算法练习day10——190328(二叉树的先序、 中序、 后序遍历, 包括递归方式和非递归方式、找到一个节点的后继节点、二叉树的序列化和反序列化)
1.实现二叉树的先序、 中序、 后序遍历, 包括递归方式和非递归方式
1.1 访问节点的顺序
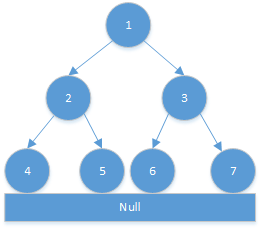
节点访问顺序如下图所示:

访问顺序:1 2 4 4 4 2 5 5 5 2 1 3 6 6 6 3 7 7 7 3 1
先序遍历:当节点第一次出现时就打印——1 2 4 5 3 6 7 (1 2 4 4 4 2 5 5 5 2 1 3 6 6 6 3 7 7 7 3 1)
中序遍历:当节点出现第二次时就打印——4 2 5 1 6 3 7 (1 2 4 4 4 2 5 5 5 2 1 3 6 6 6 3 7 7 7 3 1)
后序遍历:当节点出现第三次时才打印——4 5 2 6 7 3 1 (1 2 4 4 4 2 5 5 5 2 1 3 6 6 6 3 7 7 7 3 1)
1.2 递归实现
package Tree;public class VisitNode {public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(1);head.left = new Node(2);head.right = new Node(3);head.left.left = new Node(4);head.left.right = new Node(5);head.right.left = new Node(6);head.right.right = new Node(7);preOrder(head);System.out.println();inOrder(head);System.out.println();postOrder(head);System.out.println();}public static void preOrder(Node root) {if(root==null)return;System.out.print(root.value+" ");preOrder(root.left);preOrder(root.right);}public static void inOrder(Node root) {if(root==null)return;inOrder(root.left);System.out.print(root.value+" ");inOrder(root.right);}public static void postOrder(Node root) {if(root==null)return;postOrder(root.left);postOrder(root.right);System.out.print(root.value+" ");}
}
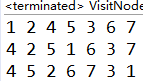
运行结果:
1.3 非递归实现
1.3.1 先序遍历
分析:
需要用到一个辅助栈。
- 先把根节点压入栈中;
- 栈不为空时,弹出一个元素,并打印;
- 若它右孩子不为空,右孩子入栈,若左孩子不为空,左孩子也入栈。

代码实现:
public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node root) {System.out.println("preOrderUnRecur:");if(root!=null) {Stack stack=new Stack();stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()) {Node cur=stack.pop();System.out.print(cur.value+" ");if(cur.right!=null)stack.push(cur.right);if(cur.left!=null)stack.push(cur.left);}}System.out.println();
} 1.3.2 中序遍历
分析:
当前节点不为空时,先把自己的压到栈中,然后向左孩子移动;
当前节点为空时,栈顶元素出栈,打印,然后向栈顶元素的右孩子移动。
步骤:
压入1,1的左孩子2,2的左孩子4。
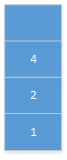
4 的左孩子为空,栈顶元素出栈:
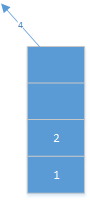
然后4向它的右孩子走,还为空,栈顶元素出栈:

然后2向它的右孩子5走,不为空,入栈:

5向左孩子走,为空,栈顶元素出栈:

5向右孩子走,还为空,栈顶元素出栈:

1向它的右孩子3走,不为空,入栈.....(后面不再赘述)
代码实现:
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node root) {System.out.println("inOrderUnRecur:");if(root!=null) {Stack stack=new Stack();while(!stack.isEmpty()||root!=null) {if(root!=null) {//以节点不为空的条件进来stack.push(root);root=root.left;}else {//以栈不为空的条件进来root=stack.pop();System.out.print(root.value+" ");root=root.right;}}}System.out.println();
} 1.3.3 后序遍历
分析:
先序遍历的打印顺序是:中左右,现在调整为中右左,就是:
先压入当前节点的右孩子,再压左孩子。
然后打印顺序就为中右左。
后序遍历打印顺序是:左右中,和目前已实现的顺序刚好相反。使用栈来实现顺序反转。
代码实现:
public static void postOrderUnRecur(Node root) {System.out.println("postOrderUnRecur:");Stack help=new Stack();if(root!=null) {Stack stack=new Stack();stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()) {Node cur=stack.pop();help.push(cur);if(cur.left!=null)stack.push(cur.left);if(cur.right!=null)stack.push(cur.right);}}while(!help.isEmpty())System.out.print(help.pop().value+" ");System.out.println();
} 2.打印一个二叉树
3.在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点
【题目】 现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node {public int value;public Node left;public Node right; public Node parent;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}
}该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。
假设有一 棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树, 树中每个节点的parent指针都正确地指向自己的父节点, 头节点的parent指向null。
只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点 node, 请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。
在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中, node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点。
3.1 分析
方法1:
可以根据给定节点的parent指针回到根节点(parent为空的节点),然后进行一次中序遍历,得到中序序列,即可得到这个节点的后继节点。——复杂度是遍历整棵树
方法2:
——复杂度是当前节点到它后继的距离。
3.2 方法2的具体分析
当前节点若有右子树,则它的后继节点是右子树的最左节点;
若当前节点没有右子树:
- 找以当前节点作为左子树最后一个节点的节点:
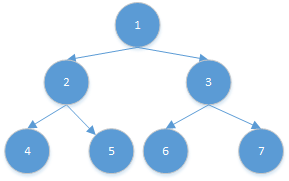
- 比如节点4,它是作为节点2的左子树的最后一个节点的,节点2即为要找的节点;
- 比如节点5,它是作为节点1的左子树的最后一个节点的,节点1即为要找的节点。
具体寻找方法:
- 当前节点通过parent指针找到父节点;
- 它是父节点的左孩子吗?
- 不是,继续往上走;
- 是,那后继节点就为这个父节点。
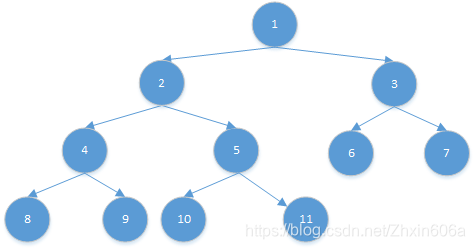
比如,给定的节点是11。
它的父节点是5,11不是5的左孩子,继续往上;
5的父节点是2,5不是2的左孩子,继续往上;
2的父节点是1,2是1的左孩子,则11的后继节点是1。
3.3 代码实现
package Tree;public class GetSuccessorNode {public static class Node{Node left;Node right;Node parent;int value;public Node(int value) {this.value=value;}}public static void main(String[] args) {Node head = new Node(6);head.parent = null;head.left = new Node(3);head.left.parent = head;head.left.left = new Node(1);head.left.left.parent = head.left;head.left.left.right = new Node(2);head.left.left.right.parent = head.left.left;head.left.right = new Node(4);head.left.right.parent = head.left;head.left.right.right = new Node(5);head.left.right.right.parent = head.left.right;head.right = new Node(9);head.right.parent = head;head.right.left = new Node(8);head.right.left.parent = head.right;head.right.left.left = new Node(7);head.right.left.left.parent = head.right.left;head.right.right = new Node(10);head.right.right.parent = head.right;Node test = head.left.left;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.left.left.right;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.left;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.left.right;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.left.right.right;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.right.left.left;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.right.left;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.right;System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);test = head.right.right; // 10's next is nullSystem.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test));}public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {if(node==null)return null;Node cur=null;if(node.right!=null) {//有右孩子,则后继是右孩子的最左节点cur=node.right;while(cur.left!=null) {//注意循环终止条件,返回最后的没有左孩子的节点,而不是返回一个null节点!!cur=cur.left;}return cur;}else {//没有右孩子,向上找符合条件的父节点cur=node.parent;while(cur!=null&&node!=cur.left) {//注意条件!应先判断cur不为null,再判断node和cur.left的关系!不能反node=cur;cur=cur.parent;} return cur;}}
}
运行结果:

3.4 找前驱节点
如果当前节点有左子树,则为左子树中最右的节点;
如果当前节点没有左子树,则:
- 当前节点通过parent指针找到父节点;
- 它是父节点的右孩子吗?
- 不是,继续往上走;
- 是,那前驱节点就为这个父节点。
4.二叉树的序列化和反序列化
记录一棵树的方式,以便后面可以恢复出来。
4.1 先序序列化
空节点用#表示
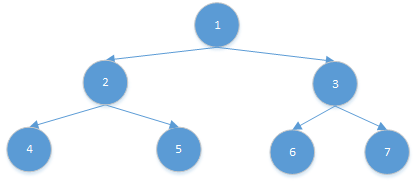
按先序遍历,得到一个字符串(节点之间用_连接):
1_2_4_#_#_5_#_#_3_6_#_#_7_#_#
4.2 反序列化
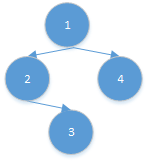
此树的先序序列化结果为:1_2_#_3_#_#_4_#_#
构建时,根据_,将字符串划分组,并放入队列中:
1、2、#、3、#、#、4、#、#
由于是先序遍历,最开始的1肯定是根;
2是1的左子树的根节点;
接着#表名,2左子树为空,则继续建2的右子树;
3为2的右子树的根节点;
#说明,3没有左子树;继续看3的右子树;
#表名3没有右子树;往上返:2的树建立完整,1还没有,继续1的右子树
接着的4是1右子树的根节点;
#表名,4没有左子树,接着建4的右子树;
#表名4没有右子树。
结束!
4.3 代码实现
public static String PreSeriaTree(Node root) {if(root==null)return "#_";String result=root.value+"_";result+=PreSeriaTree(root.left);result+=PreSeriaTree(root.right);return result;
}public static Node reconByPreString(String str) {String[] arr=str.split("_");Queue queue=new LinkedList();for(int i=0;i queue) {String value = queue.poll();if (value.equals("#")) {return null;}Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value));head.left = reconPreOrder(queue);head.right = reconPreOrder(queue);return head;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!