【练习】归并和冒泡两种方法c++将两个无序链表合并为一个升序的有序链表
定义:
struct node {int data;node* next;};
新建有头指针的链表:
struct node *head;
head = NULL;//头指针初始为空
struct node *p;
//动态申请一个空间,用来存放一个结点,并用临时指针p指向这个结点
p=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
scanf("%d",&a);
p->data=a;//将数据存储到当前结点的data域中
p->next=NULL;//设置当前结点的后继指针指向空,也就是当前结点的下一个结点为空
完整版本:
#include 合并采用先分别升序后再进行合并两个有序链表,分别升序采用双指针和递归调用。先看用归并排序:
用归并排序:
node* merge(node* p,node*p2) {//这里是合并的排序node* src = new node;src->next = nullptr;//src->data = 0;node* now = src;node* a1 = p;node* a2 = p2;while (a1 != NULL && a2 != NULL) {if (a1->data >= a2->data) {node* tem = a2->next;src->next = a2;a2 = tem;}else {node* tem = a1->next;src->next = a1;a1 = tem;}src = src->next;//合并两个有序链表 src->next=nullptr}if (a1 != NULL) src->next = a1;if (a2 != NULL)src->next = a2;return now->next;}
node* merge_sort(node* p) {//这是将一个链表进行升序if (p == nullptr || p->next == nullptr) return p;node* fast = p;node* slow = new node;slow->data = 0;slow->next = p;while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;}node* rhead = slow->next;slow->next = NULL;node* lh = merge_sort(p);node* rh = merge_sort(rhead);node* after = merge(lh, rhead);return after;
}
int main()
{srand(0);node* m = new node;m->data = rand()%5;//cout << m->data;node* n = new node;n->data = rand()%7;m->next = n;node* nn = new node;nn->data = rand()%8;n->next = nn;nn->next = nullptr;node* copy_m = m;cout << "第一个链表:";while (copy_m) {cout << copy_m->data;copy_m = copy_m->next;}cout << endl;node* m2 = new node;m2->data =rand()%18;node* n2 = new node; n2->data = rand() % 13;m2->next = n2;node* nn2 = new node;nn2->data = rand()%15;n2->next = nn2;nn2->next = nullptr;node* copy_n = m2;cout << "第二个链表:";while (copy_n) {cout << copy_n->data;copy_n = copy_n->next;}cout << endl;node*one = merge_sort(m);node*two= merge_sort(m2);node* new_m = merge(one,two);node* nice = new_m;cout << endl;cout << "合并两个有序链表后的结果:";while (nice) {cout << nice->data << "->";nice = nice->next;}
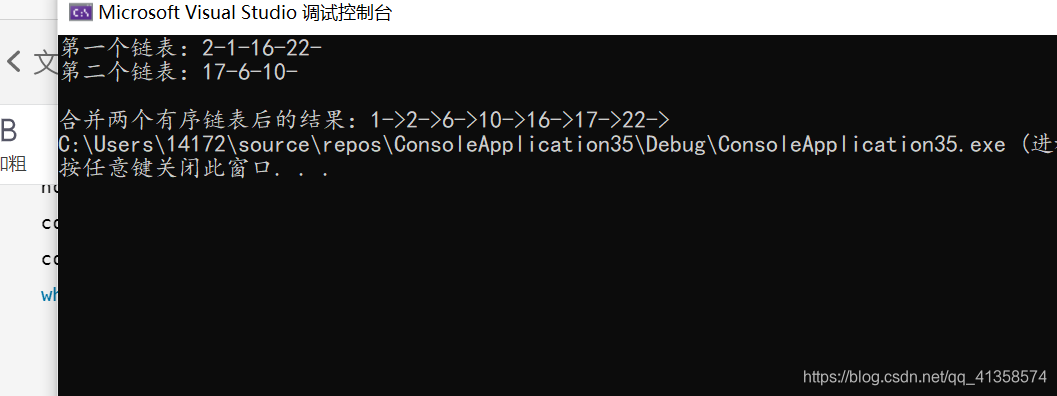
}结果:

用冒泡排序:
node* merge_sort(node* p) {//这是将一个链表进行升序if (p == nullptr || p->next == nullptr) return p;node* mana = p;node* pp = mana;for (int i = 0; i < len(p) - 1; i++) {mana = p;for (int j = 0; j < len(p) - i - 1; j++) {node* t1 = mana;node* t2 = mana->next;if (t1->data > t2->data) {int tem = t1->data;t1->data = t2->data;t2->data = tem;}mana = mana->next;}}return pp;
}
int main()
{srand(0);node* m = new node;m->data = rand()%12;//cout << m->data;node* n = new node;n->data = rand()%17;m->next = n;node* nn = new node;nn->data = rand()%18;n->next = nn;node* nnn = new node;nnn->data = rand() % 23;nnn->next = NULL;nn->next = nnn;node* copy_m = m;cout << "第一个链表:";while (copy_m) {cout << copy_m->data<<"-";copy_m = copy_m->next;}cout << endl;node* m2 = new node;m2->data =rand()%18;node* n2 = new node; n2->data = rand() % 13;m2->next = n2;node* nn2 = new node;nn2->data = rand()%15;n2->next = nn2;nn2->next = nullptr;node* copy_n = m2;cout << "第二个链表:";while (copy_n) {cout << copy_n->data << "-";copy_n = copy_n->next;}cout << endl;node*one = merge_sort(m);node*two= merge_sort(m2);node* new_m = merge(one,two);node* nice = new_m;cout << endl;cout << "合并两个有序链表后的结果:";while (nice) {cout << nice->data << "->";nice = nice->next;}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!