ros中rqt_plot画出速度曲线
ros中rqt_plot画出速度曲线
- 前言
- 一、rqt_plot是什么?
- 二、使用步骤
- 1. 代码
- 2.操作实现:
- 三、速度参数更改;
- 1. 代码
- 2.操作实现:
- 总结
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、rqt_plot是什么?
- 二、使用步骤
- 1. 代码
- 2.操作实现:
- 三、速度参数更改;
- 1. 代码
- 2.操作实现:
- 总结
前言
提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容:
例如:随着人工智能的不断发展,机器学习这门技术也越来越重要,很多人都开启了学习机器学习,本文就介绍了机器学习的基础内容。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、rqt_plot是什么?
一种工具,该工具是为了解决数据分析任务而创建的。
二、使用步骤
1. 代码
publish_node.cpp:
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h" //use data struct of std_msgs/String
#include "mbot_linux_serial.h"
#include "topic_example/speed.h"
#include 2.操作实现:
代码如下(示例):
$ roscore
$ rosrun topic_example publish_node
$ rqt_plot /myspeed
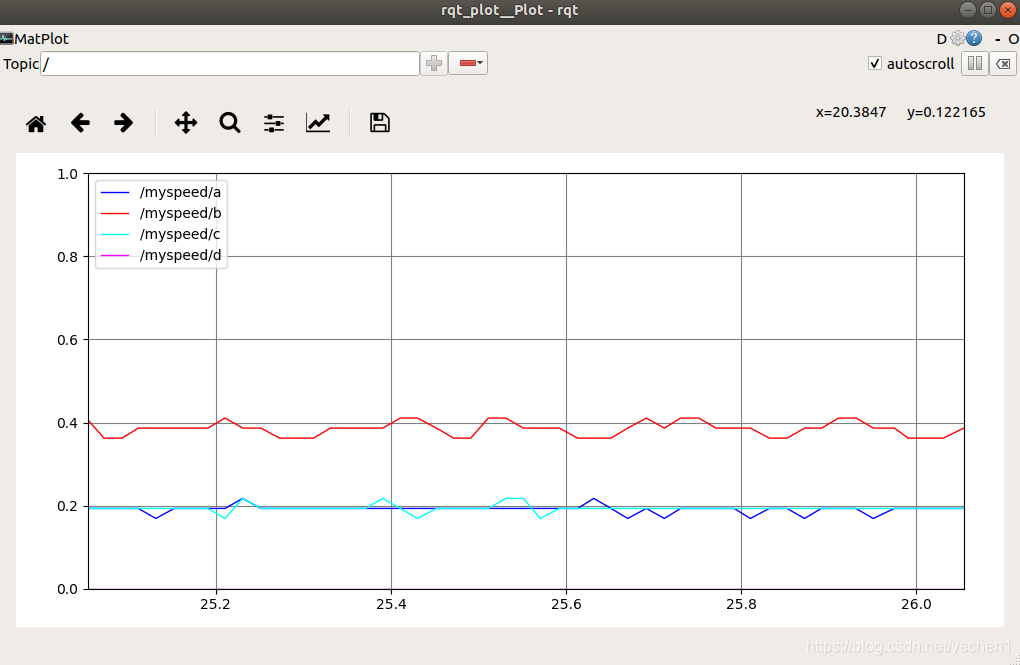
三、速度参数更改;
不完善:
1. 代码
增加节点:
speed_publisher.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 该例程将发布/speed_info话题,自定义消息类型topic_example::Personimport rospy
from topic_example.msg import speeddef velocity_publisher():# ROS节点初始化rospy.init_node('speed_publisher', anonymous=True)# 创建一个Publisher,发布名为/person_info的topic,消息类型为learning_topic::Person,队列长度10speed_info_pub = rospy.Publisher('/speed_info', speed, queue_size=10)#设置循环的频率rate = rospy.Rate(10) while not rospy.is_shutdown():# 初始化learning_topic::Person类型的消息speed_msg = speed()speed_msg.a = 0.3;speed_msg.b = 0.2;speed_msg.c = 0.4;# 发布消息speed_info_pub.publish(speed_msg)rospy.loginfo("Publsh speed message[%f, %f, %f]", speed_msg.a, speed_msg.b, speed_msg.c)# 按照循环频率延时rate.sleep()if __name__ == '__main__':try:velocity_publisher()except rospy.ROSInterruptException:pass更改:
publish_node.cpp:
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h" //use data struct of std_msgs/String
#include "mbot_linux_serial.h"
#include "topic_example/speed.h"
#include 2.操作实现:
代码如下(示例):
$ roscore
$ rosrun topic_example publish_node
$ rqt_plot /myspeed
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了 rqt_plot 的使用,而 rqt_plot 提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!