android Q 显示系统(一) VSync
VSync是垂直同步(Vertical Synchronization)的简称。基本的思路是将设备的FPS和显示屏同步起来。其目的是避免显示出现"撕裂"现象,此文章主要是在android 10的代码上追下VSync的主要流程,以后用来自己复习总结,有错误还请指出.
(1)VSync注册(接收HW_VSync)
SurfaceFlinger.h 继承自ComposerCallback
class SurfaceFlinger : private HWC2::ComposerCallback()/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------* HWC2::ComposerCallback / HWComposer::EventHandler interface*/void onVsyncReceived(int32_t sequenceId, hwc2_display_t hwcDisplayId,int64_t timestamp) override;void onHotplugReceived(int32_t sequenceId, hwc2_display_t hwcDisplayId,HWC2::Connection connection) override;void onRefreshReceived(int32_t sequenceId, hwc2_display_t hwcDisplayId) override;HWC2.h ComposerCallback定义
class ComposerCallback {public:virtual void onHotplugReceived(int32_t sequenceId, hwc2_display_t display,Connection connection) = 0;virtual void onRefreshReceived(int32_t sequenceId,hwc2_display_t display) = 0;virtual void onVsyncReceived(int32_t sequenceId, hwc2_display_t display,int64_t timestamp) = 0;virtual ~ComposerCallback() = default;
};HWC2.cpp 实现Hwc2::IComposerCallback(
ComposerHal.h --> namespace android{ namespace Hwc2 {
namespace V2_1 = hardware::graphics::composer::V2_1;
using V2_1::IComposerCallback;
}})
class ComposerCallbackBridge : public Hwc2::IComposerCallback {
public:ComposerCallbackBridge(ComposerCallback* callback, int32_t sequenceId): mCallback(callback), mSequenceId(sequenceId) {}Return onHotplug(Hwc2::Display display,IComposerCallback::Connection conn) override{HWC2::Connection connection = static_cast(conn);mCallback->onHotplugReceived(mSequenceId, display, connection);return Void();}Return onRefresh(Hwc2::Display display) override{mCallback->onRefreshReceived(mSequenceId, display);return Void();}Return onVsync(Hwc2::Display display, int64_t timestamp) override{mCallback->onVsyncReceived(mSequenceId, display, timestamp);return Void();}private:ComposerCallback* mCallback;int32_t mSequenceId;
}; 以上是将用于VSync注册的关键class,下面是真正的注册过程:
SurfaceFlinger.cpp 在init中注册HWComposer的回调
// Do not call property_set on main thread which will be blocked by init
// Use StartPropertySetThread instead.
void SurfaceFlinger::init() {/**/mCompositionEngine->getHwComposer().registerCallback(this, getBE().mComposerSequenceId);// Process any initial hotplug and resulting display changes./**/
}HWComposer.cpp 注册HWC2::Device的回调
void HWComposer::registerCallback(HWC2::ComposerCallback* callback,int32_t sequenceId) {mHwcDevice->registerCallback(callback, sequenceId);
}
HWC2.cpp 实例化ComposerCallbackBridge注册android::Hwc2::Composer的回调
void Device::registerCallback(ComposerCallback* callback, int32_t sequenceId) {if (mRegisteredCallback) {ALOGW("Callback already registered. Ignored extra registration ""attempt.");return;}mRegisteredCallback = true;sp callbackBridge(new ComposerCallbackBridge(callback, sequenceId));mComposer->registerCallback(callbackBridge);
} ComposerHal.cpp 注册hardware::graphics::composer::V2_1::IComposerClient的回调
void Composer::registerCallback(const sp& callback)
{auto ret = mClient->registerCallback(callback);if (!ret.isOk()) {ALOGE("failed to register IComposerCallback");}
}
以上为VSync的注册全过程,可以看到VSync的产生还是会受硬件控制的.
(2)VSync 从HIDL到SurfaceFlinger的分发(HW_VSync到SW_VSync)
hardware::graphics::composer::V2_1::IComposerClient.h 开始分发给Hwc2::IComposerCallback
class HalEventCallback : public Hal::EventCallback {public:HalEventCallback(const sp callback, ComposerResources* resources): mCallback(callback), mResources(resources) {}/**/void onVsync(Display display, int64_t timestamp) {auto ret = mCallback->onVsync(display, timestamp);ALOGE_IF(!ret.isOk(), "failed to send onVsync: %s", ret.description().c_str());}/**/};
HWC2.cpp 分发给class SurfaceFlinger : private HWC2::ComposerCallback
class ComposerCallbackBridge : public Hwc2::IComposerCallback {
public:ComposerCallbackBridge(ComposerCallback* callback, int32_t sequenceId): mCallback(callback), mSequenceId(sequenceId) {}/**/Return onVsync(Hwc2::Display display, int64_t timestamp) override{mCallback->onVsyncReceived(mSequenceId, display, timestamp);return Void();}/**/
}; SurfaceFlinger.cpp开始分发
void SurfaceFlinger::onVsyncReceived(int32_t sequenceId, hwc2_display_t hwcDisplayId,int64_t timestamp) {ATRACE_NAME("SF onVsync");Mutex::Autolock lock(mStateLock);// Ignore any vsyncs from a previous hardware composer.if (sequenceId != getBE().mComposerSequenceId) {return;}if (!getHwComposer().onVsync(hwcDisplayId, timestamp)) {return;}if (hwcDisplayId != getHwComposer().getInternalHwcDisplayId()) {// For now, we don't do anything with external display vsyncs.return;}bool periodChanged = false;mScheduler->addResyncSample(timestamp, &periodChanged);if (periodChanged) {mVsyncModulator.onRefreshRateChangeDetected();}
}Scheduler.cpp 将VSync传递给DispSync。如果DipSync检测到vsync周期已更改,periodChange将为true,否则为false。
void Scheduler::addResyncSample(const nsecs_t timestamp, bool* periodChanged) {bool needsHwVsync = false;*periodChanged = false;{ // Scope for the lockstd::lock_guard lock(mHWVsyncLock);if (mPrimaryHWVsyncEnabled) {needsHwVsync = mPrimaryDispSync->addResyncSample(timestamp, periodChanged);}}if (needsHwVsync) {enableHardwareVsync();} else {disableHardwareVsync(false);}
} DispSync.cpp 往SW VSync模型中添加硬件VSync时间戳样本,同时在利用已经存在硬件vsync时间戳的实时更新下一次SW VSync的时间.此文章更详细:https://blog.csdn.net/zhuawalibai/article/details/87976799
bool DispSync::addResyncSample(nsecs_t timestamp, bool* periodChanged) {Mutex::Autolock lock(mMutex);ALOGV("[%s] addResyncSample(%" PRId64 ")", mName, ns2us(timestamp));*periodChanged = false;const size_t idx = (mFirstResyncSample + mNumResyncSamples) % MAX_RESYNC_SAMPLES;mResyncSamples[idx] = timestamp;if (mNumResyncSamples == 0) {mPhase = 0;ALOGV("[%s] First resync sample: mPeriod = %" PRId64 ", mPhase = 0, ""mReferenceTime = %" PRId64,mName, ns2us(mPeriod), ns2us(timestamp));} else if (mPendingPeriod > 0) {// mNumResyncSamples > 0, so priorIdx won't overflowconst size_t priorIdx = (mFirstResyncSample + mNumResyncSamples - 1) % MAX_RESYNC_SAMPLES;const nsecs_t lastTimestamp = mResyncSamples[priorIdx];const nsecs_t observedVsync = std::abs(timestamp - lastTimestamp);if (std::abs(observedVsync - mPendingPeriod) < std::abs(observedVsync - mPeriod)) {// Observed vsync is closer to the pending period, so reset the// model and flush the pending period.resetLocked();mPeriod = mPendingPeriod;mPendingPeriod = 0;if (mTraceDetailedInfo) {ATRACE_INT("DispSync:PendingPeriod", mPendingPeriod);}*periodChanged = true;}}// Always update the reference time with the most recent timestamp.mReferenceTime = timestamp;mThread->updateModel(mPeriod, mPhase, mReferenceTime);if (mNumResyncSamples < MAX_RESYNC_SAMPLES) {mNumResyncSamples++;} else {mFirstResyncSample = (mFirstResyncSample + 1) % MAX_RESYNC_SAMPLES;}updateModelLocked();if (mNumResyncSamplesSincePresent++ > MAX_RESYNC_SAMPLES_WITHOUT_PRESENT) {resetErrorLocked();}if (mIgnorePresentFences) {// If we're ignoring the present fences we have no way to know whether// or not we're synchronized with the HW vsyncs, so we just request// that the HW vsync events be turned on.return true;}// Check against kErrorThreshold / 2 to add some hysteresis before having to// resync againbool modelLocked = mModelUpdated && mError < (kErrorThreshold / 2) && mPendingPeriod == 0;ALOGV("[%s] addResyncSample returning %s", mName, modelLocked ? "locked" : "unlocked");if (modelLocked) {mThread->lockModel();}return !modelLocked;
}DispSync.cpp fireCallbackInvocations函数遍历回调列表调用其onDispSyncEvent函数。
void fireCallbackInvocations(const std::vector& callbacks) {if (mTraceDetailedInfo) ATRACE_CALL();for (size_t i = 0; i < callbacks.size(); i++) {callbacks[i].mCallback->onDispSyncEvent(callbacks[i].mEventTime);}} DispSyncSource.h (DispSyncSource final : public VSyncSource, private DispSync::Callback)
DispSyncSource.cpp 实现 DispSync::Callback ,在自身onDispSyncEvent函数中处理VSync信号
void DispSyncSource::onDispSyncEvent(nsecs_t when) {VSyncSource::Callback* callback;{std::lock_guard lock(mCallbackMutex);callback = mCallback;if (mTraceVsync) {mValue = (mValue + 1) % 2;ATRACE_INT(mVsyncEventLabel.c_str(), mValue);}}if (callback != nullptr) {callback->onVSyncEvent(when);}
}EventThread.h (class EventThread : public android::EventThread, private VSyncSource::Callback)
EventThread.cpp 实现 DispSync::Callback,在自身onVSyncEvent去创建Event事件
void EventThread::onVSyncEvent(nsecs_t timestamp) {std::lock_guard lock(mMutex);LOG_FATAL_IF(!mVSyncState);mPendingEvents.push_back(makeVSync(mVSyncState->displayId, timestamp, ++mVSyncState->count));mCondition.notify_all();
}DisplayEventReceiver::Event makeVSync(PhysicalDisplayId displayId, nsecs_t timestamp,uint32_t count) {DisplayEventReceiver::Event event;event.header = {DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC, displayId, timestamp};event.vsync.count = count;return event;
} EventThread.cpp threadMain循环处理Event事件
void EventThread::threadMain(std::unique_lock& lock) {DisplayEventConsumers consumers;while (mState != State::Quit) {std::optional event;// Determine next event to dispatch.if (!mPendingEvents.empty()) {event = mPendingEvents.front();mPendingEvents.pop_front();switch (event->header.type) {case DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_HOTPLUG:if (event->hotplug.connected && !mVSyncState) {mVSyncState.emplace(event->header.displayId);} else if (!event->hotplug.connected && mVSyncState &&mVSyncState->displayId == event->header.displayId) {mVSyncState.reset();}break;case DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC:if (mInterceptVSyncsCallback) {mInterceptVSyncsCallback(event->header.timestamp);}break;}}bool vsyncRequested = false;// Find connections that should consume this event.auto it = mDisplayEventConnections.begin();while (it != mDisplayEventConnections.end()) {if (const auto connection = it->promote()) {vsyncRequested |= connection->vsyncRequest != VSyncRequest::None;if (event && shouldConsumeEvent(*event, connection)) {consumers.push_back(connection);}++it;} else {it = mDisplayEventConnections.erase(it);}}if (!consumers.empty()) {dispatchEvent(*event, consumers);consumers.clear();}State nextState;if (mVSyncState && vsyncRequested) {nextState = mVSyncState->synthetic ? State::SyntheticVSync : State::VSync;} else {ALOGW_IF(!mVSyncState, "Ignoring VSYNC request while display is disconnected");nextState = State::Idle;}if (mState != nextState) {if (mState == State::VSync) {mVSyncSource->setVSyncEnabled(false);} else if (nextState == State::VSync) {mVSyncSource->setVSyncEnabled(true);}mState = nextState;}if (event) {continue;}// Wait for event or client registration/request.if (mState == State::Idle) {mCondition.wait(lock);} else {// Generate a fake VSYNC after a long timeout in case the driver stalls. When the// display is off, keep feeding clients at 60 Hz.const auto timeout = mState == State::SyntheticVSync ? 16ms : 1000ms;if (mCondition.wait_for(lock, timeout) == std::cv_status::timeout) {ALOGW_IF(mState == State::VSync, "Faking VSYNC due to driver stall");LOG_FATAL_IF(!mVSyncState);mPendingEvents.push_back(makeVSync(mVSyncState->displayId,systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC),++mVSyncState->count));}}}
} EventThread.cpp dispatchEvent 分发事件给EventThreadConnection
void EventThread::dispatchEvent(const DisplayEventReceiver::Event& event,const DisplayEventConsumers& consumers) {for (const auto& consumer : consumers) {switch (consumer->postEvent(event)) {case NO_ERROR:break;case -EAGAIN:// TODO: Try again if pipe is full.ALOGW("Failed dispatching %s for %s", toString(event).c_str(),toString(*consumer).c_str());break;default:// Treat EPIPE and other errors as fatal.removeDisplayEventConnectionLocked(consumer);}}
}status_t EventThreadConnection::postEvent(const DisplayEventReceiver::Event& event) {ssize_t size = DisplayEventReceiver::sendEvents(&mChannel, &event, 1);return size < 0 ? status_t(size) : status_t(NO_ERROR);
}EventThread.cpp EventThreadConnection::postEvent分发事件
status_t EventThreadConnection::postEvent(const DisplayEventReceiver::Event& event) {ssize_t size = DisplayEventReceiver::sendEvents(&mChannel, &event, 1);return size < 0 ? status_t(size) : status_t(NO_ERROR);
}
DisplayEventReceiver.cpp EventThreadConnection通过DisplayEventReceiver::sendEvents静态方法利用mChannel(gui::BitTube)去发送事件.
public:enum {DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC = fourcc('v', 's', 'y', 'n'),DISPLAY_EVENT_HOTPLUG = fourcc('p', 'l', 'u', 'g'),DISPLAY_EVENT_CONFIG_CHANGED = fourcc('c', 'o', 'n', 'f'),};struct Event {struct Header {uint32_t type;PhysicalDisplayId displayId;nsecs_t timestamp __attribute__((aligned(8)));};struct VSync {uint32_t count;};struct Hotplug {bool connected;};struct Config {int32_t configId;};Header header;union {VSync vsync;Hotplug hotplug;Config config;};};ssize_t DisplayEventReceiver::sendEvents(gui::BitTube* dataChannel,Event const* events, size_t count)
{return gui::BitTube::sendObjects(dataChannel, events, count);
}BitTube.cpp sendObjects 会利用内置的成对的socket发送事件.
// send objects (sized blobs). All objects are guaranteed to be written or the call fails.template static ssize_t sendObjects(BitTube* tube, T const* events, size_t count) {return sendObjects(tube, events, count, sizeof(T));}ssize_t BitTube::sendObjects(BitTube* tube, void const* events, size_t count, size_t objSize) {const char* vaddr = reinterpret_cast(events);ssize_t size = tube->write(vaddr, count * objSize);// should never happen because of SOCK_SEQPACKETLOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF((size >= 0) && (size % static_cast(objSize)),"BitTube::sendObjects(count=%zu, size=%zu), res=%zd (partial events were ""sent!)",count, objSize, size);// ALOGE_IF(size<0, "error %d sending %d events", size, count);return size < 0 ? size : size / static_cast(objSize);
}ssize_t BitTube::write(void const* vaddr, size_t size) {ssize_t err, len;do {len = ::send(mSendFd, vaddr, size, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);// cannot return less than size, since we're using SOCK_SEQPACKETerr = len < 0 ? errno : 0;} while (err == EINTR);return err == 0 ? len : -err;
}
到此为止,SufaceFlinger之下的VSync分发过程就到此为止了,此前分析是从hidl开始到SufaceFlinger结束的,因为从SufaceFlinger到app的发送过程需要先分析些前提,所以此处暂做一个小结.
onVsync( hardware::graphics::composer::V2_1::IComposerClient.h)
--> onVsync(ComposerHal.h hardware::graphics::composer::V2_1::IComposerCallback)
--> onVsyncReceived(SurfaceFlinger.cpp class SurfaceFlinger : private HWC2::ComposerCallback)
--> addResyncSample(Scheduler.cpp)
--> addResyncSample(DispSync.cpp 利用硬件VSync时间戳样本实时更新SW VSync模型)
--> fireCallbackInvocations(DispSync.cpp)
--> onDispSyncEvent(DispSyncSource final : public VSyncSource, private DispSync::Callback)
--> onVSyncEvent(class EventThread : public android::EventThread, private VSyncSource::Callback)
--> mPendingEvents.push_back(makeVSync)(EventThread.cpp生成类型为DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC的DisplayEventReceiver::Event)
threadMain(EventThread.cpp 循环读取DisplayEventReceiver::Event)
--> mPendingEvents.front()/threadMain (EventThread.cpp 通过threadMain提取DisplayEventReceiver::Event)
--> dispatchEvent(EventThread.cpp)
--> postEvent(EventThread.cpp)
-->static DisplayEventReceiver::sendEvents(DisplayEventReceiver.cpp)
--> gui::BitTube::sendObjects(BitTube.h)
--> sendObjects(BitTube.cpp)
--> write(BitTube.cpp 利用socket发送数据)
以下是app与SF分别接受VSync的追踪
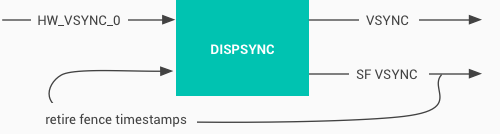
(3)VSync 从SurfaceFlinger到SurfaceFlinger的分发(SF VSync)
(a)SurfaceFlinger自己对于VSync的注册过程为
SurfaceFlinger.cpp SurfaceFlinger会先生成std::unique_ptr
SurfaceFlinger::SurfaceFlinger(Factory& factory, SkipInitializationTag): mFactory(factory),mPhaseOffsets(mFactory.createPhaseOffsets()),mInterceptor(mFactory.createSurfaceInterceptor(this)),mTimeStats(mFactory.createTimeStats()),mEventQueue(mFactory.createMessageQueue()),mCompositionEngine(mFactory.createCompositionEngine()) {}void SurfaceFlinger::onFirstRef()
{mEventQueue->init(this);
}void SurfaceFlinger::init() {/* */mSfConnectionHandle = mScheduler->createConnection("sf", mPhaseOffsets->getCurrentSfOffset(),resyncCallback, [this](nsecs_t timestamp) {mInterceptor->saveVSyncEvent(timestamp);});mEventQueue->setEventConnection(mScheduler->getEventConnection(mSfConnectionHandle));/* */
}
(b)SurfaceFlinger自己对于VSync的接收过程
MessageQueue.cpp MessageQueue的setEventConnection函数会利用EventThread中生成时预置的一个EventThreadConnection的stealReceiveChannel方法获取到EventThreadConnection的gui::BitTube,之后利用Handler传递给SurfaceFlinger
int MessageQueue::eventReceiver(int /*fd*/, int /*events*/) {ssize_t n;DisplayEventReceiver::Event buffer[8];while ((n = DisplayEventReceiver::getEvents(&mEventTube, buffer, 8)) > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (buffer[i].header.type == DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC) {mHandler->dispatchInvalidate();break;}}}return 1;
}void MessageQueue::Handler::dispatchInvalidate() {if ((android_atomic_or(eventMaskInvalidate, &mEventMask) & eventMaskInvalidate) == 0) {mQueue.mLooper->sendMessage(this, Message(MessageQueue::INVALIDATE));}
}void MessageQueue::Handler::handleMessage(const Message& message) {switch (message.what) {case INVALIDATE:android_atomic_and(~eventMaskInvalidate, &mEventMask);mQueue.mFlinger->onMessageReceived(message.what);break;case REFRESH:android_atomic_and(~eventMaskRefresh, &mEventMask);mQueue.mFlinger->onMessageReceived(message.what);break;}
}SurfaceFlinger.cpp 会在onMessageReceived中处理接到Message事件.
void SurfaceFlinger::onMessageReceived(int32_t what) NO_THREAD_SAFETY_ANALYSIS {ATRACE_CALL();switch (what) {case MessageQueue::INVALIDATE: {bool frameMissed = previousFrameMissed();bool hwcFrameMissed = mHadDeviceComposition && frameMissed;bool gpuFrameMissed = mHadClientComposition && frameMissed;ATRACE_INT("FrameMissed", static_cast(frameMissed));ATRACE_INT("HwcFrameMissed", static_cast(hwcFrameMissed));ATRACE_INT("GpuFrameMissed", static_cast(gpuFrameMissed));if (frameMissed) {mFrameMissedCount++;mTimeStats->incrementMissedFrames();}if (hwcFrameMissed) {mHwcFrameMissedCount++;}if (gpuFrameMissed) {mGpuFrameMissedCount++;}if (mUseSmart90ForVideo) {// This call is made each time SF wakes up and creates a new frame. It is part// of video detection feature.mScheduler->updateFpsBasedOnContent();}if (performSetActiveConfig()) {break;}if (frameMissed && mPropagateBackpressure) {if ((hwcFrameMissed && !gpuFrameMissed) ||mPropagateBackpressureClientComposition) {signalLayerUpdate();break;}}// Now that we're going to make it to the handleMessageTransaction()// call below it's safe to call updateVrFlinger(), which will// potentially trigger a display handoff.updateVrFlinger();bool refreshNeeded = handleMessageTransaction();refreshNeeded |= handleMessageInvalidate();updateCursorAsync();updateInputFlinger();refreshNeeded |= mRepaintEverything;if (refreshNeeded && CC_LIKELY(mBootStage != BootStage::BOOTLOADER)) {// Signal a refresh if a transaction modified the window state,// a new buffer was latched, or if HWC has requested a full// repaintsignalRefresh();}break;}case MessageQueue::REFRESH: {handleMessageRefresh();break;}}
}
SF VSync分发小结
eventReceiver (MessageQueue.cpp)
-->dispatchInvalidate(MessageQueue.cpp)
-->handleMessage(MessageQueue.cpp)
-->onMessageReceived(SurfaceFlinger.cpp)
(4)VSync 从SurfaceFlinger到app的分发
(a)app在SurfaceFlinger中对于VSync的注册过程为:
SurfaceFlinger.cpp 其中在init()中生成专属app的ConnectionHandle,用于在Scheduler中找到自己.
void SurfaceFlinger::init() {/* */mAppConnectionHandle =mScheduler->createConnection("app", mPhaseOffsets->getCurrentAppOffset(),resyncCallback,impl::EventThread::InterceptVSyncsCallback());/* */
}Scheduler.cpp 生成专属app的EventThread用于接收VSync
sp Scheduler::createConnection(const char* connectionName, int64_t phaseOffsetNs, ResyncCallback resyncCallback,impl::EventThread::InterceptVSyncsCallback interceptCallback) {const int64_t id = sNextId++;ALOGV("Creating a connection handle with ID: %" PRId64 "\n", id);std::unique_ptr eventThread =makeEventThread(connectionName, mPrimaryDispSync.get(), phaseOffsetNs,std::move(interceptCallback));auto eventThreadConnection =createConnectionInternal(eventThread.get(), std::move(resyncCallback));mConnections.emplace(id,std::make_unique(new ConnectionHandle(id),eventThreadConnection,std::move(eventThread)));return mConnections[id]->handle;
}std::unique_ptr Scheduler::makeEventThread(const char* connectionName, DispSync* dispSync, int64_t phaseOffsetNs,impl::EventThread::InterceptVSyncsCallback interceptCallback) {std::unique_ptr eventThreadSource =std::make_unique(dispSync, phaseOffsetNs, true, connectionName);return std::make_unique(std::move(eventThreadSource),std::move(interceptCallback), connectionName);
}sp Scheduler::createConnectionInternal(EventThread* eventThread,ResyncCallback&& resyncCallback) {return eventThread->createEventConnection(std::move(resyncCallback));
} 以上是在SurfaceFlinger中生成了专属app的EventThread并注册到DispSync中,此EventThread一边在循环读取着DispSync传来的VSync的事件,一边等待着应用通过SurfaceFlinger在自己中注册应用的VSync接受器IDisplayEventConnection,以下从java层开始记录此注册过程:
ViewRootImpl.java 在ViewRootImpl构造过程中,会生成一个Choreographer,Choreographer是用来协调动画、输入和绘图的时间的
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {/* */mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();/* */}Choreographer.java 中会获取当前线程的独立的一个Choreographer实例,在new Choreographer中会new一个FrameDisplayEventReceiver.
// Thread local storage for the choreographer.private static final ThreadLocal sThreadInstance =new ThreadLocal() {@Overrideprotected Choreographer initialValue() {Looper looper = Looper.myLooper();if (looper == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("The current thread must have a looper!");}Choreographer choreographer = new Choreographer(looper, VSYNC_SOURCE_APP);if (looper == Looper.getMainLooper()) {mMainInstance = choreographer;}return choreographer;}};/*** Gets the choreographer for the calling thread. Must be called from* a thread that already has a {@link android.os.Looper} associated with it.** @return The choreographer for this thread.* @throws IllegalStateException if the thread does not have a looper.*/public static Choreographer getInstance() {return sThreadInstance.get();}private Choreographer(Looper looper, int vsyncSource) {mLooper = looper;mHandler = new FrameHandler(looper);mDisplayEventReceiver = USE_VSYNC? new FrameDisplayEventReceiver(looper, vsyncSource): null;mLastFrameTimeNanos = Long.MIN_VALUE;mFrameIntervalNanos = (long)(1000000000 / getRefreshRate());mCallbackQueues = new CallbackQueue[CALLBACK_LAST + 1];for (int i = 0; i <= CALLBACK_LAST; i++) {mCallbackQueues[i] = new CallbackQueue();}// b/68769804: For low FPS experiments.setFPSDivisor(SystemProperties.getInt(ThreadedRenderer.DEBUG_FPS_DIVISOR, 1));} Choreographer.java FrameDisplayEventReceiver扩展至DisplayEventReceiver
private final class FrameDisplayEventReceiver extends DisplayEventReceiverimplements Runnable {public FrameDisplayEventReceiver(Looper looper, int vsyncSource) {super(looper, vsyncSource);}}DisplayEventReceiver.java 在其构造函数中会通过nativeInit把DisplayEventReceiver的弱引用传到Native层(方便后续通过反射回调),
/*** Creates a display event receiver.** @param looper The looper to use when invoking callbacks.* @param vsyncSource The source of the vsync tick. Must be on of the VSYNC_SOURCE_* values.*/public DisplayEventReceiver(Looper looper, int vsyncSource) {if (looper == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("looper must not be null");}mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference(this), mMessageQueue,vsyncSource);mCloseGuard.open("dispose");} android_view_DisplayEventReceiver.cpp nativeInit函数中NativeDisplayEventReceiver会在new的过程中给予其父类DisplayEventDispatcher的属性赋值,并通过receiver->initialize()与SurfaceFlinger发生联系.
NativeDisplayEventReceiver::NativeDisplayEventReceiver(JNIEnv* env,jobject receiverWeak, const sp& messageQueue, jint vsyncSource) :DisplayEventDispatcher(messageQueue->getLooper(),static_cast(vsyncSource)),mReceiverWeakGlobal(env->NewGlobalRef(receiverWeak)),mMessageQueue(messageQueue) {ALOGV("receiver %p ~ Initializing display event receiver.", this);
}static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,jobject messageQueueObj, jint vsyncSource) {sp messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);if (messageQueue == NULL) {jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");return 0;}sp receiver = new NativeDisplayEventReceiver(env,receiverWeak, messageQueue, vsyncSource);status_t status = receiver->initialize();if (status) {String8 message;message.appendFormat("Failed to initialize display event receiver. status=%d", status);jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.string());return 0;}receiver->incStrong(gDisplayEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz); // retain a reference for the objectreturn reinterpret_cast(receiver.get());
} DisplayEventDispatcher.cpp 其属性mReceiver(DisplayEventReceiver)初始化,看到这个不陌生了把,DisplayEventReceiver的静态函数曾被SurfaceFlinger中调用过,用于BitTube的数据传递,此处在正好用到了它,另外在initialize()中,我们又看到了熟悉的mLooper->addFd,
DisplayEventDispatcher::DisplayEventDispatcher(const sp& looper,ISurfaceComposer::VsyncSource vsyncSource) :mLooper(looper), mReceiver(vsyncSource), mWaitingForVsync(false) {ALOGV("dispatcher %p ~ Initializing display event dispatcher.", this);
}status_t DisplayEventDispatcher::initialize() {status_t result = mReceiver.initCheck();if (result) {ALOGW("Failed to initialize display event receiver, status=%d", result);return result;}int rc = mLooper->addFd(mReceiver.getFd(), 0, Looper::EVENT_INPUT,this, NULL);if (rc < 0) {return UNKNOWN_ERROR;}return OK;
} DisplayEventReceiver.cpp 此时是处于APP的Native运行中,那么是什么样的方法与SurfaceFlinger链接在一起的呢?
其实在BitTube创建之初,BitTube中已经生成了一对互相链接的socket,BitTube会记录这对socket的文件句柄(mReceiveFd,mSendFd),在DisplayEventReceiver的构造函数中利用IDisplayEventConnection的stealReceiveChannel方法,把此时的mReceiveFd替换为SurfaceFlinger中存在的一个BitTube的mReceiveFd,这样就形成了socket的跨线程通信.
DisplayEventReceiver::DisplayEventReceiver(ISurfaceComposer::VsyncSource vsyncSource) {sp sf(ComposerService::getComposerService());if (sf != nullptr) {mEventConnection = sf->createDisplayEventConnection(vsyncSource);if (mEventConnection != nullptr) {mDataChannel = std::make_unique();mEventConnection->stealReceiveChannel(mDataChannel.get());}}
} *** 此处附上BitTube的跨线程通信原理:

app注册到SurfaceFlinger小结:
new ViewRootImpl(ViewRootImpl.java)
-->getInstance(Choreographer.java)
--> new Choreographer(Choreographer.java)
--> new FrameDisplayEventReceiver(Choreographer.java)
--> new DisplayEventReceiver(DisplayEventReceiver.java)
--> nativeInit(android_view_DisplayEventReceiver.cpp)
--> initialize(DisplayEventDispatcher.cpp)
--> new DisplayEventReceiver(DisplayEventReceiver.cpp)
--> stealReceiveChannel(DisplayEventReceiver.cpp)
(b)SurfaceFlinger分发VSync到app的过程:
DisplayEventDispatcher.cpp此实例中会在handleEvent中利用processPendingEvents读取VSync事件,并通过dispatchVsync传递出去
int DisplayEventDispatcher::handleEvent(int, int events, void*) {if (events & (Looper::EVENT_ERROR | Looper::EVENT_HANGUP)) {ALOGE("Display event receiver pipe was closed or an error occurred. ""events=0x%x", events);return 0; // remove the callback}if (!(events & Looper::EVENT_INPUT)) {ALOGW("Received spurious callback for unhandled poll event. ""events=0x%x", events);return 1; // keep the callback}// Drain all pending events, keep the last vsync.nsecs_t vsyncTimestamp;PhysicalDisplayId vsyncDisplayId;uint32_t vsyncCount;if (processPendingEvents(&vsyncTimestamp, &vsyncDisplayId, &vsyncCount)) {ALOGV("dispatcher %p ~ Vsync pulse: timestamp=%" PRId64 ", displayId=%"ANDROID_PHYSICAL_DISPLAY_ID_FORMAT ", count=%d",this, ns2ms(vsyncTimestamp), vsyncDisplayId, vsyncCount);mWaitingForVsync = false;dispatchVsync(vsyncTimestamp, vsyncDisplayId, vsyncCount);}return 1; // keep the callback
}bool DisplayEventDispatcher::processPendingEvents(nsecs_t* outTimestamp, PhysicalDisplayId* outDisplayId, uint32_t* outCount) {bool gotVsync = false;DisplayEventReceiver::Event buf[EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];ssize_t n;while ((n = mReceiver.getEvents(buf, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE)) > 0) {ALOGV("dispatcher %p ~ Read %d events.", this, int(n));for (ssize_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {const DisplayEventReceiver::Event& ev = buf[i];switch (ev.header.type) {case DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC:// Later vsync events will just overwrite the info from earlier// ones. That's fine, we only care about the most recent.gotVsync = true;*outTimestamp = ev.header.timestamp;*outDisplayId = ev.header.displayId;*outCount = ev.vsync.count;break;case DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_HOTPLUG:dispatchHotplug(ev.header.timestamp, ev.header.displayId, ev.hotplug.connected);break;case DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_CONFIG_CHANGED:dispatchConfigChanged(ev.header.timestamp, ev.header.displayId, ev.config.configId);break;default:ALOGW("dispatcher %p ~ ignoring unknown event type %#x", this, ev.header.type);break;}}}if (n < 0) {ALOGW("Failed to get events from display event dispatcher, status=%d", status_t(n));}return gotVsync;
}android_view_DisplayEventReceiver.cpp 此处class NativeDisplayEventReceiver : public DisplayEventDispatcher,并实现了其方法dispatchVsync,用于处理VSync.处理的方法是利用之前得到的java实例DisplayEventReceiver,反射使用其方法dispatchVsync
void NativeDisplayEventReceiver::dispatchVsync(nsecs_t timestamp, PhysicalDisplayId displayId,uint32_t count) {JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();ScopedLocalRef receiverObj(env, jniGetReferent(env, mReceiverWeakGlobal));if (receiverObj.get()) {ALOGV("receiver %p ~ Invoking vsync handler.", this);env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),gDisplayEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchVsync, timestamp, displayId, count);ALOGV("receiver %p ~ Returned from vsync handler.", this);}mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "dispatchVsync");
} DisplayEventReceiver.java dispatchVsync方法中调用了onVsync方法,我们需要取器子类中找
// Called from native code.@SuppressWarnings("unused")@UnsupportedAppUsageprivate void dispatchVsync(long timestampNanos, long physicalDisplayId, int frame) {onVsync(timestampNanos, physicalDisplayId, frame);}
Choreographer.java DisplayEventReceiver的子类FrameDisplayEventReceiver重写了onVsync方法,其又利用Message.obtain(mHandler, this)的方法,使得其继承自Runnable的run()方法可以在指定的时间之后运行当前Choreographer的线程中.
@Overridepublic void onVsync(long timestampNanos, long physicalDisplayId, int frame) {// Post the vsync event to the Handler.// The idea is to prevent incoming vsync events from completely starving// the message queue. If there are no messages in the queue with timestamps// earlier than the frame time, then the vsync event will be processed immediately.// Otherwise, messages that predate the vsync event will be handled first.long now = System.nanoTime();if (timestampNanos > now) {Log.w(TAG, "Frame time is " + ((timestampNanos - now) * 0.000001f)+ " ms in the future! Check that graphics HAL is generating vsync "+ "timestamps using the correct timebase.");timestampNanos = now;}if (mHavePendingVsync) {Log.w(TAG, "Already have a pending vsync event. There should only be "+ "one at a time.");} else {mHavePendingVsync = true;}mTimestampNanos = timestampNanos;mFrame = frame;Message msg = Message.obtain(mHandler, this);msg.setAsynchronous(true);mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, timestampNanos / TimeUtils.NANOS_PER_MS);}Choreographer.java 在FrameDisplayEventReceiver的run()方法中开始进入doFrame操作
private final class FrameDisplayEventReceiver extends DisplayEventReceiverimplements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {mHavePendingVsync = false;doFrame(mTimestampNanos, mFrame);}}分发VSync到app的过程小结:
handleEvent(DisplayEventDispatcher.cpp)
-->processPendingEvents(DisplayEventDispatcher.cpp)
-->dispatchVsync(android_view_DisplayEventReceiver.cpp)
-->dispatchVsync(DisplayEventReceiver.java 利用发射机制有native层调用)
-->onVsync(Choreographer.java)
-->sendMessageAtTime(Choreographer.java 指定时间运行run()方法)
-->run(Choreographer.java)
-->doFrame(Choreographer.java)
结尾出附上大神文章(https://www.jianshu.com/p/d3e4b1805c92)中的图用来作为总结:

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!