Python计算机视觉-第4章
本章中,我们将尝试对照相机进行建模,并有效地使用这些模型。在之前的章节里, 我们已经讲述了图像到图像之间的映射和变换。为了处理三维图像和平面图像之间 的映射,我们需要在映射中加入部分照相机产生图像过程的投影特性。本章中我们 将会讲述如何确定照相机的参数,以及在具体应用中,如增强现实,如何使用图像 间的投影变换。下一章中,我们将使用照相机模型处理其他一些应用,比如多视图 及其映射。
1、针孔相机模型
(1)照相机矩阵
针孔照相机模型(有时称为射影照相机模型)是计算机视觉中广泛使用的照相机模 型。如下图所示:
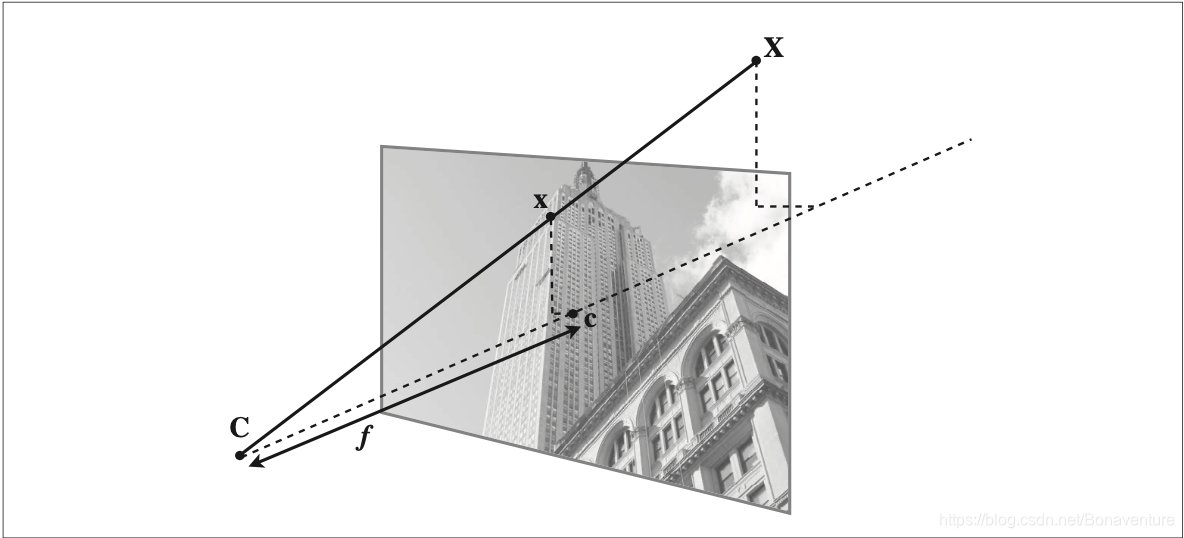
在针孔照相机中,三维点 X 投影为图像点 x(两个点都是用齐次坐标表示的),如下 所示:
![]()
这里,3×4 的矩阵 P 为照相机矩阵(或投影矩阵)。注意,在齐次坐标系中,三维 点 X 的坐标由 4 个元素组成,X=[X, Y, Z, W]。这里的标量 λ 是三维点的逆深度。如 果我们打算在齐次坐标中将最后一个数值归一化为 1,那么就会使用到它。
照相机矩阵可以分解为:
![]()
其中,R 是描述照相机方向的旋转矩阵,t 是描述照相机中心位置的三维平移向量,内标定矩阵 K 描述照相机的投影性质。 标定矩阵仅和照相机自身的情况相关,通常情况下可以写成:
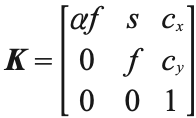
图像平面和照相机中心间的距离为焦距 f。当像素数组在传感器上偏斜的时候,需要 用到倾斜参数 s。在大多数情况下,s 可以设置成 0。也就是说:

这里,我们使用了另外的记号 fx 和 fy,两者关系为 fx=αfy。纵横比例参数 α 是在像素元素非正方形的情况下使用的。通常情况下,我们可以默认设置 α=1。经过这些假设,标定矩阵变为:

除焦距之外,标定矩阵中剩余的唯一参数为光心(有时称主点)的坐标 c=[cx,cy], 也就是光线坐标轴和图像平面的交点。因为光心通常在图像的中心,并且图像的坐 标是从左上角开始计算的,所以光心的坐标常接近于图像宽度和高度的一半。特别 强调一点,在这个例子中,唯一未知的变量是焦距 f。
(2)三维点的投影
下面来创建照相机类,用来处理我们对照相机和投影建模所需要的全部操作:
camera.py
from numpy import *
from scipy import linalgclass Camera(object):""" Class for representing pin-hole cameras. """def __init__(self,P):""" Initialize P = K[R|t] camera model. """self.P = Pself.K = None # calibration matrixself.R = None # rotationself.t = None # translationself.c = None # camera centerdef project(self,X):""" Project points in X (4*n array) and normalize coordinates. """x = dot(self.P,X)for i in range(3):x[i] /= x[2] return xdef factor(self):""" Factorize the camera matrix into K,R,t as P = K[R|t]. """# factor first 3*3 partK,R = linalg.rq(self.P[:,:3])# make diagonal of K positiveT = diag(sign(diag(K)))if linalg.det(T) < 0:T[1,1] *= -1self.K = dot(K,T)self.R = dot(T,R) # T is its own inverseself.t = dot(linalg.inv(self.K),self.P[:,3])return self.K, self.R, self.tdef center(self):""" Compute and return the camera center. """if self.c is not None:return self.celse:# compute c by factoringself.factor()self.c = -dot(self.R.T,self.t)return self.c# helper functions
def rotation_matrix(a):""" Creates a 3D rotation matrix for rotationaround the axis of the vector a. """R = eye(4)R[:3,:3] = linalg.expm([[0,-a[2],a[1]],[a[2],0,-a[0]],[-a[1],a[0],0]])return Rdef rq(A):from scipy.linalg import qrQ,R = qr(flipud(A).T)R = flipud(R.T)Q = Q.T return R[:,::-1],Q[::-1,:]
下面的例子展示如何将三维中的点投影到图像视图中。
import camera
from pylab import *
import numpy as np# 载入点
points = loadtxt('../data/model_house/3D/house.p3d').T
points = vstack((points,ones(points.shape[1])))# 设置照相机参数
P = hstack((eye(3),array([[0],[0],[-10]])))
cam = camera.Camera(P)
x = cam.project(points)# 绘制投影
figure()
plot(x[0],x[1],'k.')
show()# 创建变换
r = 0.05*np.random.rand(3)
rot = camera.rotation_matrix(r)
# 旋转矩阵和投影 figure()
for t in range(20):cam.P = dot(cam.P,rot) x = cam.project(points) plot(x[0],x[1],'k.')show()
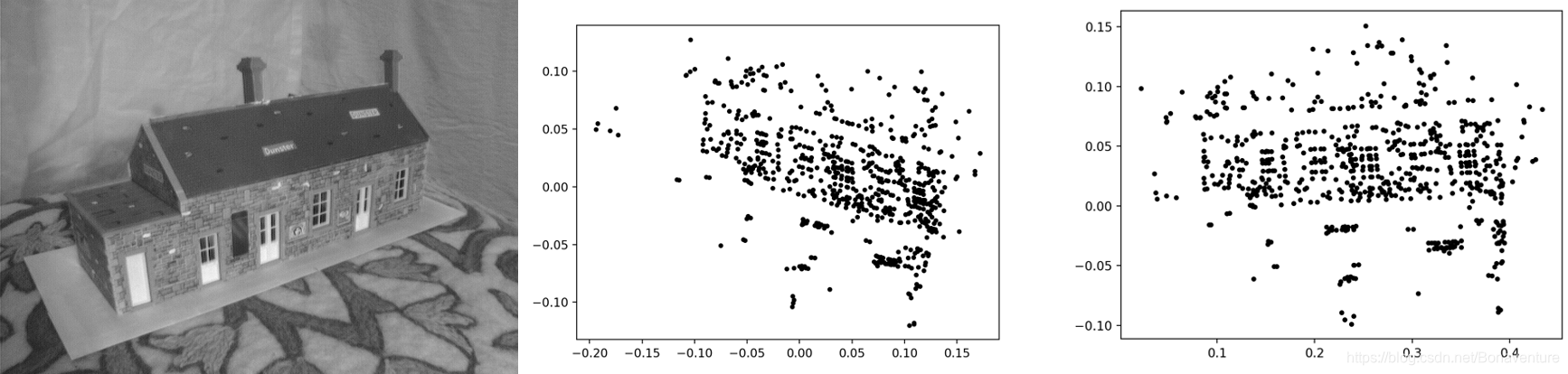
投影三维点示例:样本图像(左),图像视图中投影后的点(中);经过照相机旋转后,投影点的轨迹(右)。数据来自于牛津“Model House”数据集 。
(3)照相机矩阵的分解
在示例照相机上运行下面的代码,观察照相机矩阵分解的效果。
import camera
from numpy import *K = array([[1000,0,500],[0,1000,300],[0,0,1]])
tmp = camera.rotation_matrix([0,0,1])[:3,:3]
Rt = hstack((tmp,array([[50],[40],[30]])))
cam = camera.Camera(dot(K,Rt))print(K,Rt)
print(cam.factor())
#计算出两组数据不一样,可能是由于rq计算结果具有二义性导致(4)计算照相机中心
给定照相机投影矩阵 P,我们可以计算出空间上照相机的所在位置。照相机的中心C,是一个三维点,满足约束 PC=0。对于投影矩阵为 P=K[R|t] 的照相机,有:
![]()
照相机的中心可以由下述式子来计算:
![]()
注意,如预期一样,照相机的中心和内标定矩阵 K 无关。代码实现详见camera.py中center()函数定义。
2、照相机标定
这里我们将要介绍一个简单的照相机标定方法。大多数参数可以使用基本的假设来 设定(正方形垂直的像素,光心位于图像中心),比较难处理的是获得正确的焦距。 对于这种标定方法,你需要准备一个平面矩形的标定物体(一个书本即可)、用于测 量的卷尺和直尺,以及一个平面。下面是具体操作步骤:
-
测量你选定矩形标定物体的边长 dX 和 dY;
-
将照相机和标定物体放置在平面上,使得照相机的背面和标定物体平行,同时物
体位于照相机图像视图的中心,你可能需要调整照相机或者物体来获得良好的对
齐效果;
-
测量标定物体到照相机的距离 dZ;
-
拍摄一副图像来检验该设置是否正确,即标定物体的边要和图像的行和列对齐;
-
使用像素数来测量标定物体图像的宽度和高度 dx 和 dy。
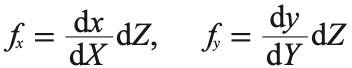
简单的照相机标定设置:进行标定实验使用的设置情况图像(左);用于标定的图像 (右)。在图像中测量标定物体的宽度和高度,以及设置中标定物体的实际物理尺寸,就可以确定焦距的大小。

3、以平面和标记物进行姿态估计
我们使用一个例子来演示如何进行姿态估计。这里借助book的两幅图像。 我们使用下面的代码来提取两幅图像的 SIFT 特征,然后使用 RANSAC 算法稳健地 估计单应性矩阵,代码实现:
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
# import pickle# If you have PCV installed, these imports should work
# from PCV.geometry import homography, camera
# from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
import homography,camera,sift
"""
This is the augmented reality and pose estimation cube example from Section 4.3.
"""def cube_points(c, wid):""" Creates a list of points for plottinga cube with plot. (the first 5 points arethe bottom square, some sides repeated). """p = []# bottomp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid]) #same as first to close plot# topp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid]) #same as first to close plot# vertical sidesp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])return array(p).Tdef my_calibration(sz):"""Calibration function for the camera (iPhone4) used in this example."""row, col = szfx = 2555*col/2592fy = 2586*row/1936K = diag([fx, fy, 1])K[0, 2] = 0.5*colK[1, 2] = 0.5*rowreturn K# compute features
sift.process_image('../data/book_frontal.JPG', 'im0.sift')
l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')sift.process_image('../data/book_perspective.JPG', 'im1.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')# match features and estimate homography
matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)model = homography.RansacModel()
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)# camera calibration
K = my_calibration((747, 1000))# 3D points at plane z=0 with sides of length 0.2
box = cube_points([0, 0, 0.1], 0.1)# project bottom square in first image
cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
# first points are the bottom square
box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))# use H to transfer points to the second image
box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H,box_cam1))# compute second camera matrix from cam1 and H
cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)# project with the second camera
box_cam2 = cam2.project(homography.make_homog(box))# 测试:将点投影在 z=0 上,应该能够得到相同的点
point = array([1,1,0,1]).T
print(homography.normalize(dot(dot(H,cam1.P),point)) )
print(cam2.project(point)) # Rt = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P)
import pickle
with open('../data/ar_camera.pkl','wb') as f: pickle.dump(K,f,0) pickle.dump(dot(linalg.inv(K),cam2.P),f)print("ar_camera.pkl is generated!")# plotting
im0 = array(Image.open('book_frontal.JPG'))
im1 = array(Image.open('book_perspective.JPG'))figure()
subplot(221)
imshow(im0)
plot(box_cam1[0, :], box_cam1[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('2D projection of bottom square')
axis('off')subplot(222)
imshow(im1)
plot(box_trans[0, :], box_trans[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('2D projection transfered with H')
axis('off')subplot(223)
imshow(im1)
plot(box_cam2[0, :], box_cam2[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('3D points projected in second image')
axis('off')show()运行结果:

4、增强现实
增强现实(Augmented Reality,AR)是将物体和相应信息放置在图像数据上的一 系列操作的总称。最经典的例子是放置一个三维计算机图形学模型,使其看起来属 于该场景;如果在视频中,该模型会随着照相机的运动很自然地移动。如上一节所 示,给定一幅带有标记平面的图像,我们能够计算出照相机的位置和姿态,使用这 些信息来放置计算机图形学模型,能够正确表示它们。在本章的最后一节,我们将 介绍如何建立一个简单的增强现实例子。其中,我们会用到两个工具包:PyGame 和 PyOpenGL。
(1)PyGame和 PyOpenGL
PyGame 是非常流行的游戏开发工具包,它可以非常简单地处理显示窗口、输入设 备、事件,以及其他内容。PyGame 是开源的,可以从 http://www.pygame.org/ 下 载。事实上,它是一个 Python 绑定的 SDL 游戏引擎。你可以查看附录 A 来获取 关于安装的帮助。你还可以查看文献 [21] 来获取关于 PyGame 工具包的更多编程 细节。
PyOpenGL 是 OpenGL 图形编程的 Python 绑定接口。OpenGL 可以安装在几乎所 有的系统上,并且具有很好的图形性能。OpenGL 具有跨平台性,能够在不同的操 作系统之间工作。关于 OpenGL 的更多信息,参见 http://www.opengl.org/。在开 始 页 面(http://www.opengl.org/wiki/Getting_started), 有 针 对 初 学 者 的 很 多 资 源。 PyOpenGL 是开源的,并且易于安装。你可以从附录 A 了解关于 PyOpenGL 更多内 容。你同样可以在项目网页 http://pyopengl.sourceforge.net/ 获取更多细节内容。
为了使用 PyGame 和 PyOpenGL 工具包来完成该应用,需要在脚本的开始部分载入下面的命令:
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
import pygame, pygame.image
from pygame.locals import *
(2)从照相机矩阵到OpenGL格式
OpenGL 使用 4×4 的矩阵来表示变换(包括三维变换和投影)。这和我们使用 的 3×4 照相机矩阵略有差别。但是,照相机与场景的变换分成了两个矩阵, GL_PROJECTION 矩阵和 GL_MODELVIEW 矩阵。GL_PROJECTION 矩阵处理图 像成像的性质,等价于我们的内标定矩阵 K。GL_MODELVIEW 矩阵处理物体和照 相机之间的三维变换关系,对应于我们照相机矩阵中的 R 和 t 部分。一个不同之处 是,假设照相机为坐标系的中心,GL_MODELVIEW 矩阵实际上包含了将物体放置 在照相机前面的变换。OpenGL 有很多特性,我们会在下面例子中一一讲解。
(3)在图像中放置虚拟物体
我们需要做的第一件事是将图像(打算放置虚拟物体的图像)作为背景添加进来。 在 OpenGL 中,该操作可以通过创建一个四边形的方式来完成,该四边形为整个视 图。完成该操作最简单的方式是绘制出四边形,同时将投影和模拟试图矩阵重置, 使得每一维的坐标范围在 -1 到 1 之间。
(4)综合集成
代码实现:
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
import pygame, pygame.image
from pygame.locals import *
from pylab import *
import pickle
import sift
import homography
import cameradef cube_points(c, wid):""" Creates a list of points for plottinga cube with plot. (the first 5 points arethe bottom square, some sides repeated). """p = []# bottomp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid]) #same as first to close plot# topp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid]) #same as first to close plot# vertical sidesp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])return array(p).Tdef my_calibration(sz):row, col = szfx = 2555*col/2592fy = 2586*row/1936K = diag([fx, fy, 1])K[0, 2] = 0.5*colK[1, 2] = 0.5*rowreturn Kdef set_projection_from_camera(K): """ 从照相机标定矩阵中获得视图 """glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)glLoadIdentity()fx = K[0,0]fy = K[1,1]fovy = 2*arctan(0.5*height/fy)*180/piaspect = (width*fy)/(height*fx)# 定义近的和远的剪裁平面 near = 0.1far = 100.0# 设定透视 gluPerspective(fovy,aspect,near,far) glViewport(0,0,width,height)def set_modelview_from_camera(Rt):""" 从照相机姿态中获得模拟视图矩阵 """glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)glLoadIdentity()# 围绕x 轴将茶壶旋转 90 度,使z 轴向上 Rx = array([[1,0,0],[0,0,-1],[0,1,0]])# 获得旋转的最佳逼近R = Rt[:,:3]U,S,V = linalg.svd(R)R = dot(U,V)R[0,:] = -R[0,:] # 改变 x 轴的符号# 获得平移量 t = Rt[:,3]# 获得 4×4 的模拟视图矩阵 M = eye(4)M[:3,:3] = dot(R,Rx) M[:3,3] = t# 转置并压平以获取列序数值 M = M.Tm = M.flatten()# 将模拟视图矩阵替换为新的矩阵 glLoadMatrixf(m)def draw_background(imname): """ 使用四边形绘制背景图像 """# 载入背景图像(应该是 .bmp 格式),转换为 OpenGL 纹理 bg_image = pygame.image.load(imname).convert() bg_data = pygame.image.tostring(bg_image,"RGBX",1)glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)glLoadIdentity()glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)# 绑定纹理glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D)glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D,glGenTextures(1)) glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D,0,GL_RGBA,width,height,0,GL_RGBA,GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,bg_data)glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST)glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST)# 创建四方形填充整个窗口glBegin(GL_QUADS)glTexCoord2f(0.0,0.0);glVertex3f(-1.0,-1.0,-1.0) glTexCoord2f(1.0,0.0);glVertex3f( 1.0,-1.0,-1.0) glTexCoord2f(1.0,1.0);glVertex3f( 1.0, 1.0,-1.0) glTexCoord2f(0.0,1.0);glVertex3f(-1.0, 1.0,-1.0) glEnd()# 清除纹理 glDeleteTextures(1)def draw_teapot(size):""" 在原点处绘制红色茶壶 """glEnable(GL_LIGHTING)glEnable(GL_LIGHT0)glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)# 绘制红色茶壶glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_AMBIENT,[0,0,0,0])glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_DIFFUSE,[0.5,0.0,0.0,0.0])glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_SPECULAR,[0.7,0.6,0.6,0.0])glMaterialf(GL_FRONT,GL_SHININESS,0.25*128.0)glutSolidTeapot(size)# # compute features
# sift.process_image('../data/book_frontal.JPG', 'im0.sift')
# l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')# sift.process_image('../data/book_perspective.JPG', 'im1.sift')
# l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')# # match features and estimate homography
# matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
# ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
# fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
# ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
# tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)# model = homography.RansacModel()
# H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)# # camera calibration
# K = my_calibration((747, 1000))# # 3D points at plane z=0 with sides of length 0.2
# box = cube_points([0, 0, 0.1], 0.1)# # project bottom square in first image
# cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
# # first points are the bottom square
# box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))# # use H to transfer points to the second image
# box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H,box_cam1))# # compute second camera matrix from cam1 and H
# cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
# A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
# A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
# cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)# # project with the second camera
# box_cam2 = cam2.project(homography.make_homog(box))# # 测试:将点投影在 z=0 上,应该能够得到相同的点
# point = array([1,1,0,1]).T
# print(homography.normalize(dot(dot(H,cam1.P),point)) )
# print(cam2.project(point)) # # Rt = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P)
# import pickle
# with open('../data/ar_camera.pkl','wb') as f:
# pickle.dump(K,f,0)
# pickle.dump(dot(linalg.inv(K),cam2.P),f)width,height = 1000,747
def setup():""" 设置窗口和 pygame 环境 """pygame.init() pygame.display.set_mode((width,height),OPENGL | DOUBLEBUF) pygame.display.set_caption('OpenGL AR demo')# 载入照相机数据
with open('../data/ar_camera.pkl','rb') as f:K = pickle.load(f) Rt = pickle.load(f)setup()
draw_background('../data/book_perspective.bmp')
set_projection_from_camera(K)
set_modelview_from_camera(Rt)
draw_teapot(0.1)pygame.display.flip()
while True:for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:sys.exit()pygame.quit()
# pygame.display.flip()如何不使用之前生成的ar_camera.pkl文件,可将注释的部分代码放开即可重新生成ar_camera.pkl文件。
运行结果:

(5)载入模型
代码实现:
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
import pygame, pygame.image
from pygame.locals import *
from pylab import *
import pickle
import sift
import homography
import cameradef cube_points(c, wid):""" Creates a list of points for plottinga cube with plot. (the first 5 points arethe bottom square, some sides repeated). """p = []# bottomp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid]) #same as first to close plot# topp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid]) #same as first to close plot# vertical sidesp.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])return array(p).Tdef my_calibration(sz):row, col = szfx = 2555*col/2592fy = 2586*row/1936K = diag([fx, fy, 1])K[0, 2] = 0.5*colK[1, 2] = 0.5*rowreturn Kdef set_projection_from_camera(K): """ 从照相机标定矩阵中获得视图 """glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)glLoadIdentity()fx = K[0,0]fy = K[1,1]fovy = 2*arctan(0.5*height/fy)*180/piaspect = (width*fy)/(height*fx)# 定义近的和远的剪裁平面 near = 0.1far = 100.0# 设定透视 gluPerspective(fovy,aspect,near,far) glViewport(0,0,width,height)def set_modelview_from_camera(Rt):""" 从照相机姿态中获得模拟视图矩阵 """glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)glLoadIdentity()# 围绕x 轴将茶壶旋转 90 度,使z 轴向上 Rx = array([[1,0,0],[0,0,-1],[0,1,0]])# 获得旋转的最佳逼近R = Rt[:,:3]U,S,V = linalg.svd(R)R = dot(U,V)R[0,:] = -R[0,:] # 改变 x 轴的符号# 获得平移量 t = Rt[:,3]# 获得 4×4 的模拟视图矩阵 M = eye(4)M[:3,:3] = dot(R,Rx) M[:3,3] = t# 转置并压平以获取列序数值 M = M.Tm = M.flatten()# 将模拟视图矩阵替换为新的矩阵 glLoadMatrixf(m)def draw_background(imname): """ 使用四边形绘制背景图像 """# 载入背景图像(应该是 .bmp 格式),转换为 OpenGL 纹理 bg_image = pygame.image.load(imname).convert() bg_data = pygame.image.tostring(bg_image,"RGBX",1)glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)glLoadIdentity()glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)# 绑定纹理glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D)glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D,glGenTextures(1)) glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D,0,GL_RGBA,width,height,0,GL_RGBA,GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,bg_data)glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST)glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST)# 创建四方形填充整个窗口glBegin(GL_QUADS)glTexCoord2f(0.0,0.0);glVertex3f(-1.0,-1.0,-1.0) glTexCoord2f(1.0,0.0);glVertex3f( 1.0,-1.0,-1.0) glTexCoord2f(1.0,1.0);glVertex3f( 1.0, 1.0,-1.0) glTexCoord2f(0.0,1.0);glVertex3f(-1.0, 1.0,-1.0) glEnd()# 清除纹理 glDeleteTextures(1)def draw_teapot(size):""" 在原点处绘制红色茶壶 """glEnable(GL_LIGHTING)glEnable(GL_LIGHT0)glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)# 绘制红色茶壶glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_AMBIENT,[0,0,0,0])glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_DIFFUSE,[0.5,0.0,0.0,0.0])glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_SPECULAR,[0.7,0.6,0.6,0.0])glMaterialf(GL_FRONT,GL_SHININESS,0.25*128.0)glutSolidTeapot(size)def load_and_draw_model(filename):""" 使用 objloader.py,从 .obj 文件中装载模型 假设路径文件夹中存在同名的 .mtl 材料设置文件 """ glEnable(GL_LIGHTING)glEnable(GL_LIGHT0)glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST) glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)# 设置模型颜色glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_AMBIENT,[0,0,0,0]) glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_DIFFUSE,[0.5,0.75,1.0,0.0]) glMaterialf(GL_FRONT,GL_SHININESS,0.25*128.0)# 从文件中载入import objloaderobj = objloader.OBJ(filename,swapyz=True) glCallList(obj.gl_list)# # compute features
# sift.process_image('../data/book_frontal.JPG', 'im0.sift')
# l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')# sift.process_image('../data/book_perspective.JPG', 'im1.sift')
# l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')# # match features and estimate homography
# matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
# ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
# fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
# ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
# tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)# model = homography.RansacModel()
# H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)# # camera calibration
# K = my_calibration((747, 1000))# # 3D points at plane z=0 with sides of length 0.2
# box = cube_points([0, 0, 0.1], 0.1)# # project bottom square in first image
# cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
# # first points are the bottom square
# box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))# # use H to transfer points to the second image
# box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H,box_cam1))# # compute second camera matrix from cam1 and H
# cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
# A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
# A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
# cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)# # project with the second camera
# box_cam2 = cam2.project(homography.make_homog(box))# # 测试:将点投影在 z=0 上,应该能够得到相同的点
# point = array([1,1,0,1]).T
# print(homography.normalize(dot(dot(H,cam1.P),point)) )
# print(cam2.project(point)) # # Rt = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P)
# import pickle
# with open('../data/ar_camera.pkl','wb') as f:
# pickle.dump(K,f,0)
# pickle.dump(dot(linalg.inv(K),cam2.P),f)width,height = 1000,747
def setup():""" 设置窗口和 pygame 环境 """pygame.init() pygame.display.set_mode((width,height),OPENGL | DOUBLEBUF) pygame.display.set_caption('OpenGL AR demo')# 载入照相机数据
with open('../data/ar_camera.pkl','rb') as f:K = pickle.load(f) Rt = pickle.load(f)setup()
draw_background('../data/book_perspective.bmp')
set_projection_from_camera(K)
set_modelview_from_camera(Rt)
# draw_teapot(0.1)
load_and_draw_model('../data/toyplane.obj')pygame.display.flip()
while True:for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:sys.exit()pygame.quit()
# pygame.display.flip()运行结果:

5、其他
(1)开发环境
本代码是在mac电脑sublimetxt编辑器python3.7.8下调试出来的,如果你要在windows/linux下编辑器/IDE的其他python版本运行的话,请对代码做相应的调整。
(2)obj和mtl文件
从http://www.oyonale.com/modeles.php网站下载toyplane.obj文件后还缺少mtl文件,如下自制mtl文件toyplane.mtl
newmtl lightblue
Kd 0.5 0.75 1.0
illum 1
运行结果会报错:
mtl = self.mtl[material]
KeyError: 'material2'
故载入模型的代码还有待调试。
(3)源码和图片
已经调试过的源码和图片详见:
https://github.com/Abonaventure/pcv-book-code.git 或 https://gitlab.com/Abonaventure/pcv-book-code.git
部分图片可能未上传可在https://pan.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=4059473268&uk=3440544532 或者原书目录http://programmingcomputervision.com下载。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!