Jdk源码——LinkedList解析
前言
本文主要针对 JDK1.8 的 LinkedList 源码进行解析,主要看源码注释,代码说明了全部实现细节。
ArrayList 相关解析可以参考 Jdk源码——ArrayList解析
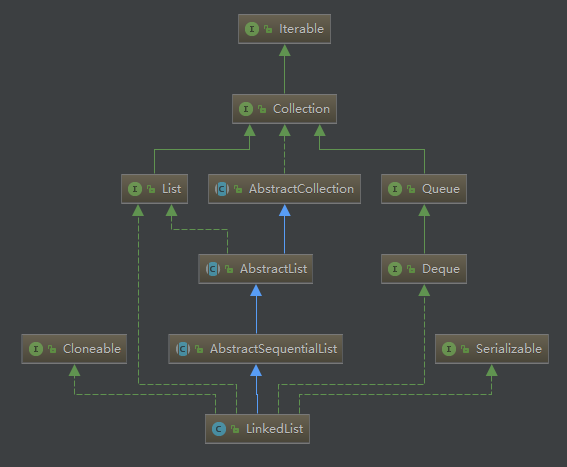
I. 继承结构
LinkedList 的继承结构如下,和 ArrayList (上一篇文章)相比,它们都实现了 Cloneable 和 Serializable 接口,都是 AbstractList 的子类,只不过 LinkedList 继承自 AbstractSequentialList,AbstractSequentialList 继承自 AbstractList。LinkedList 不支持随机访问,所以没有实现 RandomAccess 接口。
LinkedList 还额外实现了 Deque 双向队列接口,所以我们也可以把 LinkedList 当作队列使用。
Queue
Queue 接口与 List 、Set 同一级别,都是继承了 Collection 接口。
/*** 通常队列都是FIFO,优先队列的元素顺序则是根据比较器进行排序的,栈是LIFO* 不管是什么顺序,head元素都是使用remove或者poll方法移除** Queue接口没有定义阻塞队列方法,而是定义在java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue接口中** Queue的实现类通常不允许添加null元素,尽管LinkedList不禁止插入null* 即使允许, null也不应该被插入到Queue, 因为null是poll等方法在队列为空时的返回值,会产生歧义*/
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {/*** 插入元素,成功返回true,容量不足则抛出异常*/boolean add(E e);/*** 添加一个元素并返回true,如果队列已满,则返回false*/boolean offer(E e);/*** 移除并返回队列头部的元素。如果队列为空,则会抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常*/E remove();/*** 移除并返回队列头部的元素。如果队列为空,则返回null*/E poll();/*** 返回队列头部的元素。如果队列为空,则抛出一个NoSuchElementException异常*/E element();/*** 返回队列头部的元素。如果队列为空,则返回null*/E peek();
}
Deque
Deque 是继承自 Queue,Queue 是一种队列,而 Deque 则是双向队列,支持从两个端点方向检索和插入元素,因此 Deque 既可以支持 FIFO 形式也可以支持 LIFO。
/*** deque:"double ended queue" 双端队列* 和List不一样,队列不能通过索引进行访问元素**/
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {// *** 添加 *** /*** 向队列头部插入一个元素,没有空间时抛出IllegalStateException异常*/void addFirst(E e);/*** 向队列尾部插入一个元素,没有空间时抛出IllegalStateException异常*/void addLast(E e);/*** 向队列头部加入一个元素,失败时返回false*/boolean offerFirst(E e);/*** 向队列尾部加入一个元素,失败时返回false*/boolean offerLast(E e);// *** 删除 *** /*** 弹出队列头部元素,队列为空时抛出NoSuchElementException异常*/E removeFirst();/*** 弹出队列尾部元素,队列为空时抛出NoSuchElementException异常*/E removeLast();/*** 弹出队列头部元素,队列为空时返回null*/E pollFirst();/*** 弹出队列尾部元素,队列为空时返回null*/E pollLast();// *** 获取 *** /*** 获取队列头部元素,队列为空时抛出NoSuchElementException异常*/E getFirst();/*** 获取队列尾部元素,队列为空时抛出NoSuchElementException异常*/E getLast();/*** 获取队列头部元素,队列为空时返回null*/E peekFirst();/*** 获取队列尾部元素,队列为空时返回null*/E peekLast();/*** 删除第一次出现的指定元素,不存在时返回false*/boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);/*** 删除最后一次出现的指定元素,不存在时返回false*/boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);// *** 队列方法 ***boolean add(E e);boolean offer(E e);E remove();E poll();E element();E peek();// *** 栈方法 ***// 向队列头部插入一个元素,失败时抛出异常void push(E e);// 弹出队列头部元素,队列为空时抛出异常E pop();// *** Collection 方法 ***boolean remove(Object o);boolean contains(Object o);public int size();Iterator<E> iterator();/*** 返回队列反向迭代器,元素将从尾到头进行返回*/Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
AbstractSequentialList
AbstractSequentiaList 和其他 RandomAccess 主要的区别是 AbstractSequentiaList 的主要方法都是通过迭代器实现的,而不能支持随机访问,通过下标索引方式。因为迭代器移动需要一定代价,所以对于遍历访问性能上会低一些。
/*** 定义一个List可以继承该类,实现listIterator和size方法.* 实现一个可修改的列表,则需要实现list iterator的hasNext, next, hasPrevious,* previous 和index 方法*/
public abstract class AbstractSequentialList<E> extends AbstractList<E> {protected AbstractSequentialList() {}/*** 利用迭代器访问指定位置的元素*/public E get(int index) {try {return listIterator(index).next();} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}/*** 利用迭代器更新指定位置的元素,返回旧值*/public E set(int index, E element) {try {ListIterator<E> e = listIterator(index);E oldVal = e.next();e.set(element);return oldVal;} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}/*** 利用迭代器在指定位置添加元素*/public void add(int index, E element) {try {listIterator(index).add(element);} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}/*** 利用迭代器删除元素并返回*/public E remove(int index) {try {ListIterator<E> e = listIterator(index);E outCast = e.next();e.remove();return outCast;} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}// Bulk Operations/*** 利用迭代器添加集合c*/public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {try {boolean modified = false;ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator(index);Iterator<? extends E> e2 = c.iterator();while (e2.hasNext()) {e1.add(e2.next());modified = true;}return modified;} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}// Iterators/*** 返回迭代器,AbstractList中的方法,返回的是AbstractList.ListItr实例*/public Iterator<E> iterator() {return listIterator();}/*** 抽象方法,返回指定位置迭代器,类型为java.util.ListIterator*/public abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
}
II. LinkedList源码
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 的功能基本相像,此外还多了队列的功能,而且是一个双端队列,既能FIFO,也能LIFO。从实现角度上来说,LinkedList 底层数据结构是链表,所以大多数API的实现都是利用链表的遍历去实现的。
数据结构如下图所示。
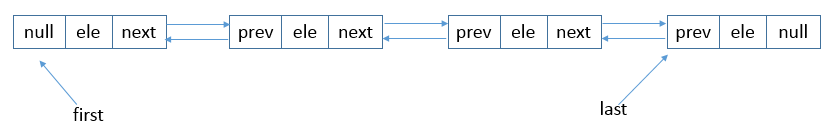
下面直接分析源码,有了 ArrayList 和前面的讲解,LinkedList 的源码应该相对简单。
/*** 实现了List和Queue接口的双端列表,实现了所有的list操作,允许null元素** LinkedList也是线程不安全的,并发修改list结构时需要手动同步* 和ArrayList一样,也可以利用Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...))同步** 该类中iterator()和listIterator()方法返回的迭代器是fail-fast的*/
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {transient int size = 0;/*** 指向头结点*/transient Node<E> first;/*** 指向尾节点*/transient Node<E> last;public LinkedList() {}/*** 创建一个包含c的LinkedList,顺序按照c的顺序*/public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}/*** 头部连接一个元素e*/private void linkFirst(E e) {final Node<E> f = first; // 原来头部final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); // 构造新节点first = newNode; // 更新头部if (f == null)last = newNode; // 初始列表元素为空情况,头尾都指向newNodeelsef.prev = newNode; // 双向链表,维护前驱指针size++;modCount++;}/*** 尾部连接一个元素e*/void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);last = newNode;if (l == null)first = newNode;elsel.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;}/*** 在非空节点succ前插入e元素*/void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// assert succ != null;final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; // 获得succ的前驱final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); // 创建节点维护前驱后继succ.prev = newNode; // 更新succ的前驱if (pred == null)first = newNode;elsepred.next = newNode; // 更新prev的后继size++;modCount++;}/*** 去除非空头节点f的连接*/private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {// assert f == first && f != null;final E element = f.item;final Node<E> next = f.next; // 新的头f.item = null;f.next = null; // help GCfirst = next;if (next == null)last = null;elsenext.prev = null; // 新头的前驱要清除size--;modCount++;return element;}/*** 去除非空尾节点l的连接*/private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {// assert l == last && l != null;final E element = l.item;final Node<E> prev = l.prev;l.item = null;l.prev = null; // help GClast = prev;if (prev == null)first = null;elseprev.next = null;size--;modCount++;return element;}/*** 去除非空节点x*/E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null;final E element = x.item;final Node<E> next = x.next;final Node<E> prev = x.prev;if (prev == null) {first = next;} else {prev.next = next;x.prev = null;}if (next == null) {last = prev;} else {next.prev = prev;x.next = null;}x.item = null;size--;modCount++;return element;}/*** 获取头节点的元素值,列表为空抛出NoSuchElementException*/public E getFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;if (f == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return f.item;}/*** 获取尾节点的元素值,列表为空抛出NoSuchElementException*/public E getLast() {final Node<E> l = last;if (l == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return l.item;}/*** 去除并返回头结点元素,列表为空抛出NoSuchElementException*/public E removeFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;if (f == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return unlinkFirst(f);}/*** 去除并返回尾结点元素,列表为空抛出NoSuchElementException*/public E removeLast() {final Node<E> l = last;if (l == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return unlinkLast(l);}/*** 头插*/public void addFirst(E e) {linkFirst(e);}/*** 尾插*/public void addLast(E e) {linkLast(e);}/*** 返回是否包含元素o*/public boolean contains(Object o) {return indexOf(o) != -1;}/*** 返回列表元素数目*/public int size() {return size;}/*** 尾插,等同addLast(E e),不过有返回值*/public boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;}/*** 删除第一个o元素节点*/public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {// 链表迭代for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null) {unlink(x);return true;}}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item)) {unlink(x);return true;}}}return false;}/*** 在尾部插入c集合*/public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {return addAll(size, c);}/*** 在index位置前插入c*/public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {// 检验index是否合法,是否属于[0,size]checkPositionIndex(index);Object[] a = c.toArray(); // c转为数组,转为数组后遍历效率就更高了int numNew = a.length;if (numNew == 0)return false;Node<E> pred, succ;if (index == size) {succ = null;pred = last;} else {succ = node(index); // index所在的节点pred = succ.prev; // index - 1所在的节点}for (Object o : a) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);if (pred == null)first = newNode;elsepred.next = newNode;pred = newNode;}if (succ == null) {last = pred;} else {pred.next = succ; // 维护插入最后一个节点与原本index节点的链succ.prev = pred;}size += numNew;modCount++;return true;}/*** 清空列表所有元素*/public void clear() {// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit// more than one generation// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iteratorfor (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {Node<E> next = x.next;x.item = null;x.next = null;x.prev = null;x = next;}first = last = null;size = 0;modCount++;}// Positional Access Operations/*** 返回指定位置节点的元素*/public E get(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return node(index).item;}/*** 更新并返回指定位置节点的元素值*/public E set(int index, E element) {checkElementIndex(index);Node<E> x = node(index);E oldVal = x.item;x.item = element;return oldVal;}/*** 在指定位置插入元素*/public void add(int index, E element) {checkPositionIndex(index);if (index == size)linkLast(element);elselinkBefore(element, node(index));}/*** 去除index位置的节点*/public E remove(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return unlink(node(index));}/*** 元素的index是否合法*/private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index < size;}/*** 插入位置的index是否合法*/private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index <= size;}/*** Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.*/private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;}// 检查元素的index是否合法,不合法抛出异常private void checkElementIndex(int index) {if (!isElementIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}// 检查插入位置的index是否合法,不合法抛出异常private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {if (!isPositionIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}/*** 返回index位置的非空节点*/Node<E> node(int index) {// assert isElementIndex(index);if (index < (size >> 1)) {Node<E> x = first;// 从头至尾遍历for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)x = x.next;return x;} else {Node<E> x = last;// 从尾至头遍历for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)x = x.prev;return x;}}// Search Operations/*** 链表遍历的方式,支持null元素的节点*/public int indexOf(Object o) {int index = 0;if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null)return index;index++;}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item))return index;index++;}}return -1;}/*** 链表遍历的方式,支持null元素的节点*/public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {int index = size;if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {index--;if (x.item == null)return index;}} else {for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {index--;if (o.equals(x.item))return index;}}return -1;}// Queue operations. 队列操作实现/*** 查询头结点,列表为空则返回null*/public E peek() {final Node<E> f = first;return (f == null) ? null : f.item;}/*** 查询头结点,列表为空则抛出NoSuchElementException*/public E element() {return getFirst();}/*** 删除并返回头结点,列表为空则返回null*/public E poll() {final Node<E> f = first;return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);}/*** 删除并返回头结点,列表为空则抛出NoSuchElementException*/public E remove() {return removeFirst();}/*** 尾插元素*/public boolean offer(E e) {return add(e);}// Deque operations 双向队列操作/*** 头插*/public boolean offerFirst(E e) {addFirst(e);return true;}/*** 尾插*/public boolean offerLast(E e) {addLast(e);return true;}/*** 查询头*/public E peekFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;return (f == null) ? null : f.item;}/*** 查询尾*/public E peekLast() {final Node<E> l = last;return (l == null) ? null : l.item;}/*** 删除并返回头结点,空列表返回null*/public E pollFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);}/*** 删除并返回尾结点,空列表返回null*/public E pollLast() {final Node<E> l = last;return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);}/*** 头插*/public void push(E e) {addFirst(e);}/*** 去头*/public E pop() {return removeFirst();}/*** 去除第一个o*/public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {return remove(o);}/*** 去除最后一个o*/public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {if (x.item == null) {unlink(x);return true;}}} else {for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {if (o.equals(x.item)) {unlink(x);return true;}}}return false;}/*** 返回一个指定位置的列表迭代器* fail-fast机制*/public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {checkPositionIndex(index);return new ListItr(index);}// 定义的列表迭代器private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {private Node<E> lastReturned;private Node<E> next;private int nextIndex;private int expectedModCount = modCount;ListItr(int index) {// assert isPositionIndex(index);next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);nextIndex = index;}public boolean hasNext() {return nextIndex < size;}public E next() {checkForComodification();if (!hasNext())throw new NoSuchElementException();lastReturned = next;next = next.next;nextIndex++;return lastReturned.item;}public boolean hasPrevious() {return nextIndex > 0;}public E previous() {checkForComodification();if (!hasPrevious())throw new NoSuchElementException();lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;nextIndex--;return lastReturned.item;}public int nextIndex() {return nextIndex;}public int previousIndex() {return nextIndex - 1;}public void remove() {checkForComodification();if (lastReturned == null)throw new IllegalStateException();Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;unlink(lastReturned);if (next == lastReturned)next = lastNext;elsenextIndex--;lastReturned = null;expectedModCount++;}public void set(E e) {if (lastReturned == null)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();lastReturned.item = e;}public void add(E e) {checkForComodification();lastReturned = null;if (next == null)linkLast(e);elselinkBefore(e, next);nextIndex++;expectedModCount++;}public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {action.accept(next.item);lastReturned = next;next = next.next;nextIndex++;}checkForComodification();}final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}// 节点内部类的定义private static class Node<E> {E item; //元素值Node<E> next; //后继节点Node<E> prev; //前驱节点Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}/*** 反向迭代器*/public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {return new DescendingIterator();}/*** 适配器,通过ListItr.previous提供降序迭代器* next方法实际的都是往前调用*/private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());public boolean hasNext() {return itr.hasPrevious();}public E next() {return itr.previous();}public void remove() {itr.remove();}}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private LinkedList<E> superClone() {try {return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone();} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {throw new InternalError(e);}}/*** LinkedList的浅拷贝 (元素内容不拷贝)*/public Object clone() {LinkedList<E> clone = superClone();// 将克隆list置为初始状态clone.first = clone.last = null;clone.size = 0;clone.modCount = 0;// 将元素添加的方式进行克隆listfor (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)clone.add(x.item);return clone;}/*** 链表遍历的方式转成数组*/public Object[] toArray() {Object[] result = new Object[size];int i = 0;for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)result[i++] = x.item;return result;}/*** 以正确的顺序返回一个包含此列表中所有元素的数组* 返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型* 如果入参a数组的大小足够容纳列表的size,则列表的数据直接复制进入a数组即可* 如果a数组容量不够,则需要开辟新数组,复制完成后返回新数组,而a数组还是原来的样子*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {if (a.length < size)a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);int i = 0;Object[] result = a;for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)result[i++] = x.item;if (a.length > size)a[size] = null;return a;}private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;/*** 列表序列化时调用,写入流中*/private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException {// Write out any hidden serialization magics.defaultWriteObject();// 写入真实数据个数s.writeInt(size);// 写入“数组的每一个元素”for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)s.writeObject(x.item);}/*** 反序列化时调用*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// Read in any hidden serialization magics.defaultReadObject();// 从输入流中读取ArrayList的“容量”int size = s.readInt();// 从输入流中将“所有的元素值”读出for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)linkLast((E)s.readObject());}
}
III. LinkedList相关
遍历方式
- 迭代器方式(性能好)
- 索引值遍历方式 (性能最差)
- foreach 遍历(性能最好,本质还是迭代器)
示例:
// 迭代器遍历
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<Integer> iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {iterator.next();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Iterator:" + (end - start) + " ms");// 顺序遍历(随机遍历)
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {linkedList.get(i);
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("for:" + (end - start) + " ms");// foreach循环遍历
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Integer i : linkedList);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("foreach:" + (end - start) + " ms");// 输出
Iterator:17 ms
for:3318 ms
foreach:1 ms
迭代删除问题
和 ArrayList 的删除问题是相似的,因为也都是 fail-fast 机制。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!