数据结构(集合)学习之Map(二)
集合
框架关系图
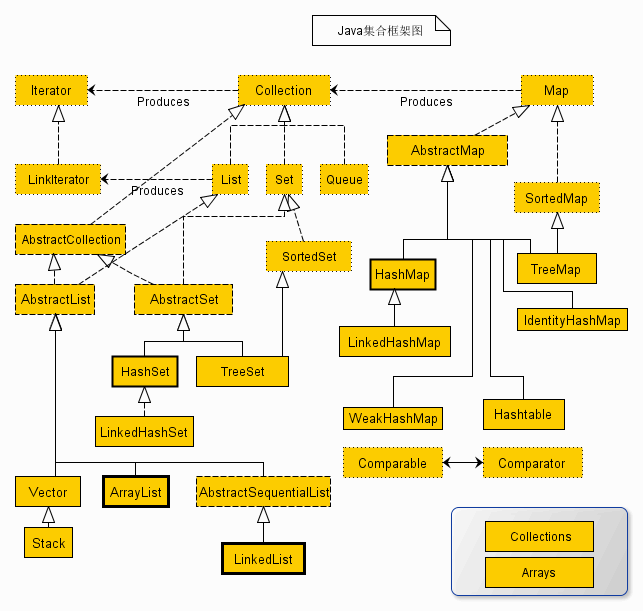
补充:HashTable父类是Dictionary,不是AbstractMap。
一:HashMap中的链循环:
一般来说HashMap中的链循环会发生在多线程操作时(虽然HashMap就不是线程安全的,一般多线程的时候也不会用它,但这种情况难免会发生)
以JDK1.7为例:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {resize(2 * table.length);//扩容方法,参数为原来数组长度的2倍hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);}createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);}void resize(int newCapacity) {Entry[] oldTable = table;//数组原来的数据int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;//原来数组的长度if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return;}Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];//以新的初始容量创建新的数组transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));//转换方法table = newTable;threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);}void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {int newCapacity = newTable.length;for (Entry e : table) {while(null != e) {Entry next = e.next;if (rehash) {e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);}int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);//e是oldTable上的Entry对象,这里算出新数组的下标e.next = newTable[i];newTable[i] = e;e = next;}}}
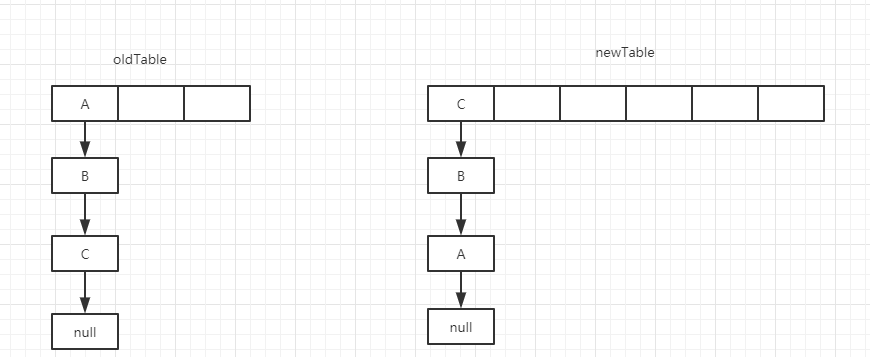
通过代码分析:当old Table中的数值都转移到newTable时,元素的顺序会进行颠倒。效果图如下:
在这种情况下,假设有两个线程同时进行扩容的操作且都进入了transfer方法时,但是因为某个情况让线程一先执行完,线程二才开始执行。
这个时候如果线程一执行完了,线程二开始的状态就是这样:
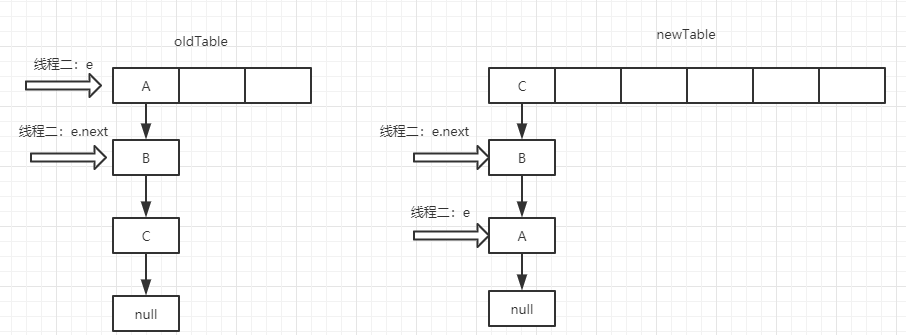
这个时候:线程二的e还是A对象,e.Next(A.Next)还是指向B,但是因为线程一的关系,实际上此时B.Next已经指向了A。于是就产生了循环:A.Next指向B,B.Next指向A。
二:hashtable
HashTable是Map接口下的一个子类,线程安全的,1.7和1.8差别不大,常和HashMap作比较,部分源码如下:
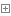
1 //hashTable默认初始容量和加载因子2 public Hashtable() {3 this(11, 0.75f);4 }5 6 //Put方法7 public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {8 // 不允许存null9 if (value == null) {10 throw new NullPointerException();11 }12 13 // key相同时新值代替老值,并把老值返回出去14 Entry tab[] = table;15 int hash = hash(key);//哈希算法16 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;17 for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {18 if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {19 V old = e.value;20 e.value = value;21 return old;22 }23 }24 25 modCount++;26 if (count >= threshold) {27 rehash();//扩容28 29 tab = table;30 hash = hash(key);31 index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;32 }33 34 Entry e = tab[index];35 tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);36 count++;37 return null;38 }39 //哈希算法40 private int hash(Object k) {41 return hashSeed ^ k.hashCode();42 }43 //扩容方法44 protected void rehash() {45 int oldCapacity = table.length;46 Entry[] oldMap = table;47 48 int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;//扩容后容量为原来的2倍再加149 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {50 if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)51 // Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets52 return;53 newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;54 }55 Entry[] newMap = new Entry[newCapacity];56 57 modCount++;58 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);59 boolean rehash = initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity);60 61 table = newMap;62 63 for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {64 for (Entry old = oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {65 Entry e = old;66 old = old.next;67 68 if (rehash) {69 e.hash = hash(e.key);70 }71 int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;72 e.next = newMap[index];73 newMap[index] = e;74 }75 }76 }77 //remove方法78 public synchronized V remove(Object key) {79 Entry tab[] = table;80 int hash = hash(key);81 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;82 for (Entry e = tab[index], prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {83 if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {84 modCount++;85 if (prev != null) {86 prev.next = e.next;87 } else {88 tab[index] = e.next;89 }90 count--;91 V oldValue = e.value;92 e.value = null;93 return oldValue;94 }95 }96 return null;97 }98 //get方法99 public synchronized V get(Object key) {
100 Entry tab[] = table;
101 int hash = hash(key);
102 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
103 for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
104 if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
105 return e.value;
106 }
107 }
108 return null;
109 }
110 //keySet方法
111 public Set keySet() {
112 if (keySet == null)
113 keySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new KeySet(), this);
114 return keySet;
115 }
116
117 private class KeySet extends AbstractSet {
118 public Iterator iterator() {
119 return getIterator(KEYS);
120 }
121 public int size() {
122 return count;
123 }
124 public boolean contains(Object o) {
125 return containsKey(o);
126 }
127 public boolean remove(Object o) {
128 return Hashtable.this.remove(o) != null;
129 }
130 public void clear() {
131 Hashtable.this.clear();
132 }
133 }
134 //entrySet方法
135 public Set> entrySet() {
136 if (entrySet==null)
137 entrySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new EntrySet(), this);
138 return entrySet;
139 }
140
141 private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet> {
142 public Iterator> iterator() {
143 return getIterator(ENTRIES);
144 }
145
146 public boolean add(Map.Entry o) {
147 return super.add(o);
148 }
149
150 public boolean contains(Object o) {
151 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
152 return false;
153 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)o;
154 Object key = entry.getKey();
155 Entry[] tab = table;
156 int hash = hash(key);
157 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
158
159 for (Entry e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next)
160 if (e.hash==hash && e.equals(entry))
161 return true;
162 return false;
163 }
164 //clear方法
165 public synchronized void clear() {
166 Entry tab[] = table;
167 modCount++;
168 for (int index = tab.length; --index >= 0; )
169 tab[index] = null;
170 count = 0;
171 }
172 //size方法和isEmpty方法
173 public synchronized int size() {
174 return count;
175 }
176
177 public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
178 return count == 0;
179 }
可以看出和HashMap比较,有以下特点:
1、初始容量为11。
2、扩容方法为:oldTable.Length*2+1。
3、不允许存null值。
4、计算hash,和获取数组下标不同:
HashTable:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
HashMap:
int hash = hash(key);//
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
5、HashTable线程安全,主要的方法都用了synchronized,加锁。
6、HashMap和HashTable父类不同
public class HashMap
public class Hashtable
7、HashTable线程安全,但因为每个主要方法上都加上了锁,所以在执行效率上会慢很多。
三:其他线程安全Map
1、synchronizedMap
通过工具类Collections的方法,返回一个HashMap,例如:Map
1 public static Map synchronizedMap(Map m) {2 return new SynchronizedMap<>(m);3 }4 5 private static class SynchronizedMap6 implements Map, Serializable {7 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1978198479659022715L;8 9 private final Map m; // Backing Map
10 final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize
11
12 SynchronizedMap(Map m) {
13 if (m==null)
14 throw new NullPointerException();
15 this.m = m;
16 mutex = this;
17 }
18
19 SynchronizedMap(Map m, Object mutex) {
20 this.m = m;
21 this.mutex = mutex;
22 }
23
24 public int size() {
25 synchronized (mutex) {return m.size();}
26 }
27 public boolean isEmpty() {
28 synchronized (mutex) {return m.isEmpty();}
29 }
30 public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
31 synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsKey(key);}
32 }
33 public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
34 synchronized (mutex) {return m.containsValue(value);}
35 }
36 public V get(Object key) {
37 synchronized (mutex) {return m.get(key);}
38 }
39
40 public V put(K key, V value) {
41 synchronized (mutex) {return m.put(key, value);}
42 }
43 public V remove(Object key) {
44 synchronized (mutex) {return m.remove(key);}
45 }
46 public void putAll(Map map) {
47 synchronized (mutex) {m.putAll(map);}
48 }
49 public void clear() {
50 synchronized (mutex) {m.clear();}
51 }
52
53 private transient Set keySet = null;
54 private transient Set> entrySet = null;
55 private transient Collection values = null;
56
57 public Set keySet() {
58 synchronized (mutex) {
59 if (keySet==null)
60 keySet = new SynchronizedSet<>(m.keySet(), mutex);
61 return keySet;
62 }
63 }
64
65 public Set> entrySet() {
66 synchronized (mutex) {
67 if (entrySet==null)
68 entrySet = new SynchronizedSet<>(m.entrySet(), mutex);
69 return entrySet;
70 }
71 }
72
73 public Collection values() {
74 synchronized (mutex) {
75 if (values==null)
76 values = new SynchronizedCollection<>(m.values(), mutex);
77 return values;
78 }
79 }
80
81 public boolean equals(Object o) {
82 if (this == o)
83 return true;
84 synchronized (mutex) {return m.equals(o);}
85 }
86 public int hashCode() {
87 synchronized (mutex) {return m.hashCode();}
88 }
89 public String toString() {
90 synchronized (mutex) {return m.toString();}
91 }
92 private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
93 synchronized (mutex) {s.defaultWriteObject();}
94 }
95 }
可以看出,原理就是在原来Map的基础上,加上锁synchronized (mutex),来让线程变得安全,但和HashTable一样,效率慢。
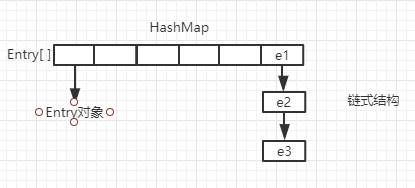
2、ConcurrentHashMap
JDK1.7中的ConcurrentHashMap:
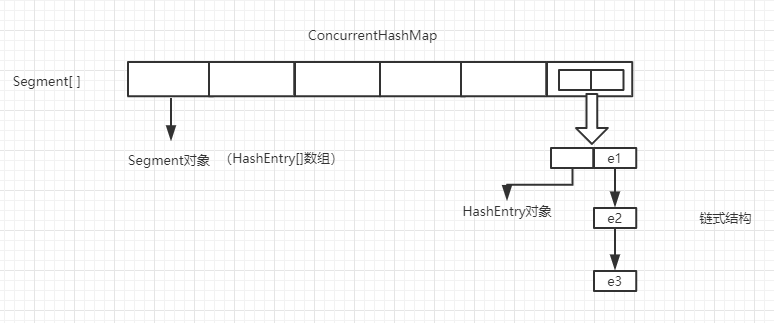
ConcurrentHashMap是线程安全的Map,继承AbstractMap。是和HashTable把整合数组共享一把锁不同,ConcurrentHashMap采用分段的思想,把HashMap分为多个段进行加锁的操作,这样既保证了线程安全性,又不会使效率像HashTable那样低。
ConcurrentHashMap的特点是分段式加锁,并利用Unsafe对象和volatile关键字来实现线程安全,他比较明显的一个局限性是并发级别一旦指定就不再更改。
结构:
代码:
1 //默认初始容量(2的幂),实际上是指的HashEntry的数量2 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;3 //默认加载因子4 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;5 //默认并发级别(实际上指的Segmengt对象的数量,初始化后不可更改)6 static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;7 //最大容量小于等于2的30次幂8 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;9 //最小SEGMENT容量(一个Segment里至少有两个HashEntry)10 static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;11 //最大SEGMENT容量容量12 static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16;13 //加锁之前的重试次数14 static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;15 //Segment数组16 final Segment[] segments;17 //计算segment位置的掩码,用于计算Segment[]下标18 final int segmentMask;19 //用于算segment位置时,hash参与运算的位数20 final int segmentShift;21 //内部类HashEntry,相当于HashMap中Entry[]中的Entry对象22 static final class HashEntry {23 final int hash;24 final K key;25 volatile V value;26 volatile HashEntry next;27 28 HashEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashEntry next) {29 this.hash = hash;30 this.key = key;31 this.value = value;32 this.next = next;33 }34 35 final void setNext(HashEntry n) {36 UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, n);37 }38 39 static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;40 static final long nextOffset;41 static {42 try {43 UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();44 Class k = HashEntry.class;45 nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset46 (k.getDeclaredField("next"));47 } catch (Exception e) {48 throw new Error(e);49 }50 }51 }52 //hash函数53 private int hash(Object k) {54 int h = hashSeed;55 56 if ((0 != h) && (k instanceof String)) {57 return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);58 }59 60 h ^= k.hashCode();61 62 h += (h << 15) ^ 0xffffcd7d;63 h ^= (h >>> 10);64 h += (h << 3);65 h ^= (h >>> 6);66 h += (h << 2) + (h << 14);67 return h ^ (h >>> 16);68 }69 //ConcurrentHashMap的构造方法70 public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {//初始容量,加载因子,并发级别71 if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)//保证参数不能小于072 throw new IllegalArgumentException();73 if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)//保证并发级别不能大于最大Segment容量74 concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;75 76 int sshift = 0;77 int ssize = 1;78 while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {79 ++sshift;//统计ssize左移的次数80 ssize <<= 1;//初始是1,通过左移然后2、4、8、16...作用是找到大于等于并发级别的2的“sshift”次幂81 }82 this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;//用于Put方法中,求Segment[]数组的下标时用83 this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;//Segmengt[].length-184 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)//如果初始容量大于最大85 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;//则选择最大容量作为容量86 int c = initialCapacity / ssize;//HashEntry[].length/Segmengt[].length,用来标记HashEntry的数量87 if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)//例如initialCapacity = 9,concurrencyLevel(ssize) = 8 ,则initialCapacity / ssize = 1,c * ssize < initialCapacity88 ++c; // 然后让C = 2, 此时 c * ssize >= initialCapacity ,这里的目的就是保证数据都被Segmengt存储。89 int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;90 while (cap < c)//拿最小的容量和刚刚计算的 c 进行比较91 cap <<= 1; // 保证最小容量是2的n次幂92 Segment s0 =93 new Segment(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),94 (HashEntry[])new HashEntry[cap]);//初始化Segment对象95 Segment[] ss = (Segment[])new Segment[ssize];//初始化Segment数组96 UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); //调用Unsafe中的方法,作用是把刚刚初始化的Segemengt对象s0,放到刚刚初始化Segment[]数组中的Segment[0],也就是第一位97 this.segments = ss;98 }99 //Put方法
100 public V put(K key, V value) {
101 Segment s;
102 if (value == null)
103 throw new NullPointerException();//不能传null,此处个人认为应该加个 key也不能为 null的判断
104 int hash = hash(key);//计算hash值
105 int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; // 计算Segmengt[]下标,即数据存储的位置
106 if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObject(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // 调用Unsafe的方法,作用是获取Segmengt[j]的对象,如果等于空
107 s = ensureSegment(j);//判断第j个位置是不是为空,保证线程安全性
108 return s.put(key, hash, value, false);//调用Segmengt对象的put方法
109 }
110
111 //Segmengt的Put方法
112 final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
113 HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);//加锁,保证线程安全
114 V oldValue;
115 try {
116 HashEntry[] tab = table;
117 int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
118 HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index);//获取该位置的第一个元素,然后遍历链表
119 for (HashEntry e = first;;) {
120 if (e != null) {
121 K k;
122 if ((k = e.key) == key ||
123 (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
124 oldValue = e.value;
125 if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
126 e.value = value;
127 ++modCount;
128 }
129 break;
130 }
131 e = e.next;
132 }
133 else {
134 if (node != null)
135 node.setNext(first);
136 else
137 node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first);
138 int c = count + 1;
139 if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
140 rehash(node);
141 else
142 setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
143 ++modCount;
144 count = c;
145 oldValue = null;
146 break;
147 }
148 }
149 } finally {
150 unlock();
151 }
152 return oldValue;
153 }
154
155 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
156 private void rehash(HashEntry node) {//扩容方法,只扩容HashEntry[],没扩容Segmengt[]
157
158 HashEntry[] oldTable = table;
159 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
160 int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
161 threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
162 HashEntry[] newTable =
163 (HashEntry[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity];
164 int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1;
165 for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) {
166 HashEntry e = oldTable[i];
167 if (e != null) {
168 HashEntry next = e.next;
169 int idx = e.hash & sizeMask;
170 if (next == null)
171 newTable[idx] = e;
172 else {
173 HashEntry lastRun = e;
174 int lastIdx = idx;
175 for (HashEntry last = next;
176 last != null;
177 last = last.next) {
178 int k = last.hash & sizeMask;
179 if (k != lastIdx) {
180 lastIdx = k;
181 lastRun = last;
182 }
183 }
184 newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun;
185
186 for (HashEntry p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
187 V v = p.value;
188 int h = p.hash;
189 int k = h & sizeMask;
190 HashEntry n = newTable[k];
191 newTable[k] = new HashEntry(h, p.key, v, n);
192 }
193 }
194 }
195 }
196 int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask;
197 node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]);
198 newTable[nodeIndex] = node;
199 table = newTable;
200 }
201
202 private HashEntry scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {
203 HashEntry first = entryForHash(this, hash);
204 HashEntry e = first;
205 HashEntry node = null;
206 int retries = -1;
207 while (!tryLock()) {
208 HashEntry f;
209 if (retries < 0) {
210 if (e == null) {
211 if (node == null)
212 node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, null);
213 retries = 0;
214 }
215 else if (key.equals(e.key))
216 retries = 0;
217 else
218 e = e.next;
219 }
220 else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
221 lock();
222 break;
223 }
224 else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
225 (f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
226 e = first = f;
227 retries = -1;
228 }
229 }
230 return node;
231 }
232
233 private void scanAndLock(Object key, int hash) {
234
235 HashEntry first = entryForHash(this, hash);
236 HashEntry e = first;
237 int retries = -1;
238 while (!tryLock()) {
239 HashEntry f;
240 if (retries < 0) {
241 if (e == null || key.equals(e.key))
242 retries = 0;
243 else
244 e = e.next;
245 }
246 else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
247 lock();
248 break;
249 }
250 else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
251 (f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
252 e = first = f;
253 retries = -1;
254 }
255 }
256 }
257
258 final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
259 if (!tryLock())
260 scanAndLock(key, hash);
261 V oldValue = null;
262 try {
263 HashEntry[] tab = table;
264 int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
265 HashEntry e = entryAt(tab, index);
266 HashEntry pred = null;
267 while (e != null) {
268 K k;
269 HashEntry next = e.next;
270 if ((k = e.key) == key ||
271 (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
272 V v = e.value;
273 if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) {
274 if (pred == null)
275 setEntryAt(tab, index, next);
276 else
277 pred.setNext(next);
278 ++modCount;
279 --count;
280 oldValue = v;
281 }
282 break;
283 }
284 pred = e;
285 e = next;
286 }
287 } finally {
288 unlock();
289 }
290 return oldValue;
291 }
292
293 final boolean replace(K key, int hash, V oldValue, V newValue) {
294 if (!tryLock())
295 scanAndLock(key, hash);
296 boolean replaced = false;
297 try {
298 HashEntry e;
299 for (e = entryForHash(this, hash); e != null; e = e.next) {
300 K k;
301 if ((k = e.key) == key ||
302 (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
303 if (oldValue.equals(e.value)) {
304 e.value = newValue;
305 ++modCount;
306 replaced = true;
307 }
308 break;
309 }
310 }
311 } finally {
312 unlock();
313 }
314 return replaced;
315 }
316
317 final V replace(K key, int hash, V value) {
318 if (!tryLock())
319 scanAndLock(key, hash);
320 V oldValue = null;
321 try {
322 HashEntry e;
323 for (e = entryForHash(this, hash); e != null; e = e.next) {
324 K k;
325 if ((k = e.key) == key ||
326 (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
327 oldValue = e.value;
328 e.value = value;
329 ++modCount;
330 break;
331 }
332 }
333 } finally {
334 unlock();
335 }
336 return oldValue;
337 }
338
339 final void clear() {
340 lock();
341 try {
342 HashEntry[] tab = table;
343 for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++)
344 setEntryAt(tab, i, null);
345 ++modCount;
346 count = 0;
347 } finally {
348 unlock();
349 }
350 }
351 }
352 //Get方法
353 public V get(Object key) {
354 Segment s;
355 HashEntry[] tab;
356 int h = hash(key);
357 long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;//先获取Segment[] 的下标
358 if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null && (tab = s.table) != null) { //用Unsafe的方法获取到Segment对象
359 //用Unsafe的方法HashEntry对象,然后遍历链表
360 for (HashEntry e = (HashEntry) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE); e != null; e = e.next) {
361 K k;
362 if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
363 return e.value;
364 }
365 }
366 return null;
367 }
JDK1.8:
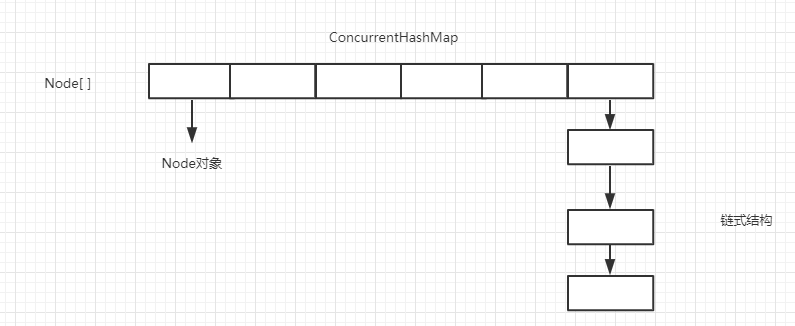
JDK1.8时,ConcurrentHashMap又放弃了分段式加锁的思想,而且也不在用Segment[]数组存值,而是采用在HashMap1.8的基础上,采用Node[] + 链表 + 红黑树 + CAS+ Synchronized 的思想保证线程安全。而且在扩容的时候,不仅要满足链表结构大于8,还要满足数据容量大于64。
1 //最大容量2 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;3 //默认容量4 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;5 //最大数组长度6 static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;7 //默认并发等级(1.7遗留,兼容以前版本)8 private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;9 //加载因子(1.7遗留,兼容以前版本)10 private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;11 //转换为红黑树的阈值(道理和HashMap1.8中一样,这里指链表长度)12 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;13 //红黑树反转成链表的阈值14 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;15 //转换为红黑树的阈值(这里指数组长度)16 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;17 //扩容转移时的最小数组分组大小18 private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;19 //本类中没提供修改的方法 用来根据n生成位置一个类似时间搓的功能20 private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;21 // 2^15-1,help resize的最大线程数22 private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1; 23 // 32-16=16,sizeCtl中记录size大小的偏移量24 private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS; 25 //表示正在转移26 static final int MOVED = -1; 27 // 表示已转换为红黑树28 static final int TREEBIN = -2; 29 // 保留30 static final int RESERVED = -3; 31 // 用在计算hash时进行安位与计算消除负hash32 static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; 33 // 可用处理器数量34 static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); 35 //构造函数36 public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {37 if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)//判断参数是否大于等于038 throw new IllegalArgumentException();39 if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) 40 initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // 容量最小为1641 long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);42 int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?43 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);//获取数组容量并保证不大于最大容量44 this.sizeCtl = cap;45 }46 //Put方法47 public V put(K key, V value) {48 return putVal(key, value, false);49 }50 51 final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {52 if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();//不允许存null53 int hash = spread(key.hashCode());//计算hash值54 int binCount = 0;55 for (Node[] tab = table;;) {56 Node f; int n, i, fh;57 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)58 tab = initTable();//懒加载,数组为空时初始化59 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {//类似Unsafe获取对象的方法获取对象60 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,61 new Node(hash, key, value, null)))//CAS,如果获取位置为空,则将数据存入62 break; 63 }64 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)//首地址处不null 并且Node的hash是-1 表示是ForwardingNode节点正在rehash扩容65 tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);//帮助扩容的方法66 else {67 V oldVal = null;68 synchronized (f) {//加锁69 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {70 if (fh >= 0) {71 binCount = 1;72 for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {73 K ek;74 if (e.hash == hash &&75 ((ek = e.key) == key ||76 (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {//遍历链表,如果key重复,值替换,老值返回出去77 oldVal = e.val;78 if (!onlyIfAbsent)79 e.val = value;80 break;81 }82 Node pred = e;83 if ((e = e.next) == null) {84 pred.next = new Node(hash, key,85 value, null);86 break;87 }88 }89 }90 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {//如果为红黑树的对象,调用红黑树的put方法91 Node p;92 binCount = 2;93 if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,94 value)) != null) {95 oldVal = p.val;96 if (!onlyIfAbsent)97 p.val = value;98 }99 }
100 }
101 }
102 if (binCount != 0) {
103 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
104 //如果链表数据超过指定阈值,转换红黑树,并且会再进行一次判断,看数组容量是否大于64,数组大于64后才会转换为红黑树
105 treeifyBin(tab, i);
106 if (oldVal != null)
107 return oldVal;
108 break;
109 }
110 }
111 }
112 addCount(1L, binCount);
113 return null;
114 }
115 //Get方法,基本和1.8HashMap一样,获取数组坐标,然后获取Node对象,并且没有加锁。
116 public V get(Object key) {
117 Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
118 int h = spread(key.hashCode());
119 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
120 (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
121 if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
122 if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
123 return e.val;
124 }
125 else if (eh < 0)
126 return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
127 while ((e = e.next) != null) {
128 if (e.hash == h &&
129 ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
130 return e.val;
131 }
132 }
133 return null;
134 }
注意:分析ConcurrentHashMap源码前,需要先了解一下CAS、Unsafe、Synchronized 、Volatile相关知识。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!