打通JAVA与内核!一个ReentrantLock锁的实现原理
写JAVA都知道,JAVA里的同学锁有几个类代码,是同步锁,魔法是并发包里的锁(JUC锁)。其中同步锁是JAVA语言文字提供的能力,在这个不展开,本文主要讨论JUC里的ReentrantLock锁。
一 JDK 层
1 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
ReentrantLock的lock(),unlock()等API实际上依赖于内部的Synchronizer(注意,不是synchronized)来实现。Synchronizer又分为FairSync和NonfairSync,顾名思义是指公平和非公平。
当调用ReentrantLock的lock方法时,实际上只是简单地转给Synchronizer的lock()方法:
代码节选自:java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.java/** Synchronizer providing all implementation mechanics */private final Sync sync;/*** Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed* into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to* represent the number of holds on the lock.*/abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
......
}public void lock() {sync.lock();}那么这个sync又是什么?我们看到Sync继承自AbstractQueueSynchronizer(AQS),AQS是并发的基石,AQS不实现任何同步接口(比如lock,unlock,countDown等),但它定义了一个并发接口资源控制逻辑的框架(一式了模板方法设计模式),它定义了获取和释放方法用于独占地(独占)获取和释放资源,以及获取共享和释放共享方法用于共享地获取和释放资源。 release用于实现ReentrantLock,而
acquireShared/releaseShared用于实现CountDownLacth,Semaphore。比如acquire的框架如下:
/*** Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.** @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and* can represent anything you like.*/public final void acquire(int arg) {if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))selfInterrupt();}整体逻辑是,先进行一次tryAcquire,成功者,继续啥事了,调用了自己的代码,如果失败,则执行addWaiter和acquireQueued。其中tryAcquire()需要子类根据自己的同步需求进行acquireQueued()和addWaiter()已经由AQS实现。addWai的作用是把当前加入到AQS内部实现的线程,而acquireQueued的作用是当tryAcquire()失败的时候激发线程。
addWaiter 的代码如下:
/*** Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.** @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared* @return the new node*/private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {//创建节点,设置关联线程和模式(独占或共享)Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failureNode pred = tail;// 如果尾节点不为空,说明同步队列已经初始化过if (pred != null) {//新节点的前驱节点设置为尾节点node.prev = pred;// 设置新节点为尾节点if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {//老的尾节点的后继节点设置为新的尾节点。 所以同步队列是一个双向列表。pred.next = node;return node;}}//如果尾节点为空,说明队列还未初始化,需要初始化head节点并加入新节点enq(node);return node;}enq(node)的代码如下:
/*** Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.* @param node the node to insert* @return node's predecessor*/private Node enq(final Node node) {for (;;) {Node t = tail;if (t == null) { // Must initialize// 如果tail为空,则新建一个head节点,并且tail和head都指向这个head节点//队列头节点称作“哨兵节点”或者“哑节点”,它不与任何线程关联if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head;} else {//第二次循环进入这个分支,node.prev = t;if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {t.next = node;return t;}}}}addWaiter执行结束后,同步驱动的结构如下所示:
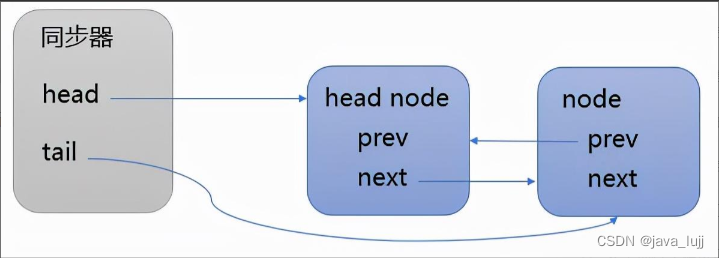
acquireQueued 的代码如下:
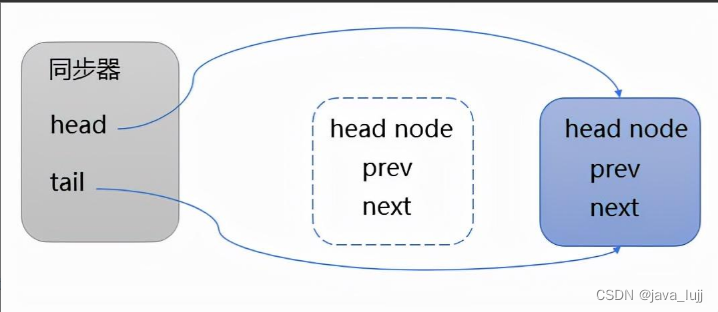
/*** Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.** @param node the node* @param arg the acquire argument* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting*/final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {boolean failed = true;try {boolean interrupted = false;for (;;) {//获取当前node的前驱nodefinal Node p = node.predecessor();//如果前驱node是head node,说明自己是第一个排队的线程,则尝试获锁if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//把获锁成功的当前节点变成head node(哑节点)。setHead(node);p.next = null; // help GCfailed = false;return interrupted;}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())interrupted = true;}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}acquireQueued 的逻辑是:
判断自己是不是同步起源中的第一个过程自己的节点,则试点进行锁定,如果成功则将其变成头节点,如下所示:
如果自己不是第一个事件的节点或者tryAcqui失败,则调用shouldParkAfterFailed,其主要逻辑是使用CAS将节点状态由INITIAL设置成SIGNAL,显示当前线程等待SIGNAL。如果设置失败,会中acquire的循环中继续重试,直到设置成功,然后调用parkAndCheckInterrupt方法。parkAndCheckInterrupt的作用是当前线程模拟挂起,等待当前把parkAndCheckInterrupt的需要借助层的能力,这是这一点的重点,在中实现死层判断。
2 重入锁
下面就让我们一起来看看 ReentrantLock 是如何基于AbstractQueueSynchronizer 实现其输入的。
ReentrantLock内部使用的FairSync和NonfairSync,它们都是AQS的子类,比如FairSync的主要代码如下:
/*** Sync object for fair locks*/static final class FairSync extends Sync {private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;final void lock() {acquire(1);}/*** Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless* recursive call or no waiters or is first.*/protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!