立体匹配网络中的domain adaptation问题:AdaStereo
文章目录
- 概述
- 损失函数
概述
-
希望讨论的问题是什么?
以PSMNet为例,其在Middlebury数据集上进行预训练得到的模型,在KITTI上的推理效果或许就不好。这篇文章就想聊聊怎么去处理不同场景下的模型的适应问题。又或者说,模型的泛化问题。 -
参考论文及相关信息为:

是商汤2020年的工作。 -
论文的效果怎么样?
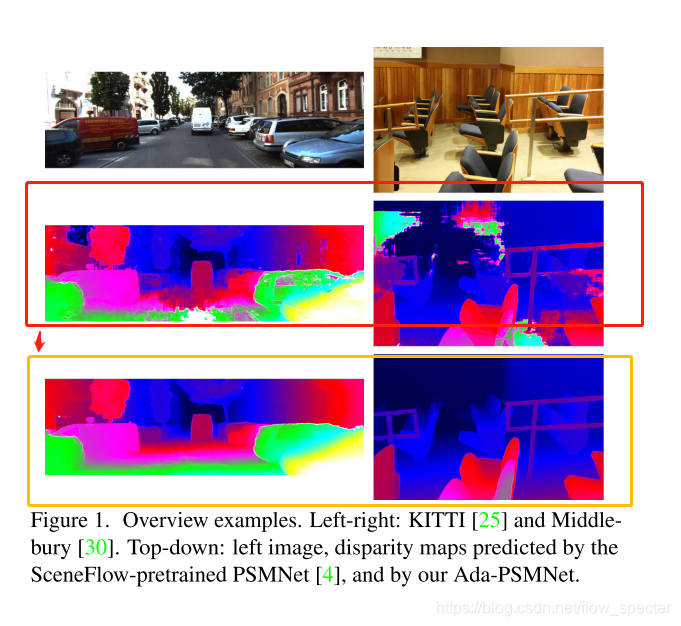
-
能否简要概述是怎么解决的问题?
假定现在有两个数据集,一个是合成数据集,数据量非常大,另一个是真实场景数据集,数据量相对小很多,文章认为这两个数据集之间的gap主要在于以下几个层面:1. input image
- “At the input image level, color and brightness are the obvious gaps.”
- 通过提出一个 non-adversarial progressive color transfer算法将输入的color space与target影像的场景进行对齐,这个过程通过网络训练完成。
2. internal cost volume
- ‘…significant differences in distributions’
- 使用了cost normalization 层,用于配准cost distribution。主要使用了两个归一化操作:channel normalization以及pixel normalization
3. output disparity
- ‘Moreover, geometries of the output disparity maps are inconsistent as well’
- self- supervised occlusion-aware reconstruction,
提出了AdaStereo,旨在构建一个标准的场景自适应网络,网络结构为:

已知:
- 作为source的大量合成数据集 ( I s t , I s r ) (I_s^t,I_s^r) (Ist,Isr)
- 合成数据集的真实视差 d s l ^ \hat{d_s^l} dsl^
- 作为target的少量真实数据集 ( I t l , I t r ) (I_t^l,I_t^r) (Itl,Itr)
希望的推理输出:
- 真实场景的视差 d t l d_t^l dtl
损失函数
整体的损失函数为:
L = L s m a i n + λ s o c c L s o c c + λ t a r L t a r + λ t o c c L t o c c + λ t s m L t s m L=L_{s}^{m a i n}+\lambda_{s}^{o c c} L_{s}^{o c c}+\lambda_{t}^{a r} L_{t}^{a r}+\lambda_{t}^{o c c} L_{t}^{o c c}+\lambda_{t}^{s m} L_{t}^{s m} L=Lsmain+λsoccLsocc+λtarLtar+λtoccLtocc+λtsmLtsm
其中的 λ \lambda λ为对应的loss weights。
损失函数中的五项具体为:
-
source domain层面的视差回归loss:
L s m a i n = S m o o t h L 1 ( d s l − d s l ^ ) L_s^{main} = Smooth_{L1}(d_s^l-\hat{d_s^l}) Lsmain=SmoothL1(dsl−dsl^) -
在souce domain层面的occlusion mask训练损失,使用binary cross entropy loss:
L s o c c = B C E ( O s l , O s l ^ ) L_s^{occ} = BCE(O_s^l,\hat{O_s^l}) Lsocc=BCE(Osl,Osl^) -
在target domain层面,the occlusion-aware appearance reconstruction loss:
L t a r = α 1 − S S I M ( I t l ⊙ ( 1 − O t l ) , I t l ‾ ⊙ ( 1 − O t l ) ) 2 + ( 1 − α ) ∥ I t l ⊙ ( 1 − O t l ) − I t l ‾ ⊙ ( 1 − O t l ) ∥ 1 \begin{aligned} L_{t}^{a r}=& \alpha \frac{1-S S I M\left(I_{t}^{l} \odot\left(1-O_{t}^{l}\right), \overline{I_{t}^{l}} \odot\left(1-O_{t}^{l}\right)\right)}{2} \\ &+(1-\alpha)\left\|I_{t}^{l} \odot\left(1-O_{t}^{l}\right)-\overline{I_{t}^{l}} \odot\left(1-O_{t}^{l}\right)\right\|_{1} \end{aligned} Ltar=α21−SSIM(Itl⊙(1−Otl),Itl⊙(1−Otl))+(1−α)∥∥∥Itl⊙(1−Otl)−Itl⊙(1−Otl)∥∥∥1其中, ⊙ \odot ⊙表示逐元素的乘法,SSIM表示simplified single scale SSIM项(3*3的block filter),以及 α \alpha α设置为0.85。
-
在target domain中,在occulusion mask上使用 L 1 L1 L1正则项:
L t o c c = ∣ ∣ O t l ∣ ∣ 1 L_t^{occ}=||O_t^l||_1 Ltocc=∣∣Otl∣∣1 -
在target-domain上,使用edge-aware项作为target-domain中的视差平滑项,其中 ∂ \partial ∂表示gradient,
L t s m = ∣ ∂ x d t l ∣ e − ∣ ∂ x I t l ∣ + ∣ ∂ y d t l ∣ e − ∣ ∂ y I t l ∣ L_{t}^{s m}=\left|\partial_{x} d_{t}^{l}\right| e^{-\left|\partial_{x} I_{t}^{l}\right|}+\left|\partial_{y} d_{t}^{l}\right| e^{-\left|\partial_{y} I_{t}^{l}\right|} Ltsm=∣∣∂xdtl∣∣e−∣∂xItl∣+∣∣∂ydtl∣∣e−∣∂yItl∣
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!