Selinux篇3 -TE规则
allow vold device:dir write
这句的意思是:允许 type 为 vold 的主体 对 type 为 device的客体 拥有 客体类别为 dir 的write 权限。根据 SELinux 规范,规则定义的格式为:
rule_name source_type target_type : class perm_set;
可以看到规则中只用到了主体和客体的 type,而动作是以操作类别与具体操作的组合体现的。
所有 rule_name 如下:
allow 表示允许主体对客体执行允许的操作;
auditallow 表示即便允许操作也要记录访问决策信息(仍然需要有 allow 规则才允许);
dontaudit 表示违反规则的决策信息也不记录(便于定位问题,已知此操作会被拒绝但不会引起真正问题);
neverallow 表示不允许主体对客体执行指定的操作;同时还有其他 dontaudit allowaudit。

常见class 定义
# file-related classes
class filesystem
class file #代表普通文件
class dir #代表目录
class fd #代表文件描述符
class lnk_file #代表链接文件
class chr_file #代表字符设备文件
......
# network-related classes
class socket #socket
class tcp_socket
class udp_socket
......
class binder #Android平台特有的binder
class zygote #Android平台特有的zygote
常见动作定义:

一个规则demo:



关键字attribute
属性关键字,适用于规则批量管理。
系统文件位置/system/sepolicy/public/attribute
此文件增加我们自己定义的属性
attribute display_service_server;
attribute wifi_keystore_service_server;
+attribute attribute_test;
此处test_service具有和domain一样的作用,作为一个属性存在,一个进程域。
然后通过对此属性进行定义。
#定义两个type,分别是A_t和B_t,它们都管理到attribute_test
type A_t attribute_test;
type B_t attribute_test;
#写一个allow语句,直接针对attribute_test
allow attribute_test C_t:file {read write};
#上面这个allow语句在编译后的安全策略文件中会被如下两条语句替代:
allow A_t C_t:file {read write};
allow B_t C_t:file {read write};
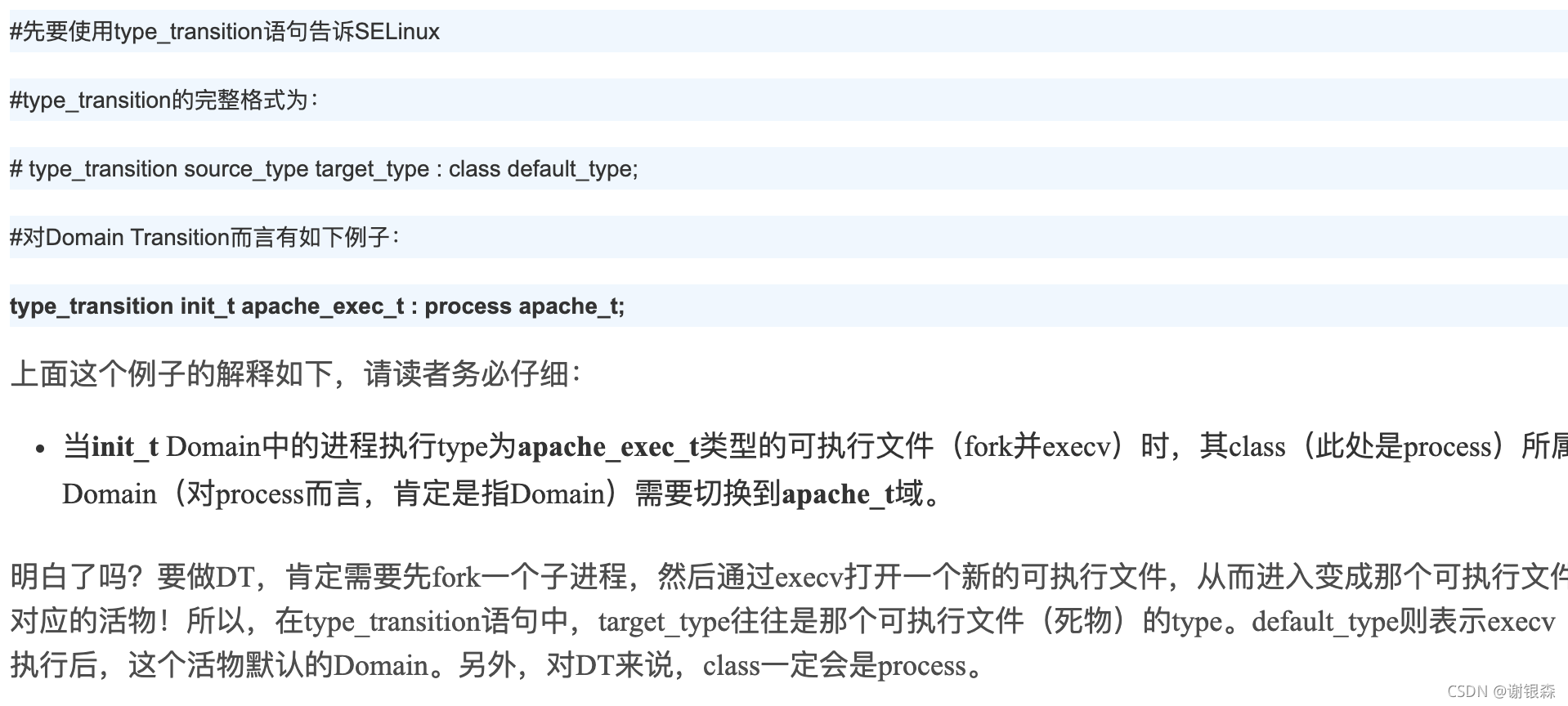
关键字type_transition
类型转换宏
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!