用原生 JS 写一个象棋小游戏
前言
最近没什么需求,借着上班摸鱼的时间,写点代码玩玩。过年的时候总是和爷爷下象棋,这次用原生JS写了一个象棋小游戏,但是技术有限,只能自己一个人左右手互博来下棋。象棋规则基本上都实现了,下面就来给大家分享一下。
我正在参与码上掘金编程挑战赛,请为我点赞吧!
一、绘制棋盘和棋子
游戏的元素是棋盘和棋子,图片都是在网上搜,然后用截图工具截下来,就可以直接使用了。棋子通过遍历数组来渲染,因为棋子的种类很多,所以给数组里的元素添加了一些属性,num值对应的是棋子的类型,type值对应棋子的阵营。公共的属性和方法写在棋子父类里,每一种的棋子都继承这个父类的属性。
**css:**
table {position: relative;width: 627px;height: 600px;margin: 0 auto;padding: 6px;border: 5px solid black;background: url(./棋盘.png);}td {width: 60px;height: 64px;border-radius: 50%;margin-right: 10px;cursor: pointer;}.bgc1 {background: url(./车.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc2 {background: url(./马.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc3 {background: url(./象.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc4 {background: url(./士.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 2px -1px;}.bgc5 {background: url(./将.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc6 {background: url(./炮.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc7 {background: url(./卒.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc8{background: url(./车2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc9{background: url(./马2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc10{background: url(./相2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc11{background: url(./仕2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc12{background: url(./帅2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc13{background: url(./炮2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.bgc14{background: url(./兵2.png);background-size: 94%;background-position: 1px 0px;}.message1,.message2{position: absolute;left: 45%;top: 40%;width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: rgba(138, 136, 136, 0.493);line-height: 100px;font-size: 60px;color: red;}.message1{display: none;}.message2{display: none;width: 200px;}.message3{position: absolute;left: 20%;top: 40%;width: 100px;height: 100px;line-height: 100px;font-size: 60px;color: red;}/* 棋子选中的样式 */.checked { transform: translateY(-15px);transition: all .2s;}/* 棋子可移动坐标显示的样式 */.showWays{position: relative;}.showWays::after{content:'';position: absolute;top: 25px;left: 25px;background-color: rgb(19, 23, 235);width: 10px;height: 10px;}
**html:**
吃!将军!红先
**js:**let list = [ // 棋盘的初始化布局,num代表棋子种类,type代表阵营[{num:1,type:1},{num:2,type:1},{num:3,type:1},{num:4,type:1},{num:5,type:1},{num:4,type:1},{num:3,type:1},{num:2,type:1},{num:1,type:1}],[{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0}],[{num:0},{num:6,type:1},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:6,type:1},{num:0}],[{num:7,type:1},{num:0},{num:7,type:1},{num:0},{num:7,type:1},{num:0},{num:7,type:1},{num:0},{num:7,type:1}],[{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0}],[{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0}],[{num:7,type:2},{num:0},{num:7,type:2},{num:0},{num:7,type:2},{num:0},{num:7,type:2},{num:0},{num:7,type:2}],[{num:0},{num:6,type:2},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:6,type:2},{num:0}],[{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0},{num:0}],[{num:1,type:2},{num:2,type:2},{num:3,type:2},{num:4,type:2},{num:5,type:2},{num:4,type:2},{num:3,type:2},{num:2,type:2},{num:1,type:2}],]let menu = { // 棋子的枚举属性0:(index,index2,item2,tr)=>{ // 无棋子return new Qi(index,index2,item2,tr,0)},1:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 车return new Ju(index,index2,item2,tr,1,type)},2:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 马return new Ma(index,index2,item2,tr,2,type)},3:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 象return new Xiang(index,index2,item2,tr,3,type)},4:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 士return new Shi(index,index2,item2,tr,4,type)},5:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 将return new Jiang(index,index2,item2,tr,5,type)},6:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 炮return new Pao(index,index2,item2,tr,6,type)},7:(index,index2,item2,tr,type)=>{ // 卒return new Zu(index,index2,item2,tr,7,type)},}let typeList = { // 下棋顺序枚举1:'黑棋',2:'红棋'}class Qi { // 棋子公共类constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){this.num = name // 棋子枚举属性this.type = type // 棋子阵营标识this.tr = trthis.td = document.createElement('td')this.y = indexthis.x = index2this.td.dataset.y = index // 给每一个td元素设置坐标this.td.dataset.x = index2 // 给每一个td元素设置坐标item2 && type == 2 ? this.td.classList.add(`bgc${item2+7}`) : this.td.classList.add(`bgc${item2}`)this.waysArr = [] // 棋子可移动坐标的存放数组tr.appendChild(this.td)}}class Ju extends Qi { // 车constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}class Ma extends Qi { // 马constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}class Xiang extends Qi { // 象constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}class Shi extends Qi { // 士constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}class Jiang extends Qi { // 将constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}class Pao extends Qi { // 炮constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}class Zu extends Qi { // 卒constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}}//封装渲染函数const render = () => {document.querySelector('table').innerHTML = ''list.forEach((item, index) => {let tr = document.createElement('tr')item.forEach((item2, index2) => {let num = list[index][index2].numlist[index][index2] = menu[num](index,index2,item2.num,tr,item2.type) // 枚举生成对应的棋子对象})document.querySelector('table').appendChild(tr)})}render()
复制代码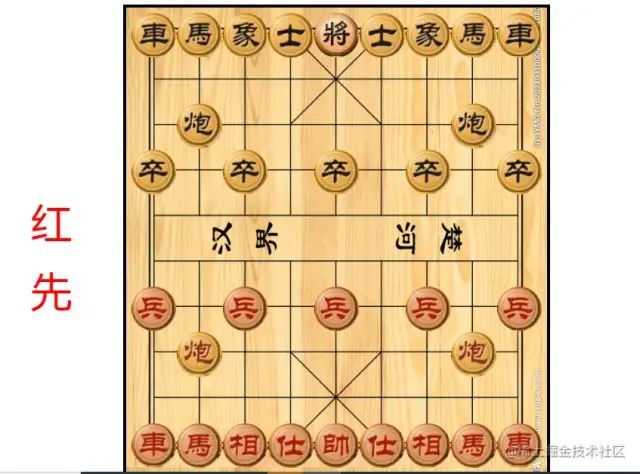
二、点击棋子后的逻辑处理
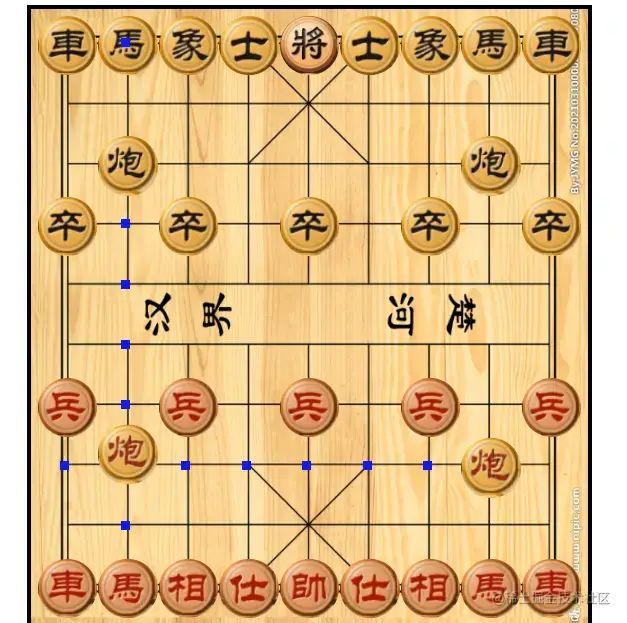
生成棋子的时候,给每一个td元素添加了坐标。所以触发点击事件的时候,通过这个坐标,就能获取到点击的元素对应的棋子对象了。第一次点击的时候,就调用棋子对象里面对应的方法。如果两次点击的地方一样,就将棋子放下来;两次点击的坐标不一样,就要调用棋子的移动方法。选中和放下通过添加和删除css,来更换状态。
let flag = 0 // 0:未选中棋子;1:选中棋子let sequence = false // true:黑棋走;false:红棋走let ele,x,yfunction clear() { // 清空数据flag = 0x = nully = null}document.querySelector('table').addEventListener('click',e=>{if(x == e.target.dataset.x && y == e.target.dataset.y){ // 两次点击的地方一样clear() // 清空数据ele.down() // 放下棋子return }x = e.target.dataset.x || xy = e.target.dataset.y || yif(list[y][x].num && !flag){ // 选中要移动的棋子ele = list[y][x]console.log(ele,'选择的棋子');flag = 1ele.checked() // 选中触发的方法}else if(flag){ // 移动棋子ele.move(x,y)clear() // 清空数据}else{console.log('此处没有棋子');clear() // 清空数据}})
复制代码选中和放下棋子的方法写在公共类里,先贴图,因为里面还有其他的代码,最后再一起附上
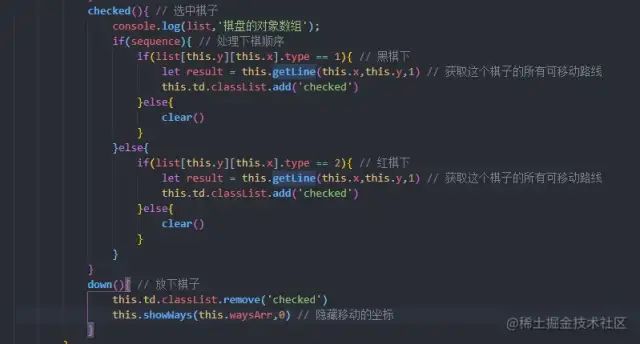
三、选中棋子之后,计算出棋子可以移动的坐标
选中棋子之后,要计算出棋子可以移动的坐标,并且通过小点的样式展示在棋盘上。因为每一个棋子的移动规则都不同,比如马走日字,象走田字并且不能过河,所以要在每一个子类里面单独去计算坐标。
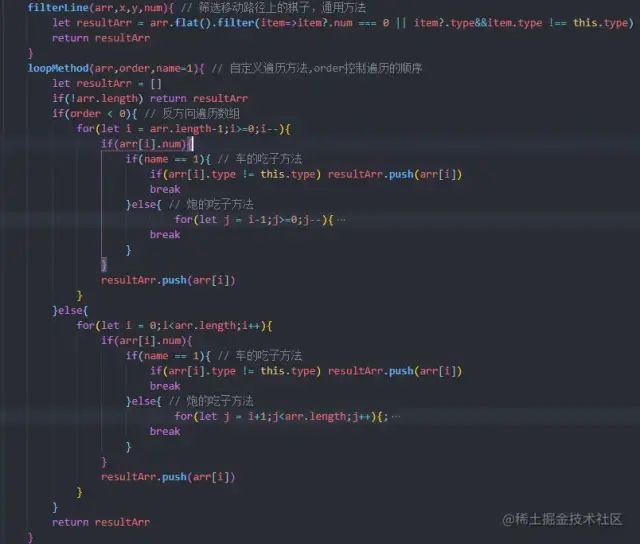
先计算出所有的坐标,比如车和炮,就计算棋子所在的x轴和y轴的所有坐标。坐标计算出来后,再把坐标上有同阵营棋子的点、以及不能走的点筛除,只留下空点的坐标或者可以被这个棋子吃掉的坐标。
计算坐标使用getLine()方法,每一个子类都需要根据象棋的规则单独计算
筛选坐标使用filterLine()方法,因为车、炮、将这3个棋的筛选计算与其他的棋子不同,所以这3个的计算方法在子类里重写,其他的棋子使用公共类里的通用方法
公共类的代码还是先贴图
下面是子类棋子的全部代码:
class Ju extends Qi { // 车constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取车棋子可以移动到的所有坐标,num值控制是否显示路径console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = list.map((item,index)=>{ // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标return index === +y? item : item[x]})let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,num) // 棋盘上展示可移动的路径return resultArr}filterLine(arr,x,y,num){ // 筛选移动路径上的棋子// 以选中棋子为中心,将x轴和y轴的点分为4份,每一份都要遍历找出满足条件的坐标,最后再合并let yArr1 = arr.slice(0,y)let yArr2 = arr.slice(y+1,arr.length)let xArr1 = arr[y].slice(0,x)let xArr2 = arr[y].slice(x+1,arr[y].length)console.log({yArr1,yArr2,xArr1,xArr2}); // loopMethod:自定义的遍历方法return [...this.loopMethod(xArr1,-1,this.num),...this.loopMethod(xArr2,1,this.num),...this.loopMethod(yArr1,-1,this.num),...this.loopMethod(yArr2,1,this.num), ]}}class Ma extends Qi { // 马constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取马可以移动到的所有坐标console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = [] // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标if(!list[y][x-1]?.num){ // 马为日字形,如果马脚有棋则不能走lineArr.push([list[y-1]?.[x-2],list[y+1]?.[x-2]]) }if(!list[y][x+1]?.num){lineArr.push([list[y+1]?.[x+2],list[y-1]?.[x+2]]) }if(!list[y-1]?.[x].num){lineArr.push([list[y-2]?.[x+1],list[y-2]?.[x-1]]) }if(!list[y+1]?.[x].num){lineArr.push([list[y+2]?.[x+1],list[y+2]?.[x-1]]) }let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,1,num) // 棋盘上展示可移动的路径return resultArr}}class Xiang extends Qi { // 象constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取象可以移动到的所有坐标,象心不能有棋子,并且不能过河console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = [] // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标if(list[y-1]?.[x-1]?.num === 0 && y!==5){lineArr.push(list[y-2][x-2]) }if(list[y+1]?.[x+1]?.num === 0 && y!==4){lineArr.push(list[y+2][x+2]) }if(list[y-1]?.[x+1]?.num === 0 && y!==5){lineArr.push(list[y-2][x+2]) }if(list[y+1]?.[x-1]?.num === 0 && y!==4){lineArr.push(list[y+2][x-2]) }let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,1,num) // 棋盘上展示可移动的路径return resultArr}}class Shi extends Qi { // 士constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取士可以移动到的所有坐标console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = [] // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标if(x==3 || x==5){ // 士只能在九宫格范围内斜着走this.type == 1 ? lineArr.push(list[1][4]) : lineArr.push(list[8][4])}else{this.type == 1 ? lineArr.push([list[0][3]],[list[0][5]],[list[2][3]],[list[2][5]]): lineArr.push([list[7][3]],[list[7][5]],[list[9][3]],[list[9][5]])}let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,1,num)return resultArr}}class Jiang extends Qi { // 将constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取将可以移动到的所有坐标console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = [] // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标lineArr.push([list[y][x+1]],[list[y][x-1]],[list[y-1]?.[x]],[list[y+1]?.[x]])let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,1,num)return resultArr}filterLine(arr,x,y,num){ // 筛选移动路径上的棋子// 获取敌方帅的坐标let resultArr = arr.filter(item=>{ // 将有棋子的坐标筛选出来,剩下的就是可以走的地方if(this.type == 1){return item[0]?.x>2&&item[0]?.x<6&&item[0]?.y>=0&&item[0]?.y<3&&item[0]?.type!=1}else{return item[0]?.x>2&&item[0]?.x<6&&item[0]?.y>=7&&item[0]?.y<10&&item[0]?.type!=2}})let shuai = list.flat().find(item=>item.num === 5 && item.type !== this.type) // 敌方帅的坐标let jiang = resultArr.flat().find(item=>item.x === shuai.x) if(jiang){ // 判断将和帅可以走的坐标里面,有没有和对方将为同一列的let res = list.flat().find(item=>{if(shuai.y>jiang.y){return item.x === jiang.x && item.y>jiang.y && item.yshuai.y && item.num}})if(!res){ // 如果两个帅在同一列,并且中间没有棋子,就不可以走,把这个坐标删除let resArr = resultArr.flat().filter(item=>!(item.x==jiang.x&&item.y==jiang.y))return resArr}}return resultArr.flat()}}class Pao extends Qi { // 炮constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取炮棋子可以移动到的所有坐标console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = list.map((item,index)=>{ // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标return index === +y? item : item[x]})let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,1,num)return resultArr}filterLine(arr,x,y,num){ // 筛选移动路径上的棋子let yArr1 = arr.slice(0,y)let yArr2 = arr.slice(y+1,arr.length)let xArr1 = arr[y].slice(0,x)let xArr2 = arr[y].slice(x+1,arr[y].length)console.log({yArr1,yArr2,xArr1,xArr2});return [...this.loopMethod(xArr1,-1,this.num),...this.loopMethod(xArr2,1,this.num),...this.loopMethod(yArr1,-1,this.num),...this.loopMethod(yArr2,1,this.num), ]}}class Zu extends Qi { // 卒constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){super(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type)}getLine(x,y,num){ // 获取卒可以移动到的所有坐标console.log(x,y,'选择棋子的坐标');let lineArr = [] // 未筛选的所有可移动的坐标if(this.type == 1 && y<5 || this.type == 2 && y>4){ // 过河前的移动路径this.type == 1?lineArr.push(list[y+1]?.[x]) : lineArr.push(list[y-1]?.[x])}else{ // 过河后的移动路径if(this.type == 1){lineArr.push([list[y+1]?.[x],list[y][x+1],list[y][x-1]])}else{lineArr.push([list[y-1]?.[x],list[y][x+1],list[y][x-1]])}}let resultArr = this.filterLine(lineArr,x,y,num) // 将路径上有棋子的坐标筛选出来this.showWays(resultArr,1,num)return resultArr}}
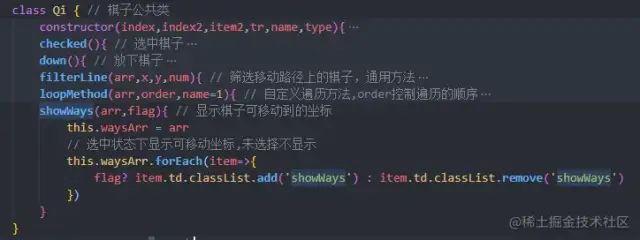
复制代码 四、计算出可移动坐标后,在棋盘上展示出来
将坐标上每一个棋子对象里对应的td元素,添加一个样式即可。放下棋子的时候,就将样式隐藏。

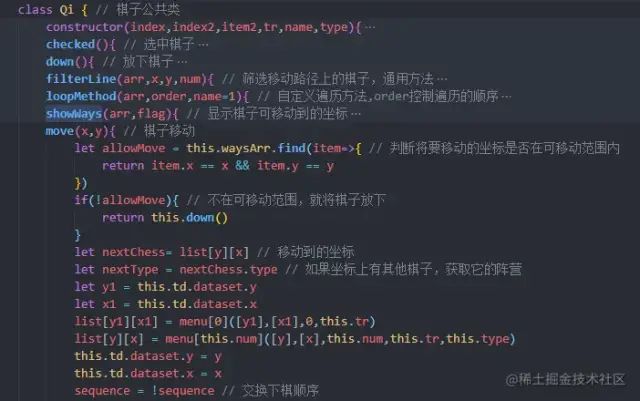
五、棋子的移动
棋子的移动就是把两个坐标里的棋子对象交换位置,只要能拿到坐标,实现这个就比较简单了。但是要判断一下第二次点击的坐标,是不是在棋子的可移动范围内,毕竟象棋移动是有规则的,不能想去哪就去哪。
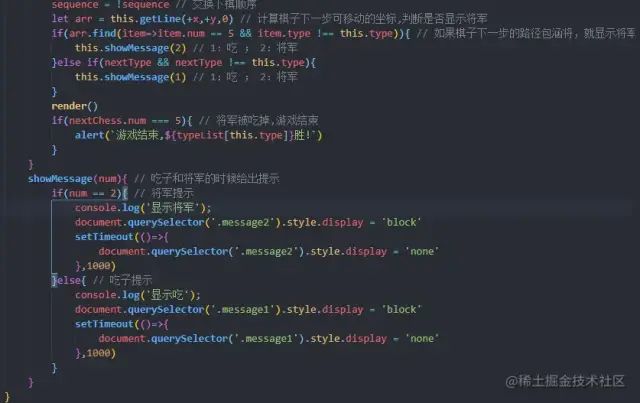
六、吃子和将军的提示,以及胜负的判断
html里已经画好了几个提示的div盒子,吃子和将军的时候显示不同的盒子即可。如果一方的将被吃掉了,那么就提示游戏结束,根据type值来判断是哪一方获胜。
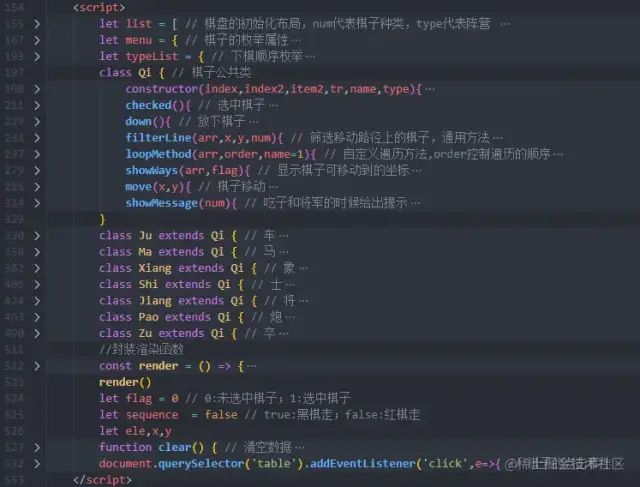
 最后附上棋子公共类的代码
最后附上棋子公共类的代码
class Qi { // 棋子公共类constructor(index,index2,item2,tr,name,type){this.num = name // 棋子枚举属性this.type = type // 棋子阵营标识this.tr = trthis.td = document.createElement('td')this.y = indexthis.x = index2this.td.dataset.y = index // 给每一个td元素设置坐标this.td.dataset.x = index2 // 给每一个td元素设置坐标item2 && type == 2 ? this.td.classList.add(`bgc${item2+7}`) : this.td.classList.add(`bgc${item2}`)this.waysArr = [] // 棋子可移动坐标的存放数组tr.appendChild(this.td)}checked(){ // 选中棋子console.log(list,'棋盘的对象数组');if(sequence){ // 处理下棋顺序if(list[this.y][this.x].type == 1){ // 黑棋下let result = this.getLine(this.x,this.y,1) // 获取这个棋子的所有可移动路线this.td.classList.add('checked')}else{clear()}}else{if(list[this.y][this.x].type == 2){ // 红棋下let result = this.getLine(this.x,this.y,1) // 获取这个棋子的所有可移动路线this.td.classList.add('checked')}else{clear()}}}down(){ // 放下棋子this.td.classList.remove('checked')this.showWays(this.waysArr,0) // 隐藏移动的坐标}filterLine(arr,x,y,num){ // 筛选移动路径上的棋子,通用方法let resultArr = arr.flat().filter(item=>item?.num === 0 || item?.type&&item.type !== this.type)return resultArr}loopMethod(arr,order,name=1){ // 自定义遍历方法,order控制遍历的顺序let resultArr = []if(!arr.length) return resultArr if(order < 0){ // 反方向遍历数组for(let i = arr.length-1;i>=0;i--){if(arr[i].num){if(name == 1){ // 车的吃子方法if(arr[i].type != this.type) resultArr.push(arr[i])break}else{ // 炮的吃子方法for(let j = i-1;j>=0;j--){if(arr[j].type != this.type && arr[j].num){resultArr.push(arr[j])break}}break}}resultArr.push(arr[i])}}else{for(let i = 0;i{flag? item.td.classList.add('showWays') : item.td.classList.remove('showWays')})}move(x,y){ // 棋子移动let allowMove = this.waysArr.find(item=>{ // 判断将要移动的坐标是否在可移动范围内return item.x == x && item.y == y})if(!allowMove){ // 不在可移动范围,就将棋子放下return this.down()}let nextChess= list[y][x] // 移动到的坐标let nextType = nextChess.type // 如果坐标上有其他棋子,获取它的阵营let y1 = this.td.dataset.ylet x1 = this.td.dataset.xlist[y1][x1] = menu[0]([y1],[x1],0,this.tr)list[y][x] = menu[this.num]([y],[x],this.num,this.tr,this.type)this.td.dataset.y = ythis.td.dataset.x = xsequence = !sequence // 交换下棋顺序let arr = this.getLine(+x,+y,0) // 计算棋子下一步可移动的坐标,判断是否显示将军if(arr.find(item=>item.num == 5 && item.type !== this.type)){ // 如果棋子下一步的路径包涵将,就显示将军this.showMessage(2) // 1:吃 ;2:将军}else if(nextType && nextType !== this.type){this.showMessage(1) // 1:吃 ;2:将军}render()if(nextChess.num === 5){ // 将军被吃掉,游戏结束alert(`游戏结束,${typeList[this.type]}胜!`)}}showMessage(num){ // 吃子和将军的时候给出提示if(num == 2){ // 将军提示console.log('显示将军');document.querySelector('.message2').style.display = 'block'setTimeout(()=>{document.querySelector('.message2').style.display = 'none'},1000)}else{ // 吃子提示console.log('显示吃');document.querySelector('.message1').style.display = 'block'setTimeout(()=>{document.querySelector('.message1').style.display = 'none'},1000)}}}
复制代码 总结
到这里这个象棋小游戏就写完了,象棋的规则和逻辑基本上都能实现了。就是判断将军的逻辑处理的不是很好,有些情况下的将军,显示不出来。如果走了某一步棋之后,导致自己的帅会被对方吃掉,按理来说这一步棋是不可以走的,这个逻辑的处理并没有写。这个象棋只能在一个电脑上面自己跟自己玩,主要是想写写代码,怕脑子上班摸鱼生锈了,有些的不好的地方欢迎指正,不喜勿喷。

关于本文
来自: 逍丶
https://juejin.cn/post/7197959897257197625

往期推荐
2023 年的前端渲染框架

使用发布订阅,构建多功能、多方向的全新 Message

如何突破技术瓶颈(适合P6以下)

最后
欢迎加我微信,拉你进技术群,长期交流学习...
欢迎关注「前端Q」,认真学前端,做个专业的技术人...

前端Q
本公众号主要分享一些技术圈(前端圈为主)相关的技术文章、工具资源、学习资料、招聘信息及其他有趣的东西...
公众号

点个在看支持我吧

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!