SSL证书校验到底在校验什么?
https用的太多了,用https的时候,不填TrustManager,用默认代码,就可以较安全地访问经过权威ca签名的host网址,啥都不用做,安逸,
当然我们也可以加载自定义TrustManager,如下:
private static OkHttpClient.Builder createBuilder(){ProxySelectorWrapper wrapper = new ProxySelectorWrapper(ProxySelector.getDefault());X509TrustManager tm = platformTrustManager();SSLSocketFactory sf = NyHttpsTrustManager.getSslSocketFactory(tm);return new OkHttpClient.Builder().connectTimeout(10, SECONDS).readTimeout(10, SECONDS).writeTimeout(10, SECONDS).proxySelector(wrapper).sslSocketFactory(sf, tm);}platformTrustManager方法其实是从OkHttp抄的,这和默认的实现也没有什么太大区别:
/*** 代码裁缝:拷贝自OkHttp* @return 系统默认信任管理器*/private static X509TrustManager platformTrustManager() {try {TrustManagerFactory trustManagerFactory = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());trustManagerFactory.init((KeyStore) null);TrustManager[] trustManagers = trustManagerFactory.getTrustManagers();if (trustManagers.length != 1 || !(trustManagers[0] instanceof X509TrustManager)) {throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected default trust managers:"+ Arrays.toString(trustManagers));}return (X509TrustManager) trustManagers[0];} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {throw new RuntimeException("No System TLS", e); // The system has no TLS. Just give up.}}自签名证书不在这篇的范围先不赘述。
TrustManagerFactory#getTrustManagers到底返回了什么呢?
public final TrustManager[] getTrustManagers() {return factorySpi.engineGetTrustManagers();}什么呢?么呢?呢?首先这个engineGet是抽象类TrustManagerFactorySpi的抽象方法:
/*** Returns one trust manager for each type of trust material.** @throws IllegalStateException if the factory is not initialized.** @return the trust managers*/protected abstract TrustManager[] engineGetTrustManagers();我们debug打断点,看看platformTrustManager方法到底返回的是什么妖怪。
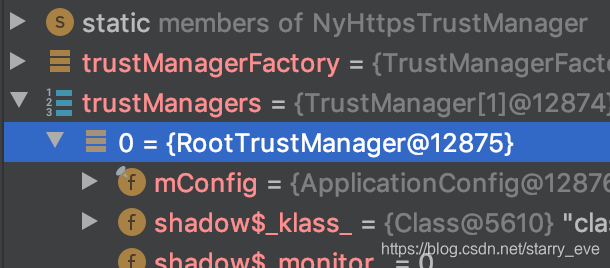
原来是RootTrustManager。
今天我们是来看怎么校验证书的(今天主要看服务器证书),所以先看下RootTrustManager的相应方法做了什么:
@Overridepublic void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType)throws CertificateException {if (mConfig.hasPerDomainConfigs()) {throw new CertificateException("Domain specific configurations require that hostname aware"+ " checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[], String, String) is used");}NetworkSecurityConfig config = mConfig.getConfigForHostname("");config.getTrustManager().checkServerTrusted(certs, authType);}我们看到:这里获取了一个config,然后从config对象掏出一个TrustManager去继续执行。我们看下这个代理TrustManager,它在NetworkSecurityConfig类中有个实例化方法:
public NetworkSecurityTrustManager getTrustManager() {synchronized(mTrustManagerLock) {if (mTrustManager == null) {mTrustManager = new NetworkSecurityTrustManager(this);}return mTrustManager;}}具体实例是类NetworkSecurityTrustManager的实例,我们看NetworkSecurityTrustManager#checkServerTrusted:
@Overridepublic void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType)throws CertificateException {checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, (String) null);}套娃,调用另一个实现:
/*** Hostname aware version of {@link #checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[], String)}.* This interface is used by conscrypt and android.net.http.X509TrustManagerExtensions do not* modify without modifying those callers.*/public List checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType,String host) throws CertificateException {List trustedChain = mDelegate.checkServerTrusted(certs, authType, host);checkPins(trustedChain);return trustedChain;} 我们先看checkPins是干嘛的?
private void checkPins(List chain) throws CertificateException {PinSet pinSet = mNetworkSecurityConfig.getPins();if (pinSet.pins.isEmpty()|| System.currentTimeMillis() > pinSet.expirationTime|| !isPinningEnforced(chain)) {return;}Set pinAlgorithms = pinSet.getPinAlgorithms();Map digestMap = new ArrayMap(pinAlgorithms.size());for (int i = chain.size() - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {X509Certificate cert = chain.get(i);byte[] encodedSPKI = cert.getPublicKey().getEncoded();for (String algorithm : pinAlgorithms) {MessageDigest md = digestMap.get(algorithm);if (md == null) {try {md = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}digestMap.put(algorithm, md);}if (pinSet.pins.contains(new Pin(algorithm, md.digest(encodedSPKI)))) {return;}}}// TODO: Throw a subclass of CertificateException which indicates a pinning failure.throw new CertificateException("Pin verification failed");} 其中PinSet是Pin的集合,Pin则包含一个摘要算法成员和一个摘要成员。这个pinSet由NetworkSecurityConfig的Builder类构造NetworkSecurityConfig时填入。
两层循环,外层循环证书链,生成encodedSPKI变量,这个是证书的公钥。
内层循环加密算法,根据加密算法生成消息摘要对象md,md对公钥encodedSPKI做摘要算法生成公钥摘要,记作digest,用算法名和公钥摘要digest生成Pin对象,如果PinSet包含pin则校验通过,否则Pin校验失败抛异常。
我们再回看NetworkSecurityTrustManager#checkServerTrusted中的mDelegate,它是一个TrustManagerImpl对象,负责真正的信任实现。
可我没有找到这类,在github上搜索:(https://github.com/google/conscrypt/blob/master/common/src/main/java/org/conscrypt/TrustManagerImpl.java)
@Overridepublic void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType)throws CertificateException {checkTrusted(chain, authType, null, null, false /* client auth */);}再看checkTrusted:
private List checkTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType,SSLSession session, SSLParameters parameters, boolean clientAuth)throws CertificateException {byte[] ocspData = null;byte[] tlsSctData = null;String hostname = null;if (session != null) {hostname = session.getPeerHost();ocspData = getOcspDataFromSession(session);tlsSctData = getTlsSctDataFromSession(session);}if (session != null && parameters != null) {String identificationAlgorithm = parameters.getEndpointIdentificationAlgorithm();if ("HTTPS".equalsIgnoreCase(identificationAlgorithm)) {ConscryptHostnameVerifier verifier = getHttpsVerifier();if (!verifier.verify(certs, hostname, session)) {throw new CertificateException("No subjectAltNames on the certificate match");}}}return checkTrusted(certs, ocspData, tlsSctData, authType, hostname, clientAuth);} 上图后三个参数是null,null,false,所以直接进入下一个方法:
private List checkTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, byte[] ocspData,byte[] tlsSctData, String authType, String host, boolean clientAuth)throws CertificateException {if (certs == null || certs.length == 0 || authType == null || authType.length() == 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("null or zero-length parameter");}if (err != null) {throw new CertificateException(err);}Set used = new HashSet();ArrayList untrustedChain = new ArrayList();ArrayList trustedChain = new ArrayList();// Initialize the chain to contain the leaf certificate. This potentially could be a trust// anchor. If the leaf is a trust anchor we still continue with path building to build the// complete trusted chain for additional validation such as certificate pinning.X509Certificate leaf = certs[0];TrustAnchor leafAsAnchor = findTrustAnchorBySubjectAndPublicKey(leaf);if (leafAsAnchor != null) {trustedChain.add(leafAsAnchor);used.add(leafAsAnchor.getTrustedCert());} else {untrustedChain.add(leaf);}used.add(leaf);return checkTrustedRecursive(certs, ocspData, tlsSctData, host, clientAuth,untrustedChain, trustedChain, used);} 这个方法构建了已使用证书、不信任证书链、信任锚点链3个集合,给下一步递归调用。
信任锚点代表TrustAnchor代表最受信任的CA,主要持有了CA的公钥或证书、CA名称等。
findTrustAnchorBySubjectAndPublicKey方法查找证书的叶子节点,如果找到了信任的锚点,则把锚点添加到信任链,并把锚点的信任证书添加到已使用。
如果没找到信任锚点则把叶子节点添加到不信任证书链。
再看递归调用的方法,下面就是核心的检查方法了,方法比较长,主要职责是尽可能地创建一个有效的证书链:
/*** Recursively build certificate chains until a valid chain is found or all possible paths are* exhausted.** The chain is built in two sections, the complete trusted path is the the combination of* {@code untrustedChain} and {@code trustAnchorChain}. The chain begins at the leaf* certificate and ends in the final trusted root certificate.** @param certs the bag of certs provided by the peer. No order is assumed.* @param host the host being connected to.* @param clientAuth if a client is being authorized instead of a server.* @param untrustedChain the untrusted section of the chain built so far. Must be mutable.* @param trustAnchorChain the trusted section of the chain built so far. Must be mutable.* @param used the set certificates used so far in path building. Must be mutable.** @return The entire valid chain starting with the leaf certificate. This is the* concatenation of untrustedChain and trustAnchorChain.** @throws CertificateException If no valid chain could be constructed. Note that there may be* multiple reasons why no valid chain exists and there is no guarantee that the most severe is* reported in this exception. As such applications MUST NOT use the specifics of this error* for trust decisions (e.g. showing the user a click through page based on the specific error).*/private List checkTrustedRecursive(X509Certificate[] certs, byte[] ocspData,byte[] tlsSctData, String host, boolean clientAuth,ArrayList untrustedChain, ArrayList trustAnchorChain,Set used) throws CertificateException {CertificateException lastException = null;X509Certificate current;if (trustAnchorChain.isEmpty()) {current = untrustedChain.get(untrustedChain.size() - 1);} else {current = trustAnchorChain.get(trustAnchorChain.size() - 1).getTrustedCert();}// Check that the certificate isn't blocklisted.checkBlocklist(current);// 1. If the current certificate in the chain is self-signed verify the chain as is.if (current.getIssuerDN().equals(current.getSubjectDN())) {return verifyChain(untrustedChain, trustAnchorChain, host, clientAuth, ocspData,tlsSctData);}// 2. Try building a chain via any trust anchors that issued the current certificate.// Note that we do not stop at the first trust anchor since it is possible that the trust// anchor is not self-signed and its issuer may be needed for additional validation such as// certificate pinning. In the common case the first trust anchor will be self-signed or// its issuer's certificate will be missing.Set anchors = findAllTrustAnchorsByIssuerAndSignature(current);boolean seenIssuer = false;for (TrustAnchor anchor : sortPotentialAnchors(anchors)) {X509Certificate anchorCert = anchor.getTrustedCert();// Avoid using certificates that have already been used.if (used.contains(anchorCert)) {continue;}seenIssuer = true;used.add(anchorCert);trustAnchorChain.add(anchor);try {return checkTrustedRecursive(certs, ocspData, tlsSctData, host, clientAuth,untrustedChain, trustAnchorChain, used);} catch (CertificateException ex) {lastException = ex;}// Could not form a valid chain via this certificate, remove it from this chain.trustAnchorChain.remove(trustAnchorChain.size() - 1);used.remove(anchorCert);}// 3. If we were unable to find additional trusted issuers, verify the current chain.// This may happen if the root of trust is not self-signed and the issuer is not// present in the trusted set.if (!trustAnchorChain.isEmpty()) {if (!seenIssuer) {return verifyChain(untrustedChain, trustAnchorChain, host, clientAuth, ocspData,tlsSctData);}// Otherwise all chains based on the current trust anchor were rejected, fail.throw lastException;}// 4. Use the certificates provided by the peer to grow the chain.// Ignore the first certificate, as that is the leaf certificate.for (int i = 1; i < certs.length; i++) {X509Certificate candidateIssuer = certs[i];// Avoid using certificates that have already been used.if (used.contains(candidateIssuer)) {continue;}if (current.getIssuerDN().equals(candidateIssuer.getSubjectDN())) {// Check the strength and validity of the certificate to prune bad certificates// early.try {candidateIssuer.checkValidity();ChainStrengthAnalyzer.checkCert(candidateIssuer);} catch (CertificateException ex) {lastException = new CertificateException("Unacceptable certificate: "+ candidateIssuer.getSubjectX500Principal(), ex);continue;}used.add(candidateIssuer);untrustedChain.add(candidateIssuer);try {return checkTrustedRecursive(certs, ocspData, tlsSctData, host, clientAuth,untrustedChain, trustAnchorChain, used);} catch (CertificateException ex) {lastException = ex;}// Could not form a valid chain via this certificate, remove it from this chain.used.remove(candidateIssuer);untrustedChain.remove(untrustedChain.size() - 1);}}// 5. Finally try the cached intermediates to handle server that failed to send them.Set intermediateAnchors =intermediateIndex.findAllByIssuerAndSignature(current);for (TrustAnchor intermediate : sortPotentialAnchors(intermediateAnchors)) {X509Certificate intermediateCert = intermediate.getTrustedCert();// Avoid using certificates that have already been used.if (used.contains(intermediateCert)) {continue;}used.add(intermediateCert);untrustedChain.add(intermediateCert);try {return checkTrustedRecursive(certs, ocspData, tlsSctData, host, clientAuth,untrustedChain, trustAnchorChain, used);} catch (CertificateException ex) {lastException = ex;}// Could not form a valid chain via this certificate, remove it from this chain.untrustedChain.remove(untrustedChain.size() - 1);used.remove(intermediateCert);}// 6. We were unable to build a valid chain, throw the last error encountered.if (lastException != null) {throw lastException;}// 7. If no errors were encountered above then verifyChain was never called because it was// not possible to build a valid chain to a trusted certificate.CertPath certPath = factory.generateCertPath(untrustedChain);throw new CertificateException(new CertPathValidatorException("Trust anchor for certification path not found.", null, certPath, -1));} current证书先从信任锚点的末尾(根节点)中取证书,如果信任锚点为空,则从不信任证书的末尾(根节点)中取。
然后马上调用checkBlocklist方法,去查看当前证书的公钥是否在block列表,如果在则直接抛异常。
1.先查看证书的签发者和当前域名是否一致,一致则是自签名证书,走verifyChain方法,verifyChain方法很长,后面分析。
2.先从当前证书找信任锚点。循环,略过已经使用的锚点,并把信任锚点加到递归的信任锚点数组trustAnchorChain里。这里再进行一次前向递归。
3.如果到这里还是没有找到有效的签发者,则直接对当前链进行校验。什么时候发生呢?root-trust不是自签名的,且签发者不在信任集合时。
4.直接尝试使用certs去填充递归的3个输入输出参数。
5.最后尝试使用缓存的中间索引去处理,再递归。
6&7.如果最后都不能组件一个有效的信任链则抛出异常。
观察:
上面递归方法中,向信任锚点数组增加对象的地方只有一处,即步骤2中。其他地方都是往未信任数组中添加元素。
步骤二中信任锚点的获取通过findAllTrustAnchorsByIssuerAndSignature方法,继续看:
/*** Find all possible issuing trust anchors of {@code cert}.*/private Set findAllTrustAnchorsByIssuerAndSignature(X509Certificate cert) {Set indexedAnchors =trustedCertificateIndex.findAllByIssuerAndSignature(cert);if (!indexedAnchors.isEmpty() || trustedCertificateStore == null) {return indexedAnchors;}Set storeAnchors = trustedCertificateStore.findAllIssuers(cert);if (storeAnchors.isEmpty()) {return indexedAnchors;}Set result = new HashSet(storeAnchors.size());for (X509Certificate storeCert : storeAnchors) {result.add(trustedCertificateIndex.index(storeCert));}return result;} 这个trustedCertificateIndex是什么东东?
是一个TrustedCertificateIndex类的对象。这是个什么类呢?这个类只有一个成员,如下图,他只做一件事,根据X509Principal去查找信任锚点的集合:
public final class TrustedCertificateIndex {private final Map> subjectToTrustAnchors= new HashMap>(); 这个类直接把subject(证书主体)和信任的证书列表(包装成锚点的列表)进行映射,方便查找,使时间复杂度降为常量级别。
这个类使用index方法把锚点插入到索引。这个类还有一个有参构造函数,会直接把传入的锚点Set建立索引。
再看trustedCertificateIndex的初始化。
看TrustManagerImpl的构造方法,发现有一个trustedCertificateIndexLocal变量,trustedCertificateIndex则会初始化为trustedCertificateIndexLocal的值,看下trustedCertificateIndexLocal的初始化。
先判断TrustManagerImpl传入的秘钥库的类型是不是AnroidCAStore类型,如果是,直接构造;如果不是,则使用trustAnchors方法把传入KeyStore中的所有证书变成一个信任锚点数组,传入到TrustedCertificateIndex的构造方法:
public TrustManagerImpl(KeyStore keyStore, CertPinManager manager,ConscryptCertStore certStore, CertBlocklist blocklist, CTLogStore ctLogStore,CTVerifier ctVerifier, CTPolicy ctPolicy) {...// if we have an AndroidCAStore, we will lazily load CAsif ("AndroidCAStore".equals(keyStore.getType())&& Platform.supportsConscryptCertStore()) {rootKeyStoreLocal = keyStore;trustedCertificateStoreLocal =(certStore != null) ? certStore : Platform.newDefaultCertStore();acceptedIssuersLocal = null;trustedCertificateIndexLocal = new TrustedCertificateIndex();} else {rootKeyStoreLocal = null;trustedCertificateStoreLocal = certStore;acceptedIssuersLocal = acceptedIssuers(keyStore);trustedCertificateIndexLocal= new TrustedCertificateIndex(trustAnchors(acceptedIssuersLocal));}上面代码中还初始化了trustedCertificateStoreLocal变量,如果是AndroidCAStore且certStore为空,则使用平台默认的Platform.newDefaultCertStore()去兜底。
回看findAllTrustAnchorsByIssuerAndSignature方法:
如果从索引找到锚点并且trustedCertificateStore 为空就直接返回锚点。这个trustedCertificateStore的值其实就是trustedCertificateStoreLocal的值,和TrustManagerImpl构造方法中传入的certStore有关。
如果没找到锚点则尝试用初始证书库trustedCertificateStore去查找锚点,会把查找到的锚点建立索引并返回。
小结:
TrustManagerImpl构造方法中,如果keystore不是是AndroidCAStore类型,则默认把keyStore建立索引。
信任证书库变量使用certStore,如果keystore是AndroidCAStore类型则尝试使用平台默认证书库。
我们再回看TrustManagerImpl的创建,是在NetworkSecurityTrustManager中:
public NetworkSecurityTrustManager(NetworkSecurityConfig config) {if (config == null) {throw new NullPointerException("config must not be null");}mNetworkSecurityConfig = config;try {TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter certStore = new TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter(config);// Provide an empty KeyStore since TrustManagerImpl doesn't support null KeyStores.// TrustManagerImpl will use certStore to lookup certificates.KeyStore store = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType());store.load(null);mDelegate = new TrustManagerImpl(store, null, certStore);} catch (GeneralSecurityException | IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}可以看到,传进去的keyStore是个空的充数的,只有certStore才会对最终的证书校验产生影响。
这里的certStore是一个TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter包装类,对config2次包装,看其对config的使用情况:
/** @hide */
public class TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter extends TrustedCertificateStore {private final NetworkSecurityConfig mConfig;public TrustedCertificateStoreAdapter(NetworkSecurityConfig config) {mConfig = config;}@Overridepublic X509Certificate findIssuer(X509Certificate cert) {TrustAnchor anchor = mConfig.findTrustAnchorByIssuerAndSignature(cert);if (anchor == null) {return null;}return anchor.certificate;}我们顺藤摸瓜,再看NetworkSecurityConfig#findTrustAnchorByIssuerAndSignature方法:
/** @hide */public TrustAnchor findTrustAnchorByIssuerAndSignature(X509Certificate cert) {for (CertificatesEntryRef ref : mCertificatesEntryRefs) {TrustAnchor anchor = ref.findByIssuerAndSignature(cert);if (anchor != null) {return anchor;}}return null;}实际证书来源是mCertificatesEntryRefs。mCertificatesEntryRefs是从哪来呢?从构造方法:
private NetworkSecurityConfig(boolean cleartextTrafficPermitted, boolean hstsEnforced,PinSet pins, List certificatesEntryRefs) {mCleartextTrafficPermitted = cleartextTrafficPermitted;mHstsEnforced = hstsEnforced;mPins = pins;mCertificatesEntryRefs = certificatesEntryRefs;// Sort the certificates entry refs so that all entries that override pins come before// non-override pin entries. This allows us to handle the case where a certificate is in// multiple entry refs by returning the certificate from the first entry ref.Collections.sort(mCertificatesEntryRefs, new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(CertificatesEntryRef lhs, CertificatesEntryRef rhs) {if (lhs.overridesPins()) {return rhs.overridesPins() ? 0 : -1;} else {return rhs.overridesPins() ? 1 : 0;}}});} 哈哈,cleartextTrafficPermitted,我们对这个字段很亲切吧,这就是安卓8出的manifest的配置:“明文传输是否被禁止”。
证书来自构造函数的最后一个参数certificatesEntryRefs。
NetworkSecurityConfig实例化的唯一来源是其Builder类,Builder类有两个添加证书的方法:addCertificatesEntryRef和addCertificatesEntryRefs。先搜索addCertificatesEntryRefs的引用者,在XmlConfigSource:
private List>> parseConfigEntry(XmlResourceParser parser, Set seenDomains,NetworkSecurityConfig.Builder parentBuilder, int configType)throws IOException, XmlPullParserException, ParserException {List>> builders = new ArrayList<>();NetworkSecurityConfig.Builder builder = new NetworkSecurityConfig.Builder();builder.setParent(parentBuilder);Set domains = new ArraySet<>();boolean seenPinSet = false;boolean seenTrustAnchors = false;boolean defaultOverridePins = configType == CONFIG_DEBUG;String configName = parser.getName();int outerDepth = parser.getDepth();// Add this builder now so that this builder occurs before any of its children. This// makes the final build pass easier.builders.add(new Pair<>(builder, domains));// Parse config attributes. Only set values that are present, config inheritence will// handle the rest.for (int i = 0; i < parser.getAttributeCount(); i++) {String name = parser.getAttributeName(i);if ("hstsEnforced".equals(name)) {builder.setHstsEnforced(parser.getAttributeBooleanValue(i,NetworkSecurityConfig.DEFAULT_HSTS_ENFORCED));} else if ("cleartextTrafficPermitted".equals(name)) {builder.setCleartextTrafficPermitted(parser.getAttributeBooleanValue(i,NetworkSecurityConfig.DEFAULT_CLEARTEXT_TRAFFIC_PERMITTED));}}// Parse the config elements.while (XmlUtils.nextElementWithin(parser, outerDepth)) {String tagName = parser.getName();if ("domain".equals(tagName)) {if (configType != CONFIG_DOMAIN) {throw new ParserException(parser,"domain element not allowed in " + getConfigString(configType));}Domain domain = parseDomain(parser, seenDomains);domains.add(domain);} else if ("trust-anchors".equals(tagName)) {if (seenTrustAnchors) {throw new ParserException(parser,"Multiple trust-anchor elements not allowed");}builder.addCertificatesEntryRefs(parseTrustAnchors(parser, defaultOverridePins));seenTrustAnchors = true;} else if ("pin-set".equals(tagName)) {if (configType != CONFIG_DOMAIN) {throw new ParserException(parser,"pin-set element not allowed in " + getConfigString(configType));}if (seenPinSet) {throw new ParserException(parser, "Multiple pin-set elements not allowed");}builder.setPinSet(parsePinSet(parser));seenPinSet = true;} else if ("domain-config".equals(tagName)) {if (configType != CONFIG_DOMAIN) {throw new ParserException(parser,"Nested domain-config not allowed in " + getConfigString(configType));}builders.addAll(parseConfigEntry(parser, seenDomains, builder, configType));} else {XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);}}if (configType == CONFIG_DOMAIN && domains.isEmpty()) {throw new ParserException(parser, "No domain elements in domain-config");}return builders;} 这TM完全就是一个manifest解析啊,看来,manifest中的配置会被当作信任证书传入。
再看另一个方法addCertificatesEntryRef的引用,一处在NetworkSecurityConfig中,这是NetworkSecurityConfig的默认创建builder:
public static Builder getDefaultBuilder(ApplicationInfo info) {Builder builder = new Builder().setHstsEnforced(DEFAULT_HSTS_ENFORCED)// System certificate store, does not bypass static pins..addCertificatesEntryRef(new CertificatesEntryRef(SystemCertificateSource.getInstance(), false));final boolean cleartextTrafficPermitted = info.targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.P&& !info.isInstantApp();builder.setCleartextTrafficPermitted(cleartextTrafficPermitted);// Applications targeting N and above must opt in into trusting the user added certificate// store.if (info.targetSdkVersion <= Build.VERSION_CODES.M && !info.isPrivilegedApp()) {// User certificate store, does not bypass static pins.builder.addCertificatesEntryRef(new CertificatesEntryRef(UserCertificateSource.getInstance(), false));}return builder;}卧槽,这个也熟悉的很呢,先把系统证书源添加进来,然后如果小于N且没有root,则把用户证书源加进来。
安卓版本>=N无法加载用户证书源。
另一个在KeyStoreConfigSource的构造方法:
public KeyStoreConfigSource(KeyStore ks) {mConfig = new NetworkSecurityConfig.Builder().addCertificatesEntryRef(// Use the KeyStore and do not override pins (of which there are none).new CertificatesEntryRef(new KeyStoreCertificateSource(ks), false)).build();}这个方法在RootTrustManagerFactorySpi类中被调用:
@Overridepublic void engineInit(KeyStore ks) throws KeyStoreException {if (ks != null) {mApplicationConfig = new ApplicationConfig(new KeyStoreConfigSource(ks));} else {mApplicationConfig = ApplicationConfig.getDefaultInstance();}}这个keystore是啥?不就是TrustManager初始化的时候传进了的吗,很熟悉是不是。见TrustManager#init:
/*** Initializes this factory with a source of certificate* authorities and related trust material.* * The provider typically uses a KeyStore as a basis for making* trust decisions.*
* For more flexible initialization, please see* {@link #init(ManagerFactoryParameters)}.** @param ks the key store, or null* @throws KeyStoreException if this operation fails*/public final void init(KeyStore ks) throws KeyStoreException {factorySpi.engineInit(ks);}
所以,TrustManager初始化的时候如果传入了秘钥库,其中的证书也会被放到信任证书源。
上面接触到了好几种ConfigSource,ConfigSource是一个接口,接口有以下几种实现:
- DefaultConfigSource
- KeyStoreConfigSource
- ManifestConfigSource
- XmlConfigSource
其中,ManifestConfigSource在内部会创建XmlConfigSource或者DefaultConfigSource,所以就简化为了两种:
- KeyStoreConfigSource
- ManifestConfigSource
上面KeyStoreConfigSource已经出现过了,当初始化TrustManager时如果传入了keystore,则用KeyStoreConfigSource将keystore包裹,用来构造ApplicationConfig对象。
而ManifestConfigSource构造方法则在NetworkSecurityConfigProvider中被调用,用来构造ApplicationConfig对象,这个ApplicationConfig对象被设为默认对象。
ApplicationConfig与ConfigSource的关系是:ApplicationConfig持有ConfigSource。
ConfigSource和NetworkSecurityConfig的关系是:ConfigSource#getDefaultConfig就得到NetworkSecurityConfig
ApplicationConfig有一个获取网络加密配置的方法,当host为空时,直接返回mDefaultConfig,这个mDefaultConfig实际上就是传入的ConfigSource调用getDefaultConfig方法的结果,如图:
public NetworkSecurityConfig getConfigForHostname(String hostname) {ensureInitialized();if (hostname == null || hostname.isEmpty() || mConfigs == null) {return mDefaultConfig;}
下面是RootTrustManager的代码,这个mConfig是ApplicationConfig对象,config实际上就是ConfigSource#getDefaultConfig返回的,如图:
@Overridepublic void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType)throws CertificateException {if (mConfig.hasPerDomainConfigs()) {throw new CertificateException("Domain specific configurations require that hostname aware"+ " checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[], String, String) is used");}NetworkSecurityConfig config = mConfig.getConfigForHostname("");config.getTrustManager().checkServerTrusted(certs, authType);}到了这里我们会发觉,默认信任什么证书,只和ApplicationConfig构造函数传进去的ConfigSource有关。
现在看ApplicationConfig的创建,一个在NetworkSecurityConfigProvider(卧槽,jca的提供器。这里先用ManifestConfigSource创建了ApplicationConfig,并把这个ApplicationConfig作为默认的实例。install的时候还初始化了Policy实例):
/** @hide */
public final class NetworkSecurityConfigProvider extends Provider {private static final String PREFIX =NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.class.getPackage().getName() + ".";public NetworkSecurityConfigProvider() {// TODO: More clever name than thissuper("AndroidNSSP", 1.0, "Android Network Security Policy Provider");put("TrustManagerFactory.PKIX", PREFIX + "RootTrustManagerFactorySpi");put("Alg.Alias.TrustManagerFactory.X509", "PKIX");}public static void install(Context context) {ApplicationConfig config = new ApplicationConfig(new ManifestConfigSource(context));ApplicationConfig.setDefaultInstance(config);int pos = Security.insertProviderAt(new NetworkSecurityConfigProvider(), 1);if (pos != 1) {throw new RuntimeException("Failed to install provider as highest priority provider."+ " Provider was installed at position " + pos);}libcore.net.NetworkSecurityPolicy.setInstance(new ConfigNetworkSecurityPolicy(config));}
}一个在NetworkSecurityPolicy(这个实例每次都new,先不管):
/*** Returns an {@link ApplicationConfig} based on the configuration for {@code packageName}.** @hide*/public static ApplicationConfig getApplicationConfigForPackage(Context context,String packageName) throws PackageManager.NameNotFoundException {Context appContext = context.createPackageContext(packageName, 0);ManifestConfigSource source = new ManifestConfigSource(appContext);return new ApplicationConfig(source);}一个在FactorySpi(如果传入了秘钥库直接用这套证书,如果没有则用默认的,默认的其实就是NetworkSecurityConfigProvider中创建的那个用ManifestConfigSource初始化的实例):
@Overridepublic void engineInit(KeyStore ks) throws KeyStoreException {if (ks != null) {mApplicationConfig = new ApplicationConfig(new KeyStoreConfigSource(ks));} else {mApplicationConfig = ApplicationConfig.getDefaultInstance();}}NetworkSecurityConfigProvider#init是在ActivityThread#handleBindApplication中调用的:
// Install the Network Security Config Provider. This must happen before the application// code is loaded to prevent issues with instances of TLS objects being created before// the provider is installed.Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install");NetworkSecurityConfigProvider.install(appContext);Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
累死了,这么长,有些细节比如如何检验证书链的还没有介绍,后面再看下。
总结一下:
TrustManagerFactory#getTrustManagers返回了RootTrustManager。
RootTrustManager持有ApplicationConfig,ApplicationConfig持有ConfigSource,ConfigSource主要有manifest和keystore两种实现,ConfigSource#getDefaultConfig得到NetworkSecurityConfig。
NetworkSecurityConfig的Builder可以关联parentBuilder,执行顺序是先自己再parent。
默认的ApplicationConfig配置在NetworkSecurityConfigProvider中创建,NetworkSecurityConfigProvider在ActivityThread#handleBinderApplication中调用。
NetworkSecurityConfig有个静态方法,可以以自己为入参构造一个TrustManager对象,这是一个TrustManagerImpl对象(这个类在sdk源码中找不到)。
TrustManagerImpl传入keystore、certStore作为参数,在平时keystore为空,以certStore作为信任证书。
TrustManagerImpl内部通过递归的形式计算证书链是否有效,从根节点(数组最后一个元素)向叶子节点去计算。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!