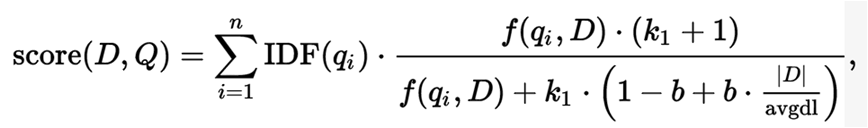Term weight algorithm in IR
1 TF-IDF
2 BM25
f是TD-IDF中的TF,|D|是文档D的长度,avgdl是语料库全部文档的平均长度。k1和b是参数。usually chosen, in absence of an advanced optimization, as k1∈[1.2,2.0] and b = 0.75 。
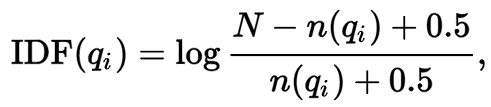
b的相关性
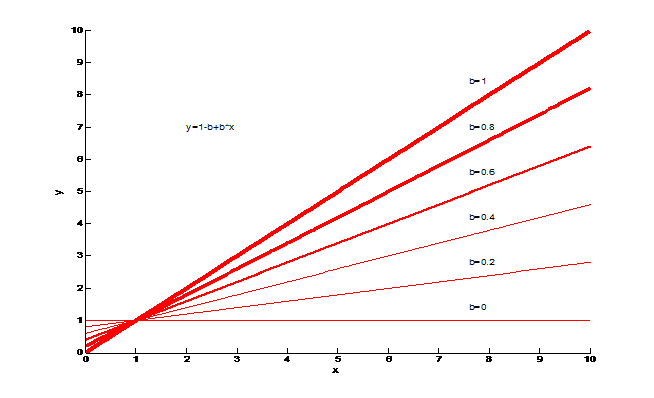
令: y=1-b+b*x, x表示|D|/avgdl, x与y的关系如上图。
b越大,文档长度对相关性得分的影响越大,反之越小。b越大时,当文档长度大于平均长度,那么相关性得分越小;反之越大。
这可以理解为,当文档较长时,包含qi的机会越大,因此,同等fi的情况下,长文档与qi的相关性应该比短文档与qi的相关性弱。
K的相关性
令: y=(tf*(k+1))./(tf+k), k与y的关系如下图。
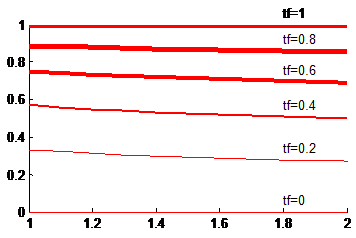
从图表明, k对相似度的影响不大。
3 DFR(divergence form randomness)
Basic Randomness Models
The DFR models are based on this simple idea: “The more the divergence of the within-document term-frequency from its frequency within the collection, the more the information carried by the word t in the document d”. In other words the term-weight is inversely related to the probability of term-frequency within the document d obtained by a model M of randomness:
weight(t|d)∝−logProbM(t∈d|Collection)
(8)
where the subscript M stands for the type of model of randomness employed to compute the probability. The basic models are derived in the following table.
| Basic DFR Models | |
| D | Divergence approximation of the binomial |
| P | Approximation of the binomial |
| BE | Bose-Einstein distribution |
| G | Geometric approximation of the Bose-Einstein |
| I(n) | Inverse Document Frequency model |
| I(F) | Inverse Term Frequency model |
| I(ne) | Inverse Expected Document Frequency model |
If the model M is the binomial distribution, then the basic model is P and computes the value:
−logProbP(t∈d|Collection)=−log(TF tf)ptfqTF−tf
where:
- TF is the term-frequency of the term t in the Collection
- tf is the term-frequency of the term t in the document d
- N is the number of documents in the Collection
- p is 1/N and q=1-p
Similarly, if the model M is the geometric distribution, then the basic model is G and computes the value:
where λ = F/N.
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!