Java 基础 (19) -- Java 8 新特性:Stream
文章目录
- 1. Stream 是什么
- 2. 创建 Stream
- 1. 通过 Collection 接口提供的 Stream
- 2. 通过 Arrays 创建 Stream 流
- 3. Stream 常见的操作
- 1. 过滤和切片
- 2. 映射
- 3. 排序
- 4. 查找与匹配
- 5. 归约 (组合)
- 6. 收集
- 4. 案例
1. Stream 是什么
Java 8 新增的 Stream 是为了解放程序员操作集合(Collection)时的生产力,之所以能解放,很大一部分原因可以归功于同时出现的 Lambda 表达式——极大的提高了编程效率和程序可读性。
Stream 通俗的说就是操作数据集合的一种手段,你可以使用它,以获取所需要的集合数据源类型。
要想操作流,首先需要有一个数据源,可以是数组或者集合。每次操作都会返回一个新的流对象,方便进行链式操作,但原有的流对象会保持不变。流的操作可以分为两种类型:中间操作,可以有多个,每次返回一个新的流,可进行链式操作;终端操作,只能有一个,每次执行完,这个流也就用光光了,无法执行下一个操作,因此只能放在最后。
中间操作不会立即执行,只有等到终端操作的时候,流才开始真正地遍历,用于映射、过滤等。通俗点说,就是一次遍历执行多个操作,性能得到了大大地提高。
Stream 流操作的整个流程是 创建流对象->对流操作->获得目标数据源操作
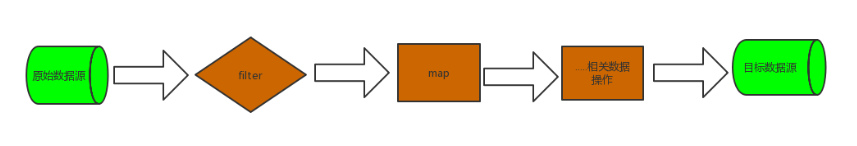
2. 创建 Stream
1. 通过 Collection 接口提供的 Stream
- 返回一个顺序流
public class CreateStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("武汉加油");list.add("中国加油");list.add("世界加油");stream = list.stream();} } - 返回一个并行流
List<Long> aList = new ArrayList<>(); Stream<Long> parallelStream = aList.parallelStream();
案例:
@Setter
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class Employee {private String name;private int age;private double basicSalary;private double dealTotalPrice;public Employee(String name, int age, double basicSalary,double dealTotalPrice) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.basicSalary = basicSalary;this.dealTotalPrice = dealTotalPrice;}/*** 员工总薪资=基本薪资+提成薪资** @return Double*/public Double getTotalSalary() {return this.basicSalary + this.dealTotalPrice * 0.04;}
}
@Testpublic void test() {Employee qingLong = new Employee("青龙", 25, 5500, 7500);Employee baiHu = new Employee("白虎", 27, 5000, 9000);Employee zhuQue = new Employee("朱雀", 22, 3800, 4500);Employee xuanWu = new Employee("玄武", 24, 3300, 3300);List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(qingLong, baiHu, zhuQue, xuanWu);// 得到一个顺序流,并获取工资大与4000的员工的姓名Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream();stream.filter(e-> e.getTotalSalary()>4000).map(Employee::getName).forEach(System.out::println); // 得到一个并行流,获取年龄大于25的员工姓名Stream<Employee> employeeStream = employees.parallelStream();employeeStream.filter(employee -> employee.getAge()>25).map(Employee::getName).forEach(System.out::println);
}
2. 通过 Arrays 创建 Stream 流
- 如果是数组的话,可以使用 Arrays.stream() 或者 Stream.of() 创建流。
查看 Stream 源码的话,你会发现 of() 方法内部其实调用了 Arrays.stream() 方法public class CreateStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {String[] arr = new String[]{"武汉加油", "中国加油", "世界加油"};Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(arr);stream = Stream.of("武汉加油", "中国加油", "世界加油"); }public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values) {return Arrays.stream(values); }
注意:数组里面是什么类型的数组,就会产生同类型的流。
- 产生 IntStream
public static IntStream stream(int[] array) {return stream(array, 0, array.length); } - 产生 LongStream
public static LongStream stream(long[] array) {return stream(array, 0, array.length); } - 产生 DoubleStream
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array) {return stream(array, 0, array.length); }
案例:
// 初始化一个数组对象
int[] arr = {11, 55, 44, 20, 45, 16};
// 通过Arrays创建流对象是IntStream
Arrays.stream(arr).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
3. Stream 常见的操作
当流创建好后,我们又该如何使用呢,常见流的操作如下 ?
1. 过滤和切片
- filter(Predicate predicate):可以从流中筛选出我们想要的元素
forEach() 方法接收的是一个 Consumer(Java 8 新增的一个函数式接口,接受一个输入参数并且无返回的操作)类型的参数,上面的 forEach 操作相当于如下代码:public class FilterStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("周杰伦");list.add("王力宏");list.add("陶喆");list.add("林俊杰");Stream<String> stream = list.stream().filter(element -> element.contains("王"));stream.forEach(System.out::println); //输出:王力宏} }for (String s : strs) {System.out.println(s); } - distinct():去除流中重复的元素
- limit(long maxSize):截取流中元素个数,类似sql查询limit
- skip(long n):跳过元素,跳过前n个元素
案例:
@Test
public void testFilter() {int[] age = {11, 22, 44, 22};System.out.println("使用filter过滤获得大于33的数组元素");Arrays.stream(age).filter(i -> i > 33).forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("去重");Arrays.stream(age).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("截取3个元素");Arrays.stream(age).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("跳过前3个元素");Arrays.stream(age).skip(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}//结果
使用filter过滤获得大于33的数组元素
44
去重
11
22
44
截取3个元素
11
22
44
跳过前3个元素
22
2. 映射
- map(Function mapper):把一个流中的元素转化成新的流中的元素
map() 方法接收的是一个 Function(Java 8 新增的一个函数式接口,接受一个输入参数 T,返回一个结果 R)类型的参数,此时参数 为 String 类的 length 方法,也就是把public class MapStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("周杰伦");list.add("王力宏");list.add("陶喆");list.add("林俊杰");Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream().map(String::length);stream.forEach(System.out::println);} }Stream的流转成一个Stream的流。//结果 3 3 2 3 - mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction mapper):接收函数式接口,将映射产生DoubleStream
- mapToLong(ToLongFunction mapper):接收函数式接口,将映射产生LongStream
- mapToInt(ToIntFunction mapper):接收函数式接口,将映射产生IntStream
- flatMap(Function extends Stream mapper):接收函数,将流中的每个值都转换一个流,然后将这些流汇成一个流
案例:
String[] arr = {"java", "scala", "php", "python", "c++"};
System.out.println("将流中的每一个元素转换成大写");
Arrays.stream(arr).map(String::toUpperCase).forEach(System.out::println);//将流中的数据转Double类型
long[] array = {1, 4, 6, 7, 12};
System.out.println("返回Double类型的Stream");
Arrays.stream(array).mapToDouble(e-> e* 100).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("返回Long类型的Stream");
Arrays.stream( array).map(e -> e + 23).forEach(System.out::println);// flatMap演示
List<List<String>> database = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> noSql = Arrays.asList("redis", "hbase", "membercache");
List<String> sql = Arrays.asList("mysql", "oracle", "db2");
database.add(noSql);
database.add(sql);
List<String> h = database.stream().flatMap(s -> s.stream().filter(si -> si.contains("h"))).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("flatMap演示");
h.stream().forEach(System.out::println);//结果
将流中的每一个元素转换成大写
JAVA
SCALA
PHP
PYTHON
C++
返回Double类型的Stream
100.0
400.0
600.0
700.0
1200.0
返回Long类型的Stream
24
27
29
30
35
flatMap演示
hbase
membercache
3. 排序
排序相对简单,以之前定义的 employee 类如下:
//employee 类中
/*** 员工总薪资=基本薪资+提成薪资** @return Double*/
public Double getTotalSalary() {return this.basicSalary + this.dealTotalPrice * 0.04;
}
Employee qingLong = new Employee("青龙", 25, 5500, 7500);
Employee baiHu = new Employee("白虎", 27, 5000, 9000);
Employee zhuQue = new Employee("朱雀", 22, 3800, 4500);
Employee xuanWu = new Employee("玄武", 24, 3300, 3300);
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(qingLong, baiHu, zhuQue, xuanWu);
System.out.println("按照薪水的大小进行排序");
employees.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getTotalSalary)).forEach(System.out::println);//结果
按照薪水的大小进行排序
Employee{name='玄武', age=24, basicSalary=3300.0, dealTotalPrice=3300.0}
Employee{name='朱雀', age=22, basicSalary=3800.0, dealTotalPrice=4500.0}
Employee{name='白虎', age=27, basicSalary=5000.0, dealTotalPrice=9000.0}
Employee{name='青龙', age=25, basicSalary=5500.0, dealTotalPrice=7500.0}
4. 查找与匹配
- allMatch(Predicate p):只要有一个元素不匹配传入的条件,就返回 false;如果全部匹配,则返回 true
- anyMatch(Predicate p):至少有一个元素匹配传入的条件,就返回 true
- noneMatch(Predicate p):只要有一个元素匹配传入的条件,就返回 false;如果全都不匹配,则返回 true
- findFirst():返回第一个元素
- findAny():返回流中任意元素
- count():返回流中的个数
- max(Comparator c):返回流中最大值
- min(Comparator c):返回流中最小值
案例:
Employee qingLong = new Employee("青龙", 25, 5500, 7500);
Employee baiHu = new Employee("白虎", 27, 5000, 9000);
Employee zhuQue = new Employee("朱雀", 22, 3800, 4500);
Employee xuanWu = new Employee("玄武", 24, 3300, 3300);
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(qingLong, baiHu, zhuQue, xuanWu);boolean b = employees.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 18);
System.out.println("判断所有的员工年龄是否大于18: "+b);boolean b1 = employees.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 35);
System.out.println("判断所有员工中有没有年龄大于35的: " + b1);boolean b2 = employees.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 35);
System.out.println("判断所有员工中没有年龄大于35的: " + b2);System.out.print("返回第一个员工的信息: ");
Optional<Employee> first = employees.stream().findFirst();
System.out.println(first.get());long count = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() > 20).count();
System.out.println("统计年龄大于20的员工个数: "+count);Optional<Employee> max = employees.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getTotalSalary));
System.out.println("统计集合中员工薪资最高的员工信息: " + max);//结果
判断所有的员工年龄是否大于18: true
判断所有员工中有没有年龄大于35的: false
判断所有员工中没有年龄大于35的: true
返回第一个员工的信息: Employee{name='青龙', age=25, basicSalary=5500.0, dealTotalPrice=7500.0}
统计年龄大于20的员工个数: 4
统计集合中员工薪资最高的员工信息: Optional[Employee{name='青龙', age=25, basicSalary=5500.0, dealTotalPrice=7500.0}]
5. 归约 (组合)
- reduce(BinaryOperator p):没有起始值,将流中的元素结合起来得到一个值返回Optional
- reduce(T iden,BinaryOperator p):有起始值,将流中的元素结合起来得到一个值T
案例1:
public class ReduceStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] ints = {0, 1, 2, 3};List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(ints);Optional<Integer> optional = list.stream().reduce((a, b) -> a + b);Optional<Integer> optional1 = list.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);System.out.println(optional.orElse(0));System.out.println(optional1.orElse(0));int reduce = list.stream().reduce(6, (a, b) -> a + b);System.out.println(reduce);int reduce1 = list.stream().reduce(6, Integer::sum);System.out.println(reduce1);}
}//结果
6
6
12
12
案例2:
Employee qingLong = new Employee("青龙", 25, 5500, 7500);
Employee baiHu = new Employee("白虎", 27, 5000, 9000);
Employee zhuQue = new Employee("朱雀", 22, 3800, 4500);
Employee xuanWu = new Employee("玄武", 24, 3300, 3300);
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(qingLong, baiHu, zhuQue, xuanWu);Optional<Double> reduce1 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getTotalSalary).reduce(Double::sum);
double v = reduce1.get();
System.out.println("reduce1="+v);System.out.println("====");int[] array = {1, 4, 6, 7, 12};
//这里第一次将0作为x的值然后数组中1作为y,然后计算后的结果是1,
//第二次将1作为x的值,然后数组中的4作为y值进行相加,
//后面以此类推,直到将所有的值都进行相加
int reduce2 = Arrays.stream(array).reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println("reduce2=" + reduce2);//结果
reduce1=18572.0
====
reduce2=30
6. 收集
既然可以把集合或者数组转成流,那么也应该有对应的方法,将流转换回去:collect() 方法就满足了这种需求。
- collect(Collector c):将流转换为其他形式
案例:
public class CollectStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("周杰伦");list.add("王力宏");list.add("陶喆");list.add("林俊杰");String[] strArray = list.stream().toArray(String[]::new);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strArray));List<Integer> list1 = list.stream().map(String::length).collect(Collectors.toList());List<String> list2 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));System.out.println(list1);System.out.println(list2);String str = list.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(", ")).toString();System.out.println(str);}
}
通过 stream() 方法创建集合的流后,再通过 map(String:length) 将其映射为字符串长度的一个新流,最后通过 collect() 方法将其转换成新的集合。
Collectors 是一个收集器的工具类,内置了一系列收集器实现,比如说 toList() 方法将元素收集到一个新的 java.util.List 中;比如说 toCollection() 方法将元素收集到一个新的 java.util.ArrayList 中;比如说 joining() 方法将元素收集到一个可以用分隔符指定的字符串中。
4. 案例
Employee qingLong = new Employee("青龙", 25, 5500, 7500);
Employee baiHu = new Employee("白虎", 27, 5000, 9000);
Employee zhuQue = new Employee("朱雀", 22, 3800, 4500);
Employee xuanWu = new Employee("玄武", 24, 3300, 3300);
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(qingLong, baiHu, zhuQue, xuanWu);// 避免空指针异常
Optional<Employee> optional = employees.stream().sorted((e1, e2) -> e1.getTotalSalary().compareTo(e2.getTotalSalary())).findFirst();
System.out.println("若空指针异常就这么处理");
optional.orElse(new Employee());
System.out.println(optional);System.out.println("返回任意一个(并行开启多个线程查找)");
Optional<Employee> any = employees.parallelStream().filter((e) -> e.getAge() > 25).findAny();
System.out.println(any);System.out.println("Max(Comparator按年龄比较)");
Optional<Employee> max = employees.stream().max(Comparator.comparing((e) -> e.getAge()));
System.out.println(max);
Optional<Double> max1 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getTotalSalary).max(Double::compare);
System.out.println(max1.get());System.out.println("流中元素接收,计算得到一个");
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Integer reduce = list.stream().reduce(0, (x, u) -> x + u);
System.out.println(reduce);Optional<Integer> reduce1 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println(reduce1.get() + "----------");System.out.println("收集元素到list");
employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();System.out.println("收集元素到LinkList");
employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)).forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("获取流中最大值");
Optional<Integer> max2 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getAge).max(Integer::compare);
System.out.println(max2.get());System.out.println("收集获取总数(集合总数)");
Long collect = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(collect);System.out.println("工资的平均值");
Double collect1 = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Employee::getTotalSalary));
System.out.println(collect1);System.out.println("获取工资的总数,综合,最小值,平均值,最大值");
DoubleSummaryStatistics collect2 = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Employee::getTotalSalary));
System.out.println(collect2);System.out.println("获取年龄最大的员工");
Optional<Employee> collect3 = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge())));
System.out.println(collect3.get());System.out.println("获取年龄最小的员工");
Optional<Double> collect4 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getTotalSalary).collect(Collectors.minBy(Double::compare));
System.out.println(collect4.get());System.out.println("按薪资分组");
Map<Double, List<Employee>> collect5 = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getTotalSalary));
System.out.println(collect5);System.out.println("薪资分区(匹配true)");
Map<Boolean, List<Employee>> collect6 = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy((e) -> e.getTotalSalary() > 5000d));
System.out.println(collect6);
//结果
若空指针异常就这么处理
Optional[Employee{name='玄武', age=24, basicSalary=3300.0, dealTotalPrice=3300.0}]返回任意一个(并行开启多个线程查找)
Optional[Employee{name='白虎', age=27, basicSalary=5000.0, dealTotalPrice=9000.0}]Max(Comparator按年龄比较)
Optional[Employee{name='白虎', age=27, basicSalary=5000.0, dealTotalPrice=9000.0}]
5800.0流中元素接收,计算得到一个
15
98----------收集元素到list
青龙
白虎
朱雀
玄武收集元素到LinkList
朱雀
青龙
玄武
白虎获取流中最大值
27收集获取总数(集合总数)
4工资的平均值
4643.0获取工资的总数,综合,最小值,平均值,最大值
DoubleSummaryStatistics{count=4, sum=18572.000000, min=3432.000000, average=4643.000000, max=5800.000000}获取年龄最大的员工
Employee{name='白虎', age=27, basicSalary=5000.0, dealTotalPrice=9000.0}获取年龄最小的员工
3432.0按薪资分组
{5360.0=[Employee{name='白虎', age=27, basicSalary=5000.0, dealTotalPrice=9000.0}], 5800.0=[Employee{name='青龙', age=25, basicSalary=5500.0, dealTotalPrice=7500.0}], 3432.0=[Employee{name='玄武', age=24, basicSalary=3300.0, dealTotalPrice=3300.0}], 3980.0=[Employee{name='朱雀', age=22, basicSalary=3800.0, dealTotalPrice=4500.0}]}薪资分区(匹配true)
{false=[Employee{name='朱雀', age=22, basicSalary=3800.0, dealTotalPrice=4500.0}, Employee{name='玄武', age=24, basicSalary=3300.0, dealTotalPrice=3300.0}], true=[Employee{name='青龙', age=25, basicSalary=5500.0, dealTotalPrice=7500.0}, Employee{name='白虎', age=27, basicSalary=5000.0, dealTotalPrice=9000.0}]}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!