强化学习实战一 迭代法实现4*4方格下的随机策略
本篇用代码演示《强化学习》第三讲中的示例——方格世界,即用动态规划算法通过迭代计算来评估4*4方格世界中的一个随机策略。具体问题是这样:
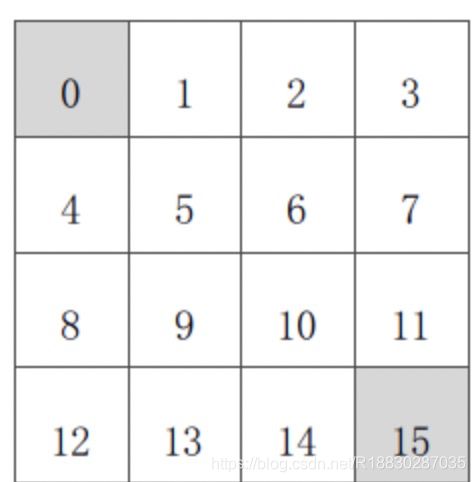
已知(如上图):
状态空间 S:S_{1} - S_{14}为非终止状态;S_{0} ,S_{15} 终止状态,图中灰色方格所示两个位置;
行为空间 A:{n, e, s, w} 对于任何非终止状态可以有向北、东、南、西移动四个行为;
转移概率 P:任何试图离开方格世界的动作其位置将不会发生改变,其余条件下将100%地转移到动作指向的位置;
即时奖励 R:任何在非终止状态间的转移得到的即时奖励均为-1,进入终止状态即时奖励为0;
衰减系数 γ:1;
当前策略π:个体采用随机行动策略,在任何一个非终止状态下有均等的几率往任意可能的方向移动,即π(n|•) = π(e|•) = π(s|•) = π(w|•) = 1/4。
问题:评估在这个方格世界里给定的策略。
该问题等同于:求解该方格世界在给定策略下的(状态)价值函数,也就是求解在给定策略下,该方格世界里每一个状态的价值。
我们使用Python编写代码解决该问题。
-
声明状态
states = [i for i in range(16)]
-
声明状态价值,并初始化各状态价值为0
values = [0 for _ in range(16)]
-
声明行为空间
actions = [“n”, “e”, “s”, “w”]
-
结合方格世界的布局特点,简易声明行为对状态的改变
ds_actions = {“n”: -4, “e”: 1, “s”: 4, “w”: -1}
-
声明衰减系数为1
gamma = 1.00
-
根据当前状态和行为确定下一状态
def nextState(s, a):next_state = sif (s%4 == 0 and a == "w") or (s<4 and a == "n") or \((s+1)%4 == 0 and a == "e") or (s > 11 and a == "s"):passelse:ds = ds_actions[a]next_state = s + dsreturn next_state
- 得到某一状态的即时奖励
def rewardOf(s):return 0 if s in [0,15] else -1
- 判断某一状态是否为终止状态
def isTerminateState(s):return s in [0,15]
- 获取某一状态的所有可能的后继状态
def getSuccessors(s):successors = []if isTerminateState(s):return successorsfor a in actions:next_state = nextState(s, a)# if s != next_state:successors.append(next_state)return successors
- 根据后继状态的价值更新某一状态的价值
def updateValue(s):sucessors = getSuccessors(s)newValue = 0 # values[s]num = 4 # len(successors)reward = rewardOf(s)for next_state in sucessors:newValue += 1.00/num * (reward + gamma * values[next_state])return newValue
- 进行一次迭代
def performOneIteration():newValues = [0 for _ in range(16)]for s in states:newValues[s] = updateValue(s)global valuesvalues = newValuesprintValue(values)- 辅助函数输出状态价值
def printValue(v):
for i in range(16):print('{0:>6.2f}'.format(v[i]),end = " ")if (i+1)%4 == 0:print("")print()
- 主函数
def main():max_iterate_times = 160cur_iterate_times = 0while cur_iterate_times <= max_iterate_times:print("Iterate No.{0}".format(cur_iterate_times))performOneIteration()cur_iterate_times += 1printValue(values)
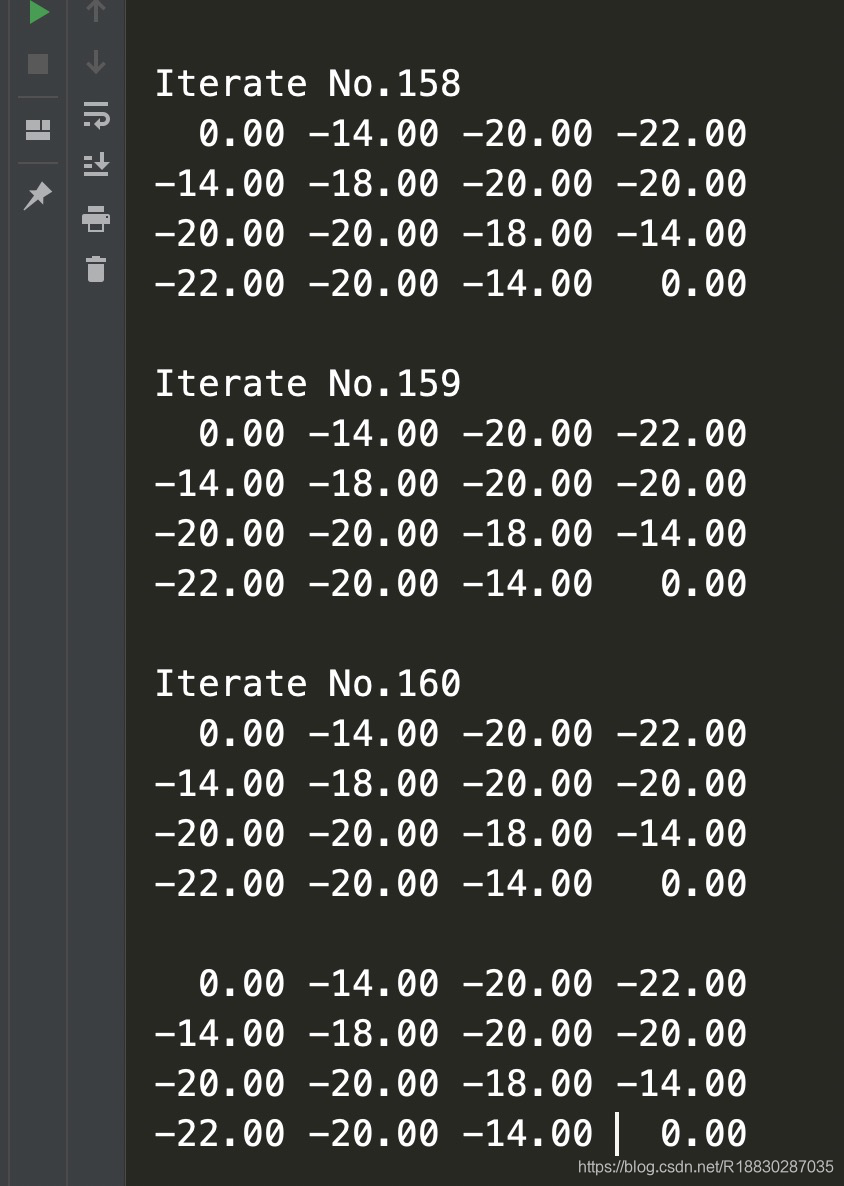
由于事先知道该算法将在150次左右收敛,我们将最大迭代次数设为了160,最后得到的价值函数如下:
The value function converges to:
0.00 -14.00 -20.00 -22.00
-14.00 -18.00 -20.00 -20.00
-20.00 -20.00 -18.00 -14.00
-22.00 -20.00 -14.00 0.00
At Iterate No.153
从以上代码我们可以看出,我们设置了一个获取某一状态所有后续可能状态的集合这么一个方法,这就是体现动态规划算法思想的地方。如果无法获取一个状态的所有可能后续状态,那么就不能使用动态规划算法来求解。此外,我们使用的是异步更新价值的方法,即某一时刻状态的价值由前一时刻状态价值来计算。
完整的Python代码如下:
'''
Implementation of small grid world example illustrated by David Silver
in his Reinforcement Learning Lecture3 - Planning by Dynamic
Programming.
Author: Qiang Ye
Date: July 1, 2017The value function converges to:0.00 -14.00 -20.00 -22.00
-14.00 -18.00 -20.00 -20.00
-20.00 -20.00 -18.00 -14.00
-22.00 -20.00 -14.00 0.00
At Iterate No.153
'''
# id of the states, 0 and 15 are terminal states
states = [i for i in range(16)]
# 0* 1 2 3
# 4 5 6 7
# 8 9 10 11
# 12 13 14 15*# initial values of states
values = [0 for _ in range(16)]# Action
actions = ["n", "e", "s", "w"]# 行为对应的状态改变量
# use a dictionary for convenient computation of next state id.
ds_actions = {"n": -4, "e": 1, "s": 4, "w": -1} # discount factor
gamma = 1.00# 根据当前状态和采取的行为计算下一个状态id以及得到的即时奖励
def nextState(s, a):next_state = sif (s%4 == 0 and a == "w") or (s<4 and a == "n") or \((s+1)%4 == 0 and a == "e") or (s > 11 and a == "s"):passelse:ds = ds_actions[a]next_state = s + dsreturn next_state# reward of a state
def rewardOf(s):return 0 if s in [0,15] else -1# check if a state is terminate state
def isTerminateState(s):return s in [0,15]# get successor states of a given state s
def getSuccessors(s):successors = []if isTerminateState(s):return successorsfor a in actions:next_state = nextState(s, a)# if s != next_state:successors.append(next_state)return successors# update the value of state s
def updateValue(s):sucessors = getSuccessors(s)newValue = 0 # values[s]num = 4 # len(successors)reward = rewardOf(s)for next_state in sucessors:newValue += 1.00/num * (reward + gamma * values[next_state])return newValue# perform one-step iteration
def performOneIteration():newValues = [0 for _ in range(16)]for s in states:newValues[s] = updateValue(s)global valuesvalues = newValuesprintValue(values)# show some array info of the small grid world
def printValue(v):for i in range(16):print('{0:>6.2f}'.format(v[i]),end = " ")if (i+1)%4 == 0:print("")print()# test function
def test():printValue(states)printValue(values)for s in states:reward = rewardOf(s)for a in actions:next_state = nextState(s, a)print("({0}, {1}) -> {2}, with reward {3}".format(s, a,next_state, reward))for i in range(200):performOneIteration()printValue(values)def main():max_iterate_times = 160cur_iterate_times = 0while cur_iterate_times <= max_iterate_times:print("Iterate No.{0}".format(cur_iterate_times))performOneIteration()cur_iterate_times += 1printValue(values)if __name__ == '__main__':main()
结果:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!