Linux音频子系统(四)PCM设备的创建
1. PCM是什么
PCM是英文Pulse-code modulation的缩写,中文译名是脉冲编码调制。PCM就是要把声音从模拟转换成数字信号的一种技术,他的原理简单地说就是利用一个固定的频率对模拟信号进行采样,采样后的信号在波形上看就像一串连续的幅值不一的脉冲,把这些脉冲的幅值按一定的精度进行量化,这些量化后的数值被连续地输出、传输、处理或记录到存储介质中,所以对于音频原始的数据是PCM格式。PCM信号的两个重要指标是:
采样频率:定义每秒从连续信号中提取并组成离散信号的采样个数
采样位数:为采集卡处理声音的解析度。这个数值越大,解析度就越高,录制和回放的声音就越真实
播放音乐时,应用程序从存储介质中读取音频数据(MP3、WMA、AAC…),经过解码后,最终送到音频驱动程序中的就是PCM数据,反过来,在录音时,音频驱动不停地把采样所得的PCM数据送回给应用程序,由应用程序完成压缩、存储等任务。所以,这就成为音频驱动的两大核心任务就是:
- playback 如何把用户空间的应用程序发过来的PCM数据,转化为人耳可以辨别的模拟音频
- capture 把mic拾取到得模拟信号,经过采样、量化,转换为PCM信号送回给用户空间的应用程序
ALSA已经为我们实现了功能强劲的PCM中间层,已经实现了播放和录音的框架性接口,自己的驱动中只要实现一些底层的需要访问硬件的函数即可。那么该层主要是起着承上启下的左右,网用户态提供交互接口,实现音频数据在用户态和内核态的拷贝,往下是触发ASOC的操作函数,实现音频数据的传输和交互。
2 PCM注册
上一章在声卡注册中,我们发现snd_register_device_for_dev不只是在声卡注册中用到,其实在PCM注册中也用到了这个接口函数。对于PCM注册直接调用了_snd_pcm_new,那么我们看看这个函数主要做了些什么?
static int _snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,int playback_count, int capture_count, bool internal,struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{struct snd_pcm *pcm;int err;static struct snd_device_ops ops = {.dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free,.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,.dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect,};if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))return -ENXIO;if (rpcm)*rpcm = NULL;pcm = kzalloc(sizeof(*pcm), GFP_KERNEL);if (pcm == NULL) {dev_err(card->dev, "Cannot allocate PCM\n");return -ENOMEM;}pcm->card = card;pcm->device = device;pcm->internal = internal;if (id)strlcpy(pcm->id, id, sizeof(pcm->id));if ((err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, playback_count)) < 0) {snd_pcm_free(pcm);return err;}if ((err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count)) < 0) {snd_pcm_free(pcm);return err;}mutex_init(&pcm->open_mutex);init_waitqueue_head(&pcm->open_wait);if ((err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_PCM, pcm, &ops)) < 0) {snd_pcm_free(pcm);return err;}if (rpcm)*rpcm = pcm;return 0;
}该函数调用kzalloc创建一个pcm之后会做以下事情
- 如果有playback stream,建立playback stream,相应的substream也同时建立
- 如果有capture stream,建立playback stream,相应的substream也同时建立
- 调用snd_device_new()把该pcm挂到声卡中,参数ops中的dev_register字段指向了函数snd_pcm_dev_register,这个回调函数会在声卡的注册阶段被调用
这里面有一个很重要的函数snd_device_new,在card里面维护了一个devices的链表,所有的外设如PCM,TIMER,CONTROL的都会加入到这个链表,并维护着自己的设备节点,上层应用通过节点来访问对应的操作接口,后面会具体的详细介绍这些内容。
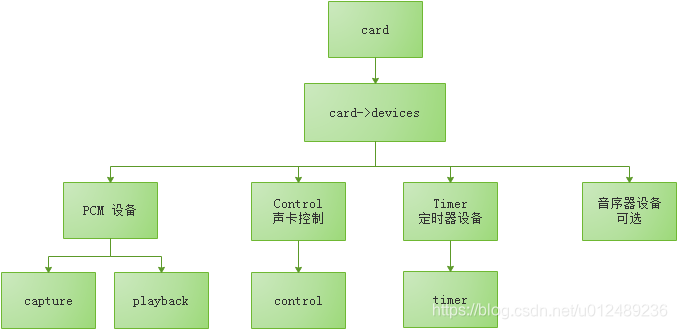
下面来看看snd_pcm_dev_register函数主要做了些什么呢?
static int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{int cidx, err;struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;struct snd_pcm_notify *notify;char str[16];struct snd_pcm *pcm;struct device *dev;if (snd_BUG_ON(!device || !device->device_data))return -ENXIO;pcm = device->device_data;mutex_lock(®ister_mutex);err = snd_pcm_add(pcm);if (err) {mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex);return err;}for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) {int devtype = -1;if (pcm->streams[cidx].substream == NULL || pcm->internal)continue;switch (cidx) {case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK:sprintf(str, "pcmC%iD%ip", pcm->card->number, pcm->device);devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK;break;case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE:sprintf(str, "pcmC%iD%ic", pcm->card->number, pcm->device);devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE;break;}/* device pointer to use, pcm->dev takes precedence if* it is assigned, otherwise fall back to card's device* if possible */dev = pcm->dev;if (!dev)dev = snd_card_get_device_link(pcm->card);/* register pcm */err = snd_register_device_for_dev(devtype, pcm->card,pcm->device,&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx],pcm, str, dev);if (err < 0) {list_del(&pcm->list);mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex);return err;}dev = snd_get_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device);if (dev) {err = sysfs_create_groups(&dev->kobj,pcm_dev_attr_groups);if (err < 0)dev_warn(dev,"pcm %d:%d: cannot create sysfs groups\n",pcm->card->number, pcm->device);put_device(dev);}for (substream = pcm->streams[cidx].substream; substream; substream = substream->next)snd_pcm_timer_init(substream);}list_for_each_entry(notify, &snd_pcm_notify_list, list)notify->n_register(pcm);mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex);return 0;
}回调函数建立了和用户空间应用程序(alsa-lib)通信所用的设备文件节点:/dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxp和/dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxc,同时做了一件最重要的事情,设备节点的ops。每个 pcm 实例对应一个 pcm 设备文件。一个 pcm 实例由一个playback stream 和一个 capture stream 组成,
const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.write = snd_pcm_write,.aio_write = snd_pcm_aio_write,.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,.release = snd_pcm_release,.llseek = no_llseek,.poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll,.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_playback_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,},{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.read = snd_pcm_read,.aio_read = snd_pcm_aio_read,.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,.release = snd_pcm_release,.llseek = no_llseek,.poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll,.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_capture_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,}
}这个ops主要是用来给alsa-lib来访问到codec底层接口的封装层,最终都会调用到底层的fops。对于PCM的主要完成了数据的播放和录音,也是通过该ops的playback和capture接口来完成。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!