Rational Krylov Method(克雷洛夫法)求解特征值问题matlab代码示例(和Arnoldi方法比较)
最基本的特征值问题分为三类:
1、标准的线性特征值问题:
Ax=λx,A∈Cn∗n
2、普遍的线性特征值问题:
Ax=λBx,A
3、普遍的艾米特正定线性特征值问题:
Ax=λBx,A
A∗=A,B∗=B>0∈Cn∗n
不妨做一个程序将RKM方法和Arnoldi方法做一个比较。
% demo routine for Rational Krylov vs Arnoldi with shift-invert
clc
clear
n = 1000;
m = 40; % subspace size
A = diag([1:1:n]); % testing matrix A of eigenvalues 1, 2, .., n% shifts: define more shift as you like
sigma1 = 101.5;
sigma2 = 121.5;% -- Rational Krylov with shifts SIGMA
m1 = floor(m/2); m2 = m-m1;
SIGMA = [repmat(sigma1, m1, 1); repmat(sigma2, m2, 1)];
%SIGMA = repmat([sigma1; sigma2], m/2, 1); % even number m[Q1, K, L] = rarnoldi(A, SIGMA, m);
[V1, E1] = eig(L(1:m,:), K(1:m,:));% pick eig of relative residual norm < tol
tol = 1.0E-6;
nA = norm(A,1);
e1 = [];
for i = 1:mlam = E1(i,i); v = Q1*(K*V1(:, i));res = norm(A*v-lam*v)/norm(v)/nA;if res[e1, lam]; end
end% -- shift invert Arnoldi with shift sigma1
sigma = sigma1;
[LL, UU, PP] = lu(A-sigma*speye(n));
Afun = @(x) UU \ (LL \ (PP*x));
[Q2, H] = arnoldi(Afun, n, m);
[V2, E2] = eig(H(1:m,:)); E2 = 1./E2 + sigma;% pick eig of relative residual norm < tol
tol = 1.0E-6;
nA = norm(A,1);
e2 = [];
for i = 1:mlam = E2(i,i); v = Q2(:,1:m)*V2(:, i);res = norm(A*v-lam*v)/norm(v)/nA;if res[e2, lam]; end
end% -- display results
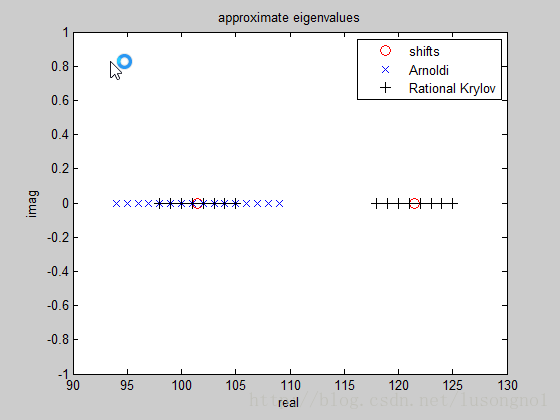
figure
plot(real([sigma1, sigma2]), imag([sigma1, sigma2]), 'or', 'DisplayName', 'shifts', 'MarkerSize', 8)
hold on;
plot(real(e2), imag(e2), 'xb', 'DisplayName', 'Arnoldi', 'MarkerSize', 8);
plot(real(e1), imag(e1), '+k', 'DisplayName', 'Rational Krylov', 'MarkerSize', 8);
legend show
xlabel('real'); ylabel('imag')
title('approximate eigenvalues')% END 用到的一些子函数就一起列在下面了:
function [V, H] = arnoldi(Afun, n, m)
% function [V, H] = arnoldi(Afun, n, m) produce an Arnoldi decomposition
% of order m for a square matri A.
% Afun(v) = A*v
% n = dim of A
%
v = randn(n,1);
v = v / norm(v);V = v;
H = zeros(m+1, m);for i = 1:mw = Afun(v);h = V'*w;w = w - V*h;gamma = norm(w);if gamma==0returnendv = w/gamma;V = [V, v];H(1:i,i) = h;H(1+i, i) = gamma;
endfunction [V, K, L] = rarnoldi(A, SIGMA, m)
% function [V, K, L] = rarnoldi(Afun, n, m) produce an rational Krylov
% decomposition of order m for a square matri A.
% SIGMA: length m vector containing shifts
%n = size(A,1);
v = randn(n,1);
v = v / norm(v);V = v;
K = zeros(m+1, m);
L = zeros(m+1, m);for i = 1:msigma = SIGMA(i);if sigma ~= infw = (A-sigma*speye(n))\v;h = V'*w;w = w - V*h;gamma = norm(w);v = w/gamma;V = [V, v];K(1:i, i) = h;K(i+1, i) = gamma;L(1:i+1, i) = sigma*K(1:i+1, i);L(i, i) = L(i, i) + 1;elsew = A*v;h = V'*w;w = w - V*h;gamma = norm(w);v = w/gamma;V = [V, v];K(i, i) = 1;L(1:i, i) = h;L(i+1, i) = gamma;end% breakdown case L(i+1, i) = K(i+1,i) = 0 is not treated.
end
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!