Linux 角度看binder原理(二)
Linux 角度看binder原理(二)
ioctl
在Linux中和设备的常用交互除了上一篇中重定向file_operations中的文件操作就是ioctl了。file_operations作为通用的设备交互手段,缺少了每个设备自己的特有操作,这时候就使ioctl作为补充。函数是int ioctl(int fd, ind cmd, …) 第一个参数就是打开设备的fd,第二个就是设备的控制指令,再后面的…传入当前控制指令需要的参数。
binder指令
binder指令存在BinderDriverCommandProtocol和BinderDriver ReturnProtocol两个enum中。
enum binder_driver_return_protocol {BR_ERROR = _IOR('r', 0, __s32),BR_OK = _IO('r', 1),BR_TRANSACTION_SEC_CTX = _IOR('r', 2,struct binder_transaction_data_secctx),BR_TRANSACTION = _IOR('r', 2, struct binder_transaction_data),BR_REPLY = _IOR('r', 3, struct binder_transaction_data),BR_ACQUIRE_RESULT = _IOR('r', 4, __s32),BR_DEAD_REPLY = _IO('r', 5),BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE = _IO('r', 6),BR_INCREFS = _IOR('r', 7, struct binder_ptr_cookie),BR_ACQUIRE = _IOR('r', 8, struct binder_ptr_cookie),BR_RELEASE = _IOR('r', 9, struct binder_ptr_cookie),BR_DECREFS = _IOR('r', 10, struct binder_ptr_cookie),BR_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE = _IOR('r', 11, struct binder_pri_ptr_cookie),BR_NOOP = _IO('r', 12),BR_SPAWN_LOOPER = _IO('r', 13),BR_FINISHED = _IO('r', 14),BR_DEAD_BINDER = _IOR('r', 15, binder_uintptr_t),BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE = _IOR('r', 16, binder_uintptr_t),BR_FAILED_REPLY = _IO('r', 17),BR_FROZEN_REPLY = _IO('r', 18),BR_ONEWAY_SPAM_SUSPECT = _IO('r', 19),};enum binder_driver_command_protocol {BC_TRANSACTION = _IOW('c', 0, struct binder_transaction_data),BC_REPLY = _IOW('c', 1, struct binder_transaction_data),BC_ACQUIRE_RESULT = _IOW('c', 2, __s32),BC_FREE_BUFFER = _IOW('c', 3, binder_uintptr_t),BC_INCREFS = _IOW('c', 4, __u32),BC_ACQUIRE = _IOW('c', 5, __u32),BC_RELEASE = _IOW('c', 6, __u32),BC_DECREFS = _IOW('c', 7, __u32),BC_INCREFS_DONE = _IOW('c', 8, struct binder_ptr_cookie),BC_ACQUIRE_DONE = _IOW('c', 9, struct binder_ptr_cookie),BC_ATTEMPT_ACQUIRE = _IOW('c', 10, struct binder_pri_desc),BC_REGISTER_LOOPER = _IO('c', 11),BC_ENTER_LOOPER = _IO('c', 12),BC_EXIT_LOOPER = _IO('c', 13),BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION = _IOW('c', 14,struct binder_handle_cookie),BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION = _IOW('c', 15,struct binder_handle_cookie),BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE = _IOW('c', 16, binder_uintptr_t),BC_TRANSACTION_SG = _IOW('c', 17, struct binder_transaction_data_sg),BC_REPLY_SG = _IOW('c', 18, struct binder_transaction_data_sg),
};
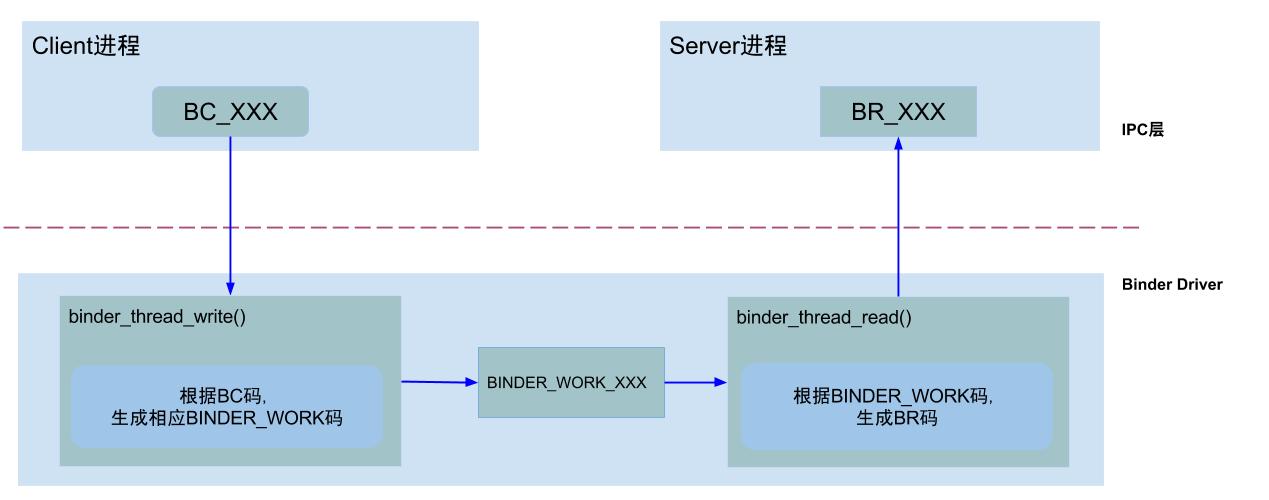
从全称也就知道了为什么有的是BC有的是BR,BC是从用户空间到驱动,BR是从驱动返回用户空间。注意这里不是client和service之间的指令和返回,而是驱动和用户空间的。这里放一张gityuan的图,很好的展示了一次ioctl的过程
binder 常见结构
在上一篇中,已经知道所有使用binder的进程都会调用open来打开设备,当设备打开的时候就会创建一个binder_proc结构体。
struct binder_proc {struct hlist_node proc_node; //proc的hash队列的的节点struct rb_root threads; //binder_thread红黑树struct rb_root nodes; //binder_node红黑树struct rb_root refs_by_desc;//binder_ref红黑树以desc为关键字struct rb_root refs_by_node;//binder_ref红黑树以node为关键字struct list_head waiting_threads;//等待线程int pid;//进程idstruct task_struct *tsk;//进程结构体const struct cred *cred;//credential机制用于权限判断struct hlist_node deferred_work_node;//延迟工作的节点int deferred_work;//延迟工作的类型int outstanding_txns;bool is_dead;bool is_frozen;bool sync_recv;bool async_recv;wait_queue_head_t freeze_wait;struct list_head todo;//当前进程的工作队列struct binder_stats stats;struct list_head delivered_death;int max_threads;//最大线程数,这里不是总得线程,是binder驱动注册的线程,用户进程可以自己注册线程到线程池但是不占用max_threads的数量int requested_threads;int requested_threads_started;int tmp_ref;long default_priority;struct dentry *debugfs_entry;struct binder_alloc alloc;//内存相关的结构被封装成了一个结构体,在老版本中的free_buffers和allocated_buffers等都在里面struct binder_context *context;spinlock_t inner_lock;spinlock_t outer_lock;struct dentry *binderfs_entry;bool oneway_spam_detection_enabled;
};
再看下和内存相关最大的binder_alloc
struct binder_alloc {struct mutex mutex; //锁struct vm_area_struct *vma;//binder内存对应的VMAstruct mm_struct *vma_vm_mm;//binder进程的内存描述符void __user *buffer;//mmap的用户空间虚拟地址。struct list_head buffers;//所有buffer的列表struct rb_root free_buffers;//空闲buffer的红黑树struct rb_root allocated_buffers;//已经分配的buffer的红黑树size_t free_async_space;//异步事务数据的内核缓冲区struct binder_lru_page *pages;//binder内存区域对应的pagesize_t buffer_size;//buffer的大小uint32_t buffer_free;//free的buffer大小int pid;//Binder proc的pidsize_t pages_high;//内存理想的阈值bool oneway_spam_detected;//是否启用单向SPAM检测
};
缓存结构体binder_buffer
struct binder_buffer {struct list_head entry; /* free and allocated entries by address */struct rb_node rb_node; /* free entry by size or allocated entry *//* by address */unsigned free:1;unsigned clear_on_free:1;unsigned allow_user_free:1;unsigned async_transaction:1;unsigned oneway_spam_suspect:1;unsigned debug_id:27;struct binder_transaction *transaction;//当前buffer交给哪个事务使用struct binder_node *target_node;//这个buffer当前交给哪个node使用size_t data_size;//数据区域的大小size_t offsets_size;//offset区域的大小size_t extra_buffers_size;void __user *user_data;//用户空间地址int pid;
};
到这里内存相关的结构体都已经展示完了。在binder_proc通过threads来管理线程池,在binder中线程的结构是binder_thread。
struct binder_thread {struct binder_proc *proc;//所属进程struct rb_node rb_node;//binder_proc中线程红黑树的中的节点struct list_head waiting_thread_node;//空闲时binder_proc中的等待队列的节点int pid;int looper; //线程的状态bool looper_need_return; struct binder_transaction *transaction_stack;//事务栈struct list_head todo;//任务队列bool process_todo;struct binder_error return_error;struct binder_error reply_error;wait_queue_head_t wait;struct binder_stats stats;atomic_t tmp_ref;bool is_dead;
};
binder_thread就已经到了比较具体执行任务的地方了,它的field都是和具体任务相关。一次进程间的通讯这个过程被封装成binder_transaction。
struct binder_transaction {int debug_id;struct binder_work work;//transaction涉及的binder work,就是进程或者线程中的todo中保存的任务结构体struct binder_thread *from;//发起binder通信的线程struct binder_transaction *from_parent;//执行本事务所依赖的其他事务struct binder_proc *to_proc;//处理binder请求的进程struct binder_thread *to_thread;//处理binder请求的线程struct binder_transaction *to_parent;//unsigned need_reply:1;//是否有返回/* unsigned is_dead:1; */ /* not used at the moment */struct binder_buffer *buffer;//本次事务分配的bufferunsigned int code;unsigned int flags;long priority;long saved_priority;kuid_t sender_euid;struct list_head fd_fixups;binder_uintptr_t security_ctx;spinlock_t lock;
};
binder通讯是一个cs架构,有client和service。在bidner驱动中就对应了binder_ref和binder_node。每一个service注册到binder之后都会有一个binder_node对应。
struct binder_node {int debug_id;spinlock_t lock;struct binder_work work; //node的任务union {struct rb_node rb_node;//binder_proc中的node红黑树中的节点struct hlist_node dead_node;};struct binder_proc *proc;//所属的binder procstruct hlist_head refs;//这里保存了所有使用当前service的客户端的binder_refint internal_strong_refs;//内部强引用int local_weak_refs;//弱引用int local_strong_refs;强引用int tmp_refs;binder_uintptr_t ptr;//service指向service内部一个引用对象binder_uintptr_t cookie;//service用户空间地址struct {/** bitfield elements protected by* proc inner_lock*/u8 has_strong_ref:1;u8 pending_strong_ref:1;u8 has_weak_ref:1;u8 pending_weak_ref:1;};struct {/** invariant after initialization*/u8 accept_fds:1;u8 txn_security_ctx:1;u8 min_priority;};bool has_async_transaction;//是否是异步任务struct list_head async_todo;//异步任务队列
};
binder_node最大的作用就是binder驱动可以通过binder_node来访问service,同时通过强弱引用来控制他的生命周期。每一个client在驱动中就是一个binder_ref。
struct binder_ref {/* Lookups needed: *//* node + proc => ref (transaction) *//* desc + proc => ref (transaction, inc/dec ref) *//* node => refs + procs (proc exit) */struct binder_ref_data data;//一个封装类,老版本中的desc等struct rb_node rb_node_desc;//binder_proc中的desc红黑树的成员struct rb_node rb_node_node;//binder_proc中的红黑树的成员struct hlist_node node_entry;//binder_node中的refs中的成员struct binder_proc *proc;//所属进程struct binder_node *node;//引用的是哪个nodestruct binder_ref_death *death;
};struct binder_ref_data {int debug_id;uint32_t desc;//引用描述符,client中持有的就是描述符,需要传递消息的时候通过传递描述符,让驱动找到引用对象int strong;//强引用计数int weak;//弱引用计数
};
到这里一次IPC通讯里常见的结构都已经清楚了
参考
《Android系统源代码情景分析》
gityuan博客
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!