【小家Spring】聊聊Spring中的格式化:Formatter、AnnotationFormatterFactory、DateFormatter以及@DateTimeFormat...
每篇一句
今天多学一个本事,明天就可以少说一句求人的话
相关阅读
【小家Spring】聊聊Spring中的数据转换类:Converter、ConverterFactory、ConversionService、ConversionServiceFactoryBean
前言
Converter只完成了数据类型的转换,却不负责输入输出数据的格式化工作,日期时间、货币等虽都以字符串形式存在,却有不同的格式。
Spring格式化框架要解决的问题是:从格式化的数据中获取真正的数据,绑定数据,将处理完成的数据输出为格式化的数据。Formatter接口就承担着这样的责任.
Converter主要是做Object与Object之间的类型转换,Formatter则是要完成任意Object与String之间的类型转换。前者适合于任何一层,而后者则主要用于web层
Formatter
org.springframework.format.Formatter顾名思义,它表示格式化。
// @since 3.0
public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {
}
它自己一个方法都木有定义,因此需要看看它的两个父接口。
Printer
格式化显示接口,将T类型的对象根据Locale信息以某种格式进行打印显示(即返回字符串形式)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Printer<T> {String print(T object, Locale locale);
}
Parser
解析接口,根据Locale信息解析字符串到T类型的对象
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Parser<T> {T parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException;
}
从这两个接口定义中我们可以很清晰的看出定义了两个相反的接口。代表着格式化和解析(功能上和转换器Converter还是蛮像的)
Formatter它的继承树如下:
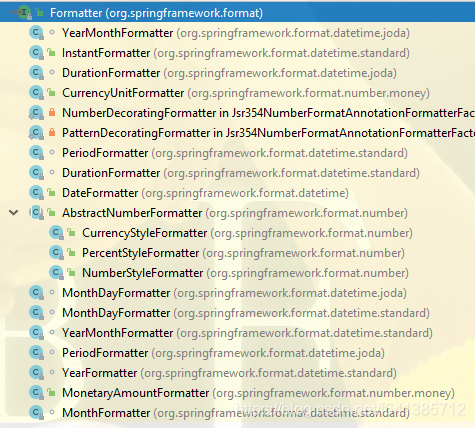
从包结构中看:
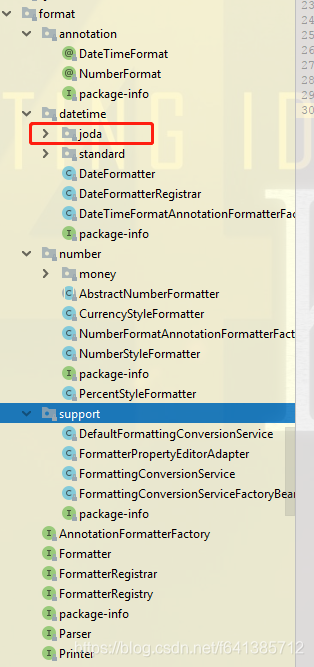
发现Spring竟然内置了对joda的支持,可见当初joda这个包的流行的程度。但是随着Java8中的JSR310日期的普及,我预言joda必将走向死亡(毕竟亲儿子才是最好的)。因此本文涉及到joda的实现都略过,只看JSR310标准实现。
InstantFormatter
对java.time.Instant时间戳的转换和解析:(相信一般很少这么使用吧~~~)
public class InstantFormatter implements Formatter<Instant> {// 如果你的请求入参串为:2007-12-03T10:15:30.00Z这种格式,是可以使用Instant接收的~~~@Overridepublic Instant parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {if (text.length() > 0 && Character.isDigit(text.charAt(0))) {// assuming UTC instant a la "2007-12-03T10:15:30.00Z"return Instant.parse(text);}else {// assuming RFC-1123 value a la "Tue, 3 Jun 2008 11:05:30 GMT"return Instant.from(DateTimeFormatter.RFC_1123_DATE_TIME.parse(text));}}// System.out.println(Instant.now())输出:2019-06-03T13:11:22.638Z@Overridepublic String print(Instant object, Locale locale) {return object.toString();}
}
CurrencyUnitFormatter
它需要javax.money.包的支持属于`JSR-354`的内容,暂时略过
PeriodFormatter/DurationFormatter/MonthDayFormatter/YearMonthFormatter/YearFormatter/MonthFormatter
他们的实现都很简单,都是调各自的parse()和toString()方法~ 就不详细说明了
DateFormatter
注意处理Java8中JSR310日期的叫做DateTimeFormatter,但它并没有实现Formatter接口,注意区分
另外注意和java.text.DateFormat的区分,它是JDK的。而这个是Spring的~ 但是Spring的这个底层实现其实还是依赖的java.text.DateFormat
这个是最为重要的一个转换,因为Spring MVC中我们经常会使用Date来接收参数和返回,因此这个转换器个人建议有必要了解一下,非常有助于了解序列化的原理啥的~~~依赖于java.text.DateFormat来处理的。
// @since 3.0 // 处理java.util.Date 和JSR310无关
public class DateFormatter implements Formatter<Date> {// 使用的标准时区~private static final TimeZone UTC = TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC");// 因为Date包含日期、时间 所以这里表述的是各自的默认支持的模版格式~~~// System.out.println(new Date()); //Mon Jun 03 21:18:45 CST 2019// System.out.println(new Timestamp(Instant.now().toEpochMilli())); //2019-06-03 21:18:45.346private static final Map<ISO, String> ISO_PATTERNS;static {Map<ISO, String> formats = new EnumMap<>(ISO.class);formats.put(ISO.DATE, "yyyy-MM-dd");formats.put(ISO.TIME, "HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX");formats.put(ISO.DATE_TIME, "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX");ISO_PATTERNS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(formats);}@Nullableprivate String pattern;private int style = DateFormat.DEFAULT; //FULL LONG MEDIUM SHORT 默认是MEDIUM @Nullableprivate String stylePattern;@Nullableprivate ISO iso;@Nullableprivate TimeZone timeZone;// 指定分析是否要宽松 默认是falseprivate boolean lenient = false;// ==========备注:上面所有参数和getDateFormat()格式化模版有关===========// 省略get/set方法public String print(Date date, Locale locale) {return getDateFormat(locale).format(date);}@Overridepublic Date parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {return getDateFormat(locale).parse(text);}// ====getDateFormat()方法,就是根据上面定义的参数生成~~~// 1、若指定了pattern参数,那就直接使用new SimpleDateFormat(this.pattern, locale)// 2、若没指定,那就根据配置项,DateFormat.getXXXInstance()...
}
Demo如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {Date date = new Date();Timestamp timestamp = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());DateFormatter dateFormatter = new DateFormatter();System.out.println(dateFormatter.print(date, Locale.CHINA)); //2019-6-3System.out.println(dateFormatter.print(timestamp, Locale.CHINA)); //2019-6-3dateFormatter.setIso(DateTimeFormat.ISO.DATE_TIME);//dateFormatter.setStyle(DateFormat.FULL);System.out.println(dateFormatter.print(date, Locale.CHINA)); //2019-06-03T13:28:44.252ZSystem.out.println(dateFormatter.print(timestamp, Locale.CHINA)); //2019-06-03T13:28:44.252Z}
AbstractNumberFormatter
对java.lang.Number进行格式化。依赖于java.text.NumberFormat来处理的,java.text.DecimalFormat是它的子类。
CurrencyStyleFormatter
以BigDecimal的格式来处理数字,当作钱币处理。
// @since 4.2
public class CurrencyStyleFormatter extends AbstractNumberFormatter {private int fractionDigits = 2; // 默认保留两位小数点@Nullableprivate RoundingMode roundingMode; // 四舍五入@Nullableprivate Currency currency; // 货币 java.util.Currency// 例如:#,#00.0# --> 1,234.56@Nullableprivate String pattern;@Overridepublic BigDecimal parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {BigDecimal decimal = (BigDecimal) super.parse(text, locale);// 对结果做四舍五入处理~~~~~~~~~~~if (this.roundingMode != null) {decimal = decimal.setScale(this.fractionDigits, this.roundingMode);} else {decimal = decimal.setScale(this.fractionDigits);}return decimal;}}
Demo:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {String curr = "1,234.56";CurrencyStyleFormatter formatter = new CurrencyStyleFormatter();//formatter.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.DOWN);formatter.setPattern("#,#00.0#"); // 若不设置格式 抛错ParseExceptionSystem.out.println(formatter.parse(curr, Locale.CHINA)); //1234.56}
PercentStyleFormatter
对百分数进行格式化,@since 4.2。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {String curr = "12%";PercentStyleFormatter formatter = new PercentStyleFormatter();System.out.println(formatter.parse(curr, Locale.CHINA)); //0.12System.out.println(formatter.print(0.12, Locale.CHINA)); //12%}
NumberStyleFormatter
数字的格式进行转换,也可以指定pattern
Demo:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {String curr = "12,000.1567";NumberStyleFormatter formatter = new NumberStyleFormatter();formatter.setPattern("#,#00.0#");System.out.println(formatter.parse(curr, Locale.CHINA)); //12000.1567System.out.println(formatter.print(0.12, Locale.CHINA)); // 00.12 看这格式化的威力}
以上。
其中最为主要的是Date的转换,以及对Number的转换(它可以转为货币、百分比、数字)
FormatterRegistry
从接口继承关系中可以看出,它既可以注册格式化器,又可议注册转换器
// @since 3.0
public interface FormatterRegistry extends ConverterRegistry {void addFormatter(Formatter<?> formatter);void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter);// 单独指定Printer和parser也是被允许的void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Printer<?> printer, Parser<?> parser);// 注册处理注解的格式化器~~~~~ AnnotationFormatterFactory的实现类~~void addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(AnnotationFormatterFactory<? extends Annotation> annotationFormatterFactory);
}
FormattingConversionService
// @since 3.0 它继承自GenericConversionService ,所以它能对Converter进行一系列的操作~~~
// 实现了接口FormatterRegistry,所以它也可以注册格式化器了
// 实现了EmbeddedValueResolverAware,所以它还能有非常强大的功能:处理占位
public class FormattingConversionService extends GenericConversionService implements FormatterRegistry, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {@Nullableprivate StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;private final Map<AnnotationConverterKey, GenericConverter> cachedPrinters = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);private final Map<AnnotationConverterKey, GenericConverter> cachedParsers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);// 最终也是交给addFormatterForFieldType去做的// getFieldType:它会拿到泛型类型。并且支持DecoratingProxy~~~@Overridepublic void addFormatter(Formatter<?> formatter) {addFormatterForFieldType(getFieldType(formatter), formatter);}// 存储都是分开存储的 读写分离// PrinterConverter和ParserConverter都是一个GenericConverter 采用内部类实现的~~~ this代表一个ConversionService// 注意:他们的ConvertiblePair必有一个类型是String.class// Locale一般都可以这么获取:LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()// 最终parse出来的result有可能也会交给conversionService.convert() 若类型能够匹配上的话@Overridepublic void addFormatterForFieldType(Class<?> fieldType, Formatter<?> formatter) {addConverter(new PrinterConverter(fieldType, formatter, this));addConverter(new ParserConverter(fieldType, formatter, this));}// 哪怕你是一个AnnotationFormatterFactory,最终也是被适配成了GenericConverter(ConditionalGenericConverter)@Overridepublic void addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(AnnotationFormatterFactory<? extends Annotation> annotationFormatterFactory) {Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = getAnnotationType(annotationFormatterFactory);// 若你自定义的实现了EmbeddedValueResolverAware接口,还可以使用占位符哟~~~~// AnnotationFormatterFactory是下面的重点内容~~~~if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null && annotationFormatterFactory instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) annotationFormatterFactory).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);}// 对每一种字段的type 都注册一个AnnotationPrinterConverter去处理~~~~~// AnnotationPrinterConverter是一个ConditionalGenericConverter// matches方法为:sourceType.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType);// 这个判断是呼应的:因为annotationFormatterFactory只会作用在指定的字段类型上的~~~不符合类型条件的不用添加Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = annotationFormatterFactory.getFieldTypes();for (Class<?> fieldType : fieldTypes) {addConverter(new AnnotationPrinterConverter(annotationType, annotationFormatterFactory, fieldType));addConverter(new AnnotationParserConverter(annotationType, annotationFormatterFactory, fieldType));}}...
}

DefaultFormattingConversionService
实际使用时,基本就是使用它。它的模式属于默认模式:就是注册了一些常用的,默认支持的转换器们。
public class DefaultFormattingConversionService extends FormattingConversionService {// 再一次看出来joda这个库的成功啊~~~private static final boolean jsr354Present;private static final boolean jodaTimePresent;static {ClassLoader classLoader = DefaultFormattingConversionService.class.getClassLoader();jsr354Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("javax.money.MonetaryAmount", classLoader);jodaTimePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("org.joda.time.LocalDate", classLoader);}public DefaultFormattingConversionService(@Nullable StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver, boolean registerDefaultFormatters) {if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {setEmbeddedValueResolver(embeddedValueResolver);}// 由此可见,它是DefaultConversionService的超集,比它强大得多的~~~DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(this);if (registerDefaultFormatters) {addDefaultFormatters(this);}}// 默认添加进去的格式化器们~~~~public static void addDefaultFormatters(FormatterRegistry formatterRegistry) {// Default handling of number values// 支持@NumberFormat注解~~~~~对数字进行格式化~formatterRegistry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());// Default handling of monetary values// JSR354使用较少~略过 银行、金融项目使用多~if (jsr354Present) {formatterRegistry.addFormatter(new CurrencyUnitFormatter());formatterRegistry.addFormatter(new MonetaryAmountFormatter());formatterRegistry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new Jsr354NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());}// Default handling of date-time values// just handling JSR-310 specific date and time types// 对JSR310的转换的支持 DateTimeFormatterRegistrar是一个FormatterRegistrarnew DateTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);// 如没有导入joda的包 那就默认使用Date吧~~~~~if (jodaTimePresent) {// handles Joda-specific types as well as Date, Calendar, Longnew JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);} else {// regular DateFormat-based Date, Calendar, Long convertersnew DateFormatterRegistrar().registerFormatters(formatterRegistry);}}
}
Spring提供了两个默认实现(其都实现了ConverterRegistry、ConversionService接口):
- DefaultConversionService:默认的类型转换服务实现;
DefaultFormattingConversionService:带数据格式化支持的类型转换服务实现,一般使用该服务实现即可。
备注:自定义Converter的场景其实蛮多的,比如最常见的
StringToPhoneNumberConverter它俩的互转,就可以定义个转换器,支持中间空格的电话号码格式~
FormatterRegistrar和
要使用Formatter,除了将其配置在FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean的formatters属性中外,还可以FormatterRegistrar注册进去。下面看到FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean的时候会很清晰:
Registers {@link Converter Converters} and {@link Formatter Formatters} with a FormattingConversionService through the {@link FormatterRegistry} SPI.
java doc里说它是一个注册Converter和Formatter的SPI
public interface FormatterRegistrar {// Register Formatters and Converters with a FormattingConversionService through a FormatterRegistry SPI. void registerFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry);
}
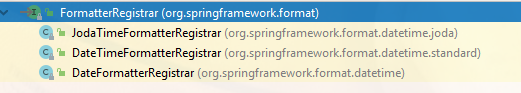
JodaTimeFormatterRegistrar:
格式化joda的LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime、ReadableInstant、Period…等等
DateTimeFormatterRegistrar:
对JSR310的那些时间类进行支持。包括:LocalDateTime、ZonedDateTime、OffsetDateTime、OffsetTime等等
@since 4.0。各种内部转换请参见:DateTimeConverters.registerConverters(registry);
DateFormatterRegistrar:
单词上注意和
DateTimeFormatterRegistrar的区别~~
这个和@DateTimeFormat也有关系,内部依赖的是上面说到的DateFormatter。
public class DateFormatterRegistrar implements FormatterRegistrar {@Overridepublic void registerFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {addDateConverters(registry); // 它是个静态方法// 对`@DateTimeFormat`的支持~~~~~// 所以如果你导入了joda包,这个注解可能会失效的~~~~需要特别注意~~~~~~~~~~~ 但下面的DateToLongConverter之类的依旧好使~// 但是你导入的是JSR310 没有这个问题~~~~registry.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation(new DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory());// In order to retain back compatibility we only register Date/Calendar// types when a user defined formatter is specified (see SPR-10105)// 如果你指定了dateFormatter,那么注册它 也来处理Calendar以及Dateif (this.dateFormatter != null) {registry.addFormatter(this.dateFormatter);registry.addFormatterForFieldType(Calendar.class, this.dateFormatter);}}// 注意:这些converter全部为内部类实现~~~~public static void addDateConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {converterRegistry.addConverter(new DateToLongConverter());converterRegistry.addConverter(new DateToCalendarConverter());converterRegistry.addConverter(new CalendarToDateConverter());converterRegistry.addConverter(new CalendarToLongConverter());converterRegistry.addConverter(new LongToDateConverter());converterRegistry.addConverter(new LongToCalendarConverter());}
}
AnnotationFormatterFactory
它是一个工厂,专门创建出处理(格式化)指定字段field上标注有指定注解的。(Spring内助了两个常用注解:@DateTimeFormat和@NumberFormat)
我们常说的,要自定义注解来处理参数的格式化,就需要实现接口来自定义一个处理类。
// @since 3.0
public interface AnnotationFormatterFactory<A extends Annotation> {// 此注解 可以作用的字段的类型~~~比如@DateTimeFormat只能作用域Date、Calendar、Long类型上~ 标注在被的类型上无效~~~Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes();// 对标注有指定注解的字段进行格式化输出~~Printer<?> getPrinter(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);// 对标注有指定注解的字段进行格式化解析~~~Parser<?> getParser(A annotation, Class<?> fieldType);
}
AnnotationFormatterFactory的继承树如下,可以看到Spring 给我们内置了一些处理器的:
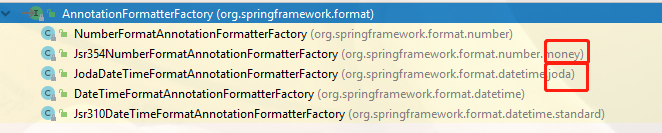
总的来说是支持了数值和日期类型(Date和JSR310、甚至joda)
NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
处理@NumberFormat对数字进行格式化。
// 还继承自EmbeddedValueResolutionSupport,所以有resolveEmbeddedValue()方法,能够处理占位符
public class NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory extends EmbeddedValueResolutionSupportimplements AnnotationFormatterFactory<NumberFormat> {// 处理Byte、Short、Integer、Long、Float、Double、BigInteger、BigDecimal等类型~~~@Overridepublic Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {return NumberUtils.STANDARD_NUMBER_TYPES;}@Overridepublic Printer<Number> getPrinter(NumberFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {return configureFormatterFrom(annotation);}@Overridepublic Parser<Number> getParser(NumberFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {return configureFormatterFrom(annotation);}// 可以看到,根据Style不同,返回的格式化器也是不同的~~~~// 显然pattern非常强大,支持到了占位符,el取值~~~private Formatter<Number> configureFormatterFrom(NumberFormat annotation) {String pattern = resolveEmbeddedValue(annotation.pattern());// 若指定了pattern,此处可以看出:直接当做数字处理NumberStyleFormatterif (StringUtils.hasLength(pattern)) {return new NumberStyleFormatter(pattern);}// 可能是钱币、百分比、数字 注意:都是使用的默认处理方式了~~~~ // @NumberFormat并不支持自定义 比如保留小数位、四舍五入等等else {Style style = annotation.style();if (style == Style.CURRENCY) {return new CurrencyStyleFormatter();}else if (style == Style.PERCENT) {return new PercentStyleFormatter();}else {return new NumberStyleFormatter();}}}}
@NumberFormat是用来验证输入的数字格式。比如一般我们这样来格式化数值:@NumberFormat(pattern="#,###.##")
@NumberFormat注解内容:
// @since 3.0 类比效果参见:java.text.NumberFormat
// 可以标注在方法上、属性field上、参数上~~~~
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
public @interface NumberFormat {Style style() default Style.DEFAULT;// 格式化数字的模版~~~ 若指定了pattern 那就使用new NumberStyleFormatter(pattern)进行格式化String pattern() default "";enum Style {// 默认值 同 NUMBERDEFAULT,NUMBER,PERCENT,CURRENCY}}
Jsr354NumberFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
也就是Jsr354的相关类型(MonetaryAmount),也是支持
@NumberFormat注解的
JSR 354定义了一套新的Java货币API:目前还是javax包内~
CurrencyUnit代表的是货币。它有点类似于现在的java.util.Currency类
MontetaryAmount代表的是某种货币的具体金额。通常它都会与某个CurrencyUnit绑定。
(略)
JodaDateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
略
DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
它和@DateTimeFormat这个注解有关,作用在Date、Calendar、Long类型上。
public class DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory extends EmbeddedValueResolutionSupportimplements AnnotationFormatterFactory<DateTimeFormat> {// 该注解只能放在下面这集中类型上面~~~~才会生效private static final Set<Class<?>> FIELD_TYPES;static {Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = new HashSet<>(4);fieldTypes.add(Date.class);fieldTypes.add(Calendar.class);fieldTypes.add(Long.class);FIELD_TYPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(fieldTypes);}@Overridepublic Set<Class<?>> getFieldTypes() {return FIELD_TYPES;}@Overridepublic Printer<?> getPrinter(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {return getFormatter(annotation, fieldType);}@Overridepublic Parser<?> getParser(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {return getFormatter(annotation, fieldType);}protected Formatter<Date> getFormatter(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {DateFormatter formatter = new DateFormatter();// style属性支持使用占位符的形式~ setStylePattern// 'S' = Small 'M' = Medium 'L' = Long 'F' = Full '-' = Omitted// 注意:这里需要同时设置两个。比如SS SM等等// 第一个表示Date日期格式,第二个表示Time事件格式~~~~ 注解默认值是SSString style = resolveEmbeddedValue(annotation.style());if (StringUtils.hasLength(style)) {formatter.setStylePattern(style);}formatter.setIso(annotation.iso());// patter也支持占位符~~~ // DateFormatter里说过,若pattern指定了,就直接使用SimpleDateFormat格式化了// 否则根据stylePattern来进行拿模版实例:return DateFormat.getTimeInstance(timeStyle, locale)//static {// Map formats = new EnumMap<>(ISO.class); // formats.put(ISO.DATE, "yyyy-MM-dd");// formats.put(ISO.TIME, "HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX");// formats.put(ISO.DATE_TIME, "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX");// ISO_PATTERNS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(formats);//}String pattern = resolveEmbeddedValue(annotation.pattern());if (StringUtils.hasLength(pattern)) {formatter.setPattern(pattern);}return formatter;}
}
@DateTimeFormat注解内容:
// @since 3.0 它比Number多一个ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE,表示它还能作为元注解标注在注解上
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
public @interface DateTimeFormat {// 默认是SS 表示否是SMALL的String style() default "SS";// 默认为null。若指定了ISO,最终也会使用SimpleDateFormat去格式化Date。// 因为String pattern = ISO_PATTERNS.get(this.iso)都对应着patter值的~~~ 见下面ISO iso() default ISO.NONE;// 默认不给你指定pattern 但是我们使用时一般都要指定~String pattern() default "";enum ISO {DATE, // yyyy-MM-dd 2000-10-31TIME, // HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX 01:30:00.000-05:00// 注意:若你什么都没有指定,默认就会按照此种格式转换为Date~~~DATE_TIME, // yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX 2000-10-31T01:30:00.000-05:00NONE}}
Jsr310DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory
它和@DateTimeFormat这个注解有关,作用在JSR310相关类型上。
注意,它也是处理标注有@DateTimeFormat注解的字段的。DateTimeFormatterRegistrar#registerFormatters方法里注册了它,从而提供了该注解对JSR310也是支持的,并且我认为比上面还重要些,大势所趋~
public class Jsr310DateTimeFormatAnnotationFormatterFactory extends EmbeddedValueResolutionSupportimplements AnnotationFormatterFactory<DateTimeFormat> {// 可以标注在这些类型上面~~~~private static final Set<Class<?>> FIELD_TYPES;static {// Create the set of field types that may be annotated with @DateTimeFormat.Set<Class<?>> fieldTypes = new HashSet<>(8);fieldTypes.add(LocalDate.class);fieldTypes.add(LocalTime.class);fieldTypes.add(LocalDateTime.class);fieldTypes.add(ZonedDateTime.class);fieldTypes.add(OffsetDateTime.class);fieldTypes.add(OffsetTime.class);FIELD_TYPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(fieldTypes);}// 往外输出的时候~~~~~~@Overridepublic Printer<?> getPrinter(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {// 使用DateTimeFormatterFactory根据注解信息创建一个java.time.format.DateTimeFormatterDateTimeFormatter formatter = getFormatter(annotation, fieldType);// Efficient ISO_LOCAL_* variants for printing since they are twice as fast...// ISO.DATE -> DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE// ISO.TIME -> DateTimeFormatter.ISO_TIME// ISO.DATE_TIME -> DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME// ISO.NONE 没有指定,就走最后的TemporalAccessorPrinter了~~~~// isLocal(fieldType) --> fieldType.getSimpleName().startsWith("Local");// System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd").format(LocalDate.now())); //2019-06-04 标准格式输出~~~~if (formatter == DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE) {if (isLocal(fieldType)) {formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE;}}else if (formatter == DateTimeFormatter.ISO_TIME) {if (isLocal(fieldType)) {formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME;}}else if (formatter == DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME) {if (isLocal(fieldType)) {formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;}}// 它的print方法为:return DateTimeContextHolder.getFormatter(this.formatter, locale).format(partial);return new TemporalAccessorPrinter(formatter);}// 它的parse方法,依赖于LocalDate.parse、OffsetTime.parse等等各自的parse方法~@Override@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Parser<?> getParser(DateTimeFormat annotation, Class<?> fieldType) {DateTimeFormatter formatter = getFormatter(annotation, fieldType);return new TemporalAccessorParser((Class<? extends TemporalAccessor>) fieldType, formatter);}
}
有了它,我们处理Date、JSR310之类的日期能达到统一的效果了。
DateTimeFormatterFactory
说白了,它就是根据一些参数比如:pattern、org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat.ISO、java.time.format.FormatStyle、java.util.TimeZone等等来创建一个java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter
// @since 4.0
public class DateTimeFormatterFactory {@Nullableprivate String pattern;@Nullableprivate ISO iso;@Nullableprivate FormatStyle dateStyle;@Nullableprivate FormatStyle timeStyle;@Nullableprivate TimeZone timeZone;// ...public void setStylePattern(String style) {Assert.isTrue(style.length() == 2, "Style pattern must consist of two characters");this.dateStyle = convertStyleCharacter(style.charAt(0));this.timeStyle = convertStyleCharacter(style.charAt(1));}@Nullableprivate FormatStyle convertStyleCharacter(char c) {switch (c) {case 'S': return FormatStyle.SHORT;case 'M': return FormatStyle.MEDIUM;case 'L': return FormatStyle.LONG;case 'F': return FormatStyle.FULL;case '-': return null;default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid style character '" + c + "'");}}public DateTimeFormatter createDateTimeFormatter() {return createDateTimeFormatter(DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM));}// fallbackFormatter表示最后的格式化器的默认值~~~~public DateTimeFormatter createDateTimeFormatter(DateTimeFormatter fallbackFormatter) {// 若指定了pattern 那就简单了~~~if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.pattern)) {// 这一句是为了兼容Joda-Time到JSR里~~String patternToUse = StringUtils.replace(this.pattern, "yy", "uu");// 采用STRICT方式格式化~~~dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(patternToUse).withResolverStyle(ResolverStyle.STRICT);} else if (this.iso != null && this.iso != ISO.NONE) { //ISO不能为null和NONEswitch (this.iso) {case DATE:dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE;break;case TIME:dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_TIME;break;case DATE_TIME:dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME;break;default:throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported ISO format: " + this.iso);}}... // 根据dateStyle和timeStyle来生成实例~~~~略}
}
通过它,我们只需要关注一些元信息,就能很快的生成出一个DateTimeFormatter来。比如我们根据注解信息,就生成出来就是这么个原理。
DateTimeFormatterFactoryBean
这里指的是org.springframework.format.datetime.standard.DateTimeFormatterFactoryBean,而不是joda包的,需要稍微注意。它借助了DateTimeFormatterFactory然后实现了一波FactoryBean,猛如虎有木有~
public class DateTimeFormatterFactoryBean extends DateTimeFormatterFactoryimplements FactoryBean<DateTimeFormatter>, InitializingBean {@Nullableprivate DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter;@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() {// 父类创建~~this.dateTimeFormatter = createDateTimeFormatter();}@Override@Nullablepublic DateTimeFormatter getObject() {return this.dateTimeFormatter;}@Overridepublic Class<?> getObjectType() {return DateTimeFormatter.class;}@Overridepublic boolean isSingleton() {return true;}}
FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean
它和上面的不同,它是用于管理转换器、格式化器们的。比如我们自己自定义了一个转换器、格式化器需要注册,都以交给它。从名字可以看出,它主要是创建一个FormattingConversionService,而它上面说了它既还有转换器,又有格式化器~~~
public class FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<FormattingConversionService>, EmbeddedValueResolverAware, InitializingBean {@Nullableprivate Set<?> converters;@Nullableprivate Set<?> formatters;// 由此可见,我们要注册formatter不仅仅可以直接注册,也可通过formatterRegistrars注册进来~@Nullableprivate Set<FormatterRegistrar> formatterRegistrars;private boolean registerDefaultFormatters = true;@Nullableprivate StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;@Nullableprivate FormattingConversionService conversionService; // 最终是它用于管理所有 备注:所有的formatter最终都是一个converter// 这里把上面字段set进来的值,进行解析~~~~拆分~~~@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() {// 由此可见,最终返回的是一个DefaultFormattingConversionServicethis.conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService(this.embeddedValueResolver, this.registerDefaultFormatters);// 把set进来的这些converters都注册进去保存着~~~ConversionServiceFactory.registerConverters(this.converters, this.conversionService);// 这里处理注册formatters和formatterRegistrars们~~~~registerFormatters(this.conversionService);}private void registerFormatters(FormattingConversionService conversionService) {if (this.formatters != null) {for (Object formatter : this.formatters) {if (formatter instanceof Formatter<?>) {conversionService.addFormatter((Formatter<?>) formatter);} else if (formatter instanceof AnnotationFormatterFactory<?>) {conversionService.addFormatterForFieldAnnotation((AnnotationFormatterFactory<?>) formatter);} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Custom formatters must be implementations of Formatter or AnnotationFormatterFactory");}}}if (this.formatterRegistrars != null) {for (FormatterRegistrar registrar : this.formatterRegistrars) {registrar.registerFormatters(conversionService);}}}@Override@Nullablepublic FormattingConversionService getObject() {return this.conversionService;}// 类型实际上为DefaultFormattingConversionService@Overridepublic Class<? extends FormattingConversionService> getObjectType() {return FormattingConversionService.class;}@Overridepublic boolean isSingleton() {return true;}}
有了它,上篇文章我们讲到我们若要注册自定义的converter的话,使用的ConversionServiceFactoryBean,而本文我们就可以使用更加强大的FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean了。
一般情况下,若是Web环境下比如Spring MVC使用转换器、格式化器。建议使用
FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean注册,其余的无所谓了。
自定义转换器/格式化器
在WebMvcConfigurationSupport有这么一句:
@Beanpublic FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {FormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();addFormatters(conversionService);return conversionService;}
它默认使用的就是DefaultFormattingConversionService,因此我们只需要addFormatters()向里添加格式化器即可。(此处conversionService既是个ConverterRegistry,又是个FormatterRegistry,所以~~~) 此处只演示在WebMvc场景下的自定义:
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {@Overridepublic void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {registry.addConverter(new PersonConverter());//registry.addFormatter();}
}
就这样我们就很方便的完成了我们对自定义转换器/格式化器~的添加。
在Spring MVC开发中,我个人认为自定义转换器、格式化器还是非常重要的一个章节,应用也可以非常的广泛。比如我们可以对请求数据进行脱敏、解密等等处理,这样都是可行的~~
若你想自己用FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean来注册转换器、格式化器们,目前来说除了自定义@Bean,还没有一个很好的用于之地
在基于xml配置中,这么做:
我们就可以自定义一个名字为conversionService的FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean,从而达到自定义注册Bean的效果。在注解驱动的情况下,这些变得更加简单方便了些~~~~(直接定义使用FormattingConversionService/DefaultFormattingConversionService即可)
选择Converter, 还是Formatter
Converter是一般工具, 可以将一种类型转换成另一种类型, 例如, 将String转换成Date, 或者Long转换成Date, Conveter既可以用在web层, 也可以用在其他层中。
Formatter只能将String转换层另一种java类型, 例如, 将String转换成Date, 但它不可能将Long转换成Date类型, 因此Formatter适用于web层, 因此, SpringMVC应用程序中, 选择Formatter比选择Converter更合适
JDK中的格式化器java.text.Format
注意是Format,不是java.util.Formatter。Formatter工具我个人认为不是特别的重点~~
Java中允许我们对指定的对象进行某种格式化,从而得到我们想要的格式化样式。
Foramt是一个抽象基类,其具体子类必须实现format方法。
public abstract class Format implements Serializable, Cloneable {...// format方法用于将对象格式化为指定模式的字符串public abstract StringBuffer format(Object obj, StringBuffer toAppendTo, FieldPosition pos);// parseObject方法用于将字符串重新解析为对象public abstract Object parseObject (String source, ParsePosition pos);...
}
Format的直接子类包括DateFormat、NumberFormat和MessageFormat。
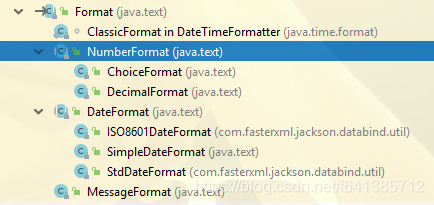
DateFormat
DateFormat根据当前语言环境格式化日期和时间。DateFormat是一个抽象类,所以不能直接new创建实例对象。但该类为我们提供了工厂方法方便我们使用。
- getDateInstance()方法,获取格式化的日期,输出样式:2015-12-10
- getDateTimeInstance()方法,获取格式化的日期和时间,输出样式:2015-12-10 10:21:41
- getTimeInstance()方法,获取格式化的时间,输出样式:10:21:41
- getInstance()方法,获取格式化的日期和时间,输出样式:15-12-10 上午10:21
例如;
DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.DEFAULT,Locale.CANADA);//获取加拿大的格式化日期
该抽象类的实例,都是返回默认的模版来显示的(SMALL、Full等等)。若都不合你意,你可以使用它的儿子–>我们最熟悉的SimpleDateFormat来指定partern作为我们自己的模版。
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("今天是yyyy-MM-dd E hh:mm:ss,是yyyy年的第DD天,在该月是第dd天");
System.out.println(format.format(date)); // 将会输出:今天是2015-12-10 星期四 09:38:16,是2015年的第344天,在该月是第10天
SimpleDateFormat是DateFormat的一个具体类,它允许我们指定格式模式从而获取我们理想的格式化日期和时间。
另外DateFormat放在java.text包中,我认为是它的败笔~
NumberFormat
注意Spring有这个注解也叫这名字,注意区分。
NumberFormat根据当前语言环境格式化数字,它也是个抽象类。
- getCurrencyInstance()方法,根据当前语言环境获取货币数值格式。传递Locale对象可以获取指定语言环境下的货币数值格式
- getInstance()和getNumberInstance()方法都会获取到常规数值格式
- getIntegerInstance()方法获取常规整数值格式,如果需要格式化的数值为小数,则会将数值四舍五入为最接近的整数
- getPercentInstance()方法获取百分比的数值格式
public static void main(String[] args) {NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.CHINA);System.out.println(format.format(439.6)); //¥439.60System.out.println(NumberFormat.getInstance().format(439.6)); //439.6System.out.println(NumberFormat.getIntegerInstance().format(439.6)); // 440 整数System.out.println(NumberFormat.getPercentInstance().format(439.6)); // 43,960%}
NumberFormat有两个具体实现子类DecimalFormat和ChoiceFormat。
DecimalFormat
DecimalFormat同SimpleDateFormat类似,允许我们指定格式模式获取我们想要的格式化数值
DecimalFormat类对于数值的小数部分,默认显示3位小数,在去掉超出小数点后面3位的部分时,会将数值四舍五入为最接近的数值格式化输出。但是我们可以对这个默认进行设置:
setMaximumFractionDigits(int newValue)方法,设置小数部分中允许的最大数字位数
setMinimumFractionDigits(int newValue)方法,设置小数部分中允许的最小数字位数,如果原数小数位数不够的话,会补零。
对于数值的整数部分,默认3个数字为一组进行显示,同样对此我们也可以自定义,使用setGroupingSize(int i)方法,设置分组中一组的位数。
setGroupingUsed(boolean value)方法设置是否使用分组,true表示使用,false表示取消分组
public static void main(String[] args) {DecimalFormat format1 = new DecimalFormat("#\u2030");System.out.println(format1.format(0.3345));//输出334‰DecimalFormat format2 = new DecimalFormat("##.##");System.out.println(format2.format(12.345));//输出12.35DecimalFormat format3 = new DecimalFormat("0000.00");System.out.println(format3.format(12.345));//输出0012.35 // 前面用0补齐了~~DecimalFormat format4 = new DecimalFormat("#.##%");System.out.println(format4.format(12.345));//输出1234.5%}
ChoiceFormat
ChoiceFormat允许将格式化运用到某个范围的数,通常与MessageFormat一同使用。
ChoiceFormat在构造方法中接收一个limits数组和一个format数组,这两个数组的长度必须相等
limits数组实际上是个区间,可开可闭,并且必须按升序排列,如果不按升序排列,格式化结果将会不正确,还可以使用\u221E(表示无穷大)。
- nextDouble(double d)静态方法查找大于d的最小double值,用在limits数组中,从而使limits数组形成一个右开区间数组,例如:
limits = {0,1,ChoiceFormat.nextDouble(1)} - nextDouble(double d, boolean positive)静态方法,如果positive参数为true,表示查找大于d的最小double值;如果positive参数为false,表示查找小于d的最大double值,这样就可以使limits形成一个左开区间数组
- previousDouble(double d)静态方法,查找小于d的最大double值
public static void main(String[] args) {double[] limits = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};String[] formats = {"星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日"};ChoiceFormat format = new ChoiceFormat(limits, formats);System.out.println(format.format(2.5));//将会输出"星期一"System.out.println(format.format(3.6)); //3.6介于3和4之间,所以会匹配3,又由于3在limits数组中的索引是0,所以会在formats数组按照索引0的值,即输出"星期一" }
ChoiceFormat类的构造方法也允许我们传入一个模式字符串,format方法会根据这个模式字符串执行格式化操作:doubleNum [占位符] formatStr
占位符可以使用#、< 、\u2264(<=)
public static void main(String[] args) {ChoiceFormat cf = new ChoiceFormat("1#is 1 | 1);System.out.println(cf.format(1));//输出"is 1"System.out.println(cf.format(2));//输出"is more than 1"System.out.println(cf.format(0));//输出"is 1"}
由上面的例子可以看出,模式字符串中的每个模式元素之间使用"|“分割,”|"前后可以添加空格以美化代码,而且必须按照升序进行书写,否则会出现java.lang.IllegalArgumentException的运行时异常
观看ChoiceFormat类的源码我们得知,实际上在内部,模式字符串还是被转换为limits和formats两个数组
MessageFormat(常用)
MessageFormat提供了以语言环境无关的生成连接消息的方式。
常用MessageFormat的静态方法format,该方法接收一个字符串的模式和一组对象(对象数组),按照模式形式将格式化的对象插入到模式中,然后返回字符串结果。
MessageFormat占位符由三种书写格式:
- {index}:
- {index,formatType}:
- {index,formatType,formatStyle}
index表示数字角标。FormatType包括number、date、 time、choice等。FormatStyle包括short、medium、long、full、integer、currency、percent等
number对应了NumberFormat,其子格式对应了DecimalFormat
date和time对应了DateFormat,其子格式对应了SimpleDateFormat
choice对应了ChoiceFormat
Demo:
public static void main(String[] args) {int planet = 7;String event = "a disturbance in the Force";String result = MessageFormat.format("At {1,time} on {1,date}, there was {2} on planet {0,number,integer}.", planet, new Date(), event);System.out.println(result); //At 15:38:07 on 2019-6-4, there was a disturbance in the Force on planet 7.}
备注:若你的模版被多次使用到,也可以使用MessageFormat的构造方法传入pattern string(模式字符串),然后调用普通的format方法。若只执行一次,可以用静态方法~
注意指定了formatType后,第三个参数formatStyle并不能随意写的。至于formatType和formatStyle的对应关系,此处不解释了
最后,我们用java处理国际化的时候,我们的properties配置文件里经常可议看到{0} {1}这样的占位符,其实最终都是交给MessageFormat去处理了的~~
注意,注意,注意:Format中的子类都是不同步,所以需要注意线程安全问题
String类中的format方法
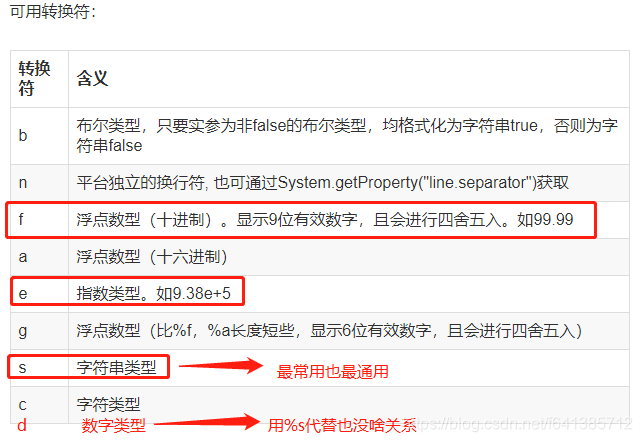
String因为过于常用,所以在JDK5的时候它提供了静态方法format方法来方便我们对字符串进行格式化。 直接看例子吧~~
public static void main(String[] args) {String result1 = String.format("小明今年%d岁,他住在%s,他的月工资有%.2f", 25, "北京市", 6633.435);System.out.println(result1);//输出:小明今年25岁,他住在北京市,他的月工资有6633.44/****************************************************/double num = 123.4567899;String result2 = String.format("%e", num);System.out.println(result2);//输出:1.234568e+02}
总结
Formatter就像Converter一样,也是将一种类型转换为另外一种类型,但是Formatter的源类型必须是String,而Converter的源类型可以是任意类型。
Spring中的Formatter其实包含了数据转换的内容,可以说是对标准数据转换的一个升级。
我们在Spring MVC中一般使用注解:@NumberFormat和@DateTimeFormat来格式化入参、出参。但是注意:这是Spring的能力,并非web的,只是我们一般在web层来使用。
Formatter更加适合Web层,而Converter则可以在任意层中。为了转换SpringMVC应用程序中的表单的用户输入,始终应该选择Formatter而不是Converter
关注A哥
| Author | A哥(YourBatman) |
|---|---|
| 个人站点 | www.yourbatman.cn |
| yourbatman@qq.com | |
| 微 信 | fsx641385712 |
活跃平台 |         |
| 公众号 | BAT的乌托邦(ID:BAT-utopia) |
| 知识星球 | BAT的乌托邦 |
| 每日文章推荐 | 每日文章推荐 |

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!