gps点集合构造 边与边无交叉的多边形(java版)
目的
- 一个点集合,可以输出多个不交叉的多边形;此类只能做到输出其中的一个,即:按夹角大小排序。(如下图左)
- 不按夹角大小排序,也能输出得到不交叉的多边形(如下图右)。所以: 实际应用中,往往还是要根据实际情况来给各点排序、输出符合需求的多边形(如下图右);纯粹依赖排序这样的纯技术思维是不可取的。
输出图例
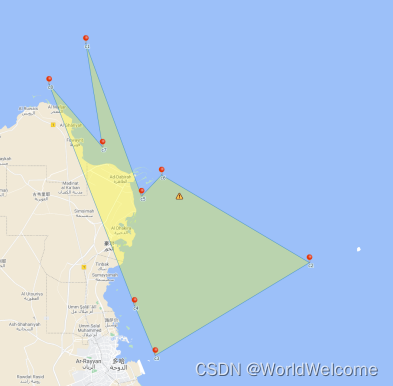
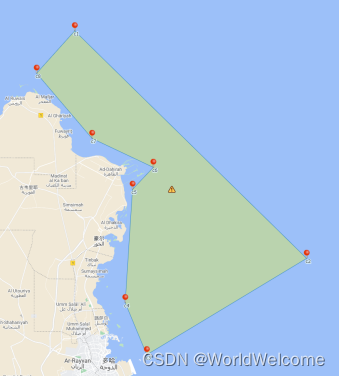
代码
1.PolygonSort
package util.polygon_sort;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;/** 点集合构造简单多边形,按逆时针,排序夹角,达到:边与边无交叉。* 一个点集合,可以输出多个不交叉的多边形;此类只能做到输出其中的一个。* 实际应用中,往往还是要根据实际情况来排序各点输出想要的多边形,而不是绝对按照夹角大小来排序。* Author:James Wang*/
public class PolygonSort{public static void main(String[] args) {/*Coordinate p1 = new Coordinate(53.0418333,24.9208333);//经度在前,纬度在后。Coordinate p2 = new Coordinate(53.0446667,24.9175); Coordinate p3 = new Coordinate(53.0448333,24.9045);Coordinate p4 = new Coordinate(53.0481667,24.9211667);Coordinate p5 = new Coordinate(53.057,24.8946667);Coordinate p6 = new Coordinate(53.0568333,24.8938333); Coordinate p7 = new Coordinate(54.0568333,24.9038333); Coordinate[] pList = { p1,p2,p3,p4,p5,p6,p7 }; Map sortedMap = sort(pList) ;for (Map.Entry entry:sortedMap.entrySet() ){System.out.println("angle=" + entry.getKey() +",坐标等于 " + entry.getValue().toString() );}*///String s = "POLYGON((63.2505 24.6003333,62.5005 24.6003333,62.5005 24.3503333,63.2505 24.3503333))";String s = "POLYGON((51.41 26.352,52.2375 25.6245,51.6675 25.3138333,51.5903333 25.4816667,51.617 25.8458333,51.6913333 25.9155,51.4716667 26.0091667,51.275 26.2171667))";s = s.substring("POLYGON((".length(),s.lastIndexOf("))"));String[] ar = s.split(",");Map sortedMap2 = sort(ar) ;for (Map.Entry entry:sortedMap2.entrySet() ){System.out.println("angle=" + entry.getKey() +",坐标等于 " + entry.getValue().toString() );} }/* https://www.cnblogs.com/andyzeng/p/3754005.html* 点集合构造 简单多边形,排序 夹角,达到:边与边无交叉。*/public static Map sort(Coordinate[] pList) {int minIdx = findMinLat(pList);Map bMap = getAngleMap(pList,minIdx);Map sortedMap = new TreeMap(new MapKeyComparator());sortedMap.putAll(bMap);/*double[] angle = getAngleList(pList,minIdx);/double[] sortedAngle = ArraySort.bubbleSort(angle,"asc");*/return sortedMap;}/** 计算每个点到最小纬度点的angle*/public static Map getAngleMap(Coordinate[] pList,int minIdx) {Map map = new HashMap();double angle = 0;for(int i=0;i" + (minIdx+1) + ":角度"+ angle); }map.put(angle,pList[i]);}return map;}/*public static double[] getAngleList(Coordinate[] pList,int minIdx) {double[] angleList = new double[pList.length];for(int i=0;i" + (minIdx+1) + ":角度"+ angleList[i]); }else {angleList[i] = 0;}}return angleList;}*//** 找到最小lat的起点point,* 起点,在所有的其它点的下面,这样 其它点到起点的角度angle,都为正值(0度~180度),容易排序*/public static int findMinLat(Coordinate[] pList) {int minIdx = 0;double min = 10000000;int minIdx2 = -1 ;for(int i=0;i=0 ) {//System.out.println( "------第2遍---------最小lat的point的序号 为: " + (minIdx+1) + "=数组游标" + minIdx + "+1");if( pList[minIdx2].getLon() > pList[minIdx].getLon() ) {return minIdx2;}else if(pList[minIdx2].getLon() > pList[minIdx].getLon() ){System.out.println( "存在完全相同的点,不正常,手工剔除它们");return -1;}}return minIdx;}public static double aTan2(Coordinate p1,Coordinate p2) {//注意这里的aTan2返回degree,not radiandouble x = p2.getLon() - p1.getLon();double y = p2.getLat() - p1.getLat();//System.out.print(y + "," + x );return Math.toDegrees( Math.atan2(y,x) );}/*java的atan2函数学习例子 */public static void test() {double d = 45;double dR = Math.toRadians(d);//角度 转 弧度//System.out.println( (d* 180) / Math.PI);System.out.println( "tag " + d+ "(角)度=弧度:" + dR + "=" + Math.tan(dR) + ",约等于1, Math.atan(dR)= " + Math.atan(dR));//0.9999999999999999 约 等于 1//System.out.println( "atag45度=" + Math.atan(dR) + ",这个非常奇怪不等于 Math.tan !!");//0.9999999999999999System.out.println( "java.lang.Math.atan2()是已知一个角的正切值(也就是 y/x),求该角的弧度值。比如:Math.atan2(1,1) = " + Math.atan2(1,1) + ",转换成角度=" + Math.toDegrees( Math.atan2(1,1) ));//0.9999999999999999double dR30 = Math.toRadians(30);System.out.println("---------");System.out.println("正玄sin 30度=1/2=" + Math.sin(dR30) + "");//System.out.println("反正玄 asin 30度=2/1=" + Math.asin(dR30) + ",1/Math.sin(dR30)=" + (1/Math.sin(dR30) ) );//System.out.println("---------");System.out.println("cos 30 度=sqrt(3)/2=" + Math.cos(dR30) + ", 而手工计算(Math.sqrt(3)/2)= " + (Math.sqrt(3)/2) );//System.out.println("tag 30 度=1/sqrt(3)=" +Math.tan(dR30) + ", 而手工计算(1/Math.sqrt(3))= " + (1/Math.sqrt(3)));// System.out.println(Math.atan(dR30) + ",squar(3)/1=" + Math.sqrt(3));// System.out.println("---------");Coordinate p1 = new Coordinate(0,0);Coordinate p2 = new Coordinate(1,1);Coordinate p3 = new Coordinate(-1,Math.sqrt(3));System.out.println( aTan2(p1,p2) + ",角度=" + Math.toDegrees(aTan2(p1,p2) ));System.out.println( aTan2(p1,p3) + ",角度=" + Math.toDegrees(aTan2(p1,p3) ));}public static Map sort(String[] strList) {Coordinate[] pList = new Coordinate[strList.length];Coordinate p = null;double lat,lon;for( int i=0;i2.Coordinate
package util.polygon_sort;public class Coordinate {double lat;double lon;public Coordinate(double lon,double lat) {//经度在前,纬度在后。this.lat = lat;this.lon = lon;}public Coordinate(String lon,String lat) {//经度在前,纬度在后。this.lat = Double.parseDouble(lat);this.lon = Double.parseDouble(lon);} public void setLat(double lat) {this.lat = lat;}public double getLat() {return lat;}public void setLon(double lon) {this.lon = lon;}public double getLon() {return lon;} @Overridepublic String toString() {return lon + " " + lat ;}
}
参考文章
几何算法:点集合构造简单多边形 - AndyZeng - 博客园
Java数学函数 Math.atan2()详解 - 己平事 - 博客园
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!
