void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; double d; } v;// 指向下一个键值对节点struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;从dictEntry的定义我们也可以看出dict通过“拉链法”来解决冲突问题。
(2)、dictType结构体
/* 定义了字典操作的公共方法,类似于adlist.h文件中list的定义,将对节点的公共操作方法统一定义。搞不明白为什么要命名为dictType */
typedef struct dictType {/* hash方法,根据关键字计算哈希值 */unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);/* 复制key */void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);/* 复制value */void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);/* 关键字比较方法 */int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);/* 销毁key */void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);/* 销毁value */void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;(3)、dictht结构体
/* 哈希表结构 */
typedef struct dictht {// 散列数组。dictEntry **table;// 散列数组的长度unsigned long size;// sizemask等于size减1unsigned long sizemask;// 散列数组中已经被使用的节点数量unsigned long used;
} dictht;/* 字典的主操作类,对dictht结构再次包装 */
typedef struct dict {// 字典类型dictType *type;// 私有数据void *privdata;// 一个字典中有两个哈希表dictht ht[2];// 数据动态迁移的下标位置long rehashidx; // 当前正在使用的迭代器的数量int iterators;
} dict;这四个结构体之间的关系如下:
2、散列函数
Redis提供了三种不同的散列函数,分别是:
(1)、使用Thomas Wang’s 32 bit Mix哈希算法,对一个整型进行哈希,该方法在dictIntHashFunction函数中实现。
(2)、使用MurmurHash2哈希算法对字符串进行哈希,该方法在dictGenHashFunction函数中实现。
(3)、在dictGenCaseHashFunction函数中提供了一种比较简单的哈希算法,对字符串进行哈希
上面这三种方法的实现具体可以参考下面的代码。至于这几种方法的优劣,这里就不展开讲了(我自己也不是很清楚),大家可以自行google一下。
3、Rehash操作
Rehash是dict一个很重要的操作。在前面我们看到dict结构体中有两个哈希表(定义为dictht ht[2])。通常情况下,dict中的所有数据(键值对)都存放在ht[0],但随着dict中数据量的增加需要进行扩容操作(为什么?数据越多,冲突的元素越多,ht[0]中的链表越长,查找效率越低),此时就需要进行rehash。dict在rehash的时先申请一个更大的空间并用ht[1]指向该空间,然后把ht[0]中的所有数据rehash到ht[1]中,数据迁移完毕后在将ht[1]赋值给ht[0]并清空ht[1]。如果这个rehash过程是一次性完成的倒是很好理解,但从其源码中我们可以看出:dict的rehash操作并不是一次性完成的,而是分成多步。具体来说dict提供了两种不同的策略:一种是每次将ht[0]中的一个bucket,也就是散列数组中对应的一个链表中的所有数据进行rehash到ht[1]中,对应的函数是_dictRehashStep。另一种是每次执行一段固定的时间,时间到了就暂停rehash操作,对应的函数是dictRehashMilliseconds。
_dictRehashStep和dictRehashMilliseconds底层都调用了dictRehash函数来进行rehash操作。实现如下:
/* 执行n步渐进式的rehash操作,如果还有key需要从旧表迁移到新表则返回1,否则返回0 */
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;// n步渐进式的rehash操作就是每次只迁移哈希数组中的n个bucketwhile(n--) {dictEntry *de, *nextde;/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */// 检查是否对整个哈希表进行了rehash操作if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {zfree(d->ht[0].table);d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);d->rehashidx = -1;return 0;}/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */// rehashidx标记的是当前rehash操作进行到了ht[0]旧表的那个位置(下标),因此需要判断它是否操作ht[0]的长度assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);// 跳过ht[0]中前面为空的位置while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++;// 得到对应的链表de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */// 下面的操作将每个节点(键值对)从ht[0]迁移到ht[1],此过程需要重新计算每个节点key的哈希值while(de) {unsigned int h;nextde = de->next;/* Get the index in the new hash table */h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];d->ht[1].table[h] = de;d->ht[0].used--;d->ht[1].used++;de = nextde;}d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;d->rehashidx++;}return 1;
}dictRehash函数执行N步rehash操作。每步中,首先判断是否已经完成了rehashN操作,判断的标准就是ht[0]的used是否为0。ht[0]的used == 0说明ht[0]中所有的链表都是空的,那么所有的元素都已经移动到ht[1]中。此时,将ht[1]赋值给ht[0],清空ht[1]。将rehashidx赋值为-1表明rehash结束。如果rehash没有结束,那么,查找ht[0]中下一个非空的桶。将这个桶中的所有数据rehash到ht[1]中。
既然rehash操作是分步进行的,那dict就可能存在这样一种状态:既有数据存放在ht[0]中,又有数据存放在ht[1]中。这样在对dict进行访问的时候就要加以区别。对于dictFind、dictDelete函数,需要遍历ht[0]和ht[1]两个表,对于dictAdd函数则需要根据当前dict是否在执行rehash操作来决定将键值对插入ht[0]还是ht[1]中。在下面的源码中,我们可以看到这些函数的具体实现。
dict的注意点大概就是这些,其它的都比较简单就直接贴代码了。大部分代码我都写了注释,如下:
dict.h头文件:
/* Hash Tables Implementation.** This file implements in-memory hash tables with insert/del/replace/find/* get-random-element operations. Hash tables will auto-resize if needed* tables of power of two in size are used, collisions are handled by* chaining. See the source code for more information... :)** Copyright (c) 2006-2012, Salvatore Sanfilippo * All rights reserved.** Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:** * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.* * Neither the name of Redis nor the names of its contributors may be used* to endorse or promote products derived from this software without* specific prior written permission.** THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.*/ #include /* Hash Tables Implementation.** This file implements in memory hash tables with insert/del/replace/find/* get-random-element operations. Hash tables will auto resize if needed* tables of power of two in size are used, collisions are handled by* chaining. See the source code for more information... :)** Copyright (c) 2006-2012, Salvatore Sanfilippo * All rights reserved.** Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:** * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.* * Neither the name of Redis nor the names of its contributors may be used* to endorse or promote products derived from this software without* specific prior written permission.** THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.*/ #include "fmacros.h"#include 本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!