PointPillars论文解析和OpenPCDet代码解析
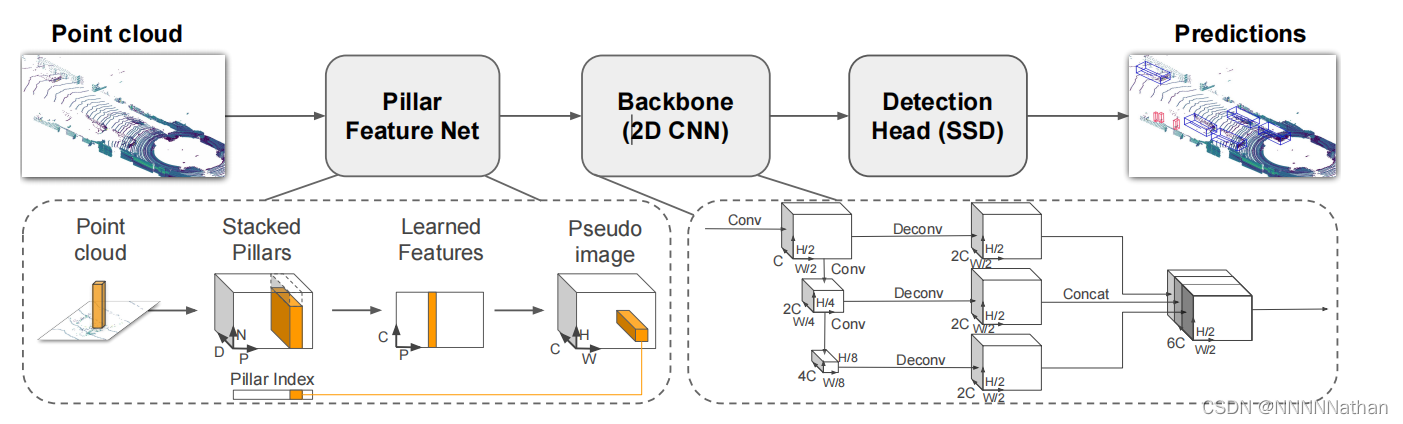
PointPillars是一个来自工业界的模型,整体思想基于图片的处理框架,直接将点云从俯视图的视角划分为一个个的Pillar(立方柱体),从而构成了类似图片的数据,然后在使用2D的检测框架进行特征提取和密集的框预测得到检测框,从而使得该模型在速度和精度都达到了一个很好的平衡。
PointPillars网络结构总览:
网络速度精度对比:
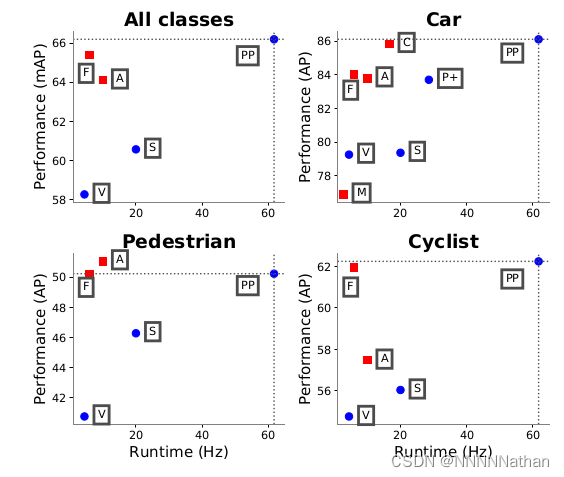
注:(PP代表pointpillars,M代表MV3D, A代表AVOD,C代表ContFuse,V代表VoxelNet,
F代表Frustum Pointnet,S代表SECOND ,P+代表PIXOR++)
本文将会以OpenPCDet的代码基础,详细解析PointPillars的每一行代码实现以及原因。
读者可以下载OpenPCDet后根据文章进行阅读和理解。
由于本人才疏学浅,解析中难免会出现不足之处,欢迎指正、讨论,有好的建议或意见都可以在评论区留言。谢谢大家!
PointPillars的论文地址为:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.05784.pdf
解析参考代码:
https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet
注释代码仓库(仓库注释实时更新):
https://github.com/Nathansong/OpenPCDdet-annotated![]() https://github.com/Nathansong/OpenPCDdet-annotated
https://github.com/Nathansong/OpenPCDdet-annotated
一 : 综述
3D检测算法通常有以下几种形式:
(1)将点云数据划纳入一个个体素(Voxel)中,构成规则的、密集分布的体素集,如有VoxelNet和SECOND。
(2)从前视和俯视角度对点云数据进行投影映射处理,获得一个个伪图片的数据。常见的模型有MV3D和AVOD。
(3)直接将点云数据映射到鸟瞰图后,再直接使用2D的检测框架的处理方法进行特征提取和RPN,实现3D的检测,如PIXOR、本文的主角pointpillar。
(4)使用pointnet直接从点云中对数据进行特征提取后获取proposals,然后根据获取的proposals进行微调,如Pointrcnn
二 : PP网络点云数据处理
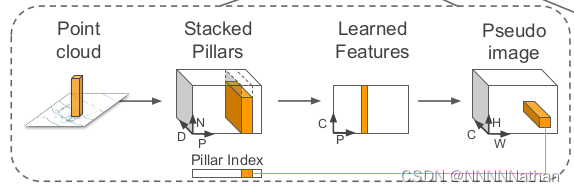
这里的处理过程直接将3D的点云信息直接从以俯视图的形式进行获取,在点云中假设有N*3个点的信息,所有的这些点都在kitti lidar坐标系xyz中(单位是米,其中x向前,y向左,z向上)。所有的这些点都会分配到均等大小的x-y平面的立方柱体中,这个立方柱就被称为pillar。如下图所示
左相机前视图

点云俯视图(左) 将点云分布到的均匀的立方柱体中(右)
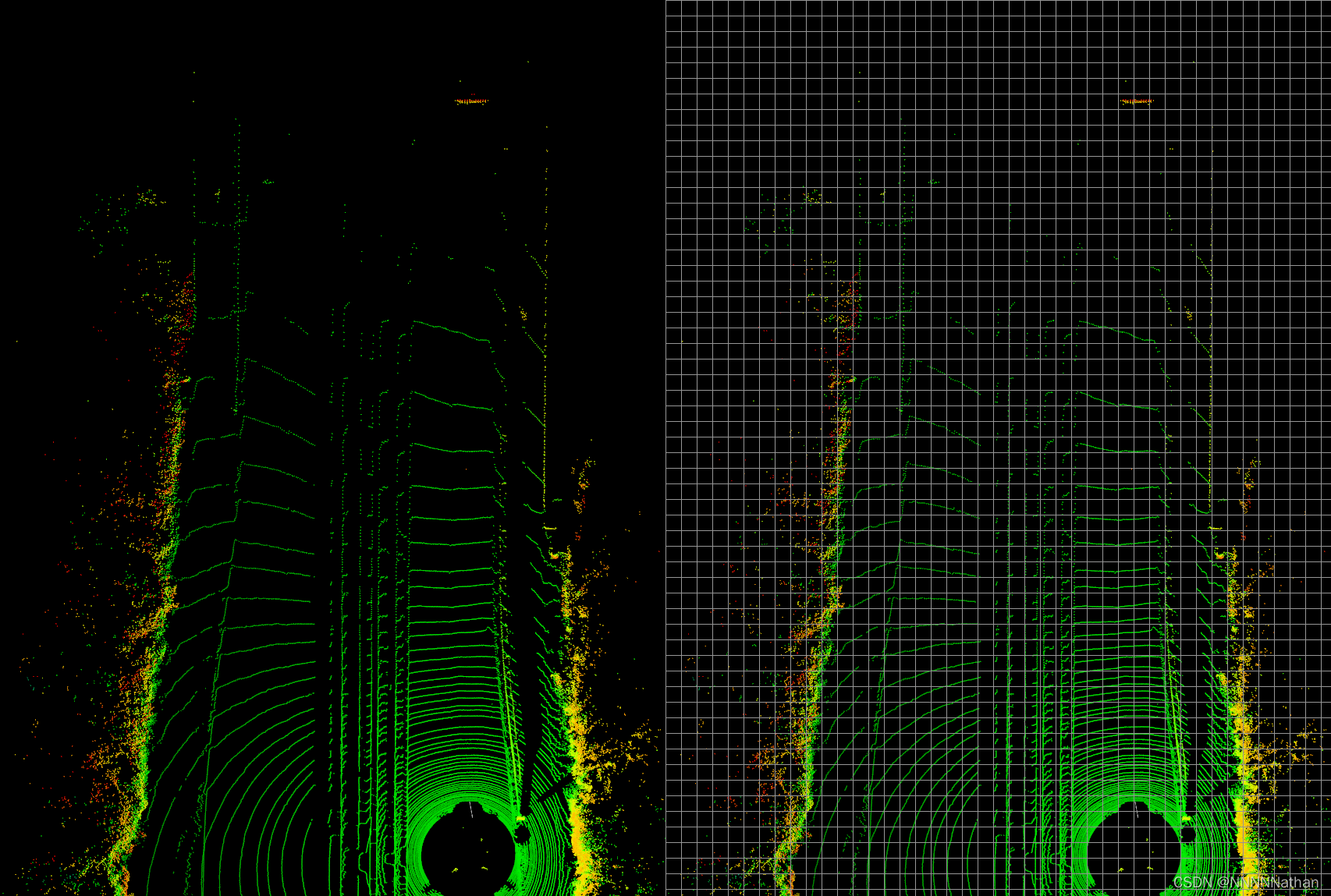
(注:此处偷懒,没有将点云转换到FOV视角中,直接从3D点云俯视图截图,仅为pillar解释)
kitti的点云数据是4维度的数据包含(x, y, z, r)其中xyz是改点在点云中的坐标,r代表了改点的反射强度(与物体材质和激光入射角度等有关);并且在将所有点放入每个pillar中的时候不需要像voxel那样考虑高度,可以将一个pillar理解为就是一个z轴上所有voxel组成在一起的。
在进行PP的数据增强时候,需要对pillar中的数据进行增强操作,需要将每个pillar中的点增加5个维度的数据,包含 x c , y c , z c , x p 和 y p,其中下标c代表了每个点云到改点所对应pillar中所有点平均值的偏移量,下标p代表了该点距离所在pillar中心点的x,y的偏移量。所有经过数据增强操作后每个点的维度是9维;包含了x,y,z, x c , y c , z c , x p 和 y p(注在openpcdet的代码实现中是10维,多了一个zp,也就是该点在z轴上与该点所处pillar的z轴中心的偏移量)
经过上述操作之后,就可以把原始的点云结构(N*3)变换成了(D,P,N),其中D代表了每个点云的特征维度,也就是每个点云9个特征,P代表了所有非空的立方柱体,N代表了每个pillar中最多会有多少个点。
注:
1、在实现的过程中,每个pillar的长宽是0.16米,在pcdet的实现中,我们只会截取前视图的部分,进行训练,因为kitti的标注是根据2号相机进行标注的,所有x轴的负方向(即车的后方)是没有标注数据的,我们会截取掉后面的数据;同时为了保证检测的可靠性,距离太远的点,由于点云过于稀疏,也会被截取。所以在pcdet的实现中,点云空间的选取范围xyz的最小值是=[0, -39.68,-3], xyz选取的最大值是[69.12, 39.68, 1]。
2、其中每个pillar中的最大点云数量是32,如果一个pillar中的点云数量超过32,那么就会随机采样,选取32个点;如果一个pillar中的点云数量少于32;那么会对这个pillar使用0样本填充。
在经过映射后,就获得了一个(D,P,N)的张量;接下来这里使用了一个简化版的pointnet网络对点云的数据进行特征提取(即将这些点通过MLP升维,然后跟着BN层和Relu激活层),得到一个(C,P,N)形状的张量,之后再使用maxpool操作提取每个pillar中最能代表该pillar的点。那么输出会变成(C,P,N)->(C,P);在经过上述操作编码后的点,需要重新放回到原来对应pillar的x,y位置上生成伪图象数据。
下面看这部分的代码实现:
预处理实现代码 pcdet/datasets/processor/data_processor.py
def transform_points_to_voxels(self, data_dict=None, config=None):"""将点云转换为pillar,使用spconv的VoxelGeneratorV2因为pillar可是认为是一个z轴上所有voxel的集合,所以在设置的时候,只需要将每个voxel的高度设置成kitti中点云的最大高度即可"""#初始化点云转换成pillar需要的参数if data_dict is None:# kitti截取的点云范围是[0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1]# 得到[69.12, 79.36, 4]/[0.16, 0.16, 4] = [432, 496, 1]grid_size = (self.point_cloud_range[3:6] - self.point_cloud_range[0:3]) / np.array(config.VOXEL_SIZE)self.grid_size = np.round(grid_size).astype(np.int64)self.voxel_size = config.VOXEL_SIZE# just bind the config, we will create the VoxelGeneratorWrapper later,# to avoid pickling issues in multiprocess spawnreturn partial(self.transform_points_to_voxels, config=config)if self.voxel_generator is None:self.voxel_generator = VoxelGeneratorWrapper(#给定每个pillar的大小 [0.16, 0.16, 4]vsize_xyz=config.VOXEL_SIZE, #给定点云的范围 [0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1]coors_range_xyz=self.point_cloud_range, #给定每个点云的特征维度,这里是x,y,z,r 其中r是激光雷达反射强度num_point_features=self.num_point_features,#给定每个pillar中最多能有多少个点 32max_num_points_per_voxel=config.MAX_POINTS_PER_VOXEL, #最多选取多少个pillar,因为生成的pillar中,很多都是没有点在里面的# 可以重上面的可视化图像中查看到,所以这里只需要得到那些非空的pillar就行max_num_voxels=config.MAX_NUMBER_OF_VOXELS[self.mode], # 16000)points = data_dict['points']# 生成pillar输出voxel_output = self.voxel_generator.generate(points)# 假设一份点云数据是N*4,那么经过pillar生成后会得到三份数据# voxels代表了每个生成的pillar数据,维度是[M,32,4]# coordinates代表了每个生成的pillar所在的zyx轴坐标,维度是[M,3],其中z恒为0# num_points代表了每个生成的pillar中有多少个有效的点维度是[m,],因为不满32会被0填充voxels, coordinates, num_points = voxel_outputif not data_dict['use_lead_xyz']:voxels = voxels[..., 3:] # remove xyz in voxels(N, 3)data_dict['voxels'] = voxelsdata_dict['voxel_coords'] = coordinatesdata_dict['voxel_num_points'] = num_pointsreturn data_dict# 下面是使用spconv生成pillar的代码 class VoxelGeneratorWrapper():def __init__(self, vsize_xyz, coors_range_xyz, num_point_features, max_num_points_per_voxel, max_num_voxels):try:from spconv.utils import VoxelGeneratorV2 as VoxelGeneratorself.spconv_ver = 1except:try:from spconv.utils import VoxelGeneratorself.spconv_ver = 1except:from spconv.utils import Point2VoxelCPU3d as VoxelGeneratorself.spconv_ver = 2if self.spconv_ver == 1:self._voxel_generator = VoxelGenerator(voxel_size=vsize_xyz,point_cloud_range=coors_range_xyz,max_num_points=max_num_points_per_voxel,max_voxels=max_num_voxels)else:self._voxel_generator = VoxelGenerator(vsize_xyz=vsize_xyz,coors_range_xyz=coors_range_xyz,num_point_features=num_point_features,max_num_points_per_voxel=max_num_points_per_voxel,max_num_voxels=max_num_voxels)def generate(self, points):if self.spconv_ver == 1:voxel_output = self._voxel_generator.generate(points)if isinstance(voxel_output, dict):voxels, coordinates, num_points = \voxel_output['voxels'], voxel_output['coordinates'], voxel_output['num_points_per_voxel']else:voxels, coordinates, num_points = voxel_outputelse:assert tv is not None, f"Unexpected error, library: 'cumm' wasn't imported properly."voxel_output = self._voxel_generator.point_to_voxel(tv.from_numpy(points))tv_voxels, tv_coordinates, tv_num_points = voxel_output# make copy with numpy(), since numpy_view() will disappear as soon as the generator is deletedvoxels = tv_voxels.numpy()coordinates = tv_coordinates.numpy()num_points = tv_num_points.numpy()return voxels, coordinates, num_points在经过上面的预处理之后,就需要使用简化版的pointnet网络对每个pillar中的数据进行特征提取了。
代码在pcdet/models/backbones_3d/vfe/pillar_vfe.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Ffrom .vfe_template import VFETemplateclass PFNLayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self,in_channels,out_channels,use_norm=True,last_layer=False):super().__init__()self.last_vfe = last_layerself.use_norm = use_normif not self.last_vfe:out_channels = out_channels // 2if self.use_norm:# 根据论文中,这是是简化版pointnet网络层的初始化# 论文中使用的是 1x1 的卷积层完成这里的升维操作(理论上使用卷积的计算速度会更快)# 输入的通道数是刚刚经过数据增强过后的点云特征,每个点云有10个特征,# 输出的通道数是64self.linear = nn.Linear(in_channels, out_channels, bias=False)# 一维BN层self.norm = nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channels, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01)else:self.linear = nn.Linear(in_channels, out_channels, bias=True)self.part = 50000def forward(self, inputs):if inputs.shape[0] > self.part:# nn.Linear performs randomly when batch size is too largenum_parts = inputs.shape[0] // self.partpart_linear_out = [self.linear(inputs[num_part * self.part:(num_part + 1) * self.part])for num_part in range(num_parts + 1)]x = torch.cat(part_linear_out, dim=0)else:# x的维度由(M, 32, 10)升维成了(M, 32, 64)x = self.linear(inputs)torch.backends.cudnn.enabled = False# BatchNorm1d层:(M, 64, 32) --> (M, 32, 64)# (pillars,num_point,channel)->(pillars,channel,num_points)# 这里之所以变换维度,是因为BatchNorm1d在通道维度上进行,对于图像来说默认模式为[N,C,H*W],通道在第二个维度上x = self.norm(x.permute(0, 2, 1)).permute(0, 2, 1) if self.use_norm else xtorch.backends.cudnn.enabled = Truex = F.relu(x)# 完成pointnet的最大池化操作,找出每个pillar中最能代表该pillar的点# x_max shape :(M, 1, 64) x_max = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)[0]if self.last_vfe:# 返回经过简化版pointnet处理pillar的结果return x_maxelse:x_repeat = x_max.repeat(1, inputs.shape[1], 1)x_concatenated = torch.cat([x, x_repeat], dim=2)return x_concatenatedclass PillarVFE(VFETemplate):"""model_cfg:NAME: PillarVFEWITH_DISTANCE: FalseUSE_ABSLOTE_XYZ: TrueUSE_NORM: TrueNUM_FILTERS: [64]num_point_features:4voxel_size:[0.16 0.16 4]POINT_CLOUD_RANGE: [0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1]"""def __init__(self, model_cfg, num_point_features, voxel_size, point_cloud_range, **kwargs):super().__init__(model_cfg=model_cfg)self.use_norm = self.model_cfg.USE_NORMself.with_distance = self.model_cfg.WITH_DISTANCEself.use_absolute_xyz = self.model_cfg.USE_ABSLOTE_XYZnum_point_features += 6 if self.use_absolute_xyz else 3if self.with_distance:num_point_features += 1self.num_filters = self.model_cfg.NUM_FILTERSassert len(self.num_filters) > 0num_filters = [num_point_features] + list(self.num_filters)pfn_layers = []for i in range(len(num_filters) - 1):in_filters = num_filters[i]out_filters = num_filters[i + 1]pfn_layers.append(PFNLayer(in_filters, out_filters, self.use_norm, last_layer=(i >= len(num_filters) - 2)))# 加入线性层,将10维特征变为64维特征self.pfn_layers = nn.ModuleList(pfn_layers)self.voxel_x = voxel_size[0]self.voxel_y = voxel_size[1]self.voxel_z = voxel_size[2]self.x_offset = self.voxel_x / 2 + point_cloud_range[0]self.y_offset = self.voxel_y / 2 + point_cloud_range[1]self.z_offset = self.voxel_z / 2 + point_cloud_range[2]def get_output_feature_dim(self):return self.num_filters[-1]def get_paddings_indicator(self, actual_num, max_num, axis=0):"""计算padding的指示Args:actual_num:每个voxel实际点的数量(M,)max_num:voxel最大点的数量(32,)Returns:paddings_indicator:表明一个pillar中哪些是真实数据,哪些是填充的0数据"""# 扩展一个维度,使变为(M,1)actual_num = torch.unsqueeze(actual_num, axis + 1)# [1, 1]max_num_shape = [1] * len(actual_num.shape)# [1, -1]max_num_shape[axis + 1] = -1# (1,32)max_num = torch.arange(max_num, dtype=torch.int, device=actual_num.device).view(max_num_shape)# (M, 32)paddings_indicator = actual_num.int() > max_numreturn paddings_indicatordef forward(self, batch_dict, **kwargs):"""batch_dict:points:(N,5) --> (batch_index,x,y,z,r) batch_index代表了该点云数据在当前batch中的indexframe_id:(4,) --> (003877,001908,006616,005355) 帧IDgt_boxes:(4,40,8)--> (x,y,z,dx,dy,dz,ry,class)use_lead_xyz:(4,) --> (1,1,1,1)voxels:(M,32,4) --> (x,y,z,r)voxel_coords:(M,4) --> (batch_index,z,y,x) batch_index代表了该点云数据在当前batch中的indexvoxel_num_points:(M,)image_shape:(4,2) 每份点云数据对应的2号相机图片分辨率batch_size:4 batch_size大小"""voxel_features, voxel_num_points, coords = batch_dict['voxels'], batch_dict['voxel_num_points'], batch_dict['voxel_coords']# 求每个pillar中所有点云的和 (M, 32, 3)->(M, 1, 3) 设置keepdim=True的,则保留原来的维度信息# 然后在使用求和信息除以每个点云中有多少个点来求每个pillar中所有点云的平均值 points_mean shape:(M, 1, 3)points_mean = voxel_features[:, :, :3].sum(dim=1, keepdim=True) / voxel_num_points.type_as(voxel_features).view(-1, 1, 1)# 每个点云数据减去该点对应pillar的平均值得到差值 xc,yc,zcf_cluster = voxel_features[:, :, :3] - points_mean# 创建每个点云到该pillar的坐标中心点偏移量空数据 xp,yp,zpf_center = torch.zeros_like(voxel_features[:, :, :3])# coords是每个网格点的坐标,即[432, 496, 1],需要乘以每个pillar的长宽得到点云数据中实际的长宽(单位米)# 同时为了获得每个pillar的中心点坐标,还需要加上每个pillar长宽的一半得到中心点坐标# 每个点的x、y、z减去对应pillar的坐标中心点,得到每个点到该点中心点的偏移量f_center[:, :, 0] = voxel_features[:, :, 0] - (coords[:, 3].to(voxel_features.dtype).unsqueeze(1) * self.voxel_x + self.x_offset)f_center[:, :, 1] = voxel_features[:, :, 1] - (coords[:, 2].to(voxel_features.dtype).unsqueeze(1) * self.voxel_y + self.y_offset)# 此处偏移多了z轴偏移 论文中没有z轴偏移f_center[:, :, 2] = voxel_features[:, :, 2] - (coords[:, 1].to(voxel_features.dtype).unsqueeze(1) * self.voxel_z + self.z_offset)# 如果使用绝对坐标,直接组合if self.use_absolute_xyz:features = [voxel_features, f_cluster, f_center]# 否则,取voxel_features的3维之后,在组合else:features = [voxel_features[..., 3:], f_cluster, f_center]# 如果使用距离信息if self.with_distance:# torch.norm的第一个2指的是求2范数,第二个2是在第三维度求范数points_dist = torch.norm(voxel_features[:, :, :3], 2, 2, keepdim=True)features.append(points_dist)# 将特征在最后一维度拼接 得到维度为(M,32,10)的张量features = torch.cat(features, dim=-1)# 每个pillar中点云的最大数量voxel_count = features.shape[1]"""由于在生成每个pillar中,不满足最大32个点的pillar会存在由0填充的数据,而刚才上面的计算中,会导致这些由0填充的数据在计算出现xc,yc,zc和xp,yp,zp出现数值,所以需要将这个被填充的数据的这些数值清0,因此使用get_paddings_indicator计算features中哪些是需要被保留真实数据和需要被置0的填充数据"""# 得到mask维度是(M, 32)# mask中指名了每个pillar中哪些是需要被保留的数据mask = self.get_paddings_indicator(voxel_num_points, voxel_count, axis=0)# (M, 32)->(M, 32, 1)mask = torch.unsqueeze(mask, -1).type_as(voxel_features)# 将feature中被填充数据的所有特征置0features *= maskfor pfn in self.pfn_layers:features = pfn(features)# (M, 64), 每个pillar抽象出一个64维特征features = features.squeeze()batch_dict['pillar_features'] = featuresreturn batch_dict
在经过简化版的pointnet网络提取出每个pillar的特征信息后,就需要将每个的pillar数据重新放回原来的坐标分布中来组成伪图像数据了。
代码在pcdet/models/backbones_2d/map_to_bev/pointpillar_scatter.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass PointPillarScatter(nn.Module):"""对应到论文中就是stacked pillars,将生成的pillar按照坐标索引还原到原空间中"""def __init__(self, model_cfg, grid_size, **kwargs):super().__init__()self.model_cfg = model_cfgself.num_bev_features = self.model_cfg.NUM_BEV_FEATURES # 64self.nx, self.ny, self.nz = grid_size # [432,496,1]assert self.nz == 1def forward(self, batch_dict, **kwargs):"""Args:pillar_features:(M,64)coords:(M, 4) 第一维是batch_index 其余维度为xyzReturns:batch_spatial_features:(batch_size, 64, 496, 432)"""# 拿到经过前面pointnet处理过后的pillar数据和每个pillar所在点云中的坐标位置# pillar_features 维度 (M, 64)# coords 维度 (M, 4)pillar_features, coords = batch_dict['pillar_features'], batch_dict['voxel_coords']# 将转换成为伪图像的数据存在到该列表中batch_spatial_features = []batch_size = coords[:, 0].max().int().item() + 1# batch中的每个数据独立处理for batch_idx in range(batch_size):# 创建一个空间坐标所有用来接受pillar中的数据# self.num_bev_features是64# self.nz * self.nx * self.ny是生成的空间坐标索引 [496, 432, 1]的乘积# spatial_feature 维度 (64,214272)spatial_feature = torch.zeros(self.num_bev_features,self.nz * self.nx * self.ny,dtype=pillar_features.dtype,device=pillar_features.device) # (64,214272)-->1x432x496=214272# 从coords[:, 0]取出该batch_idx的数据maskbatch_mask = coords[:, 0] == batch_idx# 根据mask提取坐标this_coords = coords[batch_mask, :]# this_coords中存储的坐标是z,y和x的形式,且只有一层,因此计算索引的方式如下# 平铺后需要计算前面有多少个pillar 一直到当前pillar的索引"""因为前面是将所有数据flatten成一维的了,相当于一个图片宽高为[496, 432]的图片被flatten成一维的图片数据了,变成了496*432=214272;而this_coords中存储的是平面(不需要考虑Z轴)中一个点的信息,所以要将这个点的位置放回被flatten的一位数据时,需要计算在该点之前所有行的点总和加上该点所在的列即可"""# 这里得到所有非空pillar在伪图像的对应索引位置indices = this_coords[:, 1] + this_coords[:, 2] * self.nx + this_coords[:, 3]# 转换数据类型indices = indices.type(torch.long)# 根据mask提取pillar_featurespillars = pillar_features[batch_mask, :]pillars = pillars.t()# 在索引位置填充pillarsspatial_feature[:, indices] = pillars# 将空间特征加入list,每个元素为(64, 214272)batch_spatial_features.append(spatial_feature)# 在第0个维度将所有的数据堆叠在一起batch_spatial_features = torch.stack(batch_spatial_features, 0)# reshape回原空间(伪图像) (4, 64, 214272)--> (4, 64, 496, 432)batch_spatial_features = batch_spatial_features.view(batch_size, self.num_bev_features * self.nz, self.ny,self.nx)# 将结果加入batch_dictbatch_dict['spatial_features'] = batch_spatial_featuresreturn batch_dict
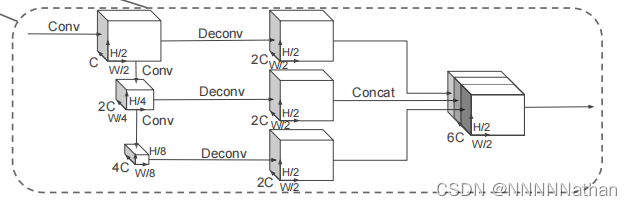
三、使用2D BackBone提取特征
经过上面的映射操作,将原来的pillar提取最大的数值后放回到相应的坐标后,就可以得到类似于图像的数据了;只有在有pillar非空的坐标处有提取的点云数据,其余地方都是0数据,所以得到的一个(batch_size,64, 432, 496)的张量还是很稀疏的。
下图是对得到的张量数据使用2D中的特征提取手段进行多尺度的特征提取和拼接融合。
这没有好解析的就是常规的卷积操作然后进行拼接即可,注意一下维度变换就可以。
最终经过所有上采样层得到的3个尺度的的信息 每个尺度的 shape 都是 (batch_size, 128, 248, 216) 在第一个维度上进行拼接得到x 维度是 (batch_size, 384, 248, 216)
代码在pcdet/models/backbones_2d/base_bev_backbone.py
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass BaseBEVBackbone(nn.Module):def __init__(self, model_cfg, input_channels):super().__init__()self.model_cfg = model_cfg# 读取下采样层参数if self.model_cfg.get('LAYER_NUMS', None) is not None:assert len(self.model_cfg.LAYER_NUMS) == len(self.model_cfg.LAYER_STRIDES) == len(self.model_cfg.NUM_FILTERS)layer_nums = self.model_cfg.LAYER_NUMSlayer_strides = self.model_cfg.LAYER_STRIDESnum_filters = self.model_cfg.NUM_FILTERSelse:layer_nums = layer_strides = num_filters = []# 读取上采样层参数if self.model_cfg.get('UPSAMPLE_STRIDES', None) is not None:assert len(self.model_cfg.UPSAMPLE_STRIDES) == len(self.model_cfg.NUM_UPSAMPLE_FILTERS)num_upsample_filters = self.model_cfg.NUM_UPSAMPLE_FILTERSupsample_strides = self.model_cfg.UPSAMPLE_STRIDESelse:upsample_strides = num_upsample_filters = []num_levels = len(layer_nums) # 2c_in_list = [input_channels, *num_filters[:-1]] # (256, 128) input_channels:256, num_filters[:-1]:64,128self.blocks = nn.ModuleList()self.deblocks = nn.ModuleList()for idx in range(num_levels): # (64,64)-->(64,128)-->(128,256) # 这里为cur_layers的第一层且stride=2cur_layers = [nn.ZeroPad2d(1),nn.Conv2d(c_in_list[idx], num_filters[idx], kernel_size=3,stride=layer_strides[idx], padding=0, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(num_filters[idx], eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),nn.ReLU()]for k in range(layer_nums[idx]): # 根据layer_nums堆叠卷积层cur_layers.extend([nn.Conv2d(num_filters[idx], num_filters[idx], kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(num_filters[idx], eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),nn.ReLU()])# 在block中添加该层# *作用是:将列表解开成几个独立的参数,传入函数 # 类似的运算符还有两个星号(**),是将字典解开成独立的元素作为形参self.blocks.append(nn.Sequential(*cur_layers))if len(upsample_strides) > 0: # 构造上采样层 # (1, 2, 4)stride = upsample_strides[idx]if stride >= 1:self.deblocks.append(nn.Sequential(nn.ConvTranspose2d(num_filters[idx], num_upsample_filters[idx],upsample_strides[idx],stride=upsample_strides[idx], bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(num_upsample_filters[idx], eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),nn.ReLU()))else:stride = np.round(1 / stride).astype(np.int)self.deblocks.append(nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(num_filters[idx], num_upsample_filters[idx],stride,stride=stride, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(num_upsample_filters[idx], eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),nn.ReLU()))c_in = sum(num_upsample_filters) # 512if len(upsample_strides) > num_levels:self.deblocks.append(nn.Sequential(nn.ConvTranspose2d(c_in, c_in, upsample_strides[-1], stride=upsample_strides[-1], bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(c_in, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),nn.ReLU(),))self.num_bev_features = c_indef forward(self, data_dict):"""Args:data_dict:spatial_features : (4, 64, 496, 432)Returns:"""spatial_features = data_dict['spatial_features']ups = []ret_dict = {}x = spatial_featuresfor i in range(len(self.blocks)):x = self.blocks[i](x)stride = int(spatial_features.shape[2] / x.shape[2])ret_dict['spatial_features_%dx' % stride] = xif len(self.deblocks) > 0: # (4,64,248,216)-->(4,128,124,108)-->(4,256,62,54)ups.append(self.deblocks[i](x))else:ups.append(x)# 如果存在上采样层,将上采样结果连接if len(ups) > 1:"""最终经过所有上采样层得到的3个尺度的的信息每个尺度的 shape 都是 (batch_size, 128, 248, 216)在第一个维度上进行拼接得到x 维度是 (batch_size, 384, 248, 216)"""x = torch.cat(ups, dim=1)elif len(ups) == 1:x = ups[0]# Fasleif len(self.deblocks) > len(self.blocks):x = self.deblocks[-1](x)# 将结果存储在spatial_features_2d中并返回data_dict['spatial_features_2d'] = xreturn data_dict
四、检测头实现
PiontPillars中的检测头采用了类似SSD的检测头设置,在openpcdet的实现中,直接使用了一个网络训练车、人、自行车三个类别;没有像原论文中对车、人使用两种不同的网络结构。因此在检测头的先验框设置上,一共有三个类别的先验框,每个先验框都有两个方向分别是BEV视角下的0度和90度,每个类别的先验证只有一种尺度信息;分别是车 [3.9, 1.6, 1.56]、人[0.8, 0.6, 1.73]、自行车[1.76, 0.6, 1.73](单位:米)。
在anchor匹配GT的过程中,使用的是2D IOU匹配方式,直接从生成的特征图也就是BEV视角进行匹配;不需要考虑高度信息。原因有二:1、因为在kitti数据集中所有的物体都是在三维空间的同一个平面中的,没有车在车上面的一个情况。 2、所有类别物体之间的高度差别不是很大,直接使用SmoothL1回归就可以得到很好的结果。 其次是每个anchor被设置为正负样本的iou阈值是:
车匹配iou阈值大于等于0.65为正样本,小于0.45为负样本,中间的不计算损失。
人匹配iou阈值大于等于0.5为正样本,小于0.35为负样本,中间的不计算损失。
自行车匹配iou阈值大于等于0.5为正样本,小于0.35为负样本,中间的不计算损失。
其中每个anchor都需要预测7个参数,分别是 (x, y, z, w, l, h, θ),其中x, y, z预测一个anchor的中心坐标在点云中的位置, w,l,h分别预测了一个anchor的长宽高数据,θ预测了box的旋转角度。
同时,因为在角度预测时候不可以区分两个完全相反的box,所以PiontPillars的检测头中还添加了对一个anchor的方向预测;这里使用了一个基于softmax的方向分类box的两个朝向信息。
代码在 pcdet/models/dense_heads/anchor_head_single.py
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nnfrom .anchor_head_template import AnchorHeadTemplateclass AnchorHeadSingle(AnchorHeadTemplate):"""Args:model_cfg: AnchorHeadSingle的配置input_channels: 384 输入通道数num_class: 3class_names: ['Car','Pedestrian','Cyclist']grid_size: (432, 496, 1)point_cloud_range: (0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1)predict_boxes_when_training: False"""def __init__(self, model_cfg, input_channels, num_class, class_names, grid_size, point_cloud_range,predict_boxes_when_training=True, **kwargs):super().__init__(model_cfg=model_cfg, num_class=num_class, class_names=class_names, grid_size=grid_size,point_cloud_range=point_cloud_range,predict_boxes_when_training=predict_boxes_when_training)# 每个点有3个尺度的个先验框 每个先验框都有两个方向(0度,90度) num_anchors_per_location:[2, 2, 2]self.num_anchors_per_location = sum(self.num_anchors_per_location) # sum([2, 2, 2])# Conv2d(512,18,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(1,1))self.conv_cls = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, self.num_anchors_per_location * self.num_class,kernel_size=1)# Conv2d(512,42,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(1,1))self.conv_box = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, self.num_anchors_per_location * self.box_coder.code_size,kernel_size=1)# 如果存在方向损失,则添加方向卷积层Conv2d(512,12,kernel_size=(1,1),stride=(1,1))if self.model_cfg.get('USE_DIRECTION_CLASSIFIER', None) is not None:self.conv_dir_cls = nn.Conv2d(input_channels,self.num_anchors_per_location * self.model_cfg.NUM_DIR_BINS,kernel_size=1)else:self.conv_dir_cls = Noneself.init_weights()# 初始化参数def init_weights(self):pi = 0.01# 初始化分类卷积偏置nn.init.constant_(self.conv_cls.bias, -np.log((1 - pi) / pi))# 初始化分类卷积权重nn.init.normal_(self.conv_box.weight, mean=0, std=0.001)def forward(self, data_dict):# 从字典中取出经过backbone处理过的信息# spatial_features_2d 维度 (batch_size, 384, 248, 216)spatial_features_2d = data_dict['spatial_features_2d']# 每个坐标点上面6个先验框的类别预测 --> (batch_size, 18, 200, 176)cls_preds = self.conv_cls(spatial_features_2d)# 每个坐标点上面6个先验框的参数预测 --> (batch_size, 42, 200, 176) 其中每个先验框需要预测7个参数,分别是(x, y, z, w, l, h, θ)box_preds = self.conv_box(spatial_features_2d)# 维度调整,将类别放置在最后一维度 [N, H, W, C] --> (batch_size, 200, 176, 18)cls_preds = cls_preds.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()# 维度调整,将先验框调整参数放置在最后一维度 [N, H, W, C] --> (batch_size ,200, 176, 42)box_preds = box_preds.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()# 将类别和先验框调整预测结果放入前向传播字典中self.forward_ret_dict['cls_preds'] = cls_predsself.forward_ret_dict['box_preds'] = box_preds# 进行方向分类预测if self.conv_dir_cls is not None:# # 每个先验框都要预测为两个方向中的其中一个方向 --> (batch_size, 12, 200, 176)dir_cls_preds = self.conv_dir_cls(spatial_features_2d)# 将类别和先验框方向预测结果放到最后一个维度中 [N, H, W, C] --> (batch_size, 248, 216, 12)dir_cls_preds = dir_cls_preds.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()# 将方向预测结果放入前向传播字典中self.forward_ret_dict['dir_cls_preds'] = dir_cls_predselse:dir_cls_preds = None"""如果是在训练模式的时候,需要对每个先验框分配GT来计算loss"""if self.training:# targets_dict = {# 'box_cls_labels': cls_labels, # (4,211200)# 'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (4,211200, 7)# 'reg_weights': reg_weights # (4,211200)# }targets_dict = self.assign_targets(gt_boxes=data_dict['gt_boxes'] # (4,39,8))# 将GT分配结果放入前向传播字典中self.forward_ret_dict.update(targets_dict)# 如果不是训练模式,则直接生成进行box的预测if not self.training or self.predict_boxes_when_training:# 根据预测结果解码生成最终结果batch_cls_preds, batch_box_preds = self.generate_predicted_boxes(batch_size=data_dict['batch_size'],cls_preds=cls_preds, box_preds=box_preds, dir_cls_preds=dir_cls_preds)data_dict['batch_cls_preds'] = batch_cls_preds # (1, 211200, 3) 70400*3=211200data_dict['batch_box_preds'] = batch_box_preds # (1, 211200, 7)data_dict['cls_preds_normalized'] = Falsereturn data_dict
五、loss计算
在Pointpillars的loss计算中,使用了与SECOND相同的loss计算方式,每个GT框都包含了 (x, y, z, w, l, h, θ)这7个参数。
1、loss理论计算
1.定位任务的回归残差定义如下:
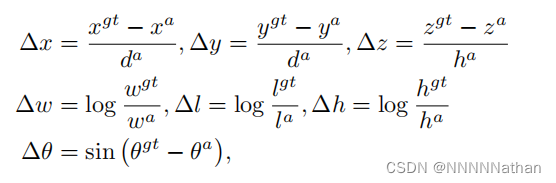
其中x^gt代表了标注框的x长度 ;x^a代表了先验框的长度信息,d^a表示先验框长度和宽度的对角线距离,定义为:![]() 。
。
因此得到的总回归损失是: 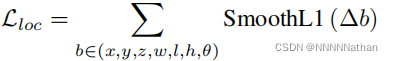 。
。
2.类别分类任务
对于每个先验框的物体类别分类,PointPillars使用了focal loss,来完成调节正负样本均衡,和难样本挖掘。公式定义如下:
![]()
其中,aplha参数和gamma参数都和RetinaNet中的设置一样,分别为0.25和2。
3.先验框方向分类
由于在角度回归的时候,不可以完全区分两个两个方向完全相反的预测框,所以在实现的时候,作者加入了对先验框的方向分类,使用softmax函数预测方向的类别。
因此总损失定义如下: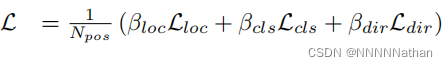
其中,系数Beta_loc为2,Beta_cls为1,Beta_dir为0.2。
2、loss计算代码实现
在loss计算的代码实现中涉及的代码量比较多,因此解析分为如下三个部分分别完成
1、先验框的生成
2、GT和先验框的匹配
3、loss计算实现
1、先验框的生成
代码在pcdet/models/dense_heads/target_assigner/anchor_generator.py
import torchclass AnchorGenerator(object):def __init__(self, anchor_range, anchor_generator_config):super().__init__()self.anchor_generator_cfg = anchor_generator_config # list:3# 得到anchor在点云中的分布范围[0, -39.68, -3, 69.12, 39.68, 1]self.anchor_range = anchor_range# 得到配置参数中所有尺度anchor的长宽高# list:3 --> 车、人、自行车[[[3.9, 1.6, 1.56]],[[0.8, 0.6, 1.73]],[[1.76, 0.6, 1.73]]]self.anchor_sizes = [config['anchor_sizes'] for config in anchor_generator_config]# 得到anchor的旋转角度,这是是弧度,也就是0度和90度# list:3 --> [[0, 1.57],[0, 1.57],[0, 1.57]]self.anchor_rotations = [config['anchor_rotations'] for config in anchor_generator_config]# 得到每个anchor初始化在点云中z轴的位置,其中在kitti中点云的z轴范围是-3米到1米# list:3 --> [[-1.78],[-0.6],[-0.6]]self.anchor_heights = [config['anchor_bottom_heights'] for config in anchor_generator_config]# 每个先验框产生的时候是否需要在每个格子的中间,# 例如坐标点为[1,1],如果需要对齐中心点的话,需要加上0.5变成[1.5, 1.5]# 默认为False# list:3 --> [False, False, False]self.align_center = [config.get('align_center', False) for config in anchor_generator_config]assert len(self.anchor_sizes) == len(self.anchor_rotations) == len(self.anchor_heights)self.num_of_anchor_sets = len(self.anchor_sizes) # 3def generate_anchors(self, grid_sizes):assert len(grid_sizes) == self.num_of_anchor_sets# 1.初始化all_anchors = []num_anchors_per_location = []# 2.三个类别的先验框逐类别生成for grid_size, anchor_size, anchor_rotation, anchor_height, align_center in zip(grid_sizes, self.anchor_sizes, self.anchor_rotations, self.anchor_heights, self.align_center):# 2 = 2x1x1 --> 每个位置产生2个anchor,这里的2代表两个方向num_anchors_per_location.append(len(anchor_rotation) * len(anchor_size) * len(anchor_height))# 不需要对齐中心点来生成先验框if align_center:x_stride = (self.anchor_range[3] - self.anchor_range[0]) / grid_size[0]y_stride = (self.anchor_range[4] - self.anchor_range[1]) / grid_size[1]# 中心对齐,平移半个网格x_offset, y_offset = x_stride / 2, y_stride / 2else:# 2.1计算每个网格的在点云空间中的实际大小# 用于将每个anchor映射回实际点云中的大小# (69.12 - 0) / (216 - 1) = 0.3214883848678234 单位:米x_stride = (self.anchor_range[3] - self.anchor_range[0]) / (grid_size[0] - 1)# (39.68 - (-39.68.)) / (248 - 1) = 0.3212955490297634 单位:米y_stride = (self.anchor_range[4] - self.anchor_range[1]) / (grid_size[1] - 1)# 由于没有进行中心对齐,所有每个点相对于左上角坐标的偏移量都是0x_offset, y_offset = 0, 0# 2.2 生成单个维度x_shifts,y_shifts和z_shifts# 以x_stride为step,在self.anchor_range[0] + x_offset和self.anchor_range[3] + 1e-5,# 产生x坐标 --> 216个点 [0, 69.12]x_shifts = torch.arange(self.anchor_range[0] + x_offset, self.anchor_range[3] + 1e-5, step=x_stride, dtype=torch.float32,).cuda()# 产生y坐标 --> 248个点 [0, 79.36]y_shifts = torch.arange(self.anchor_range[1] + y_offset, self.anchor_range[4] + 1e-5, step=y_stride, dtype=torch.float32,).cuda()"""new_tensor函数可以返回一个新的张量数据,该张量数据与指定的有相同的属性如拥有相同的数据类型和张量所在的设备情况等属性;并使用anchor_height数值个来填充这个张量"""# [-1.78]z_shifts = x_shifts.new_tensor(anchor_height)# num_anchor_size = 1# num_anchor_rotation = 2num_anchor_size, num_anchor_rotation = anchor_size.__len__(), anchor_rotation.__len__() # 1, 2# [0, 1.57] 弧度制anchor_rotation = x_shifts.new_tensor(anchor_rotation)# [[3.9, 1.6, 1.56]]anchor_size = x_shifts.new_tensor(anchor_size)# 2.3 调用meshgrid生成网格坐标x_shifts, y_shifts, z_shifts = torch.meshgrid([x_shifts, y_shifts, z_shifts])# meshgrid可以理解为在原来的维度上进行扩展,例如:# x原来为(216,)-->(216,1, 1)--> (216,248,1)# y原来为(248,)--> (1,248,1)--> (216,248,1)# z原来为 (1, ) --> (1,1,1) --> (216,248,1)# 2.4.anchor各个维度堆叠组合,生成最终anchor(1,432,496,1,2,7)# 2.4.1.堆叠anchor的位置 # [x, y, z, 3]-->[216, 248, 1, 3] 代表了每个anchor的位置信息# 其中3为该点所在映射tensor中的(z, y, x)数值anchors = torch.stack((x_shifts, y_shifts, z_shifts), dim=-1) # 2.4.2.将anchor的位置和大小进行组合,编程为将anchor扩展并复制为相同维度(除了最后一维),然后进行组合# (216, 248, 1, 3) --> (216, 248, 1 , 1, 3)# 维度分别代表了: z,y,x, 该类别anchor的尺度数量,该个anchor的位置信息anchors = anchors[:, :, :, None, :].repeat(1, 1, 1, anchor_size.shape[0], 1)# (1, 1, 1, 1, 3) --> (216, 248, 1, 1, 3)anchor_size = anchor_size.view(1, 1, 1, -1, 3).repeat([*anchors.shape[0:3], 1, 1])# anchors生成的最终结果需要有位置信息和大小信息 --> (216, 248, 1, 1, 6)# 最后一个纬度中表示(z, y, x, l, w, h)anchors = torch.cat((anchors, anchor_size), dim=-1)# 2.4.3.将anchor的位置和大小和旋转角进行组合# 在倒数第二个维度上增加一个维度,然后复制该维度一次# (216, 248, 1, 1, 2, 6) 长, 宽, 深, anchor尺度数量, 该尺度旋转角个数,anchor的6个参数anchors = anchors[:, :, :, :, None, :].repeat(1, 1, 1, 1, num_anchor_rotation, 1)# (216, 248, 1, 1, 2, 1) 两个不同方向先验框的旋转角度anchor_rotation = anchor_rotation.view(1, 1, 1, 1, -1, 1).repeat([*anchors.shape[0:3], num_anchor_size, 1, 1])# [z, y, x, num_size, num_rot, 7] --> (216, 248, 1, 1, 2, 7)# 最后一个纬度表示为anchors的位置+大小+旋转角度(z, y, x, l, w, h, theta)anchors = torch.cat((anchors, anchor_rotation), dim=-1) # [z, y, x, num_size, num_rot, 7]# 2.5 置换anchor的维度# [z, y, x, num_anchor_size, num_rot, 7]-->[x, y, z, num_anchor_zie, num_rot, 7]# 最后一个纬度代表了 : [x, y, z, dx, dy, dz, rot]anchors = anchors.permute(2, 1, 0, 3, 4, 5).contiguous()# 使得各类anchor的z轴方向从anchor的底部移动到该anchor的中心点位置# 车 : -1.78 + 1.56/2 = -1.0# 人、自行车 : -0.6 + 1.73/2 = 0.23anchors[..., 2] += anchors[..., 5] / 2all_anchors.append(anchors)# all_anchors: [(1,248,216,1,2,7),(1,248,216,1,2,7),(1,248,216,1,2,7)]# num_anchors_per_location:[2,2,2]return all_anchors, num_anchors_per_location2、GT和先验框的匹配(target assignment)
此处代码注释已经写得很详细,可以按照注释理解如果和计算GT和所有anchor的匹配;
assign_targets完成对一帧点云数据中所有的类别和anchor的正负样本分配,
assign_targets_single完成对一帧中每个类别的GT和anchor的正负样本分配。
所以一个Batch样本中anchor与GT的匹配这里是逐帧逐类别进行的。与图像目标检测中稍有不同。
代码在pcdet/models/dense_heads/target_assigner/axis_aligned_target_assigner.py
import numpy as np
import torchfrom ....ops.iou3d_nms import iou3d_nms_utils
from ....utils import box_utilsclass AxisAlignedTargetAssigner(object):def __init__(self, model_cfg, class_names, box_coder, match_height=False):super().__init__()# anchor生成配置参数anchor_generator_cfg = model_cfg.ANCHOR_GENERATOR_CONFIG# 为预测box找对应anchor的参数anchor_target_cfg = model_cfg.TARGET_ASSIGNER_CONFIG# 编码box的7个残差参数(x, y, z, w, l, h, θ) --> pcdet.utils.box_coder_utils.ResidualCoderself.box_coder = box_coder# 在PointPillars中指定正负样本的时候由BEV视角计算GT和先验框的iou,不需要进行z轴上的高度的匹配,# 想法是:1、点云中的物体都在同一个平面上,没有物体在Z轴发生重叠的情况# 2、每个类别的高度相差不是很大,直接使用SmoothL1损失就可以达到很好的高度回归效果self.match_height = match_height# 类别名称['Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist']self.class_names = np.array(class_names)# ['Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist']self.anchor_class_names = [config['class_name'] for config in anchor_generator_cfg]# anchor_target_cfg.POS_FRACTION = -1 < 0 --> None# 前景、背景采样系数 PointPillars不考虑self.pos_fraction = anchor_target_cfg.POS_FRACTION if anchor_target_cfg.POS_FRACTION >= 0 else None# 总采样数 PointPillars不考虑self.sample_size = anchor_target_cfg.SAMPLE_SIZE # 512# False 前景权重由 1/前景anchor数量 PointPillars不考虑self.norm_by_num_examples = anchor_target_cfg.NORM_BY_NUM_EXAMPLES# 类别iou匹配为正样本阈值{'Car':0.6, 'Pedestrian':0.5, 'Cyclist':0.5}self.matched_thresholds = {}# 类别iou匹配为负样本阈值{'Car':0.45, 'Pedestrian':0.35, 'Cyclist':0.35}self.unmatched_thresholds = {}for config in anchor_generator_cfg:self.matched_thresholds[config['class_name']] = config['matched_threshold']self.unmatched_thresholds[config['class_name']] = config['unmatched_threshold']self.use_multihead = model_cfg.get('USE_MULTIHEAD', False) # False# self.separate_multihead = model_cfg.get('SEPARATE_MULTIHEAD', False)# if self.seperate_multihead:# rpn_head_cfgs = model_cfg.RPN_HEAD_CFGS# self.gt_remapping = {}# for rpn_head_cfg in rpn_head_cfgs:# for idx, name in enumerate(rpn_head_cfg['HEAD_CLS_NAME']):# self.gt_remapping[name] = idx + 1def assign_targets(self, all_anchors, gt_boxes_with_classes):"""处理一批数据中所有点云的anchors和gt_boxes,计算每个anchor属于前景还是背景,为每个前景的anchor分配类别和计算box的回归残差和回归权重Args:all_anchors: [(N, 7), ...]gt_boxes_with_classes: (B, M, 8) # 最后维度数据为 (x, y, z, w, l, h, θ,class)Returns:all_targets_dict = {# 每个anchor的类别'box_cls_labels': cls_labels, # (batch_size,num_of_anchors)# 每个anchor的回归残差 -->(∆x, ∆y, ∆z, ∆l, ∆w, ∆h, ∆θ)'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (batch_size,num_of_anchors,7)# 每个box的回归权重'reg_weights': reg_weights # (batch_size,num_of_anchors)}"""# 1.初始化结果list并提取对应的gt_box和类别bbox_targets = []cls_labels = []reg_weights = []# 得到批大小batch_size = gt_boxes_with_classes.shape[0] # 4# 得到所有GT的类别gt_classes = gt_boxes_with_classes[:, :, -1] # (4,num_of_gt)# 得到所有GT的7个box参数gt_boxes = gt_boxes_with_classes[:, :, :-1] # (4,num_of_gt,7)# 2.对batch中的所有数据逐帧匹配anchor的前景和背景for k in range(batch_size):cur_gt = gt_boxes[k] # 取出当前帧中的 gt_boxes (num_of_gt,7)"""由于在OpenPCDet的数据预处理时,以一批数据中拥有GT数量最多的帧为基准,其他帧中GT数量不足,则会进行补0操作,使其成为一个矩阵,例:[[1,1,2,2,3,2],[2,2,3,1,0,0],[3,1,2,0,0,0]]因此这里从每一行的倒数第二个类别开始判断,截取最后一个非零元素的索引,来取出当前帧中真实的GT数据"""cnt = cur_gt.__len__() - 1 # 得到一批数据中最多有多少个GT# 这里的循环是找到最后一个非零的box,因为预处理的时候会按照batch最大box的数量处理,不足的进行补0while cnt > 0 and cur_gt[cnt].sum() == 0:cnt -= 1# 2.1提取当前帧非零的box和类别cur_gt = cur_gt[:cnt + 1]# cur_gt_classes 例: tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int32)cur_gt_classes = gt_classes[k][:cnt + 1].int()target_list = []# 2.2 对每帧中的anchor和GT分类别,单独计算前背景# 计算时候 每个类别的anchor是独立计算的 不同于在ssd中整体计算iou并取最大值for anchor_class_name, anchors in zip(self.anchor_class_names, all_anchors):# anchor_class_name : 车 | 行人 | 自行车# anchors : (1, 200, 176, 1, 2, 7) 7 --> (x, y, z, l, w, h, θ)if cur_gt_classes.shape[0] > 1:# self.class_names : ["car", "person", "cyclist"]# 这里减1是因为列表索引从0开始,目的是得到属于列表中gt中哪些类别是与当前处理的了类别相同,得到类别maskmask = torch.from_numpy(self.class_names[cur_gt_classes.cpu() - 1] == anchor_class_name)else:mask = torch.tensor([self.class_names[c - 1] == anchor_class_namefor c in cur_gt_classes], dtype=torch.bool)# 在检测头中是否使用多头,是的话 此处为True,默认为Falseif self.use_multihead: # Falseanchors = anchors.permute(3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 5).contiguous().view(-1, anchors.shape[-1])# if self.seperate_multihead:# selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask].clone()# if len(selected_classes) > 0:# new_cls_id = self.gt_remapping[anchor_class_name]# selected_classes[:] = new_cls_id# else:# selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask]selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask]else:# 2.2.1 计算所需的变量 得到特征图的大小feature_map_size = anchors.shape[:3] # (1, 248, 216)# 将所有的anchors展平 shape : (216, 248, 1, 1, 2, 7) --> (107136, 7)anchors = anchors.view(-1, anchors.shape[-1])# List: 根据累呗mask索引得到该帧中当前需要处理的类别 --> 车 | 行人 | 自行车selected_classes = cur_gt_classes[mask]# 2.2.2 使用assign_targets_single来单独为某一类别的anchors分配gt_boxes,# 并为前景、背景的box设置编码和回归权重single_target = self.assign_targets_single(anchors, # 该类的所有anchorcur_gt[mask], # GT_box shape : (num_of_GT_box, 7)gt_classes=selected_classes, # 当前选中的类别matched_threshold=self.matched_thresholds[anchor_class_name], # 当前类别anchor与GT匹配为正样本的阈值unmatched_threshold=self.unmatched_thresholds[anchor_class_name] # 当前类别anchor与GT匹配为负样本的阈值)target_list.append(single_target)# 到目前为止,处理完该帧单个类别和该类别anchor的前景和背景分配if self.use_multihead:target_dict = {'box_cls_labels': [t['box_cls_labels'].view(-1) for t in target_list],'box_reg_targets': [t['box_reg_targets'].view(-1, self.box_coder.code_size) for t in target_list],'reg_weights': [t['reg_weights'].view(-1) for t in target_list]}target_dict['box_reg_targets'] = torch.cat(target_dict['box_reg_targets'], dim=0)target_dict['box_cls_labels'] = torch.cat(target_dict['box_cls_labels'], dim=0).view(-1)target_dict['reg_weights'] = torch.cat(target_dict['reg_weights'], dim=0).view(-1)else:target_dict = {# feature_map_size:(1,200,176, 2)'box_cls_labels': [t['box_cls_labels'].view(*feature_map_size, -1) for t in target_list],# (1,248,216, 2, 7)'box_reg_targets': [t['box_reg_targets'].view(*feature_map_size, -1, self.box_coder.code_size)for t in target_list],# (1,248,216, 2)'reg_weights': [t['reg_weights'].view(*feature_map_size, -1) for t in target_list]}# list : 3*anchor (1, 248, 216, 2, 7) --> (1, 248, 216, 6, 7) -> (321408, 7)target_dict['box_reg_targets'] = torch.cat(target_dict['box_reg_targets'], dim=-2).view(-1, self.box_coder.code_size)# list:3 (1, 248, 216, 2) --> (1,248, 216, 6) -> (1*248*216*6, )target_dict['box_cls_labels'] = torch.cat(target_dict['box_cls_labels'], dim=-1).view(-1)# list:3 (1, 200, 176, 2) --> (1, 200, 176, 6) -> (1*248*216*6, )target_dict['reg_weights'] = torch.cat(target_dict['reg_weights'], dim=-1).view(-1)# 将结果填入对应的容器bbox_targets.append(target_dict['box_reg_targets'])cls_labels.append(target_dict['box_cls_labels'])reg_weights.append(target_dict['reg_weights'])# 到这里该batch的点云全部处理完# 3.将结果stack并返回bbox_targets = torch.stack(bbox_targets, dim=0) # (batch_size,321408,7)cls_labels = torch.stack(cls_labels, dim=0) # (batch_size,321408)reg_weights = torch.stack(reg_weights, dim=0) # (batch_size,321408)all_targets_dict = {'box_cls_labels': cls_labels, # (batch_size,321408)'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (batch_size,321408,7)'reg_weights': reg_weights # (batch_size,321408)}return all_targets_dictdef assign_targets_single(self, anchors, gt_boxes, gt_classes, matched_threshold=0.6, unmatched_threshold=0.45):"""针对某一类别的anchors和gt_boxes,计算前景和背景anchor的类别,box编码和回归权重Args:anchors: (107136, 7)gt_boxes: (该帧中该类别的GT数量,7)gt_classes: (该帧中该类别的GT数量, 1)matched_threshold:0.6unmatched_threshold:0.45Returns:前景anchorret_dict = {'box_cls_labels': labels, # (107136,)'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (107136,7)'reg_weights': reg_weights, # (107136,)}"""# ----------------------------1.初始化-------------------------------#num_anchors = anchors.shape[0] # 216 * 248 = 107136num_gt = gt_boxes.shape[0] # 该帧中该类别的GT数量# 初始化anchor对应的label和gt_id ,并置为 -1,-1表示loss计算时候不会被考虑,背景的类别被设置为0labels = torch.ones((num_anchors,), dtype=torch.int32, device=anchors.device) * -1gt_ids = torch.ones((num_anchors,), dtype=torch.int32, device=anchors.device) * -1# ---------------------2.计算该类别中anchor的前景和背景------------------------#if len(gt_boxes) > 0 and anchors.shape[0] > 0:# 1.计算该帧中某一个类别gt和对应anchors之间的iou(jaccard index)# anchor_by_gt_overlap shape : (107136, num_gt)# anchor_by_gt_overlap代表当前类别的所有anchor和当前类别中所有GT的iouanchor_by_gt_overlap = iou3d_nms_utils.boxes_iou3d_gpu(anchors[:, 0:7], gt_boxes[:, 0:7]) \if self.match_height else box_utils.boxes3d_nearest_bev_iou(anchors[:, 0:7], gt_boxes[:, 0:7])# NOTE: The speed of these two versions depends the environment and the number of anchors# anchor_to_gt_argmax = torch.from_numpy(anchor_by_gt_overlap.cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=1)).cuda()# 2.得到每一个anchor与哪个的GT的的iou最大# anchor_to_gt_argmax表示数据维度是anchor的长度,索引是gtanchor_to_gt_argmax = anchor_by_gt_overlap.argmax(dim=1)# anchor_to_gt_max得到每一个anchor最匹配的gt的iou数值anchor_to_gt_max = anchor_by_gt_overlap[torch.arange(num_anchors, device=anchors.device), anchor_to_gt_argmax]# gt_to_anchor_argmax = torch.from_numpy(anchor_by_gt_overlap.cpu().numpy().argmax(axis=0)).cuda()# 3.找到每个gt最匹配anchor的索引和iou# (num_of_gt,) 得到每个gt最匹配的anchor索引gt_to_anchor_argmax = anchor_by_gt_overlap.argmax(dim=0)# (num_of_gt,)找到每个gt最匹配anchor的iougt_to_anchor_max = anchor_by_gt_overlap[gt_to_anchor_argmax, torch.arange(num_gt, device=anchors.device)]# 4.将GT中没有匹配到的anchor的iou数值设置为-1empty_gt_mask = gt_to_anchor_max == 0 # 得到没有匹配到anchor的gt的maskgt_to_anchor_max[empty_gt_mask] = -1 # 将没有匹配到anchor的gt的iou数值设置为-1# 5.找到anchor中和gt存在最大iou的anchor索引,即前景anchor"""由于在前面的实现中,仅仅找出来每个GT和anchor的最大iou索引,但是argmax返回的是索引最小的那个,在匹配的过程中可能一个GT和多个anchor拥有相同的iou大小,所以此处要找出这个GT与所有anchors拥有相同最大iou的anchor"""# 以gt为基础,逐个anchor对应,比如第一个gt的最大iou为0.9,则在所有anchor中找iou为0.9的anchor# nonzero函数是numpy中用于得到数组array中非零元素的位置(数组索引)的函数"""矩阵比较例子 :anchors_with_max_overlap = torch.tensor([[0.78, 0.1, 0.9, 0],[0.0, 0.5, 0, 0],[0.0, 0, 0.9, 0.8],[0.78, 0.1, 0.0, 0]])gt_to_anchor_max = torch.tensor([0.78, 0.5, 0.9,0.8]) anchors_with_max_overlap = anchor_by_gt_overlap == gt_to_anchor_max# 返回的结果中包含了在anchor中与该GT拥有相同最大iou的所有anchoranchors_with_max_overlap = tensor([[ True, False, True, False],[False, True, False, False],[False, False, True, True],[ True, False, False, False]])在torch中nonzero返回的是tensor中非0元素的位置,此函数在numpy中返回的是非零元素的行列表和列列表。torch返回结果tensor([[0, 0],[0, 2],[1, 1],[2, 2],[2, 3],[3, 0]])numpy返回结果(array([0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 3]), array([0, 2, 1, 2, 3, 0])) 所以可以得到第一个GT同时与第一个anchor和最后一个anchor最为匹配 """"""所以在实际的一批数据中可以到得到结果为tensor([[33382, 9],[43852, 10],[47284, 5],[50370, 4],[58498, 8],[58500, 8],[58502, 8],[59139, 2],[60751, 1],[61183, 1],[61420, 11],[62389, 0],[63216, 13],[63218, 13],[65046, 12],[65048, 12],[65478, 12],[65480, 12],[71924, 3],[78046, 7],[80150, 6]], device='cuda:0')在第0维度拥有相同gt索引的项,在该类所有anchor中同时拥有多个与之最为匹配的anchor"""# (num_of_multiple_best_matching_for_per_GT,)anchors_with_max_overlap = (anchor_by_gt_overlap == gt_to_anchor_max).nonzero()[:, 0]# 得到这些最匹配anchor与该类别的哪个GT索引相对应# 其实和(anchor_by_gt_overlap == gt_to_anchor_max).nonzero()[:, 1]的结果一样gt_inds_force = anchor_to_gt_argmax[anchors_with_max_overlap] # (35,)# 将gt的类别赋值到对应的anchor的label中labels[anchors_with_max_overlap] = gt_classes[gt_inds_force]# 将gt的索引也赋值到对应的anchors的gt_ids中gt_ids[anchors_with_max_overlap] = gt_inds_force.int()# 6.根据matched_threshold和unmatched_threshold以及anchor_to_gt_max计算前景和背景索引,并更新labels和gt_ids"""这里对labels和gt_ids的操作应该已经包含了上面的anchors_with_max_overlap"""# 找到最匹配的anchor中iou大于给定阈值的mask #(107136,)pos_inds = anchor_to_gt_max >= matched_threshold# 找到最匹配的anchor中iou大于给定阈值的gt的索引 #(105,)gt_inds_over_thresh = anchor_to_gt_argmax[pos_inds]# 将pos anchor对应gt的类别赋值到对应的anchor的label中labels[pos_inds] = gt_classes[gt_inds_over_thresh]# 将pos anchor对应gt的索引赋值到对应的anchor的gt_id中gt_ids[pos_inds] = gt_inds_over_thresh.int()bg_inds = (anchor_to_gt_max < unmatched_threshold).nonzero()[:, 0] # 找到背景anchor索引else:bg_inds = torch.arange(num_anchors, device=anchors.device)# 找到前景anchor的索引--> (num_of_foreground_anchor,)# 106879 + 119 = 106998 < 107136 说明有一些anchor既不是背景也不是前景,# iou介于unmatched_threshold和matched_threshold之间fg_inds = (labels > 0).nonzero()[:, 0]# 到目前为止得到哪些anchor是前景和哪些anchor是背景# ------------------3.对anchor的前景和背景进行筛选和赋值--------------------## 如果存在前景采样比例,则分别采样前景和背景anchor,PointPillar中没有前背景采样操作,前背景均衡使用了focal loss损失函数if self.pos_fraction is not None: # anchor_target_cfg.POS_FRACTION = -1 < 0 --> Nonenum_fg = int(self.pos_fraction * self.sample_size) # self.sample_size=512# 如果前景anchor大于采样前景数if len(fg_inds) > num_fg:# 计算要丢弃的前景anchor数目num_disabled = len(fg_inds) - num_fg# 在前景数目中随机产生索引值,并取前num_disabled个关闭索引# 比如:torch.randperm(4)# 输出:tensor([ 2, 1, 0, 3])disable_inds = torch.randperm(len(fg_inds))[:num_disabled]# 将被丢弃的anchor的iou设置为-1labels[disable_inds] = -1# 更新前景索引fg_inds = (labels > 0).nonzero()[:, 0]# 计算所需背景数num_bg = self.sample_size - (labels > 0).sum()# 如果当前背景数大于所需背景数if len(bg_inds) > num_bg:# torch.randint在0到len(bg_inds)之间,随机产生size为(num_bg,)的数组enable_inds = bg_inds[torch.randint(0, len(bg_inds), size=(num_bg,))]# 将enable_inds的标签设置为0labels[enable_inds] = 0# bg_inds = torch.nonzero(labels == 0)[:, 0]else:# 如果该类别没有GT的话,将该类别的全部label置0,即所有anchor都是背景类别if len(gt_boxes) == 0 or anchors.shape[0] == 0:labels[:] = 0else:# anchor与GT的iou小于unmatched_threshold的anchor的类别设置类背景类别labels[bg_inds] = 0# 将前景赋对应类别"""此处分别使用了anchors_with_max_overlap和anchor_to_gt_max >= matched_threshold来对该类别的anchor进行赋值但是我个人觉得anchor_to_gt_max >= matched_threshold已经包含了anchors_with_max_overlap的那些与GT拥有最大iou的anchor了,所以我对这里的计算方式有一点好奇,为什么要分别计算两次,如果知道这里原因的小伙伴希望可以给予解答,谢谢!"""labels[anchors_with_max_overlap] = gt_classes[gt_inds_force]# ------------------4.计算bbox_targets和reg_weights--------------------## 初始化每个anchor的7个回归参数,并设置为0数值bbox_targets = anchors.new_zeros((num_anchors, self.box_coder.code_size)) # (107136,7)# 如果该帧中有该类别的GT时候,就需要对这些设置为正样本类别的anchor进行编码操作了if len(gt_boxes) > 0 and anchors.shape[0] > 0:# 使用anchor_to_gt_argmax[fg_inds]来重复索引每个anchor对应前景的GT_boxfg_gt_boxes = gt_boxes[anchor_to_gt_argmax[fg_inds], :]# 提取所有属于前景的anchorfg_anchors = anchors[fg_inds, :]"""PointPillar编码gt和前景anchor,并赋值到bbox_targets的对应位置7个参数的编码的方式为∆x = (x^gt − xa^da)/d^a , ∆y = (y^gt − ya^da)/d^a , ∆z = (z^gt − za^ha)/h^a∆w = log (w^gt / w^a) ∆l = log (l^gt / l^a) , ∆h = log (h^gt / h^a)∆θ = sin(θ^gt - θ^a) """bbox_targets[fg_inds, :] = self.box_coder.encode_torch(fg_gt_boxes, fg_anchors)# 初始化回归权重,并设置值为0reg_weights = anchors.new_zeros((num_anchors,)) # (107136,)if self.norm_by_num_examples: # PointPillars回归权重中不需要norm_by_num_examplesnum_examples = (labels >= 0).sum()num_examples = num_examples if num_examples > 1.0 else 1.0reg_weights[labels > 0] = 1.0 / num_exampleselse:reg_weights[labels > 0] = 1.0 # 将前景anchor的回归权重设置为1ret_dict = {'box_cls_labels': labels, # (107136,)'box_reg_targets': bbox_targets, # (107136,7)编码后的结果'reg_weights': reg_weights, # (107136,)}return ret_dict
3、box编码实现
此处根据论文中的公式对匹配被正样本的anchor_box和与之对应的GT-box的7个回归参数进行编码。
编码公式:
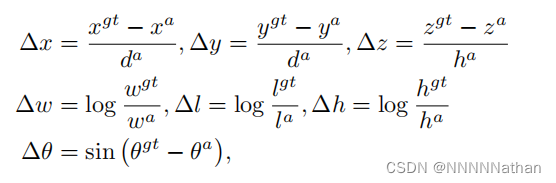
其中x^gt代表了标注框的x长度 ;x^a代表了先验框的长度信息,d^a表示先验框长度和宽度的对角线距离,定义为:![]() 。
。
代码在:pcdet/utils/box_coder_utils.py
class ResidualCoder(object):def __init__(self, code_size=7, encode_angle_by_sincos=False, **kwargs):"""loss中anchor和gt的编码与解码7个参数的编码的方式为∆x = (x^gt − xa^da)/d^a , ∆y = (y^gt − ya^da)/d^a , ∆z = (z^gt − za^ha)/h^a∆w = log (w^gt / w^a) ∆l = log (l^gt / l^a) , ∆h = log (h^gt / h^a)∆θ = sin(θ^gt - θ^a)"""super().__init__()self.code_size = code_sizeself.encode_angle_by_sincos = encode_angle_by_sincosif self.encode_angle_by_sincos:self.code_size += 1def encode_torch(self, boxes, anchors):"""Args:boxes: (N, 7 + C) [x, y, z, dx, dy, dz, heading, ...]anchors: (N, 7 + C) [x, y, z, dx, dy, dz, heading or *[cos, sin], ...]Returns:"""# 截断anchors的[dx,dy,dz],每个anchor_box的l, w, h数值如果小于1e-5则为1e-5anchors[:, 3:6] = torch.clamp_min(anchors[:, 3:6], min=1e-5)# 截断boxes的[dx,dy,dz] 每个GT_box的l, w, h数值如果小于1e-5则为1e-5boxes[:, 3:6] = torch.clamp_min(boxes[:, 3:6], min=1e-5)# If split_size_or_sections is an integer type, then tensor will be split into equally sized chunks (if possible).# Last chunk will be smaller if the tensor size along the given dimension dim is not divisible by split_size.# 这里指torch.split的第二个参数 torch.split(tensor, split_size, dim=) split_size是切分后每块的大小,不是切分为多少块!,多余的参数使用*cags接收xa, ya, za, dxa, dya, dza, ra, *cas = torch.split(anchors, 1, dim=-1)xg, yg, zg, dxg, dyg, dzg, rg, *cgs = torch.split(boxes, 1, dim=-1)# 计算anchor对角线长度diagonal = torch.sqrt(dxa ** 2 + dya ** 2)# 计算loss的公式,Δx,Δy,Δz,Δw,Δl,Δh,Δθ# ∆x = x ^ gt − xa ^ daxt = (xg - xa) / diagonal# ∆y = (y^gt − ya^da)/d^ayt = (yg - ya) / diagonal# ∆z = (z^gt − za^ha)/h^azt = (zg - za) / dza# ∆l = log(l ^ gt / l ^ a)dxt = torch.log(dxg / dxa)# ∆w = log(w ^ gt / w ^ a)dyt = torch.log(dyg / dya)# ∆h = log(h ^ gt / h ^ a)dzt = torch.log(dzg / dza)# Falseif self.encode_angle_by_sincos:rt_cos = torch.cos(rg) - torch.cos(ra)rt_sin = torch.sin(rg) - torch.sin(ra)rts = [rt_cos, rt_sin]else:rts = [rg - ra] # Δθcts = [g - a for g, a in zip(cgs, cas)]return torch.cat([xt, yt, zt, dxt, dyt, dzt, *rts, *cts], dim=-1)4、loss计算实现
在PointPillars损失计算分别有三个,每个anhcor和GT的类别分类损失、box的7个回归损失、还有一个方向角预测的分类损失构成。
1、分类损失计算:
代码在pcdet/models/dense_heads/anchor_head_template.py
def get_cls_layer_loss(self):# (batch_size, 248, 216, 18) 网络类别预测cls_preds = self.forward_ret_dict['cls_preds']# (batch_size, 321408) 前景anchor类别box_cls_labels = self.forward_ret_dict['box_cls_labels']batch_size = int(cls_preds.shape[0])# [batch_szie, num_anchors]--> (batch_size, 321408)# 关心的anchor 选取出前景背景anchor, 在0.45到0.6之间的设置为仍然是-1,不参与loss计算cared = box_cls_labels >= 0# (batch_size, 321408) 前景anchorpositives = box_cls_labels > 0# (batch_size, 321408) 背景anchornegatives = box_cls_labels == 0# 背景anchor赋予权重negative_cls_weights = negatives * 1.0# 将每个anchor分类的损失权重都设置为1cls_weights = (negative_cls_weights + 1.0 * positives).float()# 每个正样本anchor的回归损失权重,设置为1reg_weights = positives.float()# 如果只有一类if self.num_class == 1:# class agnosticbox_cls_labels[positives] = 1# 正则化并计算权重 求出每个数据中有多少个正例,即shape=(batch, 1)pos_normalizer = positives.sum(1, keepdim=True).float() # (4,1) 所有正例的和 eg:[[162.],[166.],[155.],[108.]]# 正则化回归损失-->(batch_size, 321408),最小值为1,根据论文中所述,用正样本数量来正则化回归损失reg_weights /= torch.clamp(pos_normalizer, min=1.0)# 正则化分类损失-->(batch_size, 321408),根据论文中所述,用正样本数量来正则化分类损失cls_weights /= torch.clamp(pos_normalizer, min=1.0)# care包含了背景和前景的anchor,但是这里只需要得到前景部分的类别即可不关注-1和0# cared.type_as(box_cls_labels) 将cared中为False的那部分不需要计算loss的anchor变成了0# 对应位置相乘后,所有背景和iou介于match_threshold和unmatch_threshold之间的anchor都设置为0cls_targets = box_cls_labels * cared.type_as(box_cls_labels)# 在最后一个维度扩展一次cls_targets = cls_targets.unsqueeze(dim=-1)cls_targets = cls_targets.squeeze(dim=-1)one_hot_targets = torch.zeros(*list(cls_targets.shape), self.num_class + 1, dtype=cls_preds.dtype, device=cls_targets.device) # (batch_size, 321408, 4),这里的类别数+1是考虑背景# target.scatter(dim, index, src)# scatter_函数的一个典型应用就是在分类问题中,# 将目标标签转换为one-hot编码形式 https://blog.csdn.net/guofei_fly/article/details/104308528# 这里表示在最后一个维度,将cls_targets.unsqueeze(dim=-1)所索引的位置设置为1"""dim=1: 表示按照列进行填充index=batch_data.label:表示把batch_data.label里面的元素值作为下标,去下标对应位置(这里的"对应位置"解释为列,如果dim=0,那就解释为行)进行填充src=1:表示填充的元素值为1"""# (batch_size, 321408, 4)one_hot_targets.scatter_(-1, cls_targets.unsqueeze(dim=-1).long(), 1.0)# (batch_size, 248, 216, 18) --> (batch_size, 321408, 3)cls_preds = cls_preds.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_class)# (batch_size, 321408, 3) 不计算背景分类损失one_hot_targets = one_hot_targets[..., 1:]# 计算分类损失 # [N, M] # (batch_size, 321408, 3)cls_loss_src = self.cls_loss_func(cls_preds, one_hot_targets, weights=cls_weights)# 求和并除以batch数目cls_loss = cls_loss_src.sum() / batch_size# loss乘以分类权重 --> cls_weight=1.0cls_loss = cls_loss * self.model_cfg.LOSS_CONFIG.LOSS_WEIGHTS['cls_weight']tb_dict = {'rpn_loss_cls': cls_loss.item()}return cls_loss, tb_dict与之对应的focal_loss分类计算的详细实现代码在:pcdet/utils/loss_utils.py
class SigmoidFocalClassificationLoss(nn.Module):"""多分类Sigmoid focal cross entropy loss."""def __init__(self, gamma: float = 2.0, alpha: float = 0.25):"""Args:gamma: Weighting parameter to balance loss for hard and easy examples.alpha: Weighting parameter to balance loss for positive and negative examples."""super(SigmoidFocalClassificationLoss, self).__init__()self.alpha = alpha # 0.25self.gamma = gamma # 2.0@staticmethoddef sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(input: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor):""" PyTorch Implementation for tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits:max(x, 0) - x * z + log(1 + exp(-abs(x))) inhttps://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logitsArgs:input: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor.Predicted logits for each classtarget: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor.One-hot encoded classification targetsReturns:loss: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor.Sigmoid cross entropy loss without reduction"""loss = torch.clamp(input, min=0) - input * target + \torch.log1p(torch.exp(-torch.abs(input)))return lossdef forward(self, input: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, weights: torch.Tensor):"""Args:input: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor. eg:(4, 321408, 3)Predicted logits for each class :一个anchor会预测三种类别target: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor. eg:(4, 321408, 3)One-hot encoded classification targets,:真值weights: (B, #anchors) float tensor. eg:(4, 321408)Anchor-wise weights.Returns:weighted_loss: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor after weighting."""pred_sigmoid = torch.sigmoid(input) # (batch_size, 321408, 3) f(x) = 1 / (1 + e^(-x))# 这里的加权主要是解决正负样本不均衡的问题:正样本的权重为0.25,负样本的权重为0.75# 交叉熵来自KL散度,衡量两个分布之间的相似性,针对二分类问题:# 合并形式: L = -(y * log(y^) + (1 - y) * log(1 - y^)) <--> # 分段形式:y = 1, L = -y * log(y^); y = 0, L = -(1 - y) * log(1 - y^)# 这两种形式等价,只要是0和1的分类问题均可以写成两种等价形式,针对focal loss做类似处理# 相对熵 = 信息熵 + 交叉熵, 且交叉熵是凸函数,求导时能够得到全局最优值-->(sigma(s)- y)x https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35709485alpha_weight = target * self.alpha + (1 - target) * (1 - self.alpha) # (4, 321408, 3)pt = target * (1.0 - pred_sigmoid) + (1.0 - target) * pred_sigmoidfocal_weight = alpha_weight * torch.pow(pt, self.gamma)# (batch_size, 321408, 3) 交叉熵损失的一种变形,具体推到参考上面的链接bce_loss = self.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(input, target)loss = focal_weight * bce_loss # (batch_size, 321408, 3)if weights.shape.__len__() == 2 or \(weights.shape.__len__() == 1 and target.shape.__len__() == 2):weights = weights.unsqueeze(-1)assert weights.shape.__len__() == loss.shape.__len__()# weights参数使用正anchor数目进行平均,使得每个样本的损失与样本中目标的数量无关return loss * weights2、box的回归SmoothL1损失计算和方向分类损失计算:
代码在:pcdet/models/dense_heads/anchor_head_template.py
def get_box_reg_layer_loss(self):# (batch_size, 248, 216, 42) anchor_box的7个回归参数box_preds = self.forward_ret_dict['box_preds']# (batch_size, 248, 216, 12) anchor_box的方向预测box_dir_cls_preds = self.forward_ret_dict.get('dir_cls_preds', None)# (batch_size, 321408, 7) 每个anchor和GT编码的结果box_reg_targets = self.forward_ret_dict['box_reg_targets']# (batch_size, 321408)box_cls_labels = self.forward_ret_dict['box_cls_labels']batch_size = int(box_preds.shape[0])# 获取所有anchor中属于前景anchor的mask shape : (batch_size, 321408)positives = box_cls_labels > 0# 设置回归参数为1. [True, False] * 1. = [1., 0.]reg_weights = positives.float() # (4, 211200) 只保留标签>0的值# 同cls处理pos_normalizer = positives.sum(1,keepdim=True).float() # (batch_size, 1) 所有正例的和 eg:[[162.],[166.],[155.],[108.]]reg_weights /= torch.clamp(pos_normalizer, min=1.0) # (batch_size, 321408)if isinstance(self.anchors, list):if self.use_multihead:anchors = torch.cat([anchor.permute(3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 5).contiguous().view(-1, anchor.shape[-1]) for anchor inself.anchors], dim=0)else:anchors = torch.cat(self.anchors, dim=-3) # (1, 248, 216, 3, 2, 7)else:anchors = self.anchors# (1, 248*216, 7) --> (batch_size, 248*216, 7)anchors = anchors.view(1, -1, anchors.shape[-1]).repeat(batch_size, 1, 1)# (batch_size, 248*216, 7)box_preds = box_preds.view(batch_size, -1,box_preds.shape[-1] // self.num_anchors_per_location if not self.use_multihead elsebox_preds.shape[-1])# sin(a - b) = sinacosb-cosasinb# (batch_size, 321408, 7)box_preds_sin, reg_targets_sin = self.add_sin_difference(box_preds, box_reg_targets)loc_loss_src = self.reg_loss_func(box_preds_sin, reg_targets_sin, weights=reg_weights)loc_loss = loc_loss_src.sum() / batch_sizeloc_loss = loc_loss * self.model_cfg.LOSS_CONFIG.LOSS_WEIGHTS['loc_weight'] # loc_weight = 2.0 损失乘以回归权重box_loss = loc_losstb_dict = {# pytorch中的item()方法,返回张量中的元素值,与python中针对dict的item方法不同'rpn_loss_loc': loc_loss.item()}# 如果存在方向预测,则添加方向损失if box_dir_cls_preds is not None:# (batch_size, 321408, 2)dir_targets = self.get_direction_target(anchors, box_reg_targets,dir_offset=self.model_cfg.DIR_OFFSET, # 方向偏移量 0.78539 = π/4num_bins=self.model_cfg.NUM_DIR_BINS # BINS的方向数 = 2)# 方向预测值 (batch_size, 321408, 2)dir_logits = box_dir_cls_preds.view(batch_size, -1, self.model_cfg.NUM_DIR_BINS)# 只要正样本的方向预测值 (batch_size, 321408)weights = positives.type_as(dir_logits)# (4, 211200) 除正例数量,使得每个样本的损失与样本中目标的数量无关weights /= torch.clamp(weights.sum(-1, keepdim=True), min=1.0)# 方向损失计算dir_loss = self.dir_loss_func(dir_logits, dir_targets, weights=weights)dir_loss = dir_loss.sum() / batch_size# 损失权重,dir_weight: 0.2dir_loss = dir_loss * self.model_cfg.LOSS_CONFIG.LOSS_WEIGHTS['dir_weight']# 将方向损失加入box损失box_loss += dir_losstb_dict['rpn_loss_dir'] = dir_loss.item()return box_loss, tb_dict方向分类的 target assignment,此处是指定该角度下应该是由分配到dir_bin中。
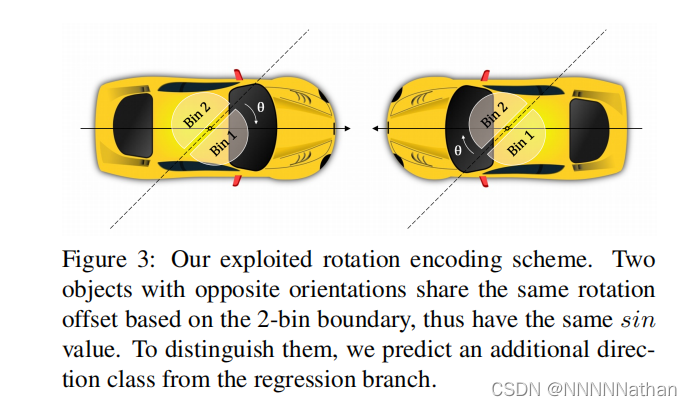
这里使用点云的坐标系减去了45度,可能的原因是:
减去dir_offset(45度)的原因可以参考这个issue: https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet/issues/80https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet/issues/80 说的呢就是因为大部分目标都集中在0度和180度,270度和90度, 这样就会导致网络在这些角度的物体的预测上面不停的摇摆。所以为了解决这个问题, 将方向分类的角度判断减去45度再进行判断,如下图所示。这里减掉45度之后,在预测推理的时候,同样预测的角度解码之后 也要减去45度再进行之后测nms等操作。
下图来自FCOS3D论文
FCOS3D:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.10956.pdf
box cls target assignment代码在:pcdet/models/dense_heads/anchor_head_template.py
def get_direction_target(anchors, reg_targets, one_hot=True, dir_offset=0, num_bins=2):batch_size = reg_targets.shape[0]# (batch_size, 321408, 7)anchors = anchors.view(batch_size, -1, anchors.shape[-1])# (batch_size, 321408)在-pi到pi之间# 由于reg_targets[..., 6]是经过编码的旋转角度,如果要回到原始角度需要重新加回anchor的角度就可以rot_gt = reg_targets[..., 6] + anchors[..., 6]"""offset_rot shape : (batch_size, 321408)rot_gt - dir_offset 由于在openpcdet中x向前,y向左,z向上,减去dir_offset(45度)的原因可以参考这个issue:https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet/issues/818说的呢就是因为大部分目标都集中在0度和180度,270度和90度,这样就会导致网络在一些物体的预测上面不停的摇摆。所以为了解决这个问题,将方向分类的角度判断减去45度再进行判断,这里减掉45度之后,在预测推理的时候,同样预测的角度解码之后也要减去45度再进行之后测nms等操作common_utils.limit_period:将角度限制在0到2*pi之间 原数据的角度在-pi到pi之间"""offset_rot = common_utils.limit_period(rot_gt - dir_offset, 0, 2 * np.pi)# (batch_size, 321408) 取值为0和1,num_bins=2dir_cls_targets = torch.floor(offset_rot / (2 * np.pi / num_bins)).long()# (batch_size, 321408)dir_cls_targets = torch.clamp(dir_cls_targets, min=0, max=num_bins - 1)if one_hot:# (batch_size, 321408, 2)dir_targets = torch.zeros(*list(dir_cls_targets.shape), num_bins, dtype=anchors.dtype,device=dir_cls_targets.device)# one-hot编码,只存在两个方向:正向和反向 (batch_size, 321408, 2)dir_targets.scatter_(-1, dir_cls_targets.unsqueeze(dim=-1).long(), 1.0)dir_cls_targets = dir_targetsreturn dir_cls_targets方向回归的smoothL1计算
代码在pcdet/utils/loss_utils.py
class WeightedSmoothL1Loss(nn.Module):"""Code-wise Weighted Smooth L1 Loss modified based on fvcore.nn.smooth_l1_losshttps://github.com/facebookresearch/fvcore/blob/master/fvcore/nn/smooth_l1_loss.py| 0.5 * x ** 2 / beta if abs(x) < betasmoothl1(x) = || abs(x) - 0.5 * beta otherwise,where x = input - target."""def __init__(self, beta: float = 1.0 / 9.0, code_weights: list = None):"""Args:beta: Scalar float.L1 to L2 change point.For beta values < 1e-5, L1 loss is computed.code_weights: (#codes) float list if not None.Code-wise weights."""super(WeightedSmoothL1Loss, self).__init__()self.beta = beta # 默认值1/9=0.111if code_weights is not None:self.code_weights = np.array(code_weights, dtype=np.float32) # [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]self.code_weights = torch.from_numpy(self.code_weights).cuda() # 将权重放到GPU上@staticmethoddef smooth_l1_loss(diff, beta):# 如果beta非常小,则直接用abs计算,否则按照正常的Smooth L1 Loss计算if beta < 1e-5:loss = torch.abs(diff)else:n = torch.abs(diff) # (batch_size, 321408, 7)# smoothL1公式,如上面所示 --> (batch_size, 321408, 7)loss = torch.where(n < beta, 0.5 * n ** 2 / beta, n - 0.5 * beta)return lossdef forward(self, input: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, weights: torch.Tensor = None):"""Args:input: (B, #anchors, #codes) float tensor.Ecoded predicted locations of objects.target: (B, #anchors, #codes) float tensor.Regression targets.weights: (B, #anchors) float tensor if not None.Returns:loss: (B, #anchors) float tensor.Weighted smooth l1 loss without reduction."""# 如果target为nan,则等于input,否则等于targettarget = torch.where(torch.isnan(target), input, target) # ignore nan targets# (batch_size, 321408, 7)diff = input - target # (batch_size, 321408, 7)# code-wise weightingif self.code_weights is not None:diff = diff * self.code_weights.view(1, 1, -1) #(batch_size, 321408, 7) 乘以box每一项的权重loss = self.smooth_l1_loss(diff, self.beta)# anchor-wise weightingif weights is not None:assert weights.shape[0] == loss.shape[0] and weights.shape[1] == loss.shape[1]# weights参数使用正anchor数目进行平均,使得每个样本的损失与样本中目标的数量无关loss = loss * weights.unsqueeze(-1)return loss方向分类损失计算:
代码在pcdet/utils/loss_utils.py
class WeightedCrossEntropyLoss(nn.Module):"""二分类Transform input to fit the formation of PyTorch official cross entropy losswith anchor-wise weighting."""def __init__(self):super(WeightedCrossEntropyLoss, self).__init__()def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, weights: torch.Tensor):"""Args:input: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor.Predited logits for each class.target: (B, #anchors, #classes) float tensor.One-hot classification targets.weights: (B, #anchors) float tensor.Anchor-wise weights.Returns:loss: (B, #anchors) float tensor.Weighted cross entropy loss without reduction"""input = input.permute(0, 2, 1) # (batch_size, 7, 321408)target = target.argmax(dim=-1) # (batch_size, 321408)# cross_entropy = log_softmax + nll_loss# 先对input进行softmax,然后取log,最后将y与经过log_softmax()函数激活后的数据,两者相乘,再求平均值,最后取反# 计算交叉熵损失并乘权重 (batch_size, 321408)loss = F.cross_entropy(input, target, reduction='none') * weightsreturn loss六、PointPillars使用的数据增强
一:数据增强
在PointPillars中使用了和SECOND网络中相似的数据增强手段:
1、包括建立类别GT和索引,在点云中随机放置15个、0个、8个的车辆、行人、自行车样本到任意点云帧中。
2、每一帧中的所有GT_box都会被随机旋转([ -pi/20 , pi/20);同时在x、y、z轴平移上随机平移,x、y、z取值来自期望为0,方差为0.25的正态分布。
3、全部点云沿x轴翻转、全局点云旋转和随机缩放操作;使用全局x、y、z轴平移来模拟定位噪声,x、y、z取值来自期望为0,方差为0.2的正态分布。
七、PointPillars测试结果和消融实验
一、测试结果
PointPillars论文KITTI数据集测试结果
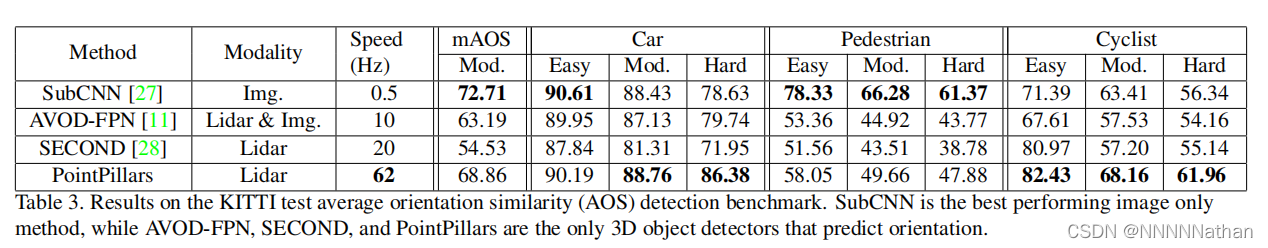
PointPillars在OpenPCDet中KITTI数据集测试结果(结果仅显示在kitti验证集moderate精度)
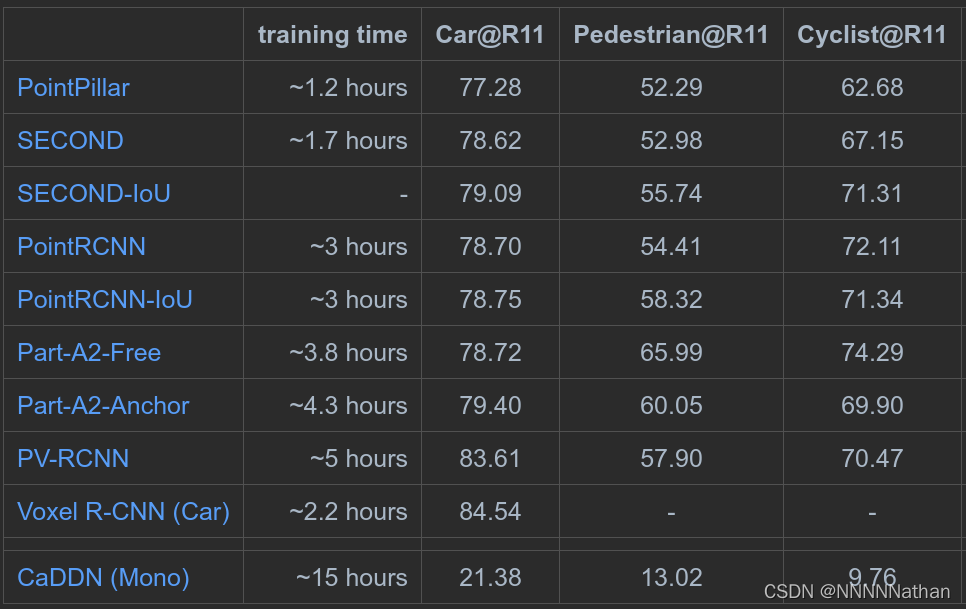
二、消融实验
1、空间分辨率
在实现中,每个pillar的长宽都设定在0.16m;如果增大这个数据的话,可以加快的推理速度,因为更大的pillars会使得整个点云中的非空pillar更少,同时计算得到的伪图象长宽也会更小,加快了pointnet 编码器和网络中CNN提取特征的速度;但是,更小的pillars可以使网络学习到更加细腻的特征,拥有更好的定位精度。测试结果如下: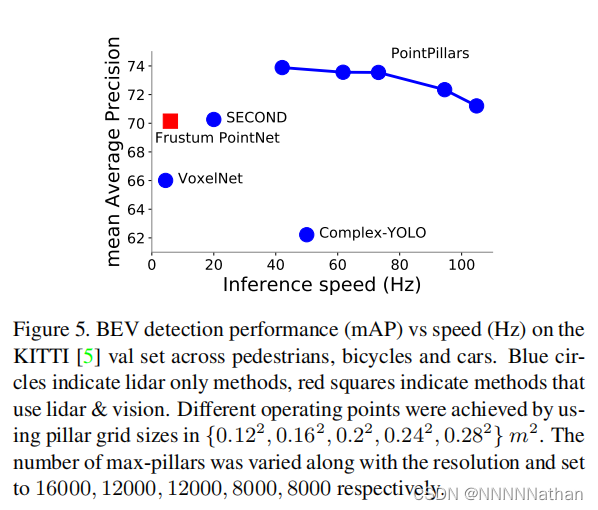
即更大的pillar带来了更快的速度,更小的pillar拥有更高的精度。
2、每个box独立进行数据增强
虽然在VxoelNet和SECOND中都推荐大量的对每个GT_Box进行数据增强;但是在PointPillars中通过实验发现,这样的操作会使得对行人的检测性能大幅度的降低,反而较少的独立数据增强效果更好。可能的原因是在每一帧点云中放入从样本库中真实采样中的GT数据减轻了对大幅度进行独立GT增强的需要。
3、点云表达特征增强
在对每个点云x、y、z、r数据进行增强的时候,PointPillars采用了和VoxelNet一样的操作,都为每个点云空间的特征加入了当前点云到当前pilar底部中心的距离,xp和yp。这一操作使得最终的整体检测性能提高了0.5map,同时也使得论文中结果更具复现性。
4、编码器
一个可以学习的编码器对于固定的编码器来说是实现网络端到端训练的重要架构。此处对PointPillars中使用不同编码器得到的结果进行了实验,结果如下: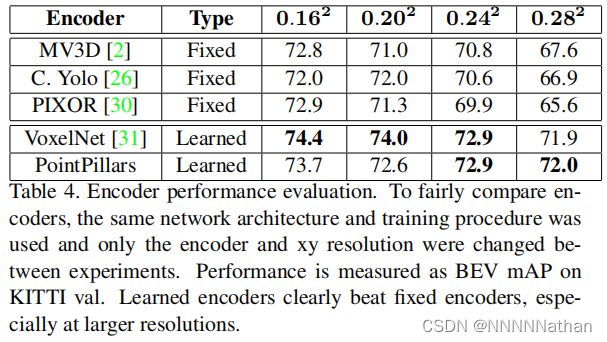
PointPillars在OpenPCDet中的推理代码实现
PointPillars点云检测在OpenPCDet推理代码详解_NNNNNathan的博客-CSDN博客在之前的文章中已经详细解析了PointPillars的论文和训练代码的实现和详解,可以参考之前的博客:PointPillars论文解析和OpenPCDet代码解析_NNNNNathan的博客-CSDN博客。本篇博客将会详细解析PointPillars模型在OpenPCDet中推理代码,并测试推理的效果。读者可以下载OpenPCDet后根据文章进行阅读和理解。由于本人才疏学浅,解析中难免会出现不足之处,欢迎指正、讨论,有好的建议或意见都可以在评论区留言。谢谢大家!PointPi...https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41366026/article/details/123065128?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
参考文章或文献:
1、https://github.com/open-mmlab/OpenPCDet/
2、https://github.com/jjw-DL/OpenPCDet-Noted/
3、使用KITTI数据集实现坐标转换 - 知乎
4、【3D目标检测】PointPillars论文和代码解析 - 知乎
5、【3D目标检测】SECOND算法解析 - 知乎
6、 https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05784
7、Sensors | Free Full-Text | SECOND: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection
8、https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.06396
9、https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.00593
10、【3D计算机视觉】从PointNet到PointNet++理论及pytorch代码_小执着的博客-CSDN博客_pointnet1
11、【3D计算机视觉】PointNet++的pytorch实现代码阅读_小执着的博客-CSDN博客_pointnet++ pytorch
12、The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite
13、KITTI数据集--参数_cuichuanchen3307的博客-CSDN博客_kitti
14、https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.10956.pdf
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!