Ransac拟合平面(C++编写实现<不使用任何库>)
Ransac拟合平面
参考链接:链接1、链接2、链接3 、最小二乘 、链接4 、一种新方法
项目背景简介:考虑到实际项目识别平面上的非编码点,非编码点的重建精度较高,基本在一个平面上,并不希望使用任何库(传统方式基于最小二乘的SVD最小特征向量),故采用本文方式。拍摄环境中存在杂点,在此方式基础上加入Ransac。此种方式也有本身的局限性。
局限性:此方法将最小化垂直于主轴的残差的平方,而不是垂直于平面的残差的平方。如果残差很小(即,所有点都靠近结果平面),则此方法可能就足够了。但是,如果您的观点更加分散,则此方法可能不是最合适的方法。
1、最小二乘优化目标方程(此方法主要在这进行简单操作)
- 方法一:传统方法参考我的另一篇博客优化d(最小化垂直于平面残差平方)
思路总结:
- 计算点的质心
- 计算相对于质心的点的协方差矩阵
- 计算协方差矩阵的最小特征向量。这是平面法线。
- 方法二:此方法将最小化垂直于平面的残差的平方转变为最小化垂直于主轴的残差的平方。
选择性优化x、y、z其中主轴,选择最大绝对值的平面法线分量进行优化。思路总结:
- 计算点的质心
- 计算相对于质心的点 的协方差矩阵
- 找到主轴(具有最大绝对值的平面法线分量)并沿该轴进行线性回归
- 方法三:此文为改进方法:X,Y和Z轴进行线性回归
思路总结:
- 计算点的质心
- 计算相对于质心的点的协方差矩阵
- 沿X,Y和Z轴进行线性回归
- 基于行列式平方的线性回归结果的权重
2、C++编写
#pragma once
#include 3、测试

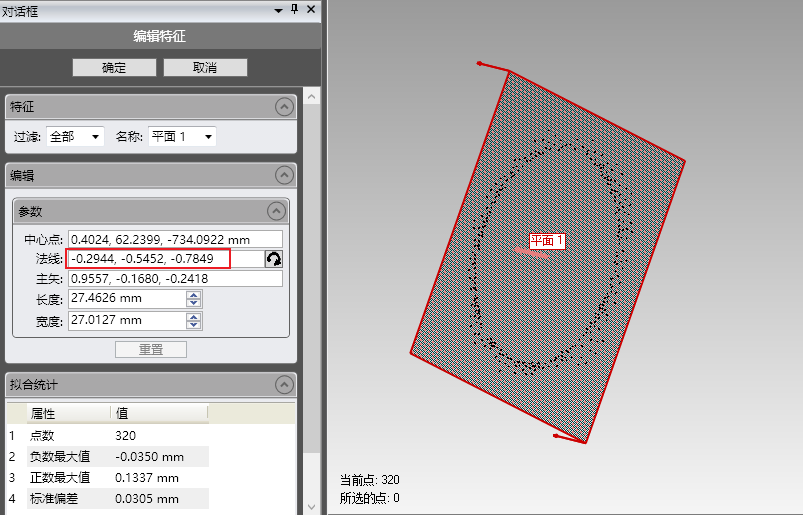
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!