一文了解 Window 层级顺序
App开发者的不知有没有发现,StatusBar 一直是盖在App 上面,不管是修改颜色,或者是写悬浮框,都无法盖住StatusBar。framework 开发,会出现一些定制,如盖住 StatusBar,不了解的可能用错,出现一些不必要的bug,官方文档也没有列出 Window 层级的规则。
所以希望通过下文给大家分享,Android 是如何制定显示层级规则的。
大概说下 Window 在 Android 中的概念
其实也可以好理解,和经常使用 Windows 操作系统一样,打开一个应用,出现界面,我们可以理解出现了一个窗口,所以 Window ≠ View
一个Activity 可以理解 对应一个 Window,理解源码的同学知道: ViewRootImpl 是对应一个 Window。
怎么看 Window 呢?
adb shell dumpsys window抽取了几个典型的Window如下:Window #2 Window{911875c u0 NavigationBar0}://导航栏ty=NAVIGATION_BARisOnScreen=trueisVisible=true
Window #4 Window{bf1a956 u0 StatusBar}://状态栏ty=STATUS_BARisOnScreen=trueisVisible=true
Window #11 Window{d377ae1 u0 InputMethod}://输入法,不显示ty=INPUT_METHODisOnScreen=falseisVisible=false
Window #12 Window{e190206 u0 com.android.settings/com.android.settings.Settings}://打开 App activityty=BASE_APPLICATIONisOnScreen=trueisVisible=true
Window #16 Window{abcabb9 u0 com.android.systemui.ImageWallpaper}://壁纸ty=WALLPAPERisOnScreen=falseisVisible=false
一般手机都会存在以上 Window,层级顺序从高 -> 低。
显示PopWindow
Window #11 Window{513f711 u0 PopupWindow:3e4bfb}:ty=APPLICATION_SUB_PANELisOnScreen=truesVisible=true
显示Dialog
Window #11 Window{a08f90b ...}:ty=APPLICATIONisOnScreen=trueisVisible=true
不难看出,Window 层级与 ty 有关系的,ty 是 type 的简写。
Window 的分类
Application Window: 应用程序窗口
type 取值范围 [1,99]
/*** Start of window types that represent normal application windows.*/
public static final int FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW = 1;
// activity 会使用 此 type
public static final int TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION = 1;
// dialog 会使用 此 type
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION = 2;
// 冷启动会显示的 Window,真正启动页面显示之前的画面
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING = 3;
// 没玩过
public static final int TYPE_DRAWN_APPLICATION = 4;
/*** End of types of application windows.*/
public static final int LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW = 99;
Sub Window: 子窗口
子窗口:顾名思义,对应有主窗口。子窗口需要附在主窗口上,如PopWindow
type 取值范围 [1000,1999]
/*** Start of types of sub-windows. The {@link #token} of these windows* must be set to the window they are attached to. These types of* windows are kept next to their attached window in Z-order, and their* coordinate space is relative to their attached window.*/
public static final int FIRST_SUB_WINDOW = 1000;
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL = FIRST_SUB_WINDOW;
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA = FIRST_SUB_WINDOW + 1;
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_SUB_PANEL = FIRST_SUB_WINDOW + 2;
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_ATTACHED_DIALOG = FIRST_SUB_WINDOW + 3;
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA_OVERLAY = FIRST_SUB_WINDOW + 4;
public static final int TYPE_APPLICATION_ABOVE_SUB_PANEL = FIRST_SUB_WINDOW + 5;
/*** End of types of sub-windows.*/
public static final int LAST_SUB_WINDOW = 1999;
System Window :系统窗口
type 取值范围 [2000,2999]
如Toast,ANR 窗口,输入法,StatusBar,NavigationBar 等。
/*** Start of system-specific window types. These are not normally* created by applications.*/
public static final int FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW = 2000;
public static final int TYPE_STATUS_BAR = FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW;
public static final int TYPE_SEARCH_BAR = FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW+1;
public static final int TYPE_PHONE = FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW+2;
/*** End of types of system windows.*/
public static final int LAST_SYSTEM_WINDOW = 2999;
之前好像看过文章说 type 值越大,层级越高,这个观点是错的。
具体层级是下面逻辑代码,返回值越大,层级越高,最终在屏幕上显示时就越靠近用户。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/WindowManagerPolicy.java
/*** Returns the layer assignment for the window type. Allows you to control how different* kinds of windows are ordered on-screen.** @param type The type of window being assigned.* @param canAddInternalSystemWindow If the owner window associated with the type we are* evaluating can add internal system windows. I.e they have* {@link Manifest.permission#INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW}. If true, alert window* types {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#isSystemAlertWindowType(int)}* can be assigned layers greater than the layer for* {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY} Else, their* layers would be lesser.* @param roundedCornerOverlay {#code true} to indicate that the owner window is rounded corner* overlay.* @return int An arbitrary integer used to order windows, with lower numbers below higher ones.*/
default int getWindowLayerFromTypeLw(int type, boolean canAddInternalSystemWindow,boolean roundedCornerOverlay) {// Always put the rounded corner layer to the top most.if (roundedCornerOverlay && canAddInternalSystemWindow) {return getMaxWindowLayer();}if (type >= FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW && type <= LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW) {return APPLICATION_LAYER;// APPLICATION_LAYER = 2}switch (type) {case TYPE_WALLPAPER:// wallpaper is at the bottom, though the window manager may move it.return 1;case TYPE_PRESENTATION:case TYPE_PRIVATE_PRESENTATION:case TYPE_DOCK_DIVIDER:case TYPE_QS_DIALOG:case TYPE_PHONE:return 3;case TYPE_SEARCH_BAR:case TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION_STARTING:return 4;case TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION:// voice interaction layer is almost immediately above apps.return 5;case TYPE_INPUT_CONSUMER:return 6;case TYPE_SYSTEM_DIALOG:return 7;case TYPE_TOAST:// toasts and the plugged-in battery thingreturn 8;case TYPE_PRIORITY_PHONE:// SIM errors and unlock. Not sure if this really should be in a high layer.return 9;case TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT:// like the ANR / app crashed dialogs// Type is deprecated for non-system apps. For system apps, this type should be// in a higher layer than TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY.return canAddInternalSystemWindow ? 13 : 10;case TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY:return 12;case TYPE_INPUT_METHOD:// on-screen keyboards and other such input method user interfaces go here.return 15;case TYPE_INPUT_METHOD_DIALOG:// on-screen keyboards and other such input method user interfaces go here.return 16;case TYPE_STATUS_BAR:return 17;case TYPE_STATUS_BAR_ADDITIONAL:return 18;case TYPE_NOTIFICATION_SHADE:return 19;case TYPE_STATUS_BAR_SUB_PANEL:return 20;case TYPE_KEYGUARD_DIALOG:return 21;case TYPE_VOLUME_OVERLAY:// the on-screen volume indicator and controller shown when the user// changes the device volumereturn 22;case TYPE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY:// the on-screen volume indicator and controller shown when the user// changes the device volumereturn canAddInternalSystemWindow ? 23 : 11;case TYPE_NAVIGATION_BAR:// the navigation bar, if available, shows atop most thingsreturn 24;case TYPE_NAVIGATION_BAR_PANEL:// some panels (e.g. search) need to show on top of the navigation barreturn 25;case TYPE_SCREENSHOT:// screenshot selection layer shouldn't go above system error, but it should cover// navigation bars at the very least.return 26;case TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR:// system-level error dialogsreturn canAddInternalSystemWindow ? 27 : 10;case TYPE_MAGNIFICATION_OVERLAY:// used to highlight the magnified portion of a displayreturn 28;case TYPE_DISPLAY_OVERLAY:// used to simulate secondary display devicesreturn 29;case TYPE_DRAG:// the drag layer: input for drag-and-drop is associated with this window,// which sits above all other focusable windowsreturn 30;case TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_OVERLAY:// overlay put by accessibility services to intercept user interactionreturn 31;case TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_MAGNIFICATION_OVERLAY:return 32;case TYPE_SECURE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY:return 33;case TYPE_BOOT_PROGRESS:return 34;case TYPE_POINTER:// the (mouse) pointer layerreturn 35;default:Slog.e("WindowManager", "Unknown window type: " + type);return 3;}
}
以上方法,返回layer,type -> layer,以上代码可以得到如下信息。
layer 取值范围 【1,36】
App 对应 APPLICATION_LAYER,值为2,仅比 TYPE_WALLPAPER 大
Window 层级具体是怎么计算的呢?
从 System Window 中 基本已经找到答案。本章节具体说下实现细节:
mBaseLayer & mSubLayer
用来计算层级的两个参数
mSubLayer:用来计算子窗口的层级,默认值为0
mBaseLayer:用来计算主窗口的层级。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.javaif (mAttrs.type >= FIRST_SUB_WINDOW && mAttrs.type <= LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {mBaseLayer = mPolicy.getWindowLayerLw(parentWindow)* TYPE_LAYER_MULTIPLIER + TYPE_LAYER_OFFSET;// layer * 10000 + 1000mSubLayer = mPolicy.getSubWindowLayerFromTypeLw(a.type);
} else {mBaseLayer = mPolicy.getWindowLayerLw(this)* TYPE_LAYER_MULTIPLIER + TYPE_LAYER_OFFSET;// layer * 10000 + 1000mSubLayer = 0;
}
WindowState 中 mBaseLayer,mSubLayer
mBaseLayer:主窗口的 type 对应 value ,计算如下
如 Activity,type 是 TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION ,getWindowLayerLw 计算返回 APPLICATION_LAYER(2),mBaseLayer = 2 * 10000 + 1000
TYPE_LAYER_MULTIPLIER:为什么要 * 10000,将阈值扩大10000倍,系统中可能存在相同类型的窗口有很多。
TYPE_LAYER_OFFSET:为了移动同一层级的一组窗口
以上两个常量具体怎么使用,没有研究,该值不影响本文的分析。
mSubLayer:计算规则如下,取值范围 [-2,3],TYPE_APPLICATION_ATTACHED_DIALOG 值为 1,APPLICATION_MEDIA_SUBLAYER 值为 -2,看到这里就可以想到子窗口是可以在主窗口下方,主窗口如果可以看到子窗口,必须透明。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/WindowManagerPolicy.javadefault int getSubWindowLayerFromTypeLw(int type) {switch (type) {case TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL:case TYPE_APPLICATION_ATTACHED_DIALOG:return APPLICATION_PANEL_SUBLAYER;// 1case TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA:return APPLICATION_MEDIA_SUBLAYER;// -2case TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA_OVERLAY:return APPLICATION_MEDIA_OVERLAY_SUBLAYER;// -1case TYPE_APPLICATION_SUB_PANEL:return APPLICATION_SUB_PANEL_SUBLAYER; // 2case TYPE_APPLICATION_ABOVE_SUB_PANEL:return APPLICATION_ABOVE_SUB_PANEL_SUBLAYER;// 3}Slog.e("WindowManager", "Unknown sub-window type: " + type);return 0;
}
Sub Window 排序
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java/*** Compares two window sub-layers and returns -1 if the first is lesser than the second in terms* of z-order and 1 otherwise.*/
private static final Comparator sWindowSubLayerComparator =new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(WindowState w1, WindowState w2) {final int layer1 = w1.mSubLayer;final int layer2 = w2.mSubLayer;if (layer1 < layer2 || (layer1 == layer2 && layer2 < 0 )) {// We insert the child window into the list ordered by// the sub-layer. For same sub-layers, the negative one// should go below others; the positive one should go// above others.return -1;}return 1;};};
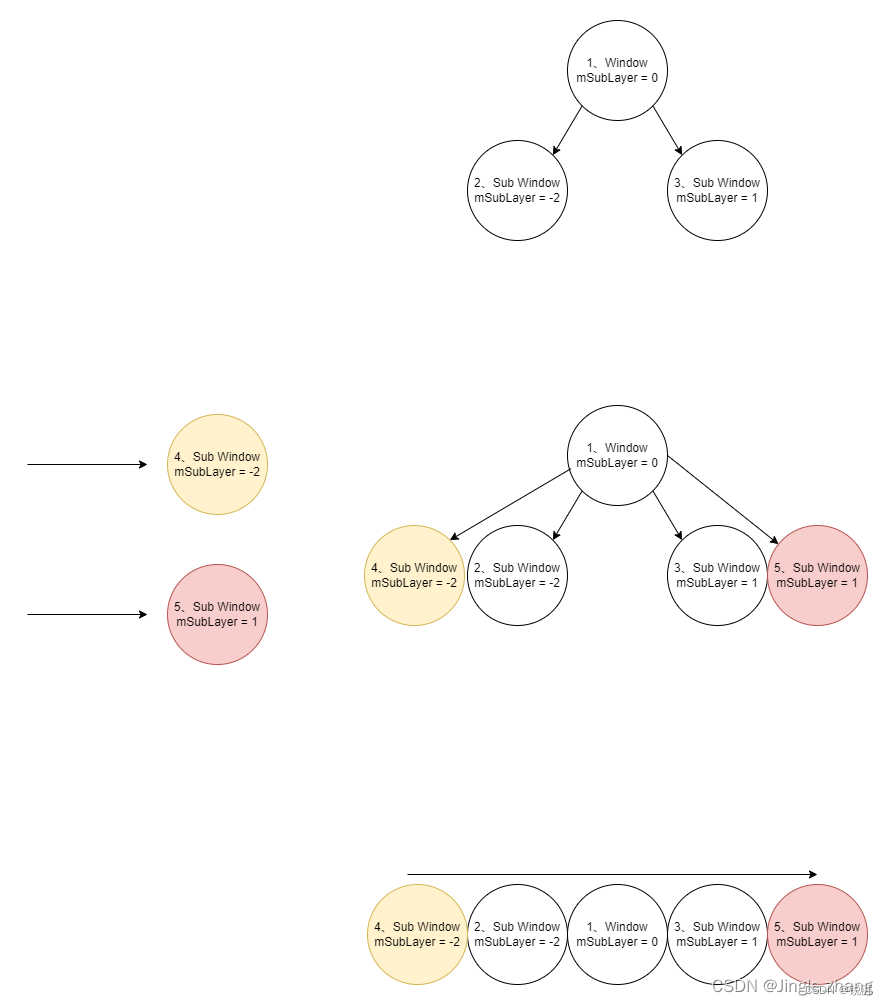
根据上文 mSubLayer 的值排序,如果是新插入的 window ,如果 sublayer 相等且为负值,放在下方,如果 sublayer 相等且为正值,放在上方。
主 Window 排序
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowToken.java/*** Compares two child window of this token and returns -1 if the first is lesser than the* second in terms of z-order and 1 otherwise.*/
private final Comparator mWindowComparator =(WindowState newWindow, WindowState existingWindow) -> {final WindowToken token = WindowToken.this;if (newWindow.mToken != token) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("newWindow=" + newWindow+ " is not a child of token=" + token);}if (existingWindow.mToken != token) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("existingWindow=" + existingWindow+ " is not a child of token=" + token);}return isFirstChildWindowGreaterThanSecond(newWindow, existingWindow) ? 1 : -1;
};protected boolean isFirstChildWindowGreaterThanSecond(WindowState newWindow,WindowState existingWindow) {// New window is considered greater if it has a higher or equal base layer.return newWindow.mBaseLayer >= existingWindow.mBaseLayer;
}
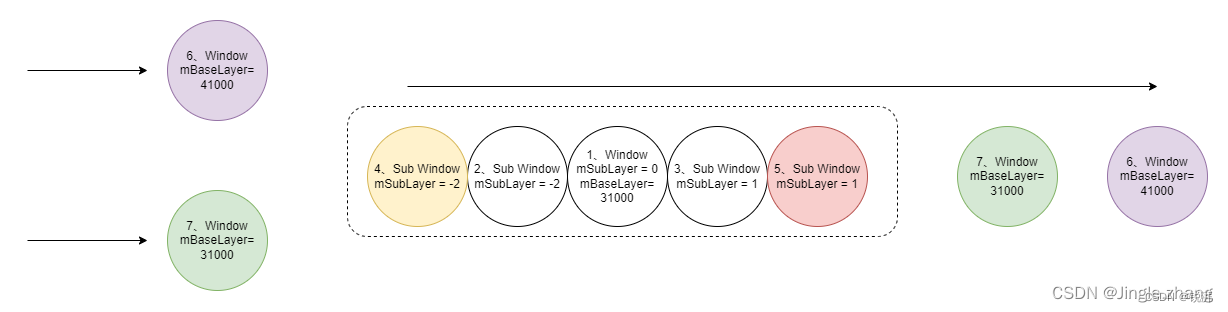
与 Sub Window 排序类似,按照 mBaseLayer 大小排序,如果是新插入的,且相等,放在上方。
总结
主 window 排序图示
子 window 排序图示
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Jingle.zhang」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_58994853/article/details/125493914
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!