算法练习day7——190325(比较器、不基于比较的排序、maxGap、数组实现栈和队列、minStack)
1.比较器
1.1 Arrays.sort()
Arrays.sort(数组)
- 若其中的数组元素时自定义类型,报错;

- 若为基本类型,则按值排序。
Arrays.sort(数组,自己定义的比较器):
- 会按定义的比较器进行比较排序。
1.2 比较器
是一个自己定义的类。
类名 implements Comparator
实现其中的public int compare(Student o1,Student o2)方法:
- 此方法返回一个负数:说明o1更小,即o1应该排在前面;
- 返回一个正数:第二个应该放在前面;
- 返回0:两个一样大
C++中重载运算符就是自己定义比较器的一种方式。
package Comparator;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;class Student{int id;String name;int age;public Student(int id,String name,int age) {this.id=id;this.name=name;this.age=age;}
}
public class ComparatorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Student[] students=new Student[3];students[0]=new Student(3,"llll",23);students[1]=new Student(2,"ssss",18);students[2]=new Student(1,"qqqq",34);//Arrays.sort(students);//printArray(students);Arrays.sort(students,new IdAscendingComparator());printArray(students);Arrays.sort(students,new IdDscendingComparator());printArray(students);Arrays.sort(students,new AgeAscendingComparator());printArray(students);Arrays.sort(students,new AgeDscendingComparator());printArray(students);}public static void printArray(Student[] arr) {for(int i=0;i{@Overridepublic int compare(Student arg0, Student arg1) {/** if(arg0arg1)* return 正数;* else* return 0;*/return arg0.id-arg1.id;}
}class IdDscendingComparator implements Comparator{@Overridepublic int compare(Student arg0, Student arg1) {return arg1.id-arg0.id;}
}class AgeAscendingComparator implements Comparator{@Overridepublic int compare(Student arg0, Student arg1) {return arg0.age-arg1.age;}
}class AgeDscendingComparator implements Comparator{@Overridepublic int compare(Student arg0, Student arg1) {return arg1.age-arg0.age;}
}
运行结果:

1.3 PriorityQueue
堆结构也可用比较器
优先级队列就是堆。
若没有给比较器,则报错。
package Comparator;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class PriorityQueueTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Student student1=new Student(3,"llll",23);Student student2=new Student(2,"ssss",18);Student student3=new Student(1,"qqqq",34);PriorityQueue heap=new PriorityQueue<>(new AgeDscendingComparator());//按age大的放在头部heap.add(student1);heap.add(student2);heap.add(student3);while(!heap.isEmpty()) {Student stu=heap.poll();//弹出堆顶元素,堆大小-1;System.out.println(stu.id+"--"+stu.name+"--"+stu.age);}}
}
运行结果:

1.4 TreeMap
红黑树结构。
系统提供的一个有序的结构,都会伴随着一个比较器的构造。这个比较器告诉这个结构怎么组织。
——基于比较的排序是重点。
2.不基于比较的排序
时间复杂度:
- 遍历数组的时间
额外空间复杂度:
都是稳定的。
与被排序的样本的实际数据状况很有关系, 所以实际中并不经常使用。
计数排序就是桶排序的一个具体体现。
3.给定一个数组, 求如果排序之后, 相邻两数的最大差值, 要求时间复杂度O(N), 且要求不能用非基于比较的排序。
3.1 举例:
原始数据:

排序之后:
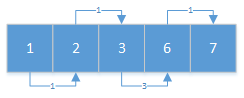
所以应该返回3.
3.2 实现方式
借用了桶的概念,但是未用桶排序。
- N个数据,准备N+1个桶;用一个全局变量记录最大差值。
- 遍历数组,找到min和max
- 若min=max,整个数组只有一种数,返回0;
- 若不等,min放入桶0,max放入桶N
- 将min~max均分成N份,对应N+1个桶,如下图:

- 其他数属于哪个范围,放入对应的桶。
- 每个桶设置三个属性:
- min
- max
- flag(boolean):表示这个桶是否有元素进入过
- 若x进入桶m时,flag=false,则令flag=true,min=max=x;
- 若y进入桶m时,flag=true,则只更新min和max
- 遍历完后,找每个桶的flag
- 若为false,直接跳下一个;
- 若为true,找到此桶的前一个非空桶,此桶的min-前非空桶的max得到这两个桶的差值。
- 更新最大差值。
3.3 最大差值肯定跨桶的原因分析
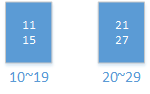
如上图,排序后,相临的两个数可能来自同一个桶(11,15),也可能来自不同的桶(15,21)。
N个数,N+1个桶,根据鸽舍原理,肯定存在一个空桶。
存在空桶,就可以说明:最大差值一定不来自相同的桶。
因为:

空桶左肯定存在离它最近的非空桶,空桶右边也肯定存在离它最近的布控的桶(最起码桶0和桶N都非空)。
左.max-右.min>桶表示的范围;
一个桶内部的两个元素的差值<桶表示的范围
所以最大差值不会是同一桶中的两个元素——只用关心不同桶的元素。
为什么不直接找非空桶,得到最大差值=左.max-右.min?
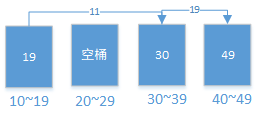
如上图,最大差值为19,是相邻两桶产生的差值。
有空桶,只是说明最大差值肯定不是在同一桶中,但不是说最大差值一定来自空桶两侧非空桶的差值。
3.4 代码实现
package Solution;public class MaxGap {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array= {3,1,6,2,7};System.out.println("maxGap="+maxGap(array));}public static int maxGap(int[] arr) { int result=0;if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {return result;}int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;int n=arr.length;for(int i=0;iarr[i]?max:arr[i];min=min 运行结果:
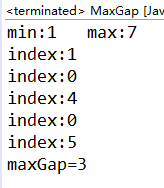
3.4.1 结果分析
元素,其中最大值为7,最小值为1。
5个元素,需要6个桶。
首先,将max-min=7-1=6进行5等分,6/5=1.2,得每段距离长1.2。
然后进行每个元素属于的桶号的计算:
- 3:(3-1)/1.2=2/1.2=1(取整);
- 6:(6-1)/1.2=5/1.2=4;
- 2:(2-1)/1.2=1/1.2=0;
所以分桶结果如下图:

所以result=3;
3.4.2 对于计算桶号的公式的分析
即就是:
先算出每段距离的长度(),再求出当前元素据起点min的距离(
),最后用后者除以前者就得到当前元素所属于的桶号(index)。
4.用数组结构实现大小固定的栈和队列
4.1 实现栈
4.1.1 分析
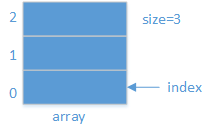
index:表示新进来的数应该放置的位置。
一个数入栈时,若index+1>size,则报错;否则这个数放在array[index]的位置,然后index++;
一个数出栈时,若index-1<0,则报错;否则弹出放在array[index-1]位置上的数,然后index--。
4.1.2 代码实现
package Solution;class ArrayStack{Integer[] array;Integer size; public ArrayStack(int initsize) {if(initsize<0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("The init size is less than 0");elsearray=new Integer[initsize];size=0;}public void push(int num) {if(size==array.length)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is full");elsearray[size++]=num;}public Integer peek() {if(size==0)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is empty");elsereturn array[size-1];}public Integer pop() {if(size==0)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is empty");elsereturn array[--size];}
} public class ArrayToStack {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayStack as=new ArrayStack(3);as.push(3);System.out.println("peek:"+as.peek());as.push(24);System.out.println("pop:"+as.pop());System.out.println("pop:"+as.pop());//System.out.println("pop:"+as.pop());}
}运行结果:
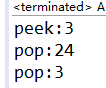
若为注释掉最后一句pop,运行结果为:
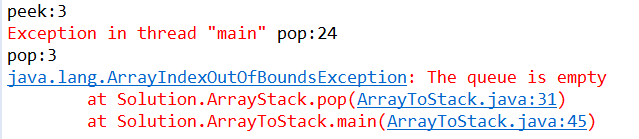
4.2 实现队列
4.2.1 分析
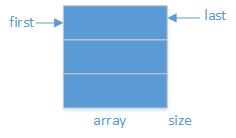
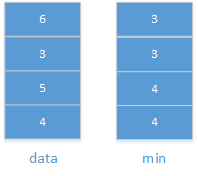
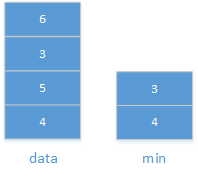
如果一个数要入队列,若size 如果一个数要出队列,若size>0,则array[first]位置上的数出队列,同时first++;否则报错。 注:当last和first到达最后一个元素时,让它们下一个位置为0位置。 (last和first之间无关系) 运行结果: 【要求】 准备两个栈:data、min 入栈: 第一个元素,压入data、min栈; 后面剩余元素,依次压入data栈;若当前入栈元素比min栈栈顶元素小,则入min栈,否则再一次压入min栈栈顶元素。 出栈: 两个栈同时弹出元素。 运行结果: 准备两个栈:data、min 入栈: 第一个元素,压入data、min栈; 后面剩余元素,依次压入data栈;若当前入栈元素比min栈栈顶元素小,则入min栈,否则不如min栈。 出栈: 若当前弹出的data栈顶元素=min栈栈顶元素,两个栈都弹出栈顶元素,否则只有data栈弹出栈顶元素。4.2.2 代码实现
package Solution;class ArrayQueue{Integer[] array;Integer first;//出队列时的下标Integer last;//入队列时的下标Integer size;public ArrayQueue(int initsize) {if(initsize<0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("The init size is less than 0");elsearray=new Integer[initsize];size=0;last=0;first=0;}public void push(int num) {if(size==array.length)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is full");else {array[last]=num;last=last==array.length-1?0:last+1;size++;}}public Integer peek() {if(size==0)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is empty");else return array[first];}public Integer poll() {if(size==0)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is empty");else {size--;first=first==array.length-1?0:first+1;return array[first];}}
}
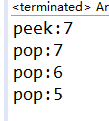
public class ArrayToQueue {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayQueue as=new ArrayQueue(3);as.push(7);System.out.println("peek:"+as.peek());as.push(6);System.out.println("pop:"+as.poll());//7出as.push(5);as.push(9);//as.push(4);System.out.println("pop:"+as.poll());//6System.out.println("pop:"+as.poll());//5}
}
5. 实现一个特殊的栈, 在实现栈的基本功能的基础上, 再实现返回栈中最小元素的操作。
1. pop、 push、 getMin操作的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
2. 设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构。5.1 方法一
5.1.1 分析:
5.1.2 代码实现
package Solution;import java.util.Stack;class MyStack{Stack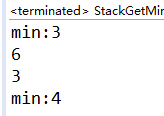
5.2 方法二
5.2.1 分析:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!