基于MCTS的网格寻路
MCTS网格寻路
1.蒙特卡洛树搜索MCTS
蒙特卡罗树搜索是一种基于树数据结构、能权衡探索与利用、在搜索空间巨大情况下仍然比较有效的的搜索算法。
1.1 MCTS基本原理
1.蒙特卡洛模拟
MCTS使用蒙特卡洛模拟来评估一个动作的价值。这个过程会进行多次,每次会随机模拟出一组可能的后继状态,然后评估这些状态的价值,最后对这些价值取平均值,作为当前状态下这个动作的价值。
2.树搜索
MCTS通过搜索一棵树来选择最优的动作。树的每个节点代表一个状态,每个节点的子节点代表在该状态下可以执行的所有动作。搜索过程从根节点开始,通过不断扩展和更新树,得到越来越多的信息来帮助选择最优的动作。
3.选择动作
在选择动作时,MCTS使用一种称为“上限置信区间(UCB)算法”的方法,来平衡探索和利用。UCB算法考虑了每个动作的价值和探索次数,以及当前节点的深度,来计算每个动作的置信区间上限,然后选择上限最高的动作。
4.扩展树
在选择完一个动作后,MCTS会扩展树,将新的状态和动作添加到树中。如果新状态是第一次遇到,就会创建一个新节点;否则,就会使用已有节点。
5.更新价值
最后,在模拟过程结束后,MCTS会将模拟结果的价值反向传播回根节点,更新所有经过的节点和动作的价值和探索次数。
通过不断重复以上步骤,MCTS会不断扩展和更新树,得到更准确的动作价值,最终选择最优的动作。
1.2 MCTS算法过程
该树搜索算法主要分为四个步骤:选择、扩展、模拟、反向传播。
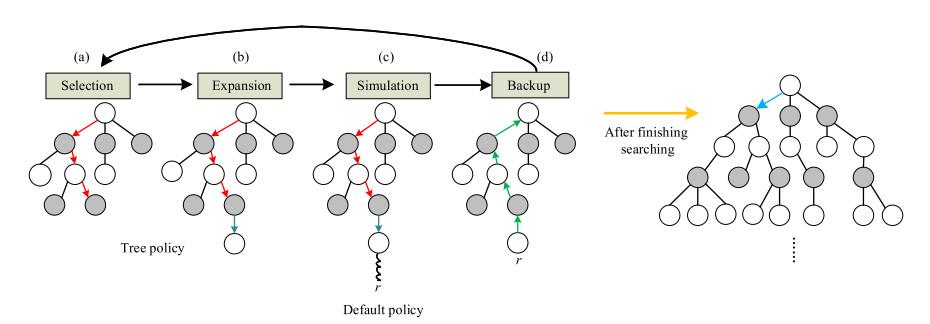
1.选择
从根节点开始,选择一个可选动作,通过UCB(Upper Confidence Bounds)算法选择UCB值最大的子节点,直到找到未扩展的节点或者达到终止状态。
2.扩展
在选择步骤中找到未扩展的节点时,随机选择一个未探索过的动作,生成一个新的子节点。
3.模拟
从扩展的子节点开始,使用随机策略进行模拟,直到达到终止状态,并返回游戏结果。
4.反向传播
将模拟得到的结果反向传播到选择路径上的所有节点,更新它们的访问次数和胜率统计信息。
重复执行以上四个步骤,直到达到时间或次数的限制。在选择动作时,UCB算法的核心是平衡探索和利用,通过选择置信区间上限最大的子节点进行探索,同时考虑子节点访问次数的影响,使得算法更加智能化和准确。
总的来说,MCTS算法的优点在于它不需要对状态空间进行完全搜索,而是通过不断模拟和反向传播来动态地调整搜索策略。它的适用范围比较广泛,可以用于解决多种博弈问题,同时具有一定的扩展性和灵活性,可以根据具体问题进行适当的改进和优化。
1.3 MCTS算法内容
MCTS伪代码:
function MCTS(root, max_iterations):for iteration in range(max_iterations):node = tree_policy(root)reward = default_policy(node)backup(node, reward)return best_child(root, 0)function tree_policy(node):while node is not a terminal node:if node is not fully expanded:return expand(node)else:node = best_child(node, exploration_constant)return nodefunction expand(node):untried_actions = node.untried_actions()action = select_action(untried_actions)child_node = node.add_child(action)return child_nodefunction default_policy(node):while node is not a terminal node:action = select_action(node.actions())node = node.do_action(action)return node.rewardfunction backup(node, reward):while node is not None:node.visits += 1node.reward += rewardnode = node.parentfunction best_child(node, exploration_constant):best_score = -1best_child = Nonefor child in node.children:score = child.reward / child.visits + exploration_constant * sqrt(log(node.visits) / child.visits)if score > best_score:best_score = scorebest_child = childreturn best_child其中,root为蒙特卡罗树的根节点,max_iterations为迭代次数。在算法中,tree_policy函数使用select_child函数选择子节点,如果该节点未完全展开,则使用expand函数扩展该节点,否则使用best_child函数选择最佳子节点。default_policy函数使用select_action函数选择随机动作,执行动作后进入下一节点。backup函数从当前节点到根节点更新所有节点的访问次数和回报。best_child函数选择具有最高置信上限值(UCT值)的子节点
UCT算法公式:
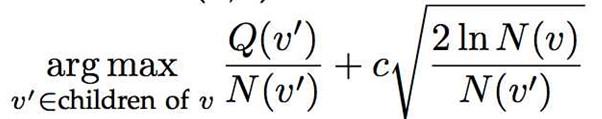
其中v'表示当前树节点,v表示父节点,Q表示这个树节点的累计奖励值,N表示这个树节点的访问次数,C是一个常量探索参数(可以控制exploitation和exploration权重),探索参数C的作用是控制探索的程度,较大的C值会更加注重探索,较小的C值则更加注重利用。
2. MCTS寻路代码
首先定义一个树的Node数据结构,用以表示MCTS的树节点。
class Node:def __init__(self, x, y):self.x = xself.y = yself.parent = Noneself.children = []self.reward = 0self.visits = 0# 该节点是否完全扩展def is_fully_expanded(self):return len(self.children) == self.num_actions()# 该节点能选择的动作数目def num_actions(self):return 4# UCT数值def ucb1_value(self, c=0.1):if self.visits == 0:return float('inf')return self.reward / self.visits + c * math.sqrt(2 * math.log(self.parent.visits) / self.visits)# 该节点是否为结束的叶子节点def is_terminal(self, goal):if (self.x, self.y) == goal:return Trueelse:return False寻路需要网格地图提供地图信息,所以定义一个Map类,表示地图数据:
class Map:def __init__(self, width, height, obstacles):self.width = widthself.height = heightself.obstacles = obstacles# 是否为有效落点def is_valid_location(self, x, y):if x < 0 or y < 0 or x >= self.width or y >= self.height:return Falsefor obstacle in self.obstacles:if obstacle[0] <= x <= obstacle[2] and obstacle[1] <= y <= obstacle[3]:return Falsereturn True接下来就是基于MCTS的路径搜寻代码:
class MCTSPathFinding:def __init__(self, map, start, goal):self.map = mapself.start = startself.goal = goaldef search(self, num_iterations, start_node):root = start_nodefor i in range(num_iterations):node = root# 选择while not node.is_terminal(self.goal):if node.is_fully_expanded():action = self.select_child(node)node = node.children[action]else:# 扩展action = len(node.children)new_x, new_y = self.get_successor(node.x, node.y, action)if self.map.is_valid_location(new_x, new_y):new_node = Node(new_x, new_y)node.children.append(new_node)new_node.parent = nodenode = new_nodebreakelse:node.children.append(None)# 模拟reward = self.rollout(node.x, node.y)# 反向传播while node is not None:node.visits += 1node.reward += rewardnode = node.parentbest_node = self.get_best_path(root)return best_node# 选取UCT值最大的子节点def select_child(self, node):max_ucb1 = -1best_action = -1for action in range(node.num_actions()):child = node.children[action]if child is None:continueucb1 = child.ucb1_value()if ucb1 > max_ucb1:max_ucb1 = ucb1best_action = actionreturn best_action# 模拟 这里模拟不再使用随机策略,而是选取离终点的曼哈顿距离近的action作为节点的下一个模拟动作,此举为加快模拟收敛速度,使其能快速到达结束态。(缺陷->若起点与终点存在 “_|” 闭合夹角障碍,会陷入障碍,无法寻出,导致寻路失败)def rollout(self, x, y):steps = 1while (x, y) != self.goal:valid_actions = []for action in range(0, 4):new_x, new_y = self.get_successor(x, y, action)if self.map.is_valid_location(new_x, new_y):valid_actions.append([new_x, new_y])steps += 1if not valid_actions or steps > 100:return -1distances = np.array([self.heuristic(valid_action, self.goal) for valid_action in valid_actions])x, y = valid_actions[np.argmin(distances)]return 1 / steps# 曼哈顿距离def heuristic(self, position, goal):dx = np.abs(position[0] - goal[0])dy = np.abs(position[1] - goal[1])return dx + dydef get_successor(self, x, y, action):actions = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]new_x = x + actions[action][0]new_y = y + actions[action][1]return new_x, new_ydef get_best_path(self, root):values = []for child in root.children:if child is None:values.append(-1)else:values.append(child.ucb1_value(0))node = root.children[np.argmax(values)]return node演示代码:
# 创建地图
map_width = 30
map_height = 20
obstacles = [(10, 5, 20, 10), (5, 15, 15, 17)]
map = Map(map_width, map_height, obstacles)# 设置起点和终点
start = (1, 1)
goal = (map_width - 2, map_height - 2)
# goal = (1, 12)# 运行MCTS寻路算法
mcts = MCTSPathFinding(map, start, goal)
node = Node(start[0], start[1])
best_path = [(start[0], start[1])]
while (node.x, node.y) != goal:node = mcts.search(1000, node)print((node.x, node.y), node.visits, node.reward)best_path.append((node.x, node.y))# 画出地图和结果
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for obstacle in obstacles:ax.add_patch(plt.Rectangle((obstacle[0], obstacle[1]), obstacle[2] - obstacle[0], obstacle[3] - obstacle[1],color='gray'))
ax.plot([start[0], goal[0]], [start[1], goal[1]], 'ro-', linewidth=2)
for i in range(len(best_path) - 1):ax.plot([best_path[i][0], best_path[i + 1][0]], [best_path[i][1], best_path[i + 1][1]], 'bo-', linewidth=2)
ax.axis('equal')
plt.show()最终结果图如下:
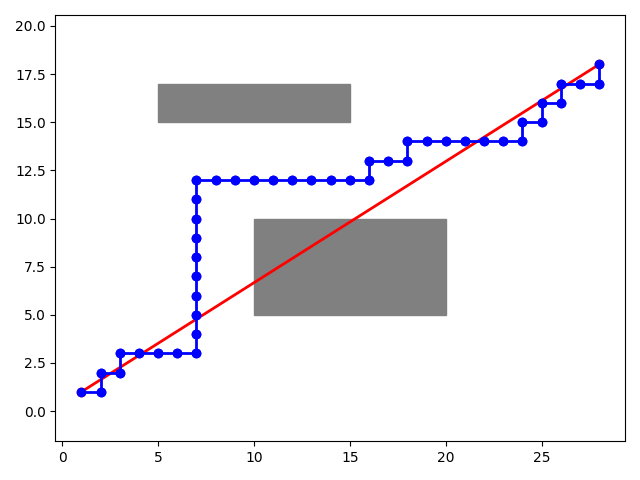
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!