springboot开发webservice服务端,发布多个webservice服务案例(带你玩转webservice)
一、情况说明:
本篇是对 springboot开发webservice服务端和客户端代码 的补充
效果:
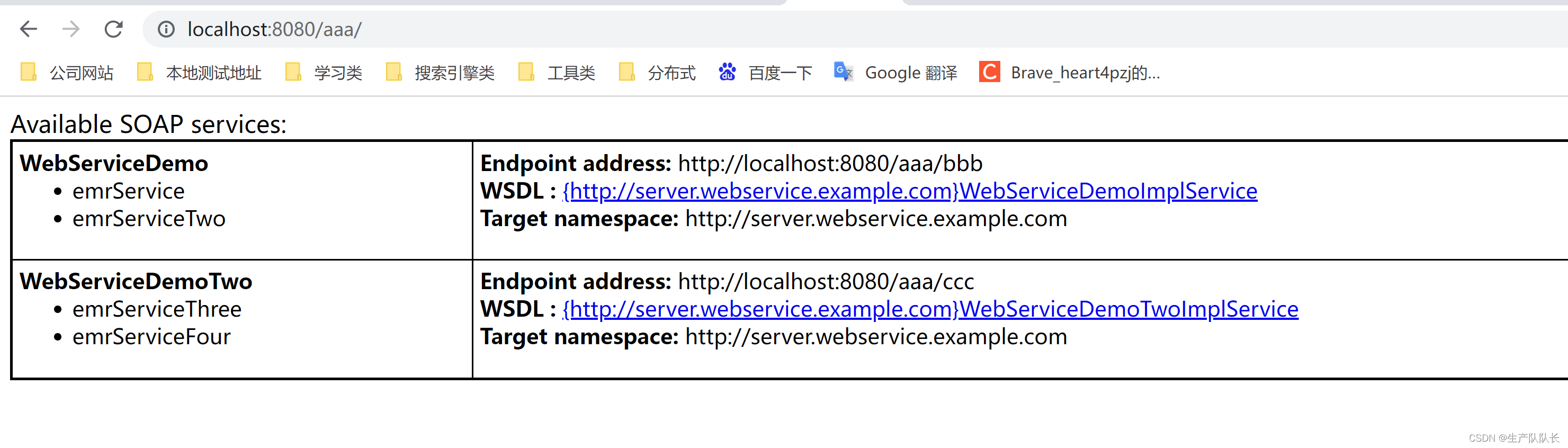
二、服务端代码:
WebServiceDemo 代码:
package com.test.springboot.service;import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebService;@WebService(name = "WebServiceDemo", targetNamespace = "http://server.webservice.example.com")
public interface WebServiceDemo {@WebMethodString emrService(@WebParam String data);@WebMethodString emrServiceTwo(@WebParam String data);
}
WebServiceDemoImpl 代码:
package com.test.springboot.service.impl;import com.test.springboot.service.WebServiceDemo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.jws.WebService;@Component
@WebService(name = "WebServiceDemo", targetNamespace = "http://server.webservice.example.com",endpointInterface = "com.test.springboot.service.WebServiceDemo")
public class WebServiceDemoImpl implements WebServiceDemo {@Overridepublic String emrService(String data) {if(null == data || "".equals(data.trim())){return "传入的参数为空";}return "调用成功,data:"+data;}@Overridepublic String emrServiceTwo(String data) {if(null == data || "".equals(data.trim())){return "传入的参数为空";}return "调用成功Two,data:"+data;}
}WebServiceDemoTwo 代码:
package com.test.springboot.service;import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebService;@WebService(name = "WebServiceDemoTwo", targetNamespace = "http://server.webservice.example.com")
public interface WebServiceDemoTwo {@WebMethodString emrServiceThree(@WebParam String data);@WebMethodString emrServiceFour(@WebParam String data);
}WebServiceDemoTwoImpl 代码
package com.test.springboot.service.impl;import com.test.springboot.service.WebServiceDemoTwo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.jws.WebService;@Component
@WebService(name = "WebServiceDemoTwo", targetNamespace = "http://server.webservice.example.com",endpointInterface = "com.test.springboot.service.WebServiceDemoTwo")
public class WebServiceDemoTwoImpl implements WebServiceDemoTwo {@Overridepublic String emrServiceThree(String data) {return null;}@Overridepublic String emrServiceFour(String data) {return null;}
}WebServiceConfig 代码[重点学习]
package com.test.springboot.config;import com.test.springboot.service.WebServiceDemo;
import com.test.springboot.service.WebServiceDemoTwo;
import org.apache.cxf.Bus;
import org.apache.cxf.bus.spring.SpringBus;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.EndpointImpl;
import org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;@Configuration
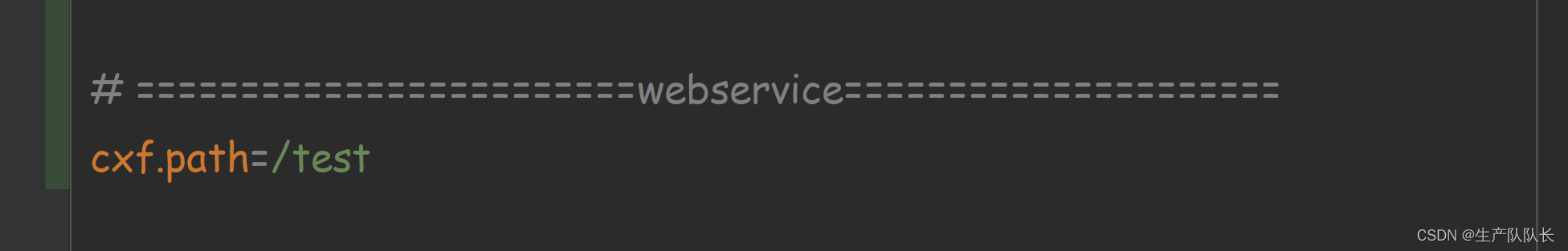
public class WebServiceConfig {@Autowiredprivate WebServiceDemo serverServiceDemo;@Autowiredprivate WebServiceDemoTwo serverServiceDemoTwo;/*** Apache CXF 核心架构是以BUS为核心,整合其他组件。* Bus是CXF的主干, 为共享资源提供一个可配置的场所,作用类似于Spring的ApplicationContext,这些共享资源包括* WSDl管理器、绑定工厂等。通过对BUS进行扩展,可以方便地容纳自己的资源,或者替换现有的资源。默认Bus实现基于Spring架构,* 通过依赖注入,在运行时将组件串联起来。BusFactory负责Bus的创建。默认的BusFactory是SpringBusFactory,对应于默认* 的Bus实现。在构造过程中,SpringBusFactory会搜索META-INF/cxf(包含在 CXF 的jar中)下的所有bean配置文件。* 根据这些配置文件构建一个ApplicationContext。开发者也可以提供自己的配置文件来定制Bus。*/@Bean(name = Bus.DEFAULT_BUS_ID)public SpringBus springBus() {return new SpringBus();}/*** 此方法作用是改变项目中服务名的前缀名,此处127.0.0.1或者localhost不能访问时,请使用ipconfig查看本机ip来访问* 此方法被注释后, 即不改变前缀名(默认是services), wsdl访问地址为 http://127.0.0.1:8080/services/ws/api?wsdl* 去掉注释后wsdl访问地址为:http://127.0.0.1:8080/soap/ws/api?wsdl* http://127.0.0.1:8080/soap/列出服务列表 或 http://127.0.0.1:8080/soap/ws/api?wsdl 查看实际的服务* 新建Servlet记得需要在启动类添加注解:@ServletComponentScan** 如果启动时出现错误:not loaded because DispatcherServlet Registration found non dispatcher servlet dispatcherServlet* 可能是springboot与cfx版本不兼容。* 同时在spring boot2.0.6之后的版本与xcf集成,不需要在定义以下方法,直接在application.properties配置文件中添加:* cxf.path=/service(默认是services)*/
// @Bean
// public ServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServlet() {
// return new ServletRegistrationBean(new CXFServlet(), "/aaa/*");
// }@Beanpublic ServletRegistrationBean newServlet() {return new ServletRegistrationBean(new CXFServlet(), "/aaa/*");}@Bean@Qualifier("sBEASEASImportClaimChannelServiceInfoSrv")public Endpoint endpoint() {EndpointImpl endpoint = new EndpointImpl(springBus(), serverServiceDemo);endpoint.publish("/bbb");return endpoint;}@Bean@Qualifier("sBEASEASImportClaimChannelServiceInfoSrx")public Endpoint endpointTwo() {EndpointImpl endpoint = new EndpointImpl(springBus(), serverServiceDemoTwo);endpoint.publish("/ccc");return endpoint;}
}
需要注意的一点:
@Beanpublic ServletRegistrationBean newServlet() {return new ServletRegistrationBean(new CXFServlet(), "/aaa/*");}
上面这块代码,决定了访问的一级路径,可以通过代码配置多个一级路径
http://localhost:8080/aaa/
这个也可以通过配置来实现,但是,找个方式只能配置1个一级路径
三、客户端调用代码
package com.test.springboot.webservice;import org.apache.cxf.endpoint.Client;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.endpoint.dynamic.JaxWsDynamicClientFactory;public class WebServiceTest {public static void main(String[] args) {String url1 = "http://localhost:8080/test/bbb?wsdl";String url2 = "http://localhost:8080/test/ccc?wsdl";
// client2(url2);client1(url1);}// 创建动态客户端public static void client1(String url) {JaxWsDynamicClientFactory dcf = JaxWsDynamicClientFactory.newInstance();Client client = dcf.createClient(url);Object[] objects = new Object[0];try {// invoke("方法名",参数1,参数2,参数3....);objects = client.invoke("emrService", "zhangsan123456");System.out.println("emrService返回数据:" + objects[0]);client.destroy();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 创建动态客户端public static void client2(String url) {JaxWsDynamicClientFactory dcf = JaxWsDynamicClientFactory.newInstance();Client client = dcf.createClient(url);Object[] objects = new Object[0];try {// invoke("方法名",参数1,参数2,参数3....);objects = client.invoke("emrServiceThree", "zhangsan789");System.out.println("emrServiceThree返回数据:" + objects[0]);client.destroy();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
总结:
1、路径
这里的访问路径的关系梳理:
http://localhost:8080/test/ccc?wsdl
test是一级路径,通过配置文件配置,cxf.path。一个web工程只能配置1个。
如果用@Bean方式注入,则可以实现多个1级路径的配置。
@Beanpublic ServletRegistrationBean newServlet() {return new ServletRegistrationBean(new CXFServlet(), "/aaa/*","/aaaa/*");}
ccc是二级路径,这个和endpoint有关,可以有多个,通过CxfConfig向springboot容器中注入多个Endpoint即可,每个endpoint对应一个二级路径。
这个Bean的注入,是关联到具体的service和serviceImpl的。
2、客户端调用
客户端调用时,确定访问路径后,我们调用时,要指定具体的方法名,可以直接在页面上看到。
这样,就可以向具体的方法发起请求了。
跟多的客户端调用案例参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/Brave_heart4pzj/article/details/126838003
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!