FutureTask原理和CompletableFuture使用
FutureTask原理解析图
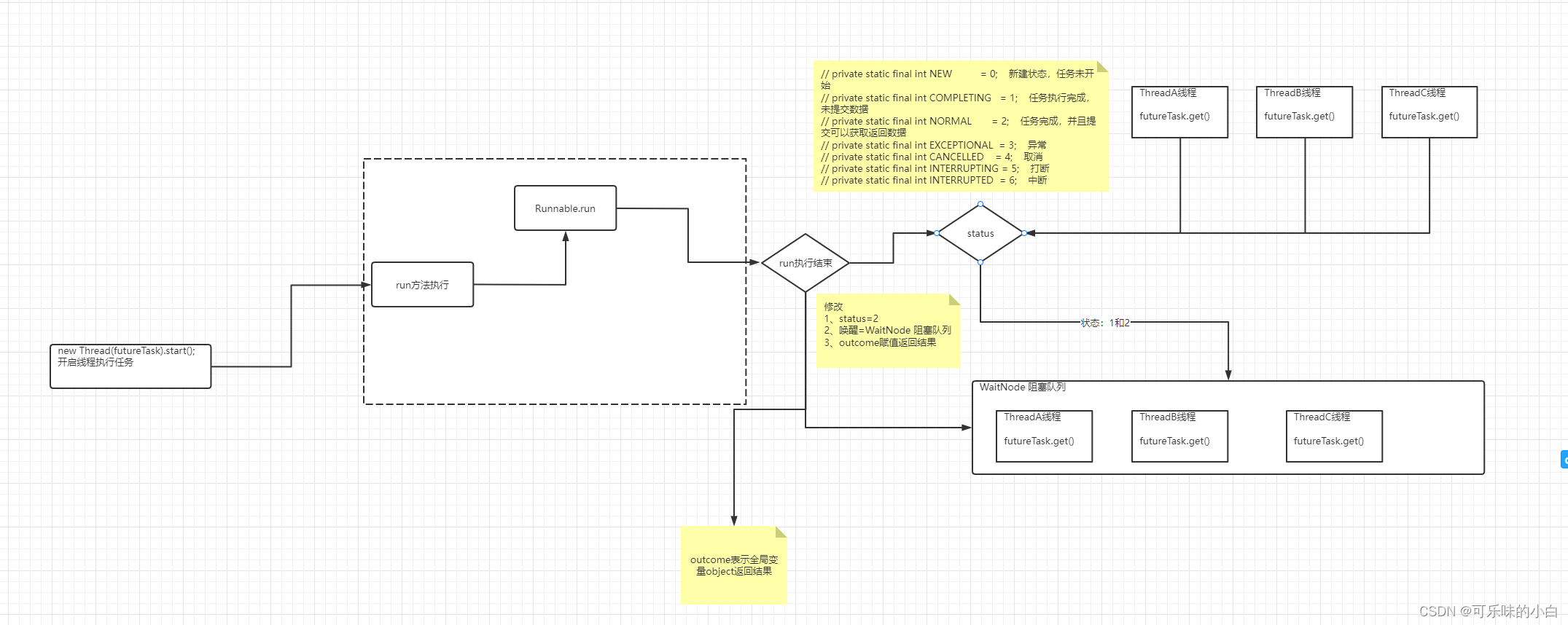
get()方法
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
// private static final int NEW = 0; 新建状态,任务未开始
// private static final int COMPLETING = 1; 任务执行完成,未提交数据
// private static final int NORMAL = 2; 任务完成,并且提交可以获取返回数据
// private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; 异常
// private static final int CANCELLED = 4; 取消
// private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; 打断
// private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; 中断int s = state; // 此任务的运行状态if (s <= COMPLETING) // 如果当前状态小于1,表示任务还未提交完成s = awaitDone(false, 0L); // 丢尽阻塞队列等待return report(s); // 任务完成返回对象
}
// 阻塞
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)throws InterruptedException {final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L; // 等待超时时间WaitNode q = null;boolean queued = false;for (;;) {if (Thread.interrupted()) {removeWaiter(q); //中断throw new InterruptedException();}int s = state;if (s > COMPLETING) { // 当前状态大于1,表示要么完成返回要么异常出问题直接返回nullif (q != null)q.thread = null;return s;}else if (s == COMPLETING) // 当前任务完成在提交返回值中Thread.yield();else if (q == null) // 阻塞队列为空q = new WaitNode();else if (!queued) // cas添加进阻塞队列当中,因为存在多个对象获取返回值queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,q.next = waiters, q);else if (timed) {nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();if (nanos <= 0L) { // 任务未完成超时,直接中断removeWaiter(q);return state;}LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos); // 阻塞拦截}elseLockSupport.park(this); // 设置拦截}
}
// 阻塞
public static void park(Object blocker) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();setBlocker(t, blocker); // 屏障阻塞UNSAFE.park(false, 0L); // 阻塞setBlocker(t, null);
}
// 返回结果
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {Object x = outcome; // outcome表示全局变量object返回对象if (s == NORMAL) //完成返回return (V)x;if (s >= CANCELLED) // 异常中断throw new CancellationException();throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
run()方法
public void run() {if (state != NEW ||!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,null, Thread.currentThread())) // 当前状态不为新建状态表示执行过return;try {Callable<V> c = callable;if (c != null && state == NEW) { // 获取任务V result;boolean ran;try {result = c.call(); //执行任务返回对象ran = true;} catch (Throwable ex) {result = null;ran = false;setException(ex);}if (ran) set(result); //修改执行任务完成}} finally {// runner must be non-null until state is settled to// prevent concurrent calls to run()runner = null;// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent// leaked interruptsint s = state;if (s >= INTERRUPTING)handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);}
}
// 修改任务执行结果状态
protected void set(V v) {if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) { // cas操作修改任务执行完毕outcome = v; // 赋值UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // cas操作修改任务执行完毕已赋值finishCompletion();}
}
// 移除所有等待的线程并唤醒
private void finishCompletion() {// assert state > COMPLETING;for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) { // 开始移除等待队列对象for (;;) {Thread t = q.thread;if (t != null) {q.thread = null;LockSupport.unpark(t); // 唤醒}WaitNode next = q.next;if (next == null)break;q.next = null; // unlink to help gcq = next;}break;}}done();callable = null; // 任务执行完毕设置为空
}
CompletableFuture常见使用方法
supplyAsync带返回值
runAsync不带返回值
- 纯消费类型的方法:没有返回值
// 单个任务执行完毕后在执行下面那个请求
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action); //当前线程同步执行
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action); // //使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool线程池执行action
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor); //使用自定义线程池执行actionpublic static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "赵云:冲冲冲";}).thenAccept(param -> {System.out.println(param);});
}// 两个任务都执行完毕在执行函数任务
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth( CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync( CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync( CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "赵云:冲冲冲";});CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "黄总:拿我意大利炮来";});f1.thenAcceptBoth(f2, (t1, t2) -> {System.out.println(t1 + t2);});
}// 其中一个任务执行完毕在执行函数任务
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor)public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "赵云:执行完毕";});CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "黄总:执行完毕";});f1.acceptEither(f2, System.out::println);
}- 有返回值类型的方法
// 单个任务执行完毕后在执行下面那个请求
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor); public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "赵云:冲冲冲";}).thenApply(s -> {return s + " 队友:GOGOGO";});System.out.println(f1.get());
}// 两个任务都执行完毕在执行函数任务
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync( CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync( CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return " 赵云:冲冲冲";});CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return " 黄总:拿我意大利炮来";});CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = f1.thenCombine(f2, (t1, t2) -> {return t2 + t1;});System.out.println(stringCompletableFuture.get());
}// 其中一个任务执行完毕在执行函数任务
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither( CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync( CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync( CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn, Executor executor);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return " 赵云:冲冲冲";});CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return " 黄总:拿我意大利炮来";});CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = f1.applyToEither(f2,t1 -> {return t1;});System.out.println(stringCompletableFuture.get());
}
- 不消费也不返回的方法
// 单个任务执行完毕后在执行下面那个请求
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action, Executor executor)public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return " 赵云:冲冲冲";});f1.thenRun(() -> {System.out.println("黄总:拿我意大利炮来");});
}// 两个任务都执行完毕在执行函数任务
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = supplyAsync(() -> {return " 赵云:冲冲冲";});CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = f1.runAfterBoth(supplyAsync(() -> {return "黄总:拿我意大利炮来";}), () -> {System.out.println("花木兰:待我归来");});System.out.println(voidCompletableFuture.get()); // 因为没用返回值 为 null
}// 其中一个任务执行完毕在执行函数任务
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> f1 = supplyAsync(() -> {return " 赵云:冲冲冲";});CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = f1.runAfterEither(supplyAsync(() -> {return "黄总:拿我意大利炮来";}), () -> {System.out.println("花木兰:待我归来");});System.out.println(voidCompletableFuture.get()); // 因为没用返回值 为 null
}
- 多任务组合
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync( Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync( Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor);public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<List<Dog>> f1 = supplyAsync(() -> {List<Dog> dogs = new ArrayList<>();dogs.add(new Dog().setName("大黄"));dogs.add(new Dog().setName("小黑"));dogs.add(new Dog().setName("麻花"));return dogs;});CompletableFuture gods = f1.thenApply(dogs -> {dogs.stream().map(dog1 ->supplyAsync(() -> {return dog1.setAge(new Random().nextInt(10));}).thenCompose(dog2 ->supplyAsync(() -> {return dog2.setColor("黄色");}))).toArray(size -> new CompletableFuture[size]);return dogs;});System.out.println(gods.get());
}public class Dog {private String name;private int age;private String color;public int getAge() {return age;}public Dog setAge(int age) {this.age = age;return this;}public String getColor() {return color;}public Dog setColor(String color) {this.color = color;return this;}public String getName() {return name;}public Dog setName(String name) {this.name = name;return this;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Dog{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", color='" + color + '\'' +'}';}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!