一文读懂Swin-Transformer
系列文章目录
记录CV领域大模型的学习历程,欢迎大家一起讨论,互相学习。
ViT,DETR(一),DETR(二)DETR(三)
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 整体框架
- 1.Patch Embedding
- 2.Patch Merging
- 3.Swin Transformer Block
- 3.1 Window Partition/Reverse
- 3.2 Window-MSA
- 3.3 Relative Position Bias
- 3.4 Shifted Window Attention
前言
Swin Transformer是2021年微软亚洲研究院发表在ICCV(ICCV 2021 best paper)上的一篇文章。Swin Transformer是继ViT之后,Transformer模型在视觉领域的又一次碰撞。该论文一经发表就已在多项视觉任务中霸榜,值得大家仔细研读。
Swin Transformer可能是CNN的完美替代方案。作者分析表明,Transformer从NLP迁移到CV上没有大放异彩主要有两点原因:1. 同样语义的词但是他们的尺寸不同,比如智能驾驶的实例分割任务中,摄像机拍到图片中的车大小不一。2. CV比起NLP需要更大的分辨率,而且CV中使用Transformer的计算复杂度是图像尺度的平方,这会导致计算量过于庞大。
相比于ViT,Swin Transfomer具有以下优点:
1.使用层级式结构(dawnsaple),可以提供各个尺度的特征信息。
2.自注意力是在小窗口计算,所以计算复杂度是线性关系而不是平方关系。
3.移动窗口的操作使得相邻的窗口有了交互。

论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030
代码地址:mmcls
整体框架
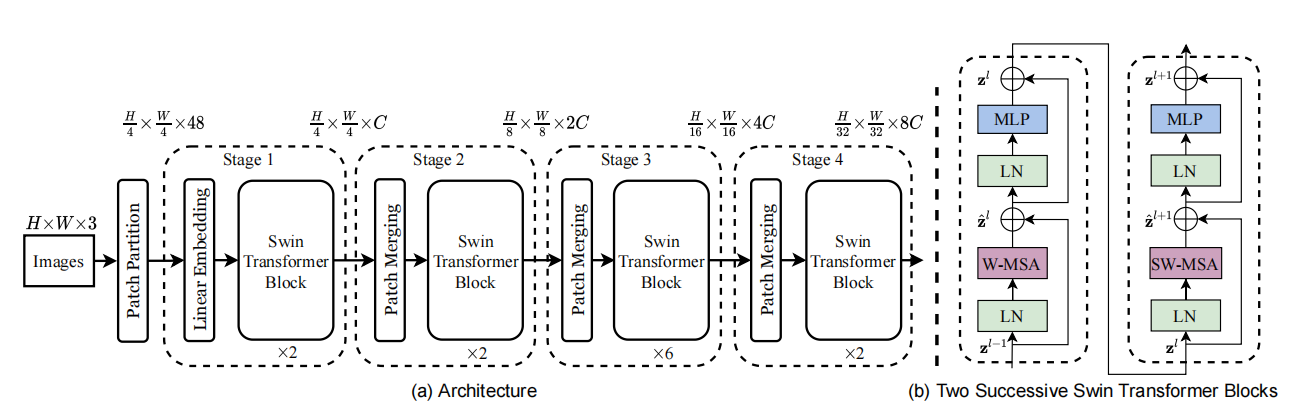 首先,我们看一下Swin的整体框架,整个模型采取层次化的设计,一共包含4个Stage,每个stage都会对输入下采样降低特征图的分辨率。流程总结如下:
首先,我们看一下Swin的整体框架,整个模型采取层次化的设计,一共包含4个Stage,每个stage都会对输入下采样降低特征图的分辨率。流程总结如下:
- 在输入开始的时候,做了一个Patch Embedding(与VIT相同,用CNN做下采样),将图片切成一个个图块,并嵌入到Embedding。
- 继而进入stages,每个stage由Patch Merging和多个Swin Transformer Block组成。其中Patch Merging模块主要在每个Stage一开始降低图片分辨率。
- Swin Transformer Block具体结构如上图(b)所示,主要是LayerNorm,MLP,Window Attention 和 Shifted Window Attention组成 。之所以Swin Transformer Block个数是2的倍数,是因为Swin Transformer Block由Window Attention和 Shifted Window Attention两个attention模块组成。
- 最后,可以根据不同任务,分别进入各自head,如分类,就会经过池化形成one-hot特征与GT做loss。
class SwinTransformer(BaseBackbone):arch_zoo = {**dict.fromkeys(['t', 'tiny'],{'embed_dims': 96,'depths': [2, 2, 6, 2],'num_heads': [3, 6, 12, 24]}),} # yapf: disabledef __init__(self,arch='tiny',img_size=224,patch_size=4,in_channels=3,window_size=7,drop_rate=0.,drop_path_rate=0.1,out_indices=(3, ),use_abs_pos_embed=False,interpolate_mode='bicubic',with_cp=False,frozen_stages=-1,norm_eval=False,pad_small_map=False,norm_cfg=dict(type='LN'),stage_cfgs=dict(),patch_cfg=dict(),init_cfg=None):super(SwinTransformer, self).__init__(init_cfg=init_cfg)self.embed_dims = self.arch_settings['embed_dims']self.depths = self.arch_settings['depths']self.num_heads = self.arch_settings['num_heads']self.num_layers = len(self.depths)self.out_indices = out_indicesself.use_abs_pos_embed = use_abs_pos_embedself.interpolate_mode = interpolate_modeself.frozen_stages = frozen_stages_patch_cfg = dict(in_channels=in_channels,input_size=img_size,embed_dims=self.embed_dims,conv_type='Conv2d',kernel_size=patch_size,stride=patch_size,norm_cfg=dict(type='LN'),)_patch_cfg.update(patch_cfg)self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(**_patch_cfg)self.patch_resolution = self.patch_embed.init_out_sizefor i, (depth,num_heads) in enumerate(zip(self.depths, self.num_heads)):if isinstance(stage_cfgs, Sequence):stage_cfg = stage_cfgs[i]else:stage_cfg = deepcopy(stage_cfgs)downsample = True if i < self.num_layers - 1 else False_stage_cfg = {'embed_dims': embed_dims[-1],'depth': depth,'num_heads': num_heads,'window_size': window_size,'downsample': downsample,'drop_paths': dpr[:depth],'with_cp': with_cp,'pad_small_map': pad_small_map,**stage_cfg}stage = SwinBlockSequence(**_stage_cfg)self.stages.append(stage)dpr = dpr[depth:]embed_dims.append(stage.out_channels)for i in out_indices:if norm_cfg is not None:norm_layer = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, embed_dims[i + 1])[1]else:norm_layer = nn.Identity()self.add_module(f'norm{i}', norm_layer)def forward(self, x):x, hw_shape = self.patch_embed(x)if self.use_abs_pos_embed:x = x + resize_pos_embed(self.absolute_pos_embed, self.patch_resolution, hw_shape,self.interpolate_mode, self.num_extra_tokens)x = self.drop_after_pos(x)outs = []for i, stage in enumerate(self.stages):x, hw_shape = stage(x, hw_shape)if i in self.out_indices:norm_layer = getattr(self, f'norm{i}')out = norm_layer(x)out = out.view(-1, *hw_shape,stage.out_channels).permute(0, 3, 1,2).contiguous()outs.append(out)return tuple(outs)
1.Patch Embedding
在输入stages之前,我们需要将图片切成一个个patch,形成tokens。这里直接使用kernel=stride=4的conv来将x:[6, 3, 224, 224]下采样生成[6, 128, 56, 56]的特征,其中128是嵌入向量的大小(即一个token的长度),6表示batch-size。最后将H,W维度展开,并移动到第一维度形成[6, 3136, 128]的tokens。
class PatchEmbed(BaseModule):def __init__(self,in_channels=3,embed_dims=768,conv_type='Conv2d',kernel_size=16,stride=16,padding='corner',dilation=1,bias=True,norm_cfg=None,input_size=None,init_cfg=None):super(PatchEmbed, self).__init__(init_cfg=init_cfg)self.embed_dims = embed_dimsif isinstance(padding, str):self.adaptive_padding = AdaptivePadding(kernel_size=kernel_size,stride=stride,dilation=dilation,padding=padding)# disable the padding of convpadding = 0else:self.adaptive_padding = Nonepadding = to_2tuple(padding)self.projection = build_conv_layer(dict(type=conv_type),in_channels=in_channels,out_channels=embed_dims,kernel_size=kernel_size,stride=stride,padding=padding,dilation=dilation,bias=bias)if norm_cfg is not None:self.norm = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, embed_dims)[1]else:self.norm = Noneif input_size:input_size = to_2tuple(input_size)# `init_out_size` would be used outside to# calculate the num_patches# e.g. when `use_abs_pos_embed` outsideself.init_input_size = input_sizeif self.adaptive_padding:pad_h, pad_w = self.adaptive_padding.get_pad_shape(input_size)input_h, input_w = input_sizeinput_h = input_h + pad_hinput_w = input_w + pad_winput_size = (input_h, input_w)# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv2d.htmlh_out = (input_size[0] + 2 * padding[0] - dilation[0] *(kernel_size[0] - 1) - 1) // stride[0] + 1w_out = (input_size[1] + 2 * padding[1] - dilation[1] *(kernel_size[1] - 1) - 1) // stride[1] + 1self.init_out_size = (h_out, w_out)else:self.init_input_size = Noneself.init_out_size = Nonedef forward(self, x):if self.adaptive_padding: ## x:[6, 3, 224, 224]x = self.adaptive_padding(x) ## x:[6, 3, 224, 224]x = self.projection(x) ## x:[6, 128, 56, 56]out_size = (x.shape[2], x.shape[3])x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) ## x:[6, 3136, 128]if self.norm is not None:x = self.norm(x)return x, out_size
2.Patch Merging
Swin采用PatchMerging的方式对输入进行下采样(除了stage1不做PatchMerging)。如下图所示,x是一个4x4的单通道特征,PatchMerging会使用一个kernel=2,stride=2,dilation=1的滑动窗口去取值。因此,就形成了4张2x2的单通道特征,将其cat完成下采样(一个4x4的特征变为2x2x4的特征),w,h维度降低为原来的1/2,channel变为原来4倍。
为了加速这个过程,mmcls使用self.sampler = nn.Unfold,原理如上所述,使用一个kernel=2,stride=2,dilation=1的滑动窗口去取值,并cat。然后,通过self.reduction(Linear(in_features=512, out_features=256, bias=False))将chennel维度降低,输出x:[6, 784, 256] (其中784=28*28,PatchMerging将56x56下采样至28x28)。

class PatchMerging(BaseModule):def __init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=2,stride=None,padding='corner',dilation=1,bias=False,norm_cfg=dict(type='LN'),init_cfg=None):super().__init__(init_cfg=init_cfg)self.in_channels = in_channelsself.out_channels = out_channelsif isinstance(padding, str):self.adaptive_padding = AdaptivePadding(kernel_size=kernel_size,stride=stride,dilation=dilation,padding=padding)# disable the padding of unfoldpadding = 0else:self.adaptive_padding = Nonepadding = to_2tuple(padding)self.sampler = nn.Unfold(kernel_size=kernel_size,dilation=dilation,padding=padding,stride=stride)sample_dim = kernel_size[0] * kernel_size[1] * in_channelsif norm_cfg is not None:self.norm = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, sample_dim)[1]else:self.norm = Noneself.reduction = nn.Linear(sample_dim, out_channels, bias=bias)def forward(self, x, input_size):B, L, C = x.shape ## x:[6, 3136, 128]H, W = input_size ## (56,56)x = x.view(B, H, W, C).permute([0, 3, 1, 2]) # B, C, H, W [6, 128, 56, 56]if self.adaptive_padding:x = self.adaptive_padding(x) ## x:[6, 128, 56, 56]H, W = x.shape[-2:]# Use nn.Unfold to merge patch. About 25% faster than original method,# but need to modify pretrained model for compatibility# if kernel_size=2 and stride=2, x should has shape (B, 4*C, H/2*W/2)x = self.sampler(x) ## x:[6, 512, 784]out_h = (H + 2 * self.sampler.padding[0] - self.sampler.dilation[0] *(self.sampler.kernel_size[0] - 1) -1) // self.sampler.stride[0] + 1out_w = (W + 2 * self.sampler.padding[1] - self.sampler.dilation[1] *(self.sampler.kernel_size[1] - 1) -1) // self.sampler.stride[1] + 1output_size = (out_h, out_w) ## (28,28)x = x.transpose(1, 2) # B, H/2*W/2, 4*C [6, 784, 512]x = self.norm(x) if self.norm else xx = self.reduction(x) ## x:[6, 784, 256]return x, output_size
3.Swin Transformer Block

Swin Transformer Block是该论文最核心的module,其中每个Block至少包含一个W-MSA(Window-MSA)与一个SW-MSA(ShiftWindow-MSA)。代码如下所示:
流程总结:
- 通过self.shift_size决定是否需要对query进行shift
- 通过self.get_attn_mask利用shift_size计算attn_mask
- 将query切成一个个窗口([6, 784, 256]->[6, 28, 28, 256]->[96, 7, 7, 256]->[96, 49, 256])
- 将query_windows与attn_mask送入self.w_msa计算多头注意力
- 将各个窗口合并回来如果之前有做shift操作,此时进行reverse shift
class ShiftWindowMSA(BaseModule):def __init__(self,embed_dims,num_heads,window_size,shift_size=0,qkv_bias=True,qk_scale=None,attn_drop=0,proj_drop=0,dropout_layer=dict(type='DropPath', drop_prob=0.),pad_small_map=False,input_resolution=None,auto_pad=None,init_cfg=None):super().__init__(init_cfg)if input_resolution is not None or auto_pad is not None:warnings.warn('The ShiftWindowMSA in new version has supported auto padding ''and dynamic input shape in all condition. And the argument ''`auto_pad` and `input_resolution` have been deprecated.',DeprecationWarning)self.shift_size = shift_sizeself.window_size = window_sizeassert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_sizeself.w_msa = WindowMSA(embed_dims=embed_dims,window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size),num_heads=num_heads,qkv_bias=qkv_bias,qk_scale=qk_scale,attn_drop=attn_drop,proj_drop=proj_drop,)self.drop = build_dropout(dropout_layer)self.pad_small_map = pad_small_mapdef forward(self, query, hw_shape):B, L, C = query.shape ##[6, 784, 256]H, W = hw_shape ##(28,28)assert L == H * W, f"The query length {L} doesn't match the input "\f'shape ({H}, {W}).'query = query.view(B, H, W, C) ## [6, 28, 28, 256]window_size = self.window_size ## 7shift_size = self.shift_size ## 0 or 3, 0->W-MSA,3->SW-MSAif min(H, W) == window_size:# If not pad small feature map, avoid shifting when the window size# is equal to the size of feature map. It's to align with the# behavior of the original implementation.shift_size = shift_size if self.pad_small_map else 0elif min(H, W) < window_size:# In the original implementation, the window size will be shrunk# to the size of feature map. The behavior is different with# swin-transformer for downstream tasks. To support dynamic input# shape, we don't allow this feature.assert self.pad_small_map, \f'The input shape ({H}, {W}) is smaller than the window ' \f'size ({window_size}). Please set `pad_small_map=True`, or ' \'decrease the `window_size`.'pad_r = (window_size - W % window_size) % window_sizepad_b = (window_size - H % window_size) % window_sizequery = F.pad(query, (0, 0, 0, pad_r, 0, pad_b))H_pad, W_pad = query.shape[1], query.shape[2]# cyclic shiftif shift_size > 0:query = torch.roll(query, shifts=(-shift_size, -shift_size), dims=(1, 2))attn_mask = self.get_attn_mask((H_pad, W_pad),window_size=window_size,shift_size=shift_size,device=query.device)# nW*B, window_size, window_size, Cquery_windows = self.window_partition(query, window_size) ## [96, 7, 7, 256] 96=6x4x4# nW*B, window_size*window_size, Cquery_windows = query_windows.view(-1, window_size**2, C) ## [96, 49, 256]# W-MSA/SW-MSA (nW*B, window_size*window_size, C)attn_windows = self.w_msa(query_windows, mask=attn_mask) ##[96, 49, 256]# merge windowsattn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, window_size, window_size, C) ##[96, 7, 7, 256]# B H' W' Cshifted_x = self.window_reverse(attn_windows, H_pad, W_pad, ## [6, 28, 28, 256]window_size)# reverse cyclic shiftif self.shift_size > 0:x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(shift_size, shift_size), dims=(1, 2)) else:x = shifted_xif H != H_pad or W != W_pad:x = x[:, :H, :W, :].contiguous()x = x.view(B, H * W, C)x = self.drop(x)return x
3.1 Window Partition/Reverse
Swin为了降低self-attention的计算量,利用Window Partition对特征[6, 28, 28, 256]
划分窗口(window_size=7),将其变换为维度为[96, 7, 7, 256]的特征,其中4x4个窗口合并到第一维度(6x4x4=96),并把窗口拉直([96, 49, 256]),送入self.w_msa中计算attention。
如下图所示,原本MSA需要对4x4的feature计算attention,通过Window Partition后,只需要对4个2x2的feature做attention。论文给出了MSA与W-MSA两者的计算量:

这个公式是咋来的,原论文中并没有细讲,这里直接引用博客。首先回忆下单头Self-Attention的公式,这个公式我们在ViT中详细介绍过。



 window_reverse则是window_partition的逆变换。
window_reverse则是window_partition的逆变换。
@staticmethoddef window_reverse(windows, H, W, window_size):B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size,window_size, -1)x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)return x@staticmethoddef window_partition(x, window_size):B, H, W, C = x.shapex = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size,window_size, C)windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous()windows = windows.view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)return windows
3.2 Window-MSA
W-MSA与SW-MSA区别在于是否对query进行cyclic shift以及reverse cyclic shift,不管是W-MSA还是SW-MSA,程序都会进入WindowMSA中进行自注意力运算,与VIT不同的是,Swin加入了relative_position_bias相对位移偏执来计算attention。
class WindowMSA(BaseModule):def __init__(self,embed_dims,window_size,num_heads,qkv_bias=True,qk_scale=None,attn_drop=0.,proj_drop=0.,init_cfg=None):super().__init__(init_cfg)self.embed_dims = embed_dimsself.window_size = window_size # Wh, Wwself.num_heads = num_headshead_embed_dims = embed_dims // num_headsself.scale = qk_scale or head_embed_dims**-0.5# define a parameter table of relative position biasself.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1),num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH 这里为什么是13*13这个维度# About 2x faster than original implWh, Ww = self.window_size #(7,7)rel_index_coords = self.double_step_seq(2 * Ww - 1, Wh, 1, Ww) #tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 26, 27, 28, 29,#30, 31, 32, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 65,#66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84]])rel_position_index = rel_index_coords + rel_index_coords.Trel_position_index = rel_position_index.flip(1).contiguous()self.register_buffer('relative_position_index', rel_position_index)self.qkv = nn.Linear(embed_dims, embed_dims * 3, bias=qkv_bias)self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)self.proj = nn.Linear(embed_dims, embed_dims)self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)def init_weights(self):super(WindowMSA, self).init_weights()trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=0.02)def forward(self, x, mask=None):"""Args:x (tensor): input features with shape of (num_windows*B, N, C)mask (tensor, Optional): mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww), value should be between (-inf, 0]."""B_, N, C = x.shapeqkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads,C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)q = q * self.scaleattn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) #49windows的query与key求相似度系数,attn=[-1,num_heads,49,49]relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[ ##在self.relative_position_bias_table中挑选self.relative_position_index个元素self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],-1) # Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nHrelative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Wwattn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0)if mask is not None:nW = mask.shape[0]attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N,N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N)attn = self.softmax(attn)else:attn = self.softmax(attn)attn = self.attn_drop(attn)x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)x = self.proj(x)x = self.proj_drop(x)return x@staticmethoddef double_step_seq(step1, len1, step2, len2):seq1 = torch.arange(0, step1 * len1, step1)seq2 = torch.arange(0, step2 * len2, step2)return (seq1[:, None] + seq2[None, :]).reshape(1, -1)
3.3 Relative Position Bias
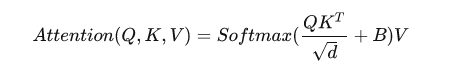
在Swin Transformer中,将特征图按7x7 的窗口大小划分为多个小窗格,单独在每个小窗格内进行Attention计算。这样一来,窗口内就相当于有 49个Token即49个像素值,这些像素是有一定的位置关系的,故在Attention计算时,需要考虑这些像素的位置关系,故提出了相对位置编码,其与NLP 中的PE是有异曲同工之妙的。
首先我们需要知道代码中的relative_position_bias_table和relative_position_index,其中前者的数据类型为Parameter为可学习参数而,后者为buffer不可学习参数。实际上参与Attention计算的B(Attention公式中) 是relative_position_bias_table这个可学习的参数,而relative_position_index则是作为一个index去取relative_position_bias_table中的值来参与运算。
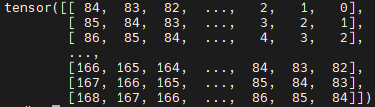
代码如下所示,Attention公式中的B是指self.relative_position_bias_table,里面存放着(2Wh-1)*(2Ww-1)(Ww=Wh=7)个可学习参数。相对位置偏执作用于 Q K T QK^T QKT之后,因此,相对位置偏执(49x49)与 Q K T QK^T QKT(49x49)的相似度是一一对应的。query中的第一个元素与k所有元素求相似度(第一个q与第一个k匹配作为中心),其相对位置索引可以从(0,0)排至(6,6),若以最后一个元素为中心那么相对索引可以从(-6,-6)排至(0,0)。这里想说明一下为什么相对位置索引需要用7x7的矩阵排列,因为窗口内的特征虽然被强行拉直变为49个元素,但它其实对应着7x7的语义信息(图片是具有宽高的二维结构),所以相对位置索引就是为了保留图片像素的位置关系而设置的,对[-6,6]13个数字排序,所有排序可能就存在13x13=169种,即在 Q K T QK^T QKT(维度49x49)矩阵中存在169个相对位置偏执索引。为了方便索引表示,将2维索引坐标拉直成1维,即通过(0-168)个数字来表示相对位置偏执的索引。通过self.double_step_seq生成0-84连续间隔为7的tensor(引用中显示了tensor)。
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 26, 27, 28, 29,
30, 31, 32, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 65,
66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84]])
最后根据广播机制构建49x49维度的相对位置偏执索引,tensor如下图所示。为什么这样可以构建相对位置偏执索引呢,我们来看下面的例子。
如果特征图的大小为2x2xN(N表示每个像素点的channels),那么经过拉直之后Q、K、V的维度都为4xN,那么QK.T 的维度就是4x4,其中第一个4表示4个像素点,第二个4表示对于每个像素点相对(包括自己在内的)四个像素点的重要程度;而相对位置编码要得到的结果也需要是4x4,其每行表示四个像素相对于某个固定像素的位置编码值。
以蓝色像素为参考点。然后用蓝色像素的绝对位置索引与其他位置索引进行相减,就得到其他位置相对蓝色像素的相对位置索引。例如黄色像素的绝对位置索引是 (0,1),则它相对蓝色像素的相对位置索引为 (0,0) − (0,1) = (0,−1) 。
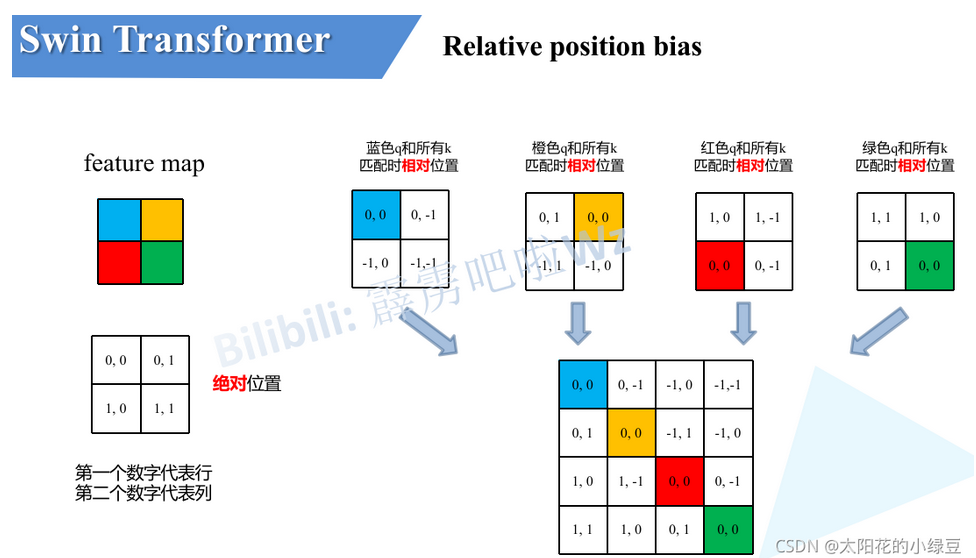 我们将黄色,红色,绿色为中心点的矩阵与蓝色中心点矩阵(蓝色q和所有k匹配时相对位置下的2x2矩阵)重合,可以得到一个3x3的矩阵(即下图第一个矩阵),只需要用0-8,9个数字就可以唯一表示它们,并以此作为相对位置偏移的索引。具体做法如下图所示,得到矩阵后先对行列分别+1,在对行元素x3,最后将行列元素分别相加。获得9个索引后,需要将蓝黄红绿4个2x2矩阵用对应位置的索引填充,并重新拉直组成4x4相对位置偏执索引。
我们将黄色,红色,绿色为中心点的矩阵与蓝色中心点矩阵(蓝色q和所有k匹配时相对位置下的2x2矩阵)重合,可以得到一个3x3的矩阵(即下图第一个矩阵),只需要用0-8,9个数字就可以唯一表示它们,并以此作为相对位置偏移的索引。具体做法如下图所示,得到矩阵后先对行列分别+1,在对行元素x3,最后将行列元素分别相加。获得9个索引后,需要将蓝黄红绿4个2x2矩阵用对应位置的索引填充,并重新拉直组成4x4相对位置偏执索引。

# define a parameter table of relative position biasself.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1),num_heads)) # 2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, nH 这里为什么是13*13这个维度# About 2x faster than original implWh, Ww = self.window_size #(7,7)rel_index_coords = self.double_step_seq(2 * Ww - 1, Wh, 1, Ww) #tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 26, 27, 28, 29,#30, 31, 32, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 65,#66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84]])rel_position_index = rel_index_coords + rel_index_coords.Trel_position_index = rel_position_index.flip(1).contiguous()self.register_buffer('relative_position_index', rel_position_index)
在 Q K T QK^T QKT相似度算完后需要加上B(self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index]),其余部分均与MSA一样,不再赘述。
3.4 Shifted Window Attention
首先,看下Swin是怎么做位移和循环填充的:
如下图所示,我们将左边的矩阵分成9块,先把左边的ADE移至右侧,再将上边的BCA移至下册,就完成了shift操作,shift的尺寸是window_size/2。
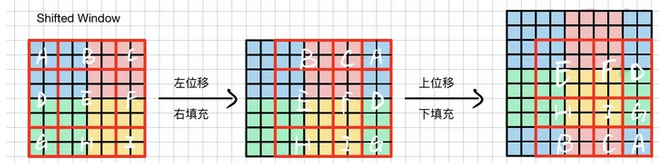
在程序中直接使用torch.roll完成。但是roll后,出现了问题,图片语义发生了变化(原来在左上角的元素,现在变换到右下角了,因此不能在一个窗口计算attention),原来通过4个窗口(左图可以分为蓝红绿黄4个窗口)可以完成attention计算,现在需要分别计算ABCDEFGHI。为了降低计算量,Swin提出了attn_mask。
if shift_size > 0:query = torch.roll(query, shifts=(-shift_size, -shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
如下图所示,SW-WSA仍用4个窗口划分该特征,这4个窗口分别包含元素E,FD,HB,IGCA。

可以看到,这样排布之后,由于E的语义没有被破坏,E和W-MSA的window是没有区别的,E的att_mask直接赋值0。F和D是切了2块。我们算F的时候,不能算D。H和B同理。IGCA需要分别计算4块attention。
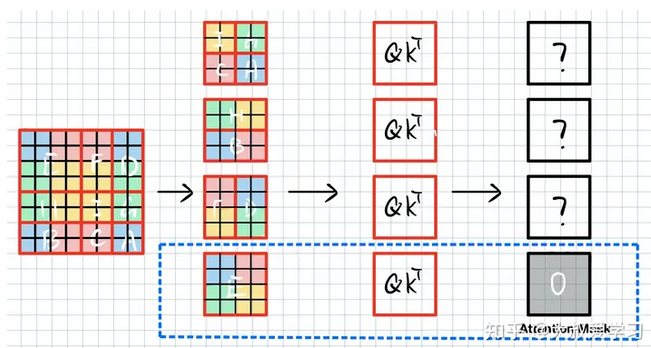
当计算F时,我们不希望右边D的信息干扰。首先将FD拉直(Swin中window_size=7,即7x7x32->49x32),如下图所示,将其沿xy轴排列,并计算self-attention( Q K T QK_T QKT是逐个元素对应求相似度,QK是相同特征,其维度=[49x49])。由于F由红色黄色块组成,因此att_mask(维度[49x49])需要把左下图中白色块mask掉,填上-100,而灰色块是F需要的,填0,D块与F块类似。
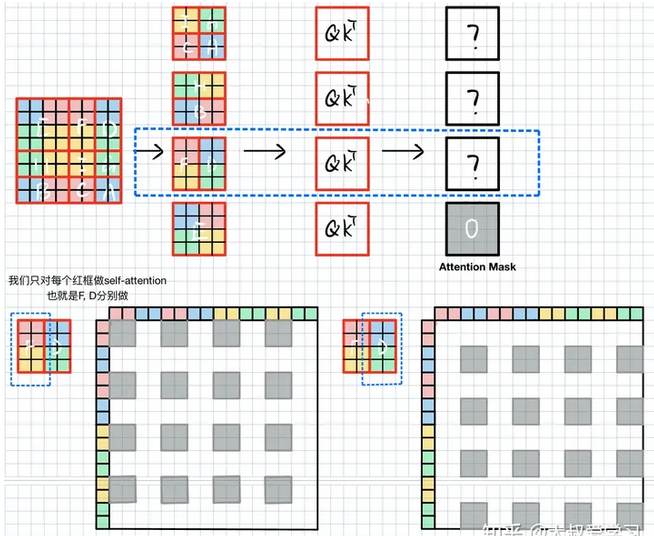
当计算HB块时,由于H,B拉直后,H占拉直后特征的前半段,B是后半段特征,因此att_mask很简单,只需要将两块灰色块填0其余-100就ok。

IGCA块则需要把对应颜色块分别用att_mask激活即可。
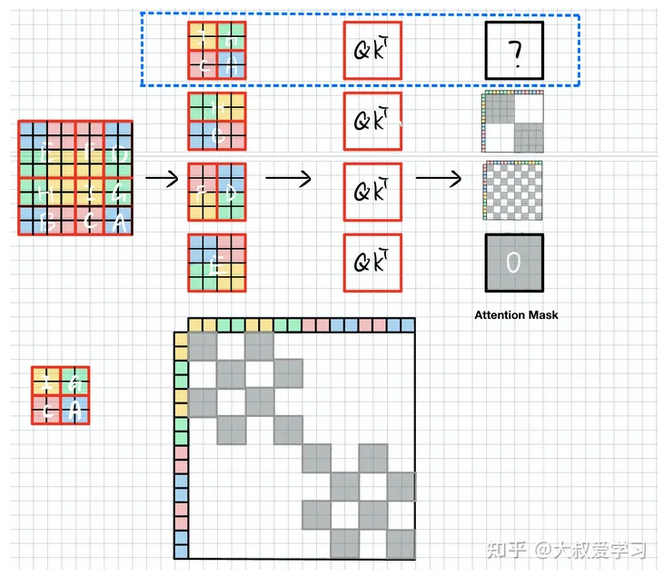
最终att_mask就如下图所示,灰色块给0,其余白色块为-100,将其与 Q K T QK^T QKT相加,softmax激活后可以把-100区域至0。这样我们就把原本需要9个window计算的self-attention,用4个window解决了。
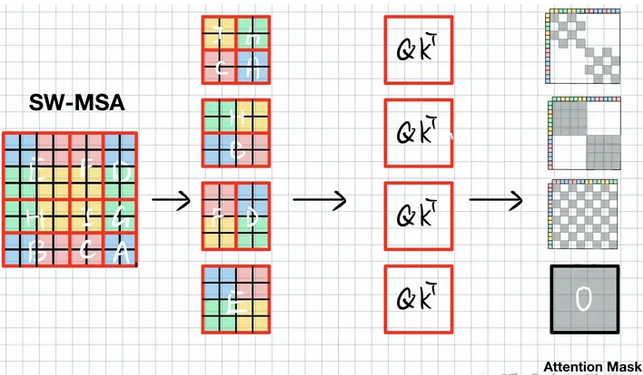
代码如下所示,window_size=7,shift_size=3,hw_shape可以是56x56,28x28,14x14,其中14x14就如上面介绍的例子类似,通过7x7的window将其分成2x2块,分别在4个window中计算self-attention,并roll reverse回去。由于roll的尺度是固定的,所以代码中直接用h_slices,w_slices绘制img_mask,如下所示。ShiftWindowMSA.window_partition将img_mask(维度[1,14,14,1])维度变成[4,7,7,1].

mask_windows 如下所示,我们将其沿xy拉直(如上面例子所述),并相减,这样获得的attn_mask 中为0的部分就是我们需要激活的部分,所有不等于0的部分则需要mask掉。
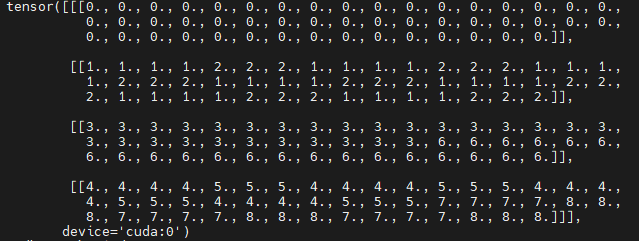
def get_attn_mask(hw_shape, window_size, shift_size, device=None):if shift_size > 0:img_mask = torch.zeros(1, *hw_shape, 1, device=device)h_slices = (slice(0, -window_size), slice(-window_size,-shift_size),slice(-shift_size, None))w_slices = (slice(0, -window_size), slice(-window_size,-shift_size),slice(-shift_size, None))cnt = 0for h in h_slices:for w in w_slices:img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cntcnt += 1# nW, window_size, window_size, 1mask_windows = ShiftWindowMSA.window_partition(img_mask, window_size)mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, window_size * window_size)attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, -100.0)attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, 0.0)else:attn_mask = Nonereturn attn_mask
28x28,56x56与14x14类似,只是多了中间很多值为0的att_mask。至此Swin就讲解完毕了。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!