Spring的学习(三,Di)
当我们学习完Spring的ioc控制反转(创建对象后),下面我们就需要来学习一下Di依赖注入的学习。
IOC的学习![]() https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/125048675
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/125048675
目录
什么叫DI(依赖注入)
J2se给对象赋值
通过构造函数进行赋值
通过Set方法
Spring方式给对象赋值(di)
构造注入
编辑
Set注入
DI(依赖注入)细节
构造注入
处理集合类型或容器类型
Set注入
什么叫DI(依赖注入)
初始化成员变量,给成员变量进行赋值。
J2se给对象赋值
通过构造函数进行赋值
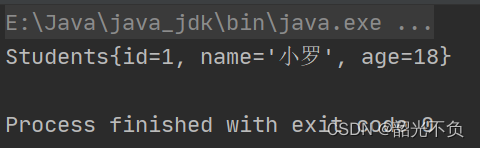
//设置构造函数public Students(int id, String name, int age) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.age = age;}//通过构造函数赋值@Testpublic void testStudent(){Students students = new Students(1,"小罗",18);System.out.println(students);}通过Set方法
//设置Set方法给对象赋值public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}import com.lsf.ssm.ioc.Students;
import org.junit.Test;import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class StudentTest {@Testpublic void testStudent01(){Students students = new Students();students.setName("小罗");students.setId(1);students.setAge(18);System.out.println(students);}}
Spring方式给对象赋值(di)
构造注入
1,搭建ioc Spring的环境
4.0.0 org.example ssm02 1.0-SNAPSHOT org.springframework spring-context 4.3.16.RELEASE junit junit 4.12 test 2,添加配置(配置文件(名称可以不同,但是不建议修改):applicationContext.xml)
3,添加代码
import com.lsf.ssm.ioc.Students;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class DiTest {@Testpublic void testStudent(){//加载spring配置文件ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");//获取对象Students students = ac.getBean("students", Students.class);System.out.println(students);}
}
Set注入
1,环境搭建(与构造注入相同)
2,添加配置(配置文件(名称可以不同,但是不建议修改):applicationContext.xml)
调用的是对象当中的Set方法,去掉SET第一个字母小写(比如 :SetId =>id )
3,添加代码
import com.lsf.ssm.ioc.Students;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class DiTest {@Testpublic void testStudent(){//加载spring配置文件ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");//获取对象Students students = ac.getBean("students", Students.class);System.out.println(students);}
}
DI(依赖注入)细节
构造注入
通过在bean—>constructor-arg子标签来实现,该子标签里有两个属性:
index:表示构造函数参数的索引
type:表示构造函数参数的类型
如果构造函数里的形参类型不一样,可以通过类型和索引都可以赋值;但是如果构造函数里的形参类型有一样,只能通过索引赋值。
当属性为基本类型时,使用value,当是对象类型时,使用rel赋值
//基本数据类型+String类型赋值
注入null值与空
//注入为null
处理属性
//设置属性
private Properties properties;public Properties getProperties() {return properties;}public void setProperties(Properties properties) {this.properties = properties;}//配置xml
value1 value1 value1 处理集合类型或容器类型
//类增加属性,设置set与get方法private int[] arrays;
public int[] getArrays() {return arrays;}public void setArrays(int[] arrays) {this.arrays = arrays;}
//xml配置
1 2 3

当集合中是对象形式
//配置对象set与get方法private List dates;public List getDates() {return dates;}public void setDates(List dates) {this.dates = dates;}//配置xml dates = students.getDates();for (Date enty:dates) {System.out.println(enty);}}
}
Set注入
调用的是对象当中的Set方法,去掉SET第一个字母小写(比如 :SetId =>id )
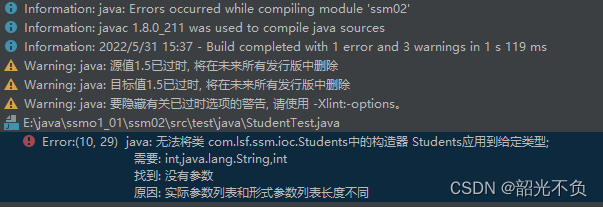
set注入先创建对象,再进行赋值(没有无参构造会报错)
当在类当中创建了,有构造方法,无参构造就不会自动生成,需要自己手动配置。不配置就会报错(就需要自己手动添加无参构造)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!