JavaSE多线程(实现、状态、同步、通信)
简介
程序: 是指令和数据的有序集合,其本身没有任何运行的含义,是一个静态的概念
进程:是正在运行的程序,也就是执行程序的一次执行过程,它是一个动态的概念,是系统资源的分配
线程:包含若干个进程,单线程指一个进程只有一条执行路径,多线程指一个进程有多条执行路径
线程实现
线程创建
继承Thread类
- 定义一个TestTread类继承Thread类
- TestTread类中重写run()方法
- 创建一个TestTread类的线程对象
- 调用start()方法启动线程
public class TestTread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {System.out.println("run()....");}}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个线程对象TestTread testTread = new TestTread();//启动线程testTread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { System.out.println("main()....");}}
}案例:网图下载
public class TestThread2 extends Thread{private String url;private String name;public TestThread2(String url, String name){this.url = url;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void run() {WebDownloader webDownloader = new WebDownloader();webDownloader.downloader(url,name);System.out.println("下载了文件名为:" + name);}public static void main(String[] args) {TestThread2 t1 = new TestThread2("https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png", "1.png");TestThread2 t2 = new TestThread2("https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png", "2.png");TestThread2 t3 = new TestThread2("https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png", "3.png");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();}
}//下载器class WebDownloader {//下载方法public void downloader(String url, String name) {try {FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("IO异常,downloader方法出现问题");}}}
实现Runnable接口
- 定义一个TestThread3类实现Runnable接口
- TestThread3类中重写run()方法
- 创建TestThread3类的对象
- 创意Thread类的对象,并将TestThread3类的对象作为构造方法的参数
- 调用start()方法启动线程
public class TestThread3 implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {System.out.println("run()....");}}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个线程对象TestThread3 testTread = new TestThread3();//创建线程对象,通过线程对象来开启我们的线程,代理Thread thread = new Thread(testTread);//启动线程thread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {System.out.println("main()....");}}
}
案例:火车票
public class TestThread4 implements Runnable {private int ticketNums= 10;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){if (ticketNums <= 0) {break;}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ ticketNums-- + "张票");}}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个线程对象TestThread4 testTread = new TestThread4();new Thread(testTread, "小明").start();new Thread(testTread, "小红").start();new Thread(testTread, "小张").start();}
}
实现Callable接口(了解)
- 实现Callable接口,需要返回值类型
- 重写call方法,需要抛出异常
- 创建目标对象
- 创建执行服务:ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
- 提交执行:Future result1 = ser.submit(11)
- 获取结果:boolean r1 = result1.get()
- 关闭服务:ser.shutdownNow();
public class Test03_CreateCallable_Demo implements Callable<Boolean> {private String url;private String name;public Test03_CreateCallable_Demo(String url, String name){this.url = url;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic Boolean call() {WebDownloader webDownloader = new WebDownloader();webDownloader.downloader(url, name);System.out.println("下载了文件名为:" + name);return true;}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Test03_CreateCallable_Demo t1 = new Test03_CreateCallable_Demo("https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png", "1.png");Test03_CreateCallable_Demo t2 = new Test03_CreateCallable_Demo("https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png", "2.png");Test03_CreateCallable_Demo t3 = new Test03_CreateCallable_Demo("https://img-home.csdnimg.cn/images/20201124032511.png", "3.png");//创建执行服务ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);//提交执行Future<Boolean> b1 = service.submit(t1);Future<Boolean> b2 = service.submit(t2);Future<Boolean> b3 = service.submit(t3);//获取结果boolean res1 = b1.get();boolean res2 = b2.get();boolean res3 = b3.get();service.shutdown();}//下载器class WebDownloader {//下载方法public void downloader(String url, String name) {try {FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("IO异常,downloader方法出现问题");}}}
}
Thread和Runnable对比
- Thread
- 子类继承Thread类
- 子类对象.start() 启动
- 不建议使用,因为是单继承
- Runnable
- 子类实现Runnable接口
- 创建线程对象,传入子类对象, 然后调用.start() 启动
- 推荐,避免单继承局限性
静态代理
代理是设计模式的一种,其原理就是通过代理对象去访问目标对象,并且外部只能访问到代理对象
也就是说可以在目标对象实现的基础上,通过代理对象扩展目标对象的功能
public class Test04_StaticProxy {public static void main(String[] args) {UserProxy userProxy = new UserProxy(new User());userProxy.sing();}
}interface IUser {void sing();
}class User implements IUser {@Overridepublic void sing() {System.out.println("唱歌");}
}class UserProxy implements IUser {private IUser target;public UserProxy(IUser target){this.target = target;}@Overridepublic void sing() {this.target.sing();}
}
public class Test04_StaticProxy_Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(()-> System.out.println("哈哈哈")).start();new UserProxy(new User()).sing();}
}
Lamda表达式
函数式接口
任何一个接口,如果只包含一个抽象方法,那么就叫函数式接口
interface ILike{void lamba();
}
实现
案例1
public class Test05_Lamba {public static void main(String[] args) {Like like = new Like();like.lamba();}}interface ILike{void lamba();
}class Like implements ILike{@Overridepublic void lamba() {System.out.println("I like lamda");}
}
优化1(静态内部类)
public class Test05_Lamba {//静态内部类,增加关键字staticstatic class Like implements ILike{@Overridepublic void lamba() {System.out.println("I like lamda");}}public static void main(String[] args) {Like like = new Like();like.lamba();}}interface ILike{void lamba();
}
优化2(局部内部类)
public class Test05_Lamba {public static void main(String[] args) {//局部内部类class Like implements ILike{@Overridepublic void lamba() {System.out.println("I like lamda");}}Like like = new Like();like.lamba();}}interface ILike{void lamba();
}
优化3(匿名内部类)
public class Test05_Lamba {public static void main(String[] args) {//匿名内部类,没有类的名称,必须借助接口或者父类ILike like = new ILike() {@Overridepublic void lamba() {System.out.println("I like lamda");}};like.lamba();}
}interface ILike{void lamba();
}
优化4
public class Test05_Lamba {public static void main(String[] args) {ILike like = () -> System.out.println("I like lamda");like.lamba();}
}interface ILike{void lamba();
}
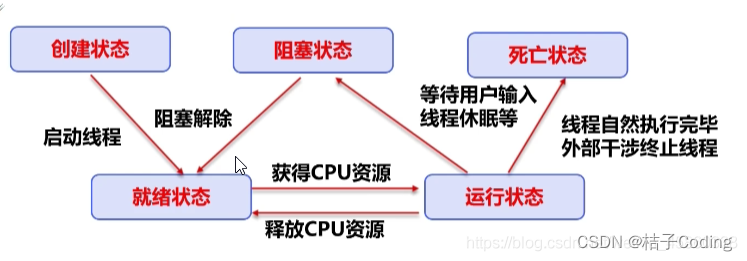
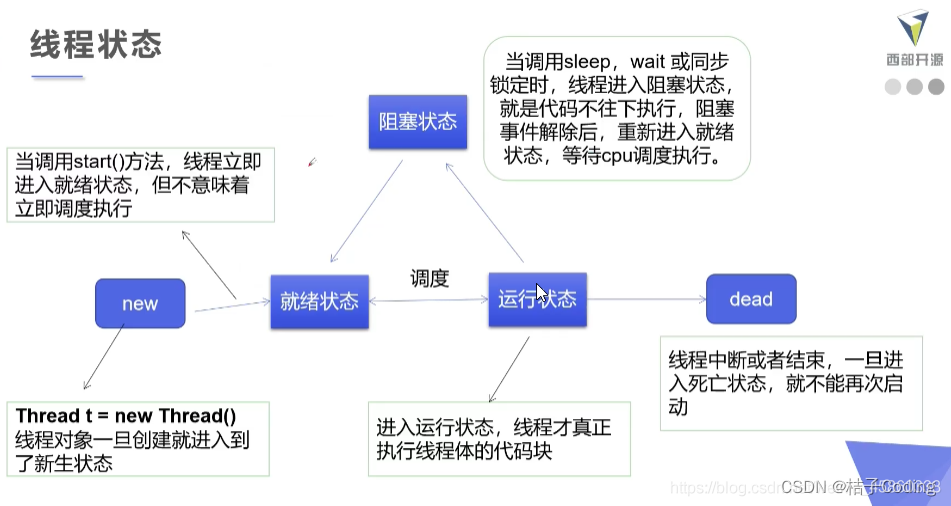
线程状态
五大状态
线程方法
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RaPcMHUe-1677308936390)(多线程.assets/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl80NTg2MDMzOA==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70#pic_center-1677217798461-6.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8a047f666c12494898e57f04746527be.png)
线程停止
- 不推荐JDK已经废弃的方法,例如thread.stop()
- 建议使用一个标志位进行终止变量,放flag==flase时,线程停止
public class Test04_Stop implements Runnable{private boolean flag = true;@Overridepublic void run() {int i = 0;while (flag) {System.out.println("run()---->" + i++);}}public void stop(){this.flag = false;}public static void main(String[] args) {Test04_Stop test04_stop = new Test04_Stop();new Thread(test04_stop).start();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println("main..." + i);if (i == 90) {test04_stop.stop();System.out.println("该线程停止了");}}}
}
线程休眠
- sleep 指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数
- sleep存在异常InterruptedException
- sleep时间到达后线程进入就绪状态
- 每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
public class Test05_Sleep implements Runnable{private int ticketNums= 10;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){if (ticketNums <= 0) {break;}try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ ticketNums-- + "张票");}}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个线程对象Test02_CreateRunnable_Demo testTread = new Test02_CreateRunnable_Demo();new Thread(testTread, "小明").start();new Thread(testTread, "小红").start();new Thread(testTread, "小张").start();}
}
public class Test05_Sleep_Demo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {int i= 10;while (true){Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(i--);if (i <= 0) {break;}}}
}
线程礼让
- 让当前正在执行的线程停止,但不阻塞
- 将线程油运行状态修改为就绪状态
- CPU重新调度,礼让随机,不一定成功
public class Test06_Yield {public static void main(String[] args) {testYield testYield = new testYield();new Thread(testYield, "a").start();new Thread(testYield, "b").start();new Thread(testYield, "c").start();new Thread(testYield, "d").start();}}class testYield implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---> START");Thread.yield();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---> END");}
}
线程插队
- join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞
- 等同于插队
public class Test07_Join implements Runnable{public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Test07_Join join = new Test07_Join();Thread thread = new Thread(join);thread.start();for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {if (i == 18) {System.out.println("来了");thread.join();}System.out.println("main" + i);}}@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {System.out.println("run()---->" + i);}}
}
线程状态观测
- NEW 尚未启动的线程
- RUNNABLE 正在执行的线程
- BLOCKED 被阻塞等待监视器执行的线程
- WAITING 正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作的线程
- TIMED_WAITING 正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作达到指定时间的线程
- TERMINATED 已退出的线程
public class Test08_State {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("run()" + i);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("//");});
// test8 test8 = new test8();
// Thread thread = new Thread(test8);Thread.State state = thread.getState();System.out.println("1" + state);//启动thread.start();state = thread.getState();System.out.println("2" + state);while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {Thread.sleep(1000);state = thread.getState();System.out.println("3" + state);}}
}//class test8 implements Runnable{
// @Override
// public void run() {
// for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// System.out.println("run()" + i);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// System.out.println("//");
// }
//}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jjFjOoVg-1677308936390)(多线程.assets/image-20230224160734924.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4111ac65cab4406f9798db8d19fee29e.png)
线程优先级
- 一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进去就绪状态的所有线程,然后根据优先级决定调用那个线程来执行
- 改变和获取优先级 .getPriority() .setPriority()
- 线程的优先级
- MIN_PRIORITY = 1
- NORM_PRIORITY = 5
- NORM_PRIORITY = 10
- 优先级的设定建议在调用 .start() 之前
public class Test09_Priority {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" +Thread.currentThread().getName());Test09 test09 = new Test09();Thread thread1 = new Thread(test09, "1");Thread thread2 = new Thread(test09, "2");Thread thread3 = new Thread(test09, "3");Thread thread4 = new Thread(test09, "4");Thread thread5 = new Thread(test09, "5");thread1.start();thread2.setPriority(1);thread2.start();thread3.setPriority(8);thread3.start();thread4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);thread4.start();thread5.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);thread5.start();}}class Test09 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" +Thread.currentThread().getName());}
}
守护线程
- .setDaemon(true)将此线程标记为守护进程线程
- 必须在启动线程之前调用此方法。
public class Test10_guard {public static void main(String[] args) {You you = new You();God god = new God();Thread thread = new Thread(god);//将此线程标记为守护进程线程,必须在启动线程之前调用此方法。thread.setDaemon(true);thread.start();new Thread(you).start();}}class You implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println("You()");}}
}class God implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("God()");}
}
线程同步
同步方法
-
synchronized 控制对“对象”的访问,每个对象对应一把锁,每个synchronized方法都必须获得调用该方法的锁才能执行,否则线程会阻塞
-
方法一但执行,就独占该锁,直到该方法返回才释放锁,后面被阻塞的线程才能获得这个锁,继续执行
/*** 安全的购买火车票方法*/
public class Test12_SafeBuyTicket{public static void main(String[] args) {BuyTicket2 ticket2 = new BuyTicket2();new Thread(ticket2, "小明").start();new Thread(ticket2, "小红").start();new Thread(ticket2, "小张").start();}}class BuyTicket2 implements Runnable{private int ticketNums= 10;Boolean flag = true;public void run() {//买票while (flag) {try {buy();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//synchronized 同步方法,锁的是thisprivate synchronized void buy() {if (ticketNums <= 0) {flag = false;return;}//线程延迟try {Thread.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ ticketNums-- + "张票");}
}同步块
- 同步块 synchronized (Object) {}
public class Test12_SafeList {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {new Thread(() -> {synchronized (list) {list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());}}).start();}try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(list.size());}}
死锁
多个线程在执行任务时,由于竞争资源而造成的阻塞现象,也就是说两个线程在各自拥有锁的情况下,又尝试获取别人的锁,从而导致程序进入阻塞状态
public class Test13_DeadLock {public static void main(String[] args) {Makeup makeup = new Makeup(0, "灰姑娘");Makeup makeup1 = new Makeup(1, "白雪公主");makeup.start();makeup1.start();}
}//口红
class Lipstick{}//镜子
class Mirror{}class Makeup extends Thread{//需要的资源只有一份,用static保证只有一份static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();int choice;//选择String girlName;//使用化妆品的人public Makeup(int choice, String girlName) {this.choice = choice;this.girlName = girlName;}@Overridepublic void run() {//化妆try {makeup();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {if (choice == 0) {synchronized (lipstick) {//获得口红的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");Thread.sleep(1000);synchronized (mirror) {//一秒钟后想获得镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");}}} else {synchronized (mirror) {//获得镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");Thread.sleep(2000);synchronized (lipstick) {//二秒钟后想获得口红的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");}}}}
}
解决方法,修改部分代码
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {if (choice == 0) {synchronized (lipstick) {//获得口红的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");Thread.sleep(1000);}synchronized (mirror) {//一秒钟后想获得镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");}} else {synchronized (mirror) {//获得镜子System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得镜子的锁");Thread.sleep(2000);}synchronized (lipstick) {//二秒钟后想获得口红的锁System.out.println(this.girlName + "获得口红的锁");}}}
产生死锁条件
- 互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用
- 请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资而阻塞时,对于获取的资源不变
- 不剥夺条件:进程已获取的资源,在未使用完之前,不能强行剥夺
- 循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系
Lock(锁)
- JDK5以后提供了一种通过显示定义同步锁对象来进行同步
public class Test14_Lock {public static void main(String[] args) {testLock testLock = new testLock();new Thread(testLock).start();new Thread(testLock).start();new Thread(testLock).start();}}class testLock implements Runnable {int tickerNums = 10;private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();@Overridepublic void run() {lock.lock();try {while (true) {if (tickerNums <= 0) {break;}try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(tickerNums--);}}finally {lock.unlock();}}
}
synchroized与Lock对比
- synchroized
- 隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
- 有代码块锁和方法锁
- Lock
- 显示锁,手动开启和关闭
- 只有代码块锁
- 使用很少的时间去处理,性能更好,并且扩展性高
线程通信问题
线程通信一定是多个线程在操作同一个资源才需要通信
- wait() 表示线程一直等待,直到其他线程通知,和sleep不一样,该方法会释放锁
- wait(long timeout) 指定等待的毫秒数
- notify() 唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程
- notifyAll() 唤醒同一个对象上所有调用wai()方法的线程,优先级别高的线程优先调用
生产者和消费者
生产者和消费者是一个非常经典的多线程协作的模式,它包含了两个线程
- 一个是生产者线程负责生产数据
- 一个是消费者线程负责消费数据
为了解耦生产者和消费者之间的关系,通常会采用共享的数据区域,就像是一个仓库
- 生产者生产数据之后直接放置在共享区域内,并不关心消费者的行为
- 消费者只需要从共享区域内消费数据,并不关系生产者的行为
/*** 线程通讯*/
public class Test15 {public static void main(String[] args) {Box box = new Box();//生产者Producer producer = new Producer(box);//消费者Customer customer = new Customer(box);Thread t1 = new Thread(producer);Thread t2 = new Thread(customer);t1.start();t2.start();}
}/*** 奶箱类*/
class Box{private int nums; //第几瓶奶private boolean state = false; //奶箱状态//存储牛奶public synchronized void put(int nums){//如果有牛奶等待消费if (state) {try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//如果没有牛奶,就生产牛奶this.nums = nums;System.out.println("送奶工将第" +this.nums + "瓶奶放入奶箱");//修改奶箱状态state = true;//唤醒其他线程notifyAll();}//获取牛奶public synchronized void get(){//如果没有牛奶,就等待生产if (!state) {try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("用户拿到第" +this.nums + "瓶奶");//修改奶箱状态state = false;//唤醒其他线程notifyAll();}}/*** 生产者*/
class Producer implements Runnable{private Box box;public Producer(Box box) {this.box = box;}//调用存储牛奶的操作@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {box.put(i);}}
}/*** 消费者*/
class Customer implements Runnable{private Box box;public Customer(Box box) {this.box = box;}//模拟取牛奶的过程@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){box.get();}}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!