为什么Integer i1=100;Integer i2=100;i1=i2输出为true,将值改为200时,输出为false
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
目录
一、问题描述
二、解释
总结
一、问题描述
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i1 = 100;Integer i2 = 100;Integer i3 = 200;Integer i4 = 200;System.out.println(i1 == i2);//trueSystem.out.println(i3 == i4);//false}
}输出结果
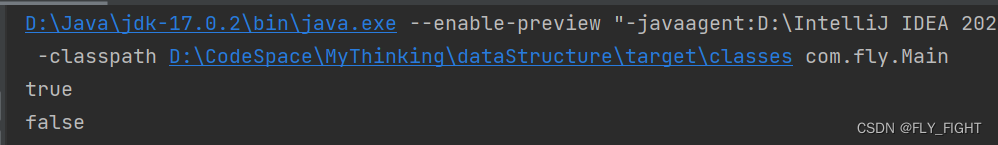
为什么会这样呢?按之前的想法,==用于引用类型比较中,比较的是它们的引用地址,应该输出两个false
二、解释
先了解Java自动装箱和拆箱的概念
1)装箱就是自动将基本数据类型转换为包装类型,比如int->Integer,调用方法为Integer的valueOf(int)方法
2)拆箱就是将包装类型装换为基本数据类型,比如Integer->int,调用方法为Integer的intValue方法
Integer i1=100;实际为Integer i1=Integer.valueOf(100);
vulueOf(int)方法源码如下:
@IntrinsicCandidatepublic static Integer valueOf(int i) {if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];return new Integer(i);}调用valueOf(int i)时,先判断i的值是否在缓存区IntegerCache中,在则无需新创建对象,否则要创建新对象
IntegerCache源码如下:
private static class IntegerCache {static final int low = -128;static final int high;static final Integer[] cache;static Integer[] archivedCache;static {// high value may be configured by propertyint h = 127;String integerCacheHighPropValue =VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {try {h = Math.max(parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue), 127);// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUEh = Math.min(h, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.}}high = h;// Load IntegerCache.archivedCache from archive, if possibleCDS.initializeFromArchive(IntegerCache.class);int size = (high - low) + 1;// Use the archived cache if it exists and is large enoughif (archivedCache == null || size > archivedCache.length) {Integer[] c = new Integer[size];int j = low;for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {c[i] = new Integer(j++);}archivedCache = c;}cache = archivedCache;// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;}缓存的数据范围为[-128,127],
得出结论: 如果数值在 [-128,127] 之间, 便返回指向 IntegerCache.cache 中已经存在的对象的引用;否则创建一个新的 Integer 对象。总结
1、==在引用数据中的使用,比较的时两者的引用地址。
2、自动装箱、自动拆箱是Java SE5之后提供,使得基本数据类型和包装类型自动转换
3、Integer与int之间的转换,在[-127,128]范围内,Integer使用了缓存,没有创建新的对象
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!