【Python】scikit-image中的threshold_multiotsu函数
这篇主要是想调用threshold_multiotsu,但是该函数只有在scikit-image0.16.0版本以上才有,但是0.16.0版本以上仅支持python3.6及以上版本。但是我现在所有的环境都是python3.5,为了能使用该函数,从scikit-image中将这部分内容抠取出来。
新建文件test.py
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npfrom skimage import data
from multi_level.multi_thresh import threshold_multiotsu# Setting the font size for all plots.
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 9# The input image.
image = data.camera()# Applying multi-Otsu threshold for the default value, generating
# three classes.
thresholds = threshold_multiotsu(image)# Using the threshold values, we generate the three regions.
regions = np.digitize(image, bins=thresholds)fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 3.5))# Plotting the original image.
ax[0].imshow(image, cmap='gray')
ax[0].set_title('Original')
ax[0].axis('off')# Plotting the histogram and the two thresholds obtained from
# multi-Otsu.
ax[1].hist(image.ravel(), bins=255)
ax[1].set_title('Histogram')
for thresh in thresholds:ax[1].axvline(thresh, color='r')# Plotting the Multi Otsu result.
ax[2].imshow(regions, cmap='Accent')
ax[2].set_title('Multi-Otsu result')
ax[2].axis('off')plt.subplots_adjust()plt.show()新建文件multi_thresh.py
import numpy as np
import pyximport
pyximport.install()
from multi_level._multiotsu import (_get_multiotsu_thresh_indices_lut, _get_multiotsu_thresh_indices)_integer_types = (np.byte, np.ubyte, # 8 bitsnp.short, np.ushort, # 16 bitsnp.intc, np.uintc, # 16 or 32 or 64 bitsnp.int_, np.uint, # 32 or 64 bitsnp.longlong, np.ulonglong) # 64 bits
_integer_ranges = {t: (np.iinfo(t).min, np.iinfo(t).max)for t in _integer_types}
dtype_range = {np.bool_: (False, True),np.bool8: (False, True),np.float16: (-1, 1),np.float32: (-1, 1),np.float64: (-1, 1)}
dtype_range.update(_integer_ranges)_supported_types = list(dtype_range.keys())def dtype_limits(image, clip_negative=False):"""Return intensity limits, i.e. (min, max) tuple, of the image's dtype.Parameters----------image : ndarrayInput image.clip_negative : bool, optionalIf True, clip the negative range (i.e. return 0 for min intensity)even if the image dtype allows negative values.Returns-------imin, imax : tupleLower and upper intensity limits."""imin, imax = dtype_range[image.dtype.type]if clip_negative:imin = 0return imin, imaxdef _offset_array(arr, low_boundary, high_boundary):"""Offset the array to get the lowest value at 0 if negative."""if low_boundary < 0:offset = low_boundarydyn_range = high_boundary - low_boundary# get smallest dtype that can hold both minimum and offset maximumoffset_dtype = np.promote_types(np.min_scalar_type(dyn_range),np.min_scalar_type(low_boundary))if arr.dtype != offset_dtype:# prevent overflow errors when offsettingarr = arr.astype(offset_dtype)arr = arr - offsetelse:offset = 0return arr, offsetdef _bincount_histogram(image, source_range):"""Efficient histogram calculation for an image of integers.This function is significantly more efficient than np.histogram butworks only on images of integers. It is based on np.bincount.Parameters----------image : arrayInput image.source_range : string'image' determines the range from the input image.'dtype' determines the range from the expected range of the imagesof that data type.Returns-------hist : arrayThe values of the histogram.bin_centers : arrayThe values at the center of the bins."""if source_range not in ['image', 'dtype']:raise ValueError('Incorrect value for `source_range` argument: {}'.format(source_range))if source_range == 'image':image_min = int(image.min().astype(np.int64))image_max = int(image.max().astype(np.int64))elif source_range == 'dtype':image_min, image_max = dtype_limits(image, clip_negative=False)image, offset = _offset_array(image, image_min, image_max)hist = np.bincount(image.ravel(), minlength=image_max - image_min + 1)bin_centers = np.arange(image_min, image_max + 1)if source_range == 'image':idx = max(image_min, 0)hist = hist[idx:]return hist, bin_centersdef histogram(image, nbins=256, source_range='image', normalize=False):"""Return histogram of image.Unlike `numpy.histogram`, this function returns the centers of bins anddoes not rebin integer arrays. For integer arrays, each integer value hasits own bin, which improves speed and intensity-resolution.The histogram is computed on the flattened image: for color images, thefunction should be used separately on each channel to obtain a histogramfor each color channel.Parameters----------image : arrayInput image.nbins : int, optionalNumber of bins used to calculate histogram. This value is ignored forinteger arrays.source_range : string, optional'image' (default) determines the range from the input image.'dtype' determines the range from the expected range of the imagesof that data type.normalize : bool, optionalIf True, normalize the histogram by the sum of its values.Returns-------hist : arrayThe values of the histogram.bin_centers : arrayThe values at the center of the bins.See Also--------cumulative_distributionExamples-------->>> from skimage import data, exposure, img_as_float>>> image = img_as_float(data.camera())>>> np.histogram(image, bins=2)(array([107432, 154712]), array([ 0. , 0.5, 1. ]))>>> exposure.histogram(image, nbins=2)(array([107432, 154712]), array([ 0.25, 0.75]))"""sh = image.shapeif len(sh) == 3 and sh[-1] < 4:raise("This might be a color image. The histogram will be ""computed on the flattened image. You can instead ""apply this function to each color channel.")image = image.flatten()# For integer types, histogramming with bincount is more efficient.if np.issubdtype(image.dtype, np.integer):hist, bin_centers = _bincount_histogram(image, source_range)else:if source_range == 'image':hist_range = Noneelif source_range == 'dtype':hist_range = dtype_limits(image, clip_negative=False)else:ValueError('Wrong value for the `source_range` argument')hist, bin_edges = np.histogram(image, bins=nbins, range=hist_range)bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2.if normalize:hist = hist / np.sum(hist)return hist, bin_centersdef threshold_multiotsu(image, classes=3, nbins=256):r"""Generate `classes`-1 threshold values to divide gray levels in `image`.The threshold values are chosen to maximize the total sum of pairwisevariances between the thresholded graylevel classes. See Notes and [1]_for more details.Parameters----------image : (N, M) ndarrayGrayscale input image.classes : int, optionalNumber of classes to be thresholded, i.e. the number of resultingregions.nbins : int, optionalNumber of bins used to calculate the histogram. This value is ignoredfor integer arrays.Returns-------thresh : arrayArray containing the threshold values for the desired classes.Raises------ValueErrorIf ``image`` contains less grayscale value then the desirednumber of classes.Notes-----This implementation relies on a Cython function whose complexityis :math:`O\left(\frac{Ch^{C-1}}{(C-1)!}\right)`, where :math:`h`is the number of histogram bins and :math:`C` is the number ofclasses desired.The input image must be grayscale.References----------.. [1] Liao, P-S., Chen, T-S. and Chung, P-C., "A fast algorithm formultilevel thresholding", Journal of Information Science andEngineering 17 (5): 713-727, 2001. Available at::DOI:`10.6688/JISE.2001.17.5.1`.. [2] Tosa, Y., "Multi-Otsu Threshold", a java plugin for ImageJ.Available at:Examples-------->>> from skimage.color import label2rgb>>> from skimage import data>>> image = data.camera()>>> thresholds = threshold_multiotsu(image)>>> regions = np.digitize(image, bins=thresholds)>>> regions_colorized = label2rgb(regions)"""if len(image.shape) > 2 and image.shape[-1] in (3, 4):msg = ("threshold_multiotsu is expected to work correctly only for ""grayscale images; image shape {0} looks like an RGB image")raise (msg.format(image.shape))# calculating the histogram and the probability of each gray level.prob, bin_centers = histogram(image.ravel(),nbins=nbins,source_range='image',normalize=True)prob = prob.astype('float32')nvalues = np.count_nonzero(prob)if nvalues < classes:msg = ("The input image has only {} different values. ""It can not be thresholded in {} classes")raise ValueError(msg.format(nvalues, classes))elif nvalues == classes:thresh_idx = np.where(prob > 0)[0][:-1]else:# Get threshold indicestry:thresh_idx = _get_multiotsu_thresh_indices_lut(prob, classes - 1)except MemoryError:# Don't use LUT if the number of bins is too large (if the# image is uint16 for example): in this case, the# allocated memory is too large.thresh_idx = _get_multiotsu_thresh_indices(prob, classes - 1)thresh = bin_centers[thresh_idx]return thresh 新建文件_multiotsu.pyx
#cython: cdivision=True
#cython: boundscheck=False
#cython: nonecheck=False
#cython: wraparound=False
import numpy as npcimport numpy as cnp
cimport cythondef _get_multiotsu_thresh_indices_lut(float [::1] prob,Py_ssize_t thresh_count):"""Finds the indices of Otsu thresholds according to the valuesoccurence probabilities.This implementation uses a LUT to reduce the number of floatingpoint operations (see [1]_). The use of the LUT reduces thecomputation time at the price of more memory consumption.Parameters----------prob : arrayValue occurence probabilities.thresh_count : intThe desired number of thresholds (classes-1).Returns-------py_thresh_indices : ndarrayThe indices of the desired thresholds.References----------.. [1] Liao, P-S., Chen, T-S. and Chung, P-C., "A fast algorithm formultilevel thresholding", Journal of Information Science andEngineering 17 (5): 713-727, 2001. Available at::DOI:`10.6688/JISE.2001.17.5.1`"""cdef Py_ssize_t nbins = prob.shape[0]py_thresh_indices = np.empty(thresh_count, dtype=np.intp)cdef Py_ssize_t[::1] thresh_indices = py_thresh_indicescdef Py_ssize_t[::1] current_indices = np.empty(thresh_count, dtype=np.intp)cdef float [::1] var_btwcls = np.zeros((nbins * (nbins + 1)) / 2,dtype=np.float32)cdef float [::1] zeroth_moment = np.empty(nbins, dtype=np.float32)cdef float [::1] first_moment = np.empty(nbins, dtype=np.float32)with nogil:_set_var_btwcls_lut(prob, nbins, var_btwcls, zeroth_moment,first_moment)_set_thresh_indices_lut(var_btwcls, hist_idx=0,thresh_idx=0, nbins=nbins,thresh_count=thresh_count, sigma_max=0,current_indices=current_indices,thresh_indices=thresh_indices)return py_thresh_indicescdef void _set_var_btwcls_lut(float [::1] prob,Py_ssize_t nbins,float [::1] var_btwcls,float [::1] zeroth_moment,float [::1] first_moment) nogil:"""Builds the lookup table containing the variance between classes.The variance between classes are stored in``var_btwcls``. ``zeroth_moment`` and ``first_moment`` are buffersfor storing the first row of respectively the zeroth and firstorder moments lookup table (respectively H, P and S in [1]_).Parameters----------prob : arrayValue occurence probabilities.nbins : intThe number of intensity values.var_btwcls : arrayThe upper triangular part of the lookup table containing thevariance between classes (referred to as H in [1]_). Its sizeis equal to nbins*(nbins + 1) / 2.zeroth_moment : arrayFirst row of the zeroth order moments LUT (referred to as P in[1]_).first_moment : arrayFirst row of the first order moments LUT (referred to as S in[1]_).Notes-----Only the first rows of the moments lookup tables are necessary tobuild the lookup table containing the variance betweenclasses. ``var_btwcls`` is stored in the compressed uppertriangular matrix form (i.e. the seros of the lower triangularpart are not stored).References----------.. [1] Liao, P-S., Chen, T-S. and Chung, P-C., "A fast algorithm formultilevel thresholding", Journal of Information Science andEngineering 17 (5): 713-727, 2001. Available at::DOI:`10.6688/JISE.2001.17.5.1`"""cdef cnp.intp_t i, j, idxcdef float zeroth_moment_ij, first_moment_ijzeroth_moment[0] = prob[0]first_moment[0] = prob[0]for i in range(1, nbins):zeroth_moment[i] = zeroth_moment[i - 1] + prob[i]first_moment[i] = first_moment[i - 1] + i * prob[i]if zeroth_moment[i] > 0:var_btwcls[i] = (first_moment[i]**2) / zeroth_moment[i]idx = nbinsfor i in range(1, nbins):for j in range(i, nbins):zeroth_moment_ij = zeroth_moment[j] - zeroth_moment[i - 1]if zeroth_moment_ij > 0:first_moment_ij = first_moment[j] - first_moment[i - 1]var_btwcls[idx] = (first_moment_ij**2) / zeroth_moment_ijidx += 1cdef float _get_var_btwclas_lut(float [::1] var_btwcls, Py_ssize_t i,Py_ssize_t j, Py_ssize_t nbins) nogil:"""Returns the variance between classes stored in compressed uppertriangular matrix form at the desired 2D indices.Parameters----------var_btwcls : arrayThe lookup table containing the variance between classes incompressed upper triangular matrix form.i, j : int2D indices in the uncompressed lookup table.nbins : intThe number of columns in the lookup table.Returns-------value : floatThe value of the lookup table corresponding to index (i, j)."""cdef cnp.intp_t idx = (i * (2 * nbins - i + 1)) / 2 + j - ireturn var_btwcls[idx]cdef float _set_thresh_indices_lut(float[::1] var_btwcls, Py_ssize_t hist_idx,Py_ssize_t thresh_idx, Py_ssize_t nbins,Py_ssize_t thresh_count, float sigma_max,Py_ssize_t[::1] current_indices,Py_ssize_t[::1] thresh_indices) nogil:"""Recursive function for finding the indices of the thresholdsmaximizing the variance between classes sigma.This implementation use a lookup table of variance between classesto perform a brute force evaluation of sigma over all thecombinations of threshold to find the indices maximizing sigma(see [1]_).Parameters----------var_btwcls : arrayThe upper triangular part of the lookup table containing thevariance between classes (referred to as H in [1]_). Its sizeis equal to nbins*(nbins + 1) / 2.hist_idx : intCurrent index in the histogram.thresh_idx : intCurrent index in thresh_indices.nbins : intnumber of bins used in the histogramthresh_count : intThe desired number of thresholds (classes-1).sigma_max : floatCurrent maximum variance between classes.current_indices : arrayCurrent evalueted threshold indices.thresh_indices : arrayThe indices of thresholds maximizing the variance betweenclasses.Returns-------max_sigma : floatMaximum variance between classes.Notes-----For any candidate current_indices {t_0, ..., t_n}, sigma equalsvar_btwcls[0, t_0] + var_btwcls[t_0+1, t_1] + ...+ var_btwcls[t_(i-1) + 1, t_i] + ... + var_btwcls[t_n, nbins-1]References----------.. [1] Liao, P-S., Chen, T-S. and Chung, P-C., "A fast algorithm formultilevel thresholding", Journal of Information Science andEngineering 17 (5): 713-727, 2001. Available at::DOI:`10.6688/JISE.2001.17.5.1`"""cdef cnp.intp_t idxcdef float sigmaif thresh_idx < thresh_count:for idx in range(hist_idx, nbins - thresh_count + thresh_idx):current_indices[thresh_idx] = idxsigma_max = _set_thresh_indices_lut(var_btwcls, hist_idx=idx + 1,thresh_idx=thresh_idx + 1,nbins=nbins,thresh_count=thresh_count,sigma_max=sigma_max,current_indices=current_indices,thresh_indices=thresh_indices)else:sigma = (_get_var_btwclas_lut(var_btwcls, 0, current_indices[0], nbins)+ _get_var_btwclas_lut(var_btwcls,current_indices[thresh_count - 1] + 1,nbins - 1, nbins))for idx in range(thresh_count - 1):sigma += _get_var_btwclas_lut(var_btwcls, current_indices[idx] + 1,current_indices[idx + 1], nbins)if sigma > sigma_max:sigma_max = sigmathresh_indices[:] = current_indices[:]return sigma_maxdef _get_multiotsu_thresh_indices(float [::1] prob, Py_ssize_t thresh_count):"""Finds the indices of Otsu thresholds according to the valuesoccurence probabilities.This implementation, as opposed to `_get_multiotsu_thresh_indices_lut`,does not use LUT. It is therefore slower.Parameters----------prob : arrayValue occurence probabilities.thresh_count : intThe desired number of threshold.Returns-------py_thresh_indices : arrayThe indices of the desired thresholds."""cdef Py_ssize_t nbins = prob.shape[0]py_thresh_indices = np.empty(thresh_count, dtype=np.intp)cdef Py_ssize_t[::1] thresh_indices = py_thresh_indicescdef Py_ssize_t[::1] current_indices = np.empty(thresh_count, dtype=np.intp)cdef float [::1] zeroth_moment = np.empty(nbins, dtype=np.float32)cdef float [::1] first_moment = np.empty(nbins, dtype=np.float32)with nogil:_set_moments_lut_first_row(prob, nbins, zeroth_moment, first_moment)_set_thresh_indices(zeroth_moment, first_moment, hist_idx=0,thresh_idx=0, nbins=nbins,thresh_count=thresh_count, sigma_max=0,current_indices=current_indices,thresh_indices=thresh_indices)return py_thresh_indicescdef void _set_moments_lut_first_row(float [::1] prob,Py_ssize_t nbins,float [::1] zeroth_moment,float [::1] first_moment) nogil:"""Builds the first rows of the zeroth and first moments lookup tablenecessary to the computation of the variance between class.Parameters----------prob : arrayValue occurence probabilities.nbins : intThe number of intensity values.zeroth_moment : arrayFirst row of the zeroth order moments LUT (referred to as P in[1]_).first_moment : arrayFirst row of the first order moments LUT (referred to as S in[1]_).References----------.. [1] Liao, P-S., Chen, T-S. and Chung, P-C., "A fast algorithm formultilevel thresholding", Journal of Information Science andEngineering 17 (5): 713-727, 2001. Available at::DOI:`10.6688/JISE.2001.17.5.1`"""cdef cnp.intp_t izeroth_moment[0] = prob[0]first_moment[0] = prob[0]for i in range(1, nbins):zeroth_moment[i] = zeroth_moment[i - 1] + prob[i]first_moment[i] = first_moment[i - 1] + i * prob[i]cdef float _get_var_btwclas(float [::1] zeroth_moment,float [::1] first_moment,Py_ssize_t i, Py_ssize_t j) nogil:"""Computes the variance between two classes.Parameters----------zeroth_moment : arrayFirst row of the zeroth order moments LUT (referred to as P in[1]_).first_moment : arrayFirst row of the first order moments LUT (referred to as S in[1]_).i, j : intThe indices of the two considred classes.Returns-------value : floatThe variance between the classes i and j."""cdef float zeroth_moment_ij, first_moment_ijif i == 0:if zeroth_moment[i] > 0:return (first_moment[j]**2) / zeroth_moment[j]else:zeroth_moment_ij = zeroth_moment[j] - zeroth_moment[i - 1]if zeroth_moment_ij > 0:first_moment_ij = first_moment[j] - first_moment[i - 1]return (first_moment_ij**2) / zeroth_moment_ijreturn 0cdef float _set_thresh_indices(float[::1] zeroth_moment,float[::1] first_moment,Py_ssize_t hist_idx,Py_ssize_t thresh_idx, Py_ssize_t nbins,Py_ssize_t thresh_count, float sigma_max,Py_ssize_t[::1] current_indices,Py_ssize_t[::1] thresh_indices) nogil:"""Recursive function for finding the indices of the thresholdsmaximizing the variance between classes sigma.This implementation uses the first rows of the zeroth and firstmoments lookup table to compute the variance between class andperforms a brute force evaluation of sigma over all thecombinations of threshold to find the indices maximizing sigma(see [1]_)..Parameters----------zeroth_moment : arrayFirst row of the zeroth order moments LUT (referred to as P in[1]_).first_moment : arrayFirst row of the first order moments LUT (referred to as S in[1]_).hist_idx : intCurrent index in the histogram.thresh_idx : intCurrent index in thresh_indices.nbins : intnumber of bins used in the histogramthresh_count : intThe desired number of thresholds (classes-1).sigma_max : floatCurrent maximum variance between classes.current_indices : arrayCurrent evalueted threshold indices.thresh_indices : arrayThe indices of thresholds maximizing the variance betweenclasses.Returns-------max_sigma : floatMaximum variance between classes.References----------.. [1] Liao, P-S., Chen, T-S. and Chung, P-C., "A fast algorithm formultilevel thresholding", Journal of Information Science andEngineering 17 (5): 713-727, 2001. Available at::DOI:`10.6688/JISE.2001.17.5.1`"""cdef cnp.intp_t idxcdef float sigmaif thresh_idx < thresh_count:for idx in range(hist_idx, nbins - thresh_count + thresh_idx):current_indices[thresh_idx] = idxsigma_max = _set_thresh_indices(zeroth_moment,first_moment,hist_idx=idx + 1,thresh_idx=thresh_idx + 1,nbins=nbins,thresh_count=thresh_count,sigma_max=sigma_max,current_indices=current_indices,thresh_indices=thresh_indices)else:sigma = (_get_var_btwclas(zeroth_moment, first_moment, 0,current_indices[0])+ _get_var_btwclas(zeroth_moment, first_moment,current_indices[thresh_count - 1] + 1,nbins - 1))for idx in range(thresh_count - 1):sigma += _get_var_btwclas(zeroth_moment, first_moment,current_indices[idx] + 1,current_indices[idx + 1])if sigma > sigma_max:sigma_max = sigmathresh_indices[:] = current_indices[:]return sigma_max
新建文件setup.py
from distutils.core import setup
from distutils.extension import Extension
from Cython.Build import cythonize
from Cython.Distutils import build_ext
import numpy as np# ext_module = cythonize("TestOMP.pyx")
ext_module = Extension("_multiotsu",["_multiotsu.pyx"],
)setup(cmdclass={'build_ext': build_ext},ext_modules=[ext_module],include_dirs=[np.get_include()]
) 编译_multiotsu.pyx,首先cd到该文件所在目录,然后使用python setup.py build_ext --inplace,然后会出现以下文件夹
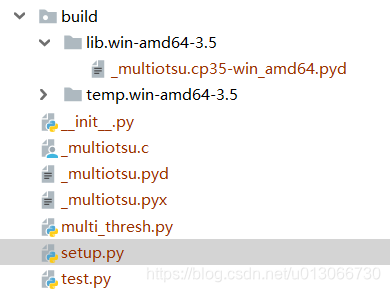
将_multiotsu.cp35-win_amd64.pyd复制到与_multiotsu.pyx同一文件夹下,然后重命名为_multiotsu.pyd。
直接python test.py命令即可。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!