操作系统 实验七 动态分区分配方式的模拟
前言,最后一个样例也就是实验指导书的样例,的截图显示最佳适应算法存在bug,相邻分区没有进行合并,这个bug已经修复。
实验七 动态分区分配方式的模拟
一、实验目的
- 了解动态分区分配方式中使用的数据结构和分配算法,并进一步加深对动态分区存储管理方式及其实现过程的理解。
二、实验环境
-
硬件环境:计算机一台,局域网环境;
-
软件环境: Windows或Linux操作系统, C语言编程环境。
三、实验内容
-
用C语言分别实现采用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法的动态分区分配过程alloc( )和回收过程free( )。其中,空闲分区通过空闲分区链来管理:在进行内存分配时,系统优先使用空闲区低端的空间。
-
假设初始状态下,可用的内存空间为640KB,并有下列的请求序列:
- 作业1申请130KB。
- 作业2申请60KB。
- 作业3申请100KB。
- 作业2释放60KB。
- 作业4申请200KB。
- 作业3释放100KB。
- 作业1释放130KB。
- 作业5申请140KB。
- 作业6申请60KB。
- 作业7申请50KB。
- 作业6释放60KB。
请分别采用首次适应算法和最佳适应算法,对内存块进行分配和回收,要求每次分配和回收后显示出空闲分区链的情况。
/** @Description:* @version:* @Author:* @Date: 2021-05-27 09:11:39* @LastEditors: Please set LastEditors* @LastEditTime: 2021-05-28 15:13:05*/
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include - 验证回收内存时内存块前邻接:

该测试数据的两算法结果相同
- 验证后邻接:

该测试数据的两算法结果相同
-
验证前后都邻接:

该测试数据的两算法结果相同
-
验证存在阻塞作业的情况:
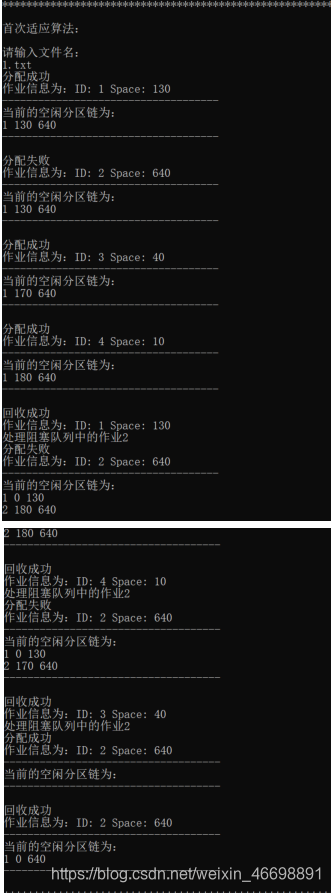
该测试数据的两算法结果相同
-
验证多个阻塞作业的情况:
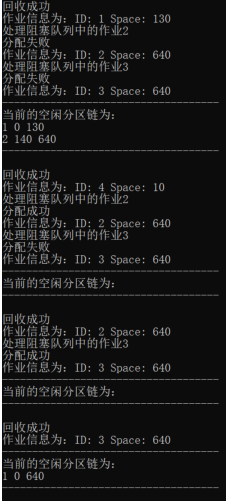
-
验证最佳适应:


-
验证实验指导书的例子:


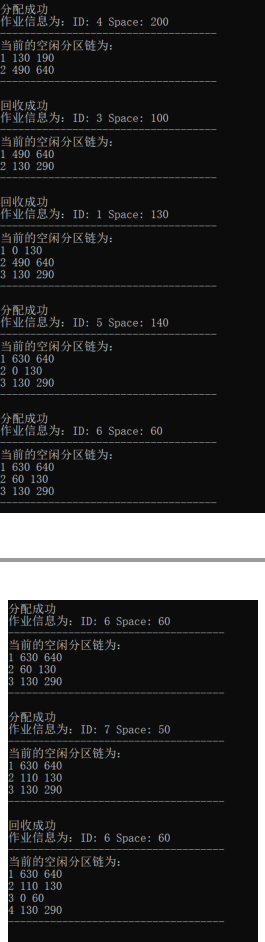
四、实验总结
- 结合实验情况,谈谈你对存储管理的理解和体会。
- 存储管理可以有效地对外部存储资源和内存进行管理,可以完成存储分配,存储共享,存储保护,存储扩充,地址映射等重要功能,对操作系统的性能有很重要的影响。首次适应算法和最佳适应算法是存储管理中两个十分重要的页面置换算法。
- 首次适应算法从空闲分区链首开始查找,直至找到一个能满足其大小要求的空闲分区为止。然后再按照作业的大小,从该分区中划出一块内存分配给请求者,余下的空闲分区仍留在空闲分区链中。该算法倾向于使用内存中低地址部分的空闲区,在高地址部分的空闲区很少被利用,从而保留了高地址部分的大空闲区,为以后到达的大作业分配大的内存空间创造了条件。但是低地址部分不断被划分,留下许多难以利用、很小的空闲区,而每次查找又都从低地址部分开始,会增加查找的开销。
- 最佳适应算法总是把既能满足要求,又是最小的空闲分区分配给作业。为了加速查找,该算法将所有的空闲区按大小排序后,以递增顺序形成一个空白链。这样每次找到的第一个满足要求的空闲区,必然是最优的。这样,每次分配给文件的都是最合适该文件大小的分区,但是内存中留下许多难以利用的小的空闲区。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!