【Java基础】使用Java8新的日期和时间API
文章目录
- 简介
- java8是如何处理时间及日期的
- LocalDate
- LocalTime
- LocalDateTime
- Instant
- Clock
- Duration
- Period
- TemporalAdjuster
- 时间单位-ChronoUnit枚举类
- 与日期(Date)和日历(Calendar)的兼容性
- DateTimeFormatter
- ZoneId
- java6/java7对日期时间的处理
- 其他历法
- SpringBoot中如何处理LocalDateTime
简介
Java三次引入处理时间的API,JDK1.0中包含了一个Date类,但大多数方法在java1.1引入Calendar类之后被弃用了。 它的实例都是可变的,而且它的API很难使用,比如月份是从0开始这种反人类的设置。java8引入的java.time API 已经纠正了之前的问题。它已经完全实现了JSR310规范。
在Java 8之前,所有关于时间和日期的API都存在各种使用方面的缺陷,主要有:
-
在
java1.0中,对日期时间的支持只能依赖java.util.Date类。,这个类无法表示日期,只能以毫秒的精度表示时间。更糟糕的是它的易用性,比如:年份的起始日期选择是1990年,月份的起始从0开始。 -
java1.1中,Date类中的很多方法被废弃了,取而代之的是java.util.Calendar类。Calendar类也有类似的和设计缺陷,导致使用这些方法写出的代码非常容易出错。比如月份依旧是从0开始计算(拿掉了由1990年开始计算年份这一设计)。更糟的是,有的特性只在某一个类有提供,比如用于语言无关方式格式化和解析日期或时间的DateFormat方法就只在Date类有。 -
java.util.Date和java.util.Calendar类易用性差,不支持时区,且线程不安全的,开发者难以调试这些api的并发问题,需要编写额外的代码来处理线程安全。J
ava 8中引入的新的Date和Time API是不可变的和线程安全的,使得这些痛点得以解决。 -
用于格式化日期的类java.text.DateFormat是一个抽象类,需要实例化一个SimpleDateFormat对象来处理日期格式化,并且DateFormat是
非线程安全,在多线程程序中调用同一个DateFormat对象,会得到意想不到的结果。 -
对日期的计算方式繁琐,而且容易出错,因为月份是从0开始的,从Calendar中获取的月份需要加一才能表示当前月份。
-
Java出现了一些第三方的日期处理框架解决以上问题,例如
Joda-Time, date4j,threetenbp,等开源项目。,于是Java 8中引入了一套标准的用于处理时间和日期API。新的日期API是JSR-310规范的实现,Joda-Time框架的作者正是JSR-310的规范的倡导者,所以能从Java 8的日期API中看到很多Joda-Time的特性 -
新的时间API是以
ISO为中心的,并遵循 date, time, duration 和 periods的一致域模型。提供了一些非常实用方法以支持最常见的操作。不再需要我们自己封装一些时间操作类。 -
ZonedDate和Time -在旧的时间api中开发人员必须编写额外的逻辑来处理旧API的时区逻辑,Java8 中加入了对时区的支持,带时区的时间为分别为:ZonedDate、ZonedTime、ZonedDateTime。其中每个时区都对应着 ID,地区ID都为 “{区域}/{城市}”的格式。
java8引入了一套全新的时间日期API
java.time包中的是类是不可变且线程安全的。新的时间及日期API位于java.time中,下面是一些关键类
-
Instant——它代表的是时间戳,用来获取时间线上的一个点(瞬时/时间戳) -
LocalDate—— 表示没有时区,只含年月日的日期,比如2014-01-14。它可以用来存储生日,周年纪念日,入职日期等,是不可变且线程安全的 -
LocalTime——它代表的是没有时区,只含时分秒的时间 ,是不可变且线程安全的 -
LocalDateTime——它表示没有时区的,同时包含年月日时分秒的日期时间,是不可变且线程安全 -
ZonedDateTime——包含时区的完整的日期时间,偏移量是以UTC/格林威治时间为基准的。 -
ZoneId: 时区ID,用来确定Instant和LocalDateTime互相转换的规则 -
Clock: 用于访问当前时刻、日期、时间,用到时区 -
Duration: 用秒和纳秒表示时间的数量(长短),用于计算两个日期的“时间”间隔 -
Period: 用于计算两个“日期”间隔
其中,LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime是新API里的基础对象
java8是如何处理时间及日期的
LocalDate
- LocalDate类表示一个没有时区,只含年月日的日期。可以通过LocalDate的静态方法
of()创建一个实例,LocalDate也包含一些方法用来获取年份,月份,天,星期几等: - 它可以用来存储生日,周年纪念日,入职日期等,是不可变且线程安全的
@Testpublic void TestLocalDate() {//1.获取当前日期LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();System.out.println("now=》" + now.getYear() + "-" + now.getMonthValue() + "-" + now.getDayOfMonth());//2.设置指定日期LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.of(2019, 11, 5); // 初始化一个日期:2019-11-5int year = localDate.getDayOfYear(); // 年份:2019Month month = localDate.getMonth(); // 月份:DECEMBERint dayOfMonth = localDate.getDayOfMonth(); // 月份中的第几天:5DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = localDate.getDayOfWeek(); // 一周的第几天:THURSDAYint length = localDate.lengthOfMonth(); // 月份的天数:boolean leapYear = localDate.isLeapYear(); // 是否是闰年System.out.println("dayOfYear=》" + year + ",month=》" + month + ",dayOfMonth=》" + dayOfMonth+ ",dayOfWeek=》" + dayOfWeek + ",lengthOfMonth=》" + length+ ",isLeapYear=》" + leapYear);//3.日期字符串转换LocalDate//LocalDate.parse(String dateStr) 默认格式为 DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE 即:2011-12-03LocalDate formatDate = LocalDate.parse("2011-12-03", DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE);System.out.println("formatDate=》"+formatDate);//4.日期相减//要使上面日期相减的代码正确编译,你需要使用静态导入TemporalAdjusters对象:// import static java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters.*;LocalDate minus1 = formatDate.minusDays(5); //当前日期减5天LocalDate minus2 = formatDate.minusDays(-1); //当前日期+1天System.out.println("formatDate=》" + formatDate + ", 减5 :" + minus1 + ",加1 " + minus2);LocalDate currentLocalDate = LocalDate.of(2017,01,05);LocalDate date1 = currentLocalDate.withYear(2016); // 修改为 2016-01-05LocalDate date2 = currentLocalDate.withMonth(2); // 修改为 2017-02-05LocalDate date3 = currentLocalDate.withDayOfMonth(1); // 修改为 2017-01-01LocalDate date4 = currentLocalDate.plusYears(1); // 增加一年 2018-01-05LocalDate date5 = currentLocalDate.minusMonths(2); // 减少两个月 2016-11-05LocalDate date6 = currentLocalDate.plus(5, ChronoUnit.DAYS); // 增加5天 2017-01-10LocalDate date7 = currentLocalDate.with(TemporalAdjusters.nextOrSame(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)); // 返回下一个距离当前时间最近的星期日LocalDate date9 = currentLocalDate.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastInMonth(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY)); // 返回本月最后一个星期六//5.时间间隔(LocalDate,LocalTime,LocalDateTime,Instant也都实现了ChronoLocalDate接口的until方法)Long date10 = currentLocalDate.until(LocalDate.of(2017, 01, 25),ChronoUnit.DAYS); // 将此日期和其他日期之间的时间间隔计算为指定数值Period date11 = currentLocalDate.until(LocalDate.of(2017, 01, 25)); // 将此日期和其他日期之间的时间间隔计算为Period}
执行结果:
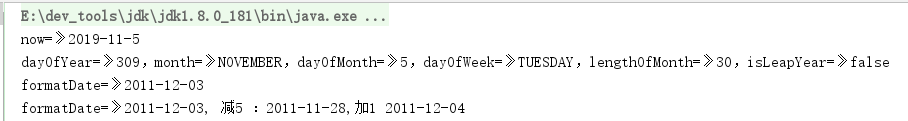
要使上面日期相减的代码正确编译,你需要使用静态导入TemporalAdjusters对象:
import static java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters.*;
所有的日期类都实现了TemporalAdjusters类
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| dayOfWeekInMonth | 返回同一个月中每周的第几天 |
| firstDayOfMonth | 返回当月的第一天 |
| firstDayOfNextMonth | 返回下月的第一天 |
| firstDayOfNextYear | 返回下一年的第一天 |
| firstDayOfYear | 返回本年的第一天 |
| firstInMonth | 返回同一个月中第一个星期几 |
| lastDayOfMonth | 返回当月的最后一天 |
| lastDayOfNextMonth | 返回下月的最后一天 |
| lastDayOfNextYear | 返回下一年的最后一天 |
| lastDayOfYear | 返回本年的最后一天 |
| lastInMonth | 返回同一个月中最后一个星期几 |
| next / previous | 返回后一个/前一个给定的星期几 |
| nextOrSame / previousOrSame | 返回后一个/前一个给定的星期几,如果这个值满足条件,直接返回 |
日期类LocalDate,LocalTime,LocalDateTime,Instant也都实现了
ChronoLocalDate接口,并对里面的方法进行了各自的重写
如:计算时间间隔方法
- long until(Temporal endExclusive, TemporalUnit unit)
LocalTime
它代表的是没有时区,只含时分秒的时间 ,是不可变且线程安全的,用法和LocalDate差不多
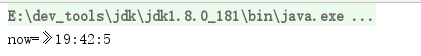
@Testpublic void TestLocalTime() {//1.获取当前日期时间LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();}
执行结果:
LocalDateTime
- LocalDateTime类是LocalDate和LocalTime的结合体,它表示没有时区的,同时包含年月日时分秒的日期时间,是不可变且线程安全,可以通过of()方法直接创建
- 它同时表示了日期和时间,但不带有时区信息,可以直接创建,也可以通过合并日期和时间对象构造。
- 调用LocalDate的atTime()方法或LocalTime的atDate()方法将LocalDate或LocalTime合并成一个LocalDateTime
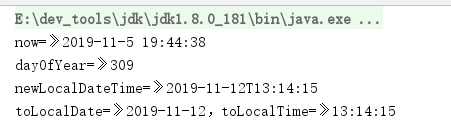
@Testpublic void testLocalDateTime() {//1.获取当前日期时间LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println("now=》" + now.getYear() + "-" + now.getMonthValue() + "-" + now.getDayOfMonth() + " "+ now.getHour() + ":" + now.getMinute() + ":" + + now.getSecond());//2.设置指定日期LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 11, 5, 14, 29, 35);int dayOfYear = localDateTime.getDayOfYear(); //一年第几天System.out.println("dayOfYear=》" + dayOfYear);// 3.将 LocalDate 和 LocalTime 组合成一个 LocalDateTimeLocalDate localDate = LocalDate.of(2019, 11, 12);LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.of(13, 14, 15);LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(localDate, localTime);System.out.println("newLocalDateTime=》" + newLocalDateTime);//4.将LocalDateTime 分割成LocalDate和LocalTimeLocalDate toLocalDate = newLocalDateTime.toLocalDate();LocalTime toLocalTime = newLocalDateTime.toLocalTime();System.out.println("toLocalDate=》" + toLocalDate + ",toLocalTime=》" + toLocalTime);}
执行结果:
Instant
- Instant用于表示一个时间戳,它与我们常使用的System.currentTimeMillis()有些类似,不过Instant可以精确到纳秒(Nano-Second),System.currentTimeMillis()方法只精确到毫秒(Milli-Second)。
- 如果查看Instant源码,发现它的内部使用了两个常量,seconds表示从1970-01-01 00:00:00开始到现在的秒数,nanos表示纳秒部分(nanos的值不会超过999,999,999)。
- Instant除了使用now()方法创建外,还可以通过ofEpochSecond方法创建
@Testpublic void testInstant() {//1.获取当前毫秒数Instant now = Instant.now();System.out.println("now=>" + now);// instant实例System.out.println("toEpochMilli()=>" + now.toEpochMilli());//获取毫秒数Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochSecond(120, 100000);// ofEpochSecond()方法的第一个参数为秒,第二个参数为纳秒,// 上面的代码表示从1970-01-01 00:00:00开始后两分钟的10万纳秒的时刻,控制台上的输出为:System.out.println("ofEpochSecond()=》" + instant);System.out.println("toEpochMilli()=》" + instant.toEpochMilli());}
执行结果:

Clock
获取某个时区下当前的瞬时时间、日期,代替System.currentTimelnMillis()与TimeZone.getDefault()方法
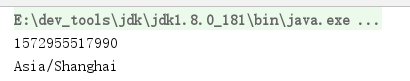
@Testpublic void testClock() {//1.获取系统默认的瞬时时间System.out.println( Clock.systemDefaultZone().millis());//获取//2.获取UTC瞬时时间Clock clock = Clock.systemUTC();System.out.println(clock.millis());//获取UTC的瞬时时间}
执行结果
Duration
- Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔
- Duration的内部实现与Instant类似,也是包含两部分:seconds表示秒,nanos表示纳秒。
- 两者的区别是Instant用于表示一个时间戳(或者说是一个时间点),而Duration表示一个时间段,所以Duration类中不包含now()静态方法。
- 还可以可以通过Duration.between()方法创建一个指定范围的Duration对象
@Testpublic void testDuration() {//1.计算两个时间段的总天数/小时数/分钟数/秒数/毫秒数/纳秒数 例如:计算2019-11-11 02:03:04 - 2019-11-11 05:03:04LocalDateTime from = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 11, 11, 2, 3, 4); // 2019-10-01 02:03:04LocalDateTime to = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 11, 11, 5, 3, 4); // 2019-11-11 05:03:04Duration duration = Duration.between(from, to); // 表示从 2017-01-05 10:07:00 到 2017-02-05 10:07:00 这段时间long days = duration.toDays(); // 这段时间的总天数long hours = duration.toHours(); // 这段时间的小时数long minutes = duration.toMinutes(); // 这段时间的分钟数long seconds = duration.getSeconds(); // 这段时间的秒数long milliSeconds = duration.toMillis(); // 这段时间的毫秒数long nanoSeconds = duration.toNanos(); // 这段时间的纳秒数System.out.println("toDays()=》" + days + ",toHours()=》" + hours + ",toMinutes()=》" + minutes + ",toSeconds()=》" + seconds+ ",toMillis()=》" + milliSeconds + ",toNanos()=》" + nanoSeconds);//2. 创建时间段// Duration对象还可以通过of()方法创建,该方法接受一个时间段长度,和一个时间单位作为参数:Duration duration1 = Duration.of(5, ChronoUnit.DAYS); // 5天Duration duration2 = Duration.of(1000, ChronoUnit.MILLIS); // 1000毫秒Duration duration3 = duration2.minusMillis(500);//减少当前时间段毫秒数 duration2 - 500 毫秒 = 500System.out.println("duration1=》" + duration1.getSeconds() + ",duration2=》" + duration2.toMillis());System.out.println("duration3=》" + duration3.toMillis());}
执行结果:

Period
- Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔
- Period在概念上和Duration类似,区别在于Period是以年月日来衡量一个时间段
@Testpublic void testPeriod() {//1. 创建日期时间段 例如:比如2年3个月6天:Period period = Period.of(2, 3, 6);System.out.println("addTo()=》"+period.addTo(LocalDate.now()));// 当前时间新增 2年2个月6天System.out.println("toTotalMonths()=》"+period.toTotalMonths());// 总月数System.out.println("getYears()=》"+period.getYears());// 获取年System.out.println("getMonths()=》"+period.getMonths());// 获取月System.out.println("getDays()=》"+period.getDays());// 获取日//2.计算日期段 例如:2019-10-01 到 2019-11-05 这段时间Period betweenPeriod = Period.between(LocalDate.of(2019, 10, 1),LocalDate.of(2019, 11, 5));System.out.println("\ngetYears()=》"+betweenPeriod.getYears());// 获取年System.out.println("getMonths()=》"+betweenPeriod.getMonths());// 获取月System.out.println("getDays()=》"+betweenPeriod.getDays());// 获取日}
执行结果:

TemporalAdjuster
日期数学计算。例如,要获得“本月第二个星期六”或“下周二”。
public void testAdjusters() {//Get the current dateLocalDate date1 = LocalDate.now();System.out.println("Current date: " + date1);//get the next tuesdayLocalDate nextTuesday = date1.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.TUESDAY));System.out.println("Next Tuesday on : " + nextTuesday);//get the second saturday of next monthLocalDate firstInYear = LocalDate.of(date1.getYear(), date1.getMonth(), 1);LocalDate secondSaturday = firstInYear.with(TemporalAdjusters.nextOrSame(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY)).with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY));System.out.println("Second saturday on : " + secondSaturday);}时间单位-ChronoUnit枚举类
实现了 日期单位接口TemporalUnit,是java8提供的一组标准的日期单位枚举类型
常用单位由ChronoUnit提供,其他单位提供在IsoFields中提供
- CENTURIES: 代表一个世纪概念的单位。
- DAYS: 代表一天的单位。
- DECADES: 代表十年的单位。
- ERAS: 代表一个时代的单位。
- HALF_DAYS: 代表AM / PM使用的半天的的单位。
- HOURS: 代表一小时的单位。
- MICROS: 代表微秒的的单位。
- MILLENNIA: 代表千年的单位。
- MILLIS: 代表毫秒的单位。
- MINUTES: 代表一分钟的单位。
- MONTHS: 代表一个月的单位。
- NANOS: 代表纳秒的单位,最小支持的时间单位。
- SECONDS: 代表秒的单位。
- WEEKS 代表一周的单位。
- YEARS 代表一年的单位。
public void testChromoUnits() {//Get the current dateLocalDate today = LocalDate.now();System.out.println("Current date: " + today);//add 1 week to the current dateLocalDate nextWeek = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.WEEKS);System.out.println("Next week: " + nextWeek);//add 1 month to the current dateLocalDate nextMonth = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.MONTHS);System.out.println("Next month: " + nextMonth);//add 1 year to the current dateLocalDate nextYear = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.YEARS);System.out.println("Next year: " + nextYear);//add 10 years to the current dateLocalDate nextDecade = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DECADES);System.out.println("Date after ten year: " + nextDecade);}
与日期(Date)和日历(Calendar)的兼容性
Java 8添加了toInstant()方法,该方法有助于将旧API中的Date和Calendar实例转换为新的Date Time API
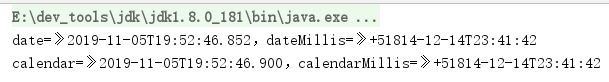
@Testpublic void testDateAndCalendaCompatibilityr(){//Date 转 LocalDateTimeLocalDateTime date = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(new Date().toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault());//Calendar 转 LocalDateTimeLocalDateTime calendar = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Calendar.getInstance().toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault());//通过 Date().getTime() 创建 LocalDateTime / System.currentTimeMillis()LocalDateTime dateMillis = LocalDateTime.ofEpochSecond( System.currentTimeMillis(), 0, ZoneOffset.UTC);//通过 Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis( 创建 LocalDateTimeLocalDateTime calendarMillis = LocalDateTime.ofEpochSecond(Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis(), 0, ZoneOffset.UTC);System.out.println("date=》"+date+",dateMillis=》"+dateMillis.toString());System.out.println("calendar=》"+calendar+",calendarMillis=》"+calendarMillis);}
执行结果:
DateTimeFormatter
日期时间格式化
- 新的日期API中提供了一个DateTimeFormatter类用于处理日期格式化操作,它被包含在java.time.format包中,
- Java 8的日期类有一个format()方法用于将日期格式化为字符串,该方法接收一个DateTimeFormatter类型参数
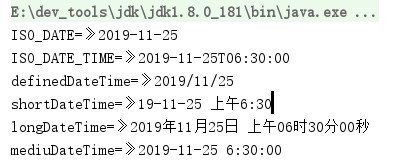
@Testpublic void testDateTimeFormat(){// 1.创建指定时间的LocalDateTimeLocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2019,11, 25, 6, 30);// 传递ISO日期格式以格式化本地日期 结果是:2019-11-25String isoDate= localDateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE);System.out.println("ISO_DATE=》"+isoDate);// 格式成 ISO_DATE_TIME 结果是:2019-11-25T06:30:00String isoDateTime = localDateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);System.out.println("ISO_DATE_TIME=》"+isoDateTime);//该DateTimeFormatter提供多种标准格式选项。也可以提供自定义模式来格式化方法,如下所示,它将返回LocalDate为2015/01/25:String definedDateTime = localDateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd"));System.out.println("definedDateTime=》"+definedDateTime);//我们可以将格式样式传递为SHORT(短),LONG(长)或MEDIUM(中等)作为格式化选项的一部分。下面的代码示例输出2015年1月25日06:30:00 SHORT/LONG/MEDIUMString shortDateTime = localDateTime.format( DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.SHORT));String longDateTime = localDateTime.format( DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG));String mediuDateTime = localDateTime.format( DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM));System.out.println("shortDateTime =》"+shortDateTime);System.out.println("longDateTime=》"+longDateTime);System.out.println("mediuDateTime=》"+mediuDateTime);}
执行结果
ZoneId
- Java 8中的时区操作被很大程度上简化了,新的时区类java.time.ZoneId是原有的java.util.TimeZone类的替代品。
- ZoneId对象可以通过ZoneId.of()方法创建,也可以通过ZoneId.systemDefault()获取系统默认时区:
@Testpublic void testTimeZone(){//1.获取默认时区ZoneId systemZoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();System.out.println("systemZoneId=》"+systemZoneId);// 输出 systemZoneId=》Asia/Shanghai//2.获取指定时区,of()方法接收一个“区域/城市”的字符串作为参数ZoneId shanghaiZoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");System.out.println("shanghaiZoneId=》"+shanghaiZoneId);// 输出 shanghaiZoneId=》Asia/Shanghai//3.通过getAvailableZoneIds()方法获取所有合法的“区域/城市”字符串:Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();System.out.println("zoneIds=》"+zoneIds);// 输出 zoneIds=》[Asia/Aden, America/Cuiaba, Etc/GMT+9, Etc/GMT+8, Africa/Nairobi.......]//4.老的时区类TimeZone转换为ZoneId,Java 8也提供了转化方法:ZoneId oldToNewZoneId = TimeZone.getDefault().toZoneId();System.out.println("oldToNewZoneId=》"+oldToNewZoneId);// 输出 oldToNewZoneId=》Asia/Shanghai//5. 通过ZoneId,我们就可以将一个LocalDate、LocalTime或LocalDateTime对象转化为ZonedDateTime对象:LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.of(localDateTime, shanghaiZoneId);System.out.println("zonedDateTime=》"+zonedDateTime);//6. ZonedDateTime对象由两部分构成,LocalDateTime和ZoneId,// 其中2019-11-05T19:18:06.951部分为LocalDateTime,+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]部分为ZoneId。//另一种表示时区的方式是使用ZoneOffset,它是以当前时间和世界标准时间(UTC)/格林威治时间(GMT)的偏差来计算,例如:ZoneOffset zoneOffset = ZoneOffset.of("+09:00");LocalDateTime newDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = OffsetDateTime.of(newDateTime, zoneOffset);System.out.println("offsetDateTime=》"+offsetDateTime);}
执行结果

java6/java7对日期时间的处理
- Java 7或Java 6这些老项目来说可以使用 Joda-Time/date4j/threetenbp
- 事实上,Java 8 Date Time API由Joda-Time库(Stephen Colebourne)和Oracle共同领导。该库提供了Java 8 Date Time项目中支持的几乎所有功能
其他历法
-
Java中使用的历法是ISO 8601日历系统,它是世界民用历法,也就是我们所说的公历。平
年有365天,闰年是366天。闰年的定义是:非世纪年,能被4整除;世纪年能被400整除。为了计算的一致性,公元1年的前一年被当做公元0年,以此类推。 -
此外Java 8还提供了4套其他历法(很奇怪为什么没有汉族人使用的农历),每套历法都包含一个日期类,分别是:
- ThaiBuddhistDate:泰国佛教历
- MinguoDate:中华民国历
- JapaneseDate:日本历
- HijrahDate:伊斯兰历
-
时区指的是地球上共享同一标准时间的地区。每个时区都有一个唯一标识符,同时还有一个地区/城市(Asia/Tokyo)的格式以及从格林威治时间开始的一个偏移时间。比如说,东京的偏移时间就是+09:00
SpringBoot中如何处理LocalDateTime
后台传LocalDateTime到前台
- 将LocalDateTime字段
以时间戳的方式返回给前端, 添加日期转化类
/*** LocalDateTime Json数据转换器*/
public class LocalDateTimeConverter extends JsonSerializer<LocalDateTime> {@Overridepublic void serialize(LocalDateTime value, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider serializers) throws IOException {gen.writeNumber(value.toInstant(ZoneOffset.of("+8")).toEpochMilli());}
}
并在 LocalDateTime字段上添加@JsonSerialize(using=LocalDateTimeConverter.class)注解,如下:
@JsonSerialize(using=LocalDateTimeConverter.class)
protected LocalDateTime gmtModified;
将LocalDateTime字段以指定格式化日期的方式返回给前端在 LocalDateTime字段上添加 @JsonFormat(shape=JsonFormat.Shape.STRING,pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")注解即可,如下:
@JsonFormat(shape=JsonFormat.Shape.STRING, pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
protected LocalDateTime gmtModified;
前台传LocalDateTime到后台
- 对前端传入的日期进行格式化 在
LocalDateTime字段上添加@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")注解即可,如下:
@DateTimeFormat(pattern ="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
protected LocalDateTime gmtModified;
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!