Feign设计原理
什么是Feign?
Feign 的英文表意为“假装,伪装,变形”, 是一个http请求调用的轻量级框架,可以以Java接口注解的方式调用Http请求,而不用像Java中通过封装HTTP请求报文的方式直接调用。Feign通过处理注解,将请求模板化,当实际调用的时候,传入参数,根据参数再应用到请求上,进而转化成真正的请求,这种请求相对而言比较直观。
Feign被广泛应用在Spring Cloud 的解决方案中,是学习基于Spring Cloud 微服务架构不可或缺的重要组件。
开源项目地址:
https://github.com/OpenFeign/feign
Feign解决了什么问题?
封装了Http调用流程,更适合面向接口化的变成习惯
在服务调用的场景中,我们经常调用基于Http协议的服务,而我们经常使用到的框架可能有HttpURLConnection、Apache HttpComponnets、OkHttp3 、Netty等等,这些框架在基于自身的专注点提供了自身特性。而从角色划分上来看,他们的职能是一致的提供Http调用服务。具体流程如下:
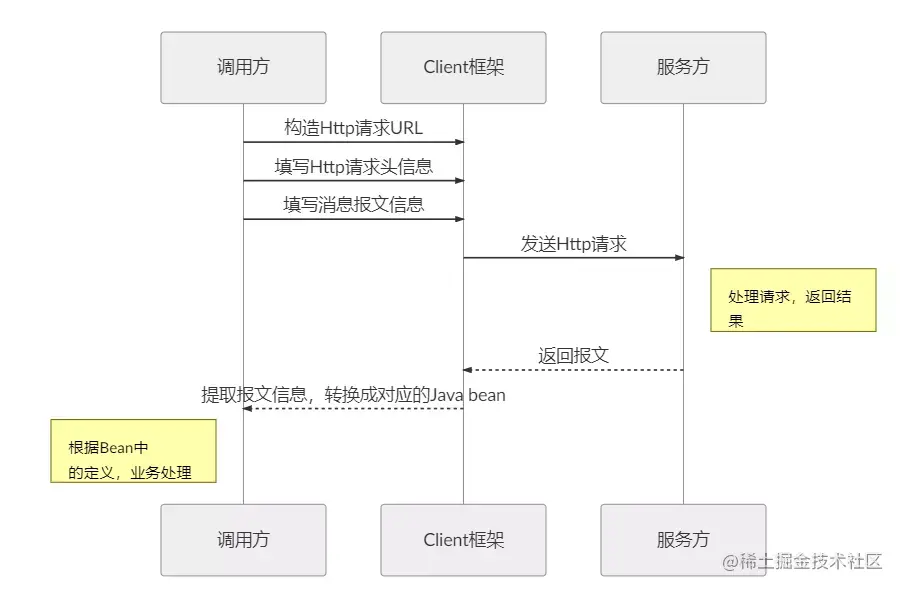
Feign是如何设计的?
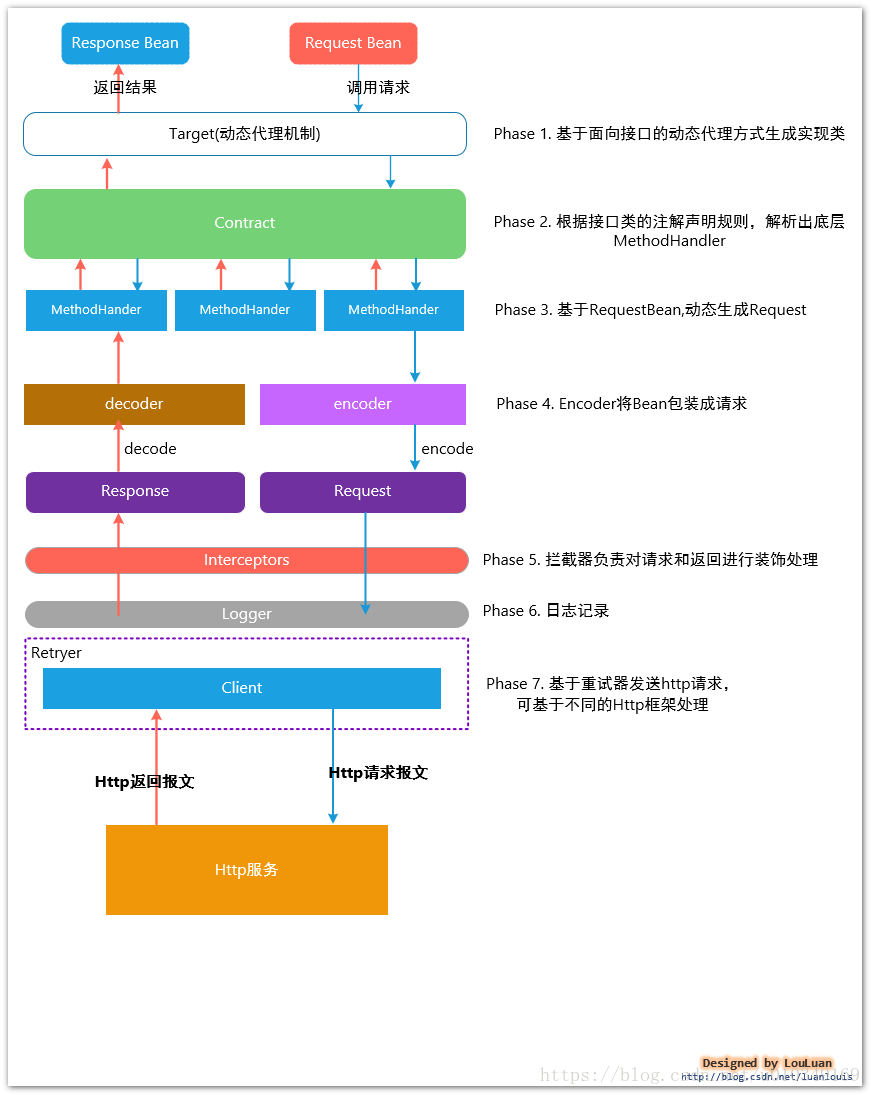
PHASE 1. 基于面向接口的动态代理方式生成实现类(jdk动态代理)
在使用feign 时,会定义对应的接口类,在接口类上使用Http相关的注解,标识HTTP请求参数信息,如下所示:
interface GitHub {@RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")List contributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo);
}public static class Contributor {String login;int contributions;
}public class MyApp {public static void main(String... args) {GitHub github = Feign.builder().decoder(new GsonDecoder()).target(GitHub.class, "https://api.github.com");// Fetch and print a list of the contributors to this library.List contributors = github.contributors("OpenFeign", "feign");for (Contributor contributor : contributors) {System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")");}}
}
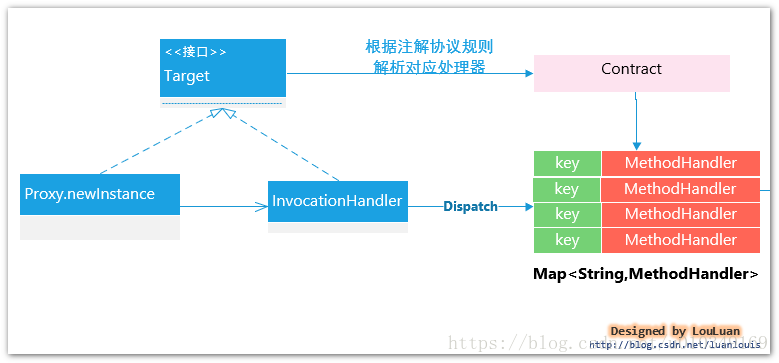
在Feign 底层,通过基于面向接口的动态代理方式生成实现类,将请求调用委托到动态代理实现类,基本原理如下所示:
public class ReflectiveFeign extends Feign{///省略部分代码@Overridepublic T newInstance(Target target) {//根据接口类和Contract协议解析方式,解析接口类上的方法和注解,转换成内部的MethodHandler处理方式Map nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);Map methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap();List defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList();for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {continue;} else if(Util.isDefault(method)) {DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);methodToHandler.put(method, handler);} else {methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));}}InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);// 基于Proxy.newProxyInstance 为接口类创建动态实现,将所有的请求转换给InvocationHandler 处理。T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{target.type()}, handler);for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);}return proxy;}//省略部分代码
PHASE 2. 根据Contract协议规则,解析接口类的注解信息,解析成内部表现:
Feign 定义了转换协议,定义如下:
/*** Defines what annotations and values are valid on interfaces.*/
public interface Contract {/*** Called to parse the methods in the class that are linked to HTTP requests.* 传入接口定义,解析成相应的方法内部元数据表示* @param targetType {@link feign.Target#type() type} of the Feign interface.*/// TODO: break this and correct spelling at some pointList parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class targetType);
}
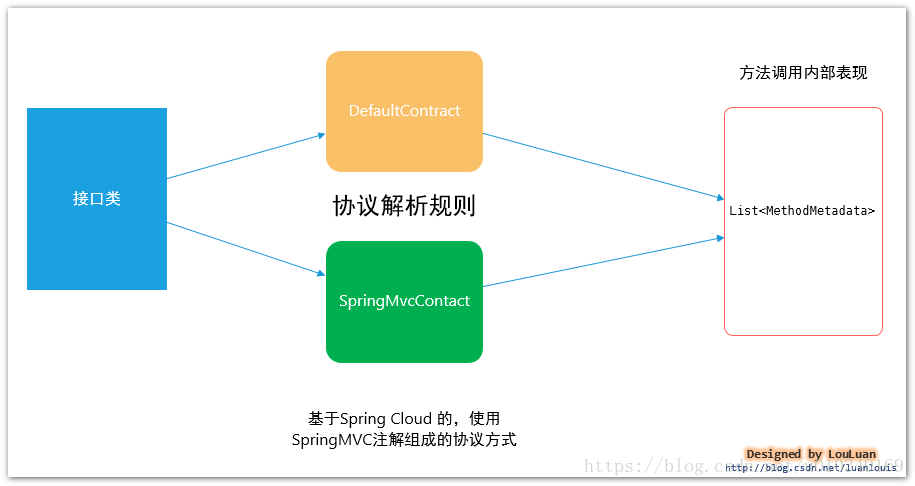
默认Contract 实现
Feign 默认有一套自己的协议规范,规定了一些注解,可以映射成对应的Http请求,如官方的一个例子:
public interface GitHub {@RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")List getContributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repository);class Contributor {String login;int contributions;}
} 上述的例子中,尝试调用GitHub.getContributors(“foo”,“myrepo”)的的时候,会转换成如下的HTTP请求:
GET /repos/foo/myrepo/contributors
HOST XXXX.XXX.XXX
Feign 默认的协议规范
具体FeignContract 是如何解析的,不在本文的介绍范围内,详情请参考代码:
feign/Contract.java at master · OpenFeign/feign · GitHub
基于Spring MVC的协议规范SpringMvcContract:
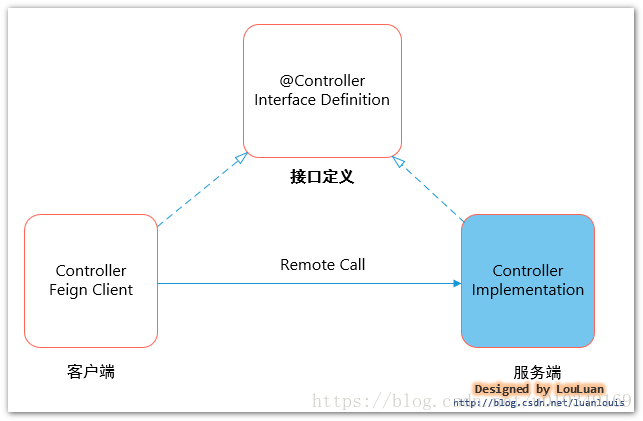
当前Spring Cloud 微服务解决方案中,为了降低学习成本,采用了Spring MVC的部分注解来完成 请求协议解析,也就是说 ,写客户端请求接口和像写服务端代码一样:客户端和服务端可以通过SDK的方式进行约定,客户端只需要引入服务端发布的SDK API,就可以使用面向接口的编码方式对接服务:
我们团队内部就是按照这种思路,结合Spring Boot Starter 的特性,定义了服务端starter,
服务消费者在使用的时候,只需要引入Starter,就可以调用服务。这个比较适合平台无关性,接口抽象出来的好处就是可以根据服务调用实现方式自有切换:可以基于简单的Http服务调用;
可以基于Spring Cloud 微服务架构调用;
可以基于Dubbo SOA服务治理
这种模式比较适合在SaSS混合软件服务的模式下自有切换,根据客户的硬件能力选择合适的方式部署,也可以基于自身的服务集群部署微服务
至于Spring Cloud 是如何实现 协议解析的,可参考代码:
https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign/blob/master/spring-cloud-openfeign-core/src/main/java/org/springframework/cloud/openfeign/support/SpringMvcContract.java
当然,目前的Spring MVC的注解并不是可以完全使用的,有一些注解并不支持,如@GetMapping,@PutMapping 等,仅支持使用@RequestMapping 等,另外注解继承性方面也有些问题;具体限制细节,每个版本能会有些出入,可以参考上述的代码实现,比较简单。
Spring Cloud 没有基于Spring MVC 全部注解来做Feign 客户端注解协议解析,个人认为这个是一个不小的坑。在刚入手Spring Cloud 的时候,就碰到这个问题。后来是深入代码才解决的… 这个应该有人写了增强类来处理,暂且不表,先MARK一下,是一个开源代码练手的好机会。
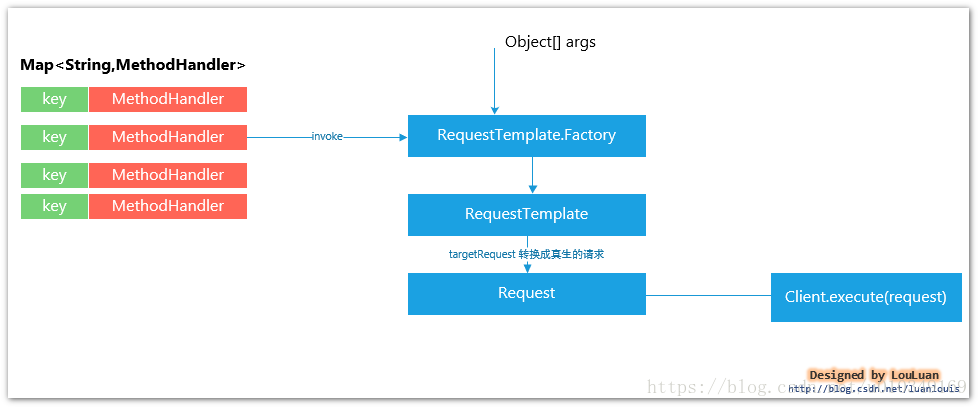
PHASE 3. 基于 RequestBean,动态生成Request
根据传入的Bean对象和注解信息,从中提取出相应的值,来构造Http Request 对象:
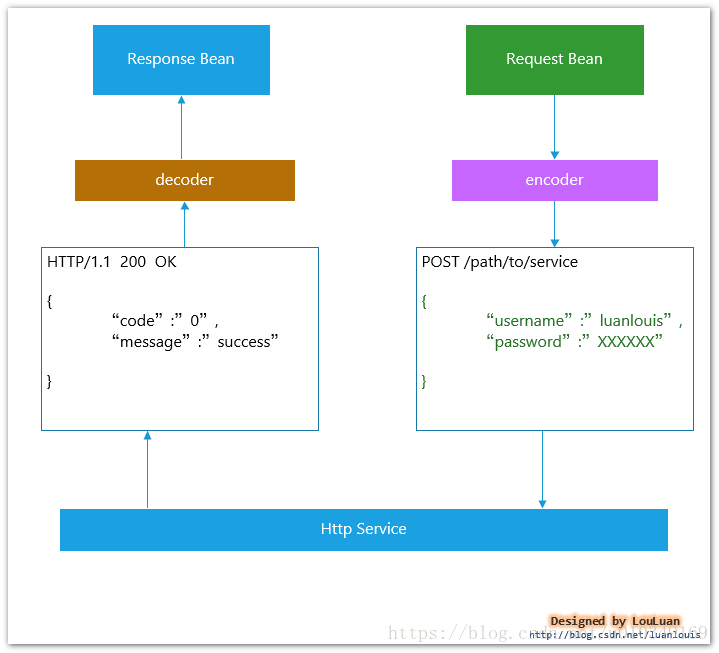
PHASE 4. 使用Encoder 将Bean转换成 Http报文正文(消息解析和转码逻辑)
Feign 最终会将请求转换成Http 消息发送出去,传入的请求对象最终会解析成消息体,如下所示:
在接口定义上Feign做的比较简单,抽象出了Encoder 和decoder 接口:
public interface Encoder {/** Type literal for {@code Map}, indicating the object to encode is a form. */Type MAP_STRING_WILDCARD = Util.MAP_STRING_WILDCARD;/*** Converts objects to an appropriate representation in the template.* 将实体对象转换成Http请求的消息正文中* @param object what to encode as the request body.* @param bodyType the type the object should be encoded as. {@link #MAP_STRING_WILDCARD}* indicates form encoding.* @param template the request template to populate.* @throws EncodeException when encoding failed due to a checked exception.*/void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) throws EncodeException;/*** Default implementation of {@code Encoder}.*/class Default implements Encoder {@Overridepublic void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) {if (bodyType == String.class) {template.body(object.toString());} else if (bodyType == byte[].class) {template.body((byte[]) object, null);} else if (object != null) {throw new EncodeException(format("%s is not a type supported by this encoder.", object.getClass()));}}}
}
public interface Decoder {/*** Decodes an http response into an object corresponding to its {@link* java.lang.reflect.Method#getGenericReturnType() generic return type}. If you need to wrap* exceptions, please do so via {@link DecodeException}.* 从Response 中提取Http消息正文,通过接口类声明的返回类型,消息自动装配* @param response the response to decode * @param type {@link java.lang.reflect.Method#getGenericReturnType() generic return type} of* the method corresponding to this {@code response}.* @return instance of {@code type}* @throws IOException will be propagated safely to the caller.* @throws DecodeException when decoding failed due to a checked exception besides IOException.* @throws FeignException when decoding succeeds, but conveys the operation failed.*/Object decode(Response response, Type type) throws IOException, DecodeException, FeignException;/** Default implementation of {@code Decoder}. */public class Default extends StringDecoder {@Overridepublic Object decode(Response response, Type type) throws IOException {if (response.status() == 404) return Util.emptyValueOf(type);if (response.body() == null) return null;if (byte[].class.equals(type)) {return Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream());}return super.decode(response, type);}}
}目前Feign 有以下实现:
| Encoder/ Decoder 实现 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| JacksonEncoder,JacksonDecoder | 基于 Jackson 格式的持久化转换协议 |
| GsonEncoder,GsonDecoder | 基于Google GSON 格式的持久化转换协议 |
| SaxEncoder,SaxDecoder | 基于XML 格式的Sax 库持久化转换协议 |
| JAXBEncoder,JAXBDecoder | 基于XML 格式的JAXB 库持久化转换协议 |
| ResponseEntityEncoder,ResponseEntityDecoder | Spring MVC 基于 ResponseEntity< T > 返回格式的转换协议 |
| SpringEncoder,SpringDecoder | 基于Spring MVC HttpMessageConverters 一套机制实现的转换协议 ,应用于Spring Cloud 体系中 |
PHASE 5. 拦截器负责对请求和返回进行装饰处理
在请求转换的过程中,Feign 抽象出来了拦截器接口,用于用户自定义对请求的操作:
public interface RequestInterceptor {/*** 可以在构造RequestTemplate 请求时,增加或者修改Header, Method, Body 等信息* Called for every request. Add data using methods on the supplied {@link RequestTemplate}.*/void apply(RequestTemplate template);
}
比如,如果希望Http消息传递过程中被压缩,可以定义一个请求拦截器:
public class FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor extends BaseRequestInterceptor {/*** Creates new instance of {@link FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor}.** @param properties the encoding properties*/protected FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor(FeignClientEncodingProperties properties) {super(properties);}/*** {@inheritDoc}*/@Overridepublic void apply(RequestTemplate template) {// 在Header 头部添加相应的数据信息addHeader(template, HttpEncoding.ACCEPT_ENCODING_HEADER, HttpEncoding.GZIP_ENCODING,HttpEncoding.DEFLATE_ENCODING);}
}
PHASE 6. 日志记录
在发送和接收请求的时候,Feign定义了统一的日志门面来输出日志信息 , 并且将日志的输出定义了四个等级:
| 级别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NONE | 不做任何记录 |
| BASIC | 只记录输出Http 方法名称、请求URL、返回状态码和执行时间 |
| HEADERS | 记录输出Http 方法名称、请求URL、返回状态码和执行时间 和 Header 信息 |
| FULL | 记录Request 和Response的Header,Body和一些请求元数据 |
public abstract class Logger {protected static String methodTag(String configKey) {return new StringBuilder().append('[').append(configKey.substring(0, configKey.indexOf('('))).append("] ").toString();}/*** Override to log requests and responses using your own implementation. Messages will be http* request and response text.** @param configKey value of {@link Feign#configKey(Class, java.lang.reflect.Method)}* @param format {@link java.util.Formatter format string}* @param args arguments applied to {@code format}*/protected abstract void log(String configKey, String format, Object... args);protected void logRequest(String configKey, Level logLevel, Request request) {log(configKey, "---> %s %s HTTP/1.1", request.method(), request.url());if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.HEADERS.ordinal()) {for (String field : request.headers().keySet()) {for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(request.headers(), field)) {log(configKey, "%s: %s", field, value);}}int bodyLength = 0;if (request.body() != null) {bodyLength = request.body().length;if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) {StringbodyText =request.charset() != null ? new String(request.body(), request.charset()) : null;log(configKey, ""); // CRLFlog(configKey, "%s", bodyText != null ? bodyText : "Binary data");}}log(configKey, "---> END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength);}}protected void logRetry(String configKey, Level logLevel) {log(configKey, "---> RETRYING");}protected Response logAndRebufferResponse(String configKey, Level logLevel, Response response,long elapsedTime) throws IOException {String reason = response.reason() != null && logLevel.compareTo(Level.NONE) > 0 ?" " + response.reason() : "";int status = response.status();log(configKey, "<--- HTTP/1.1 %s%s (%sms)", status, reason, elapsedTime);if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.HEADERS.ordinal()) {for (String field : response.headers().keySet()) {for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(response.headers(), field)) {log(configKey, "%s: %s", field, value);}}int bodyLength = 0;if (response.body() != null && !(status == 204 || status == 205)) {// HTTP 204 No Content "...response MUST NOT include a message-body"// HTTP 205 Reset Content "...response MUST NOT include an entity"if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) {log(configKey, ""); // CRLF}byte[] bodyData = Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream());bodyLength = bodyData.length;if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal() && bodyLength > 0) {log(configKey, "%s", decodeOrDefault(bodyData, UTF_8, "Binary data"));}log(configKey, "<--- END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength);return response.toBuilder().body(bodyData).build();} else {log(configKey, "<--- END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength);}}return response;}protected IOException logIOException(String configKey, Level logLevel, IOException ioe, long elapsedTime) {log(configKey, "<--- ERROR %s: %s (%sms)", ioe.getClass().getSimpleName(), ioe.getMessage(),elapsedTime);if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) {StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();ioe.printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(sw));log(configKey, sw.toString());log(configKey, "<--- END ERROR");}return ioe;}
PHASE 7 . 基于重试器发送HTTP请求
Feign 内置了一个重试器,当HTTP请求出现IO异常时,Feign会有一个最大尝试次数发送请求,以下是Feign核心
代码逻辑:
final class SynchronousMethodHandler implements MethodHandler {// 省略部分代码@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {//根据输入参数,构造Http 请求。RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);// 克隆出一份重试器Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();// 尝试最大次数,如果中间有结果,直接返回while (true) {try {return executeAndDecode(template);} catch (RetryableException e) {retryer.continueOrPropagate(e);if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel);}continue;}}}
重试器有如下几个控制参数:
| 重试参数 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| period | 初始重试时间间隔,当请求失败后,重试器将会暂停 初始时间间隔(线程 sleep 的方式)后再开始,避免强刷请求,浪费性能 | |
| maxPeriod | 当请求连续失败时,重试的时间间隔将按照:long interval = (long) (period * Math.pow(1.5, attempt - 1)); 计算,按照等比例方式延长,但是最大间隔时间为 maxPeriod, 设置此值能够避免 重试次数过多的情况下执行周期太长 | |
| maxAttempts | 最大重试次数 |
具体的代码实现可参考:
https://github.com/OpenFeign/feign/blob/master/core/src/main/java/feign/Retryer.java
PHASE 8. 发送Http请求
Feign 真正发送HTTP请求是委托给 feign.Client 来做的:
public interface Client {/*** Executes a request against its {@link Request#url() url} and returns a response.* 执行Http请求,并返回Response* @param request safe to replay.* @param options options to apply to this request.* @return connected response, {@link Response.Body} is absent or unread.* @throws IOException on a network error connecting to {@link Request#url()}.*/Response execute(Request request, Options options) throws IOException;}
Feign 默认底层通过JDK 的 java.net.HttpURLConnection 实现了feign.Client接口类,在每次发送请求的时候,都会创建新的HttpURLConnection 链接,这也就是为什么默认情况下Feign的性能很差的原因。可以通过拓展该接口,使用Apache HttpClient 或者OkHttp3等基于连接池的高性能Http客户端,我们项目内部使用的就是OkHttp3作为Http 客户端。
如下是Feign 的默认实现,供参考:
public static class Default implements Client {private final SSLSocketFactory sslContextFactory;private final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier;/*** Null parameters imply platform defaults.*/public Default(SSLSocketFactory sslContextFactory, HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {this.sslContextFactory = sslContextFactory;this.hostnameVerifier = hostnameVerifier;}@Overridepublic Response execute(Request request, Options options) throws IOException {HttpURLConnection connection = convertAndSend(request, options);return convertResponse(connection).toBuilder().request(request).build();}HttpURLConnection convertAndSend(Request request, Options options) throws IOException {final HttpURLConnectionconnection =(HttpURLConnection) new URL(request.url()).openConnection();if (connection instanceof HttpsURLConnection) {HttpsURLConnection sslCon = (HttpsURLConnection) connection;if (sslContextFactory != null) {sslCon.setSSLSocketFactory(sslContextFactory);}if (hostnameVerifier != null) {sslCon.setHostnameVerifier(hostnameVerifier);}}connection.setConnectTimeout(options.connectTimeoutMillis());connection.setReadTimeout(options.readTimeoutMillis());connection.setAllowUserInteraction(false);connection.setInstanceFollowRedirects(true);connection.setRequestMethod(request.method());Collection contentEncodingValues = request.headers().get(CONTENT_ENCODING);booleangzipEncodedRequest =contentEncodingValues != null && contentEncodingValues.contains(ENCODING_GZIP);booleandeflateEncodedRequest =contentEncodingValues != null && contentEncodingValues.contains(ENCODING_DEFLATE);boolean hasAcceptHeader = false;Integer contentLength = null;for (String field : request.headers().keySet()) {if (field.equalsIgnoreCase("Accept")) {hasAcceptHeader = true;}for (String value : request.headers().get(field)) {if (field.equals(CONTENT_LENGTH)) {if (!gzipEncodedRequest && !deflateEncodedRequest) {contentLength = Integer.valueOf(value);connection.addRequestProperty(field, value);}} else {connection.addRequestProperty(field, value);}}}// Some servers choke on the default accept string.if (!hasAcceptHeader) {connection.addRequestProperty("Accept", "*/*");}if (request.body() != null) {if (contentLength != null) {connection.setFixedLengthStreamingMode(contentLength);} else {connection.setChunkedStreamingMode(8196);}connection.setDoOutput(true);OutputStream out = connection.getOutputStream();if (gzipEncodedRequest) {out = new GZIPOutputStream(out);} else if (deflateEncodedRequest) {out = new DeflaterOutputStream(out);}try {out.write(request.body());} finally {try {out.close();} catch (IOException suppressed) { // NOPMD}}}return connection;}Response convertResponse(HttpURLConnection connection) throws IOException {int status = connection.getResponseCode();String reason = connection.getResponseMessage();if (status < 0) {throw new IOException(format("Invalid status(%s) executing %s %s", status,connection.getRequestMethod(), connection.getURL()));}Map> headers = new LinkedHashMap>();for (Map.Entry> field : connection.getHeaderFields().entrySet()) {// response messageif (field.getKey() != null) {headers.put(field.getKey(), field.getValue());}}Integer length = connection.getContentLength();if (length == -1) {length = null;}InputStream stream;if (status >= 400) {stream = connection.getErrorStream();} else {stream = connection.getInputStream();}return Response.builder().status(status).reason(reason).headers(headers).body(stream, length).build();}}
Feign 的性能怎么样?
Feign 整体框架非常小巧,在处理请求转换和消息解析的过程中,基本上没什么时间消耗。真正影响性能的,是处理Http请求的环节。
如上所述,由于默认情况下,Feign采用的是JDK的HttpURLConnection,所以整体性能并不高,刚开始接触Spring Cloud 的同学,如果没注意这些细节,可能会对Spring Cloud 有很大的偏见。
我们项目内部使用的是OkHttp3 作为连接客户端。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「亦山」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/82821294
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!