机器人学学习笔记(1)20211118
课程连接在此:【机器人理论最好中文入门课程 没有之一】 机械臂 系统 结构 旋转矩阵 变换矩阵 DH模型 运动学正逆解 轨迹规划 动力学 控制 遥控操作 教程_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Chapter1—Spatial Representation and Transformation
1.1Position,Orientation and Frames
①Position Vector
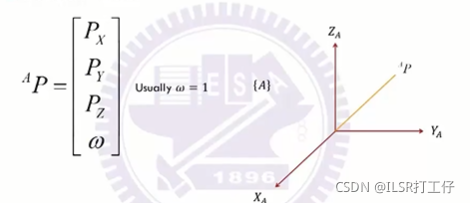
在A坐标系中表示p的位置
② Orientation
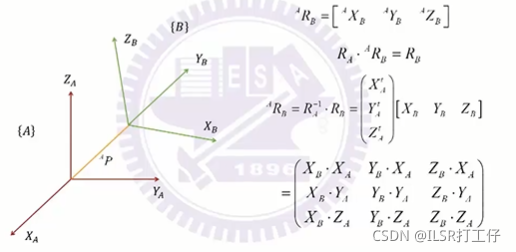
(9个元素有3个自由度是因为有6个限制因素:3*长度=1;3个向量两两互相垂直;)
旋转矩阵的范矩阵是其转置
![]()
1.2Mapping Between Frames
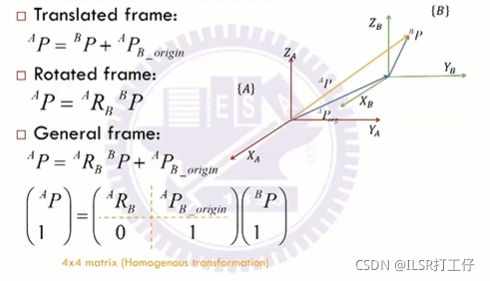
- 平行运动具有可交换性
- 旋转没有交换性
Rotation(not commutative)

选择特殊轴(xyz)作为旋转轴——(把复杂系统变简单)分量彼此不会有关系
General
顺着z轴转和移动z是最在意的方向,y是被选定的方向,x是在其基础上就定下来的
前乘与后乘的选择
后乘:A×B表示B相对于A旋转
前乘:B×A表示基座是世界坐标系
Compound
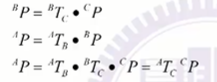
Inversion

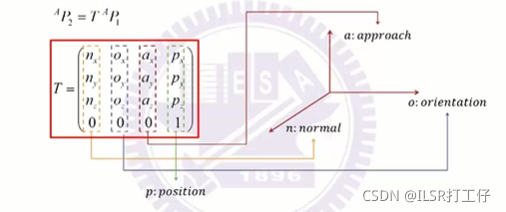
1.3 Transfomation
General Rotstion Transformation
Rotation about an arbitrary vector k from origin
First find a coordinate frame C

Rotating T about is equivalent to rotating Xaround Z axis of frame C

Given a rotational transformation R

1.4
Equate R to (
)
Define Trace (A)=sum of diagonal components of matrix A
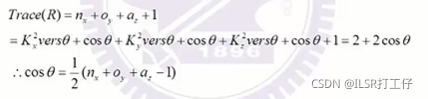
接近0时,突变比较明显,所以在计算时计算量很大,因此选择tan

有正负合理,有两个解。选择正号的,选择角度比较小的,整的时候小于180°

Another set:

From the largest element of noa,the largest of k(xyz)can be determined
1.5Three Angle Rotation : Euler angles,RPY Angles
Euler Angels:
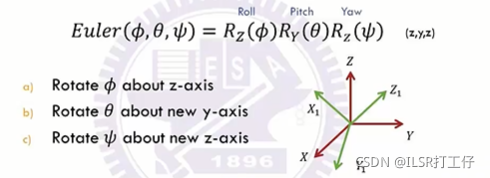
当y轴转0时会出现退化
RPY Angels

Euler transformation solution

For Euler z-y-z

1.6 specification of position
Cylindrical Coordinates
*
*
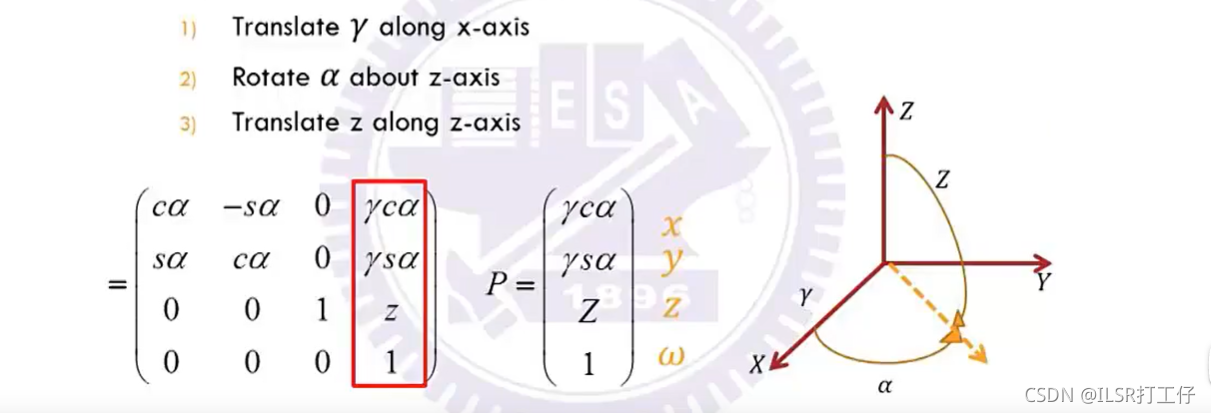
旋转轴和平移轴时可能会比较简单;
Spheriacal Coordiantes

Summary

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!