Astar算法实现象棋中马的寻路问
Astar算法实现象棋中马的寻路问题
-
环境与配置
编程语言:C语言
操作系统:Ubuntu 20.10
编译器:vs code -
具体分析
- 问题说明:给定任意大小棋盘,以及任意初始位置和目标位置,以象棋中马的行动规则,计算从初始位置到目标位置所需的最短步数。
- Astar算法作为启发式搜索的重要算法,不同于深度优先、宽度优先等盲目搜索算法,通过对open表中各个节点估价函数的计算并排序(不同图搜索算法的根本区别),从而逐步靠近目标值。估价函数f(x) = g(x) + h(x),g(x)为当前节点已消耗的代价,h(x)为当前节点到达目标剩余的代价,一般用h*(x)估计值进行估计h(x)。具体算法内容可自行百度。
- 在该问题中,g(x)为节点x走到当前位置的最短步数,h(x)为节点x当前位置与目标位置的的距离
- open表和close表可使用双向链表构建
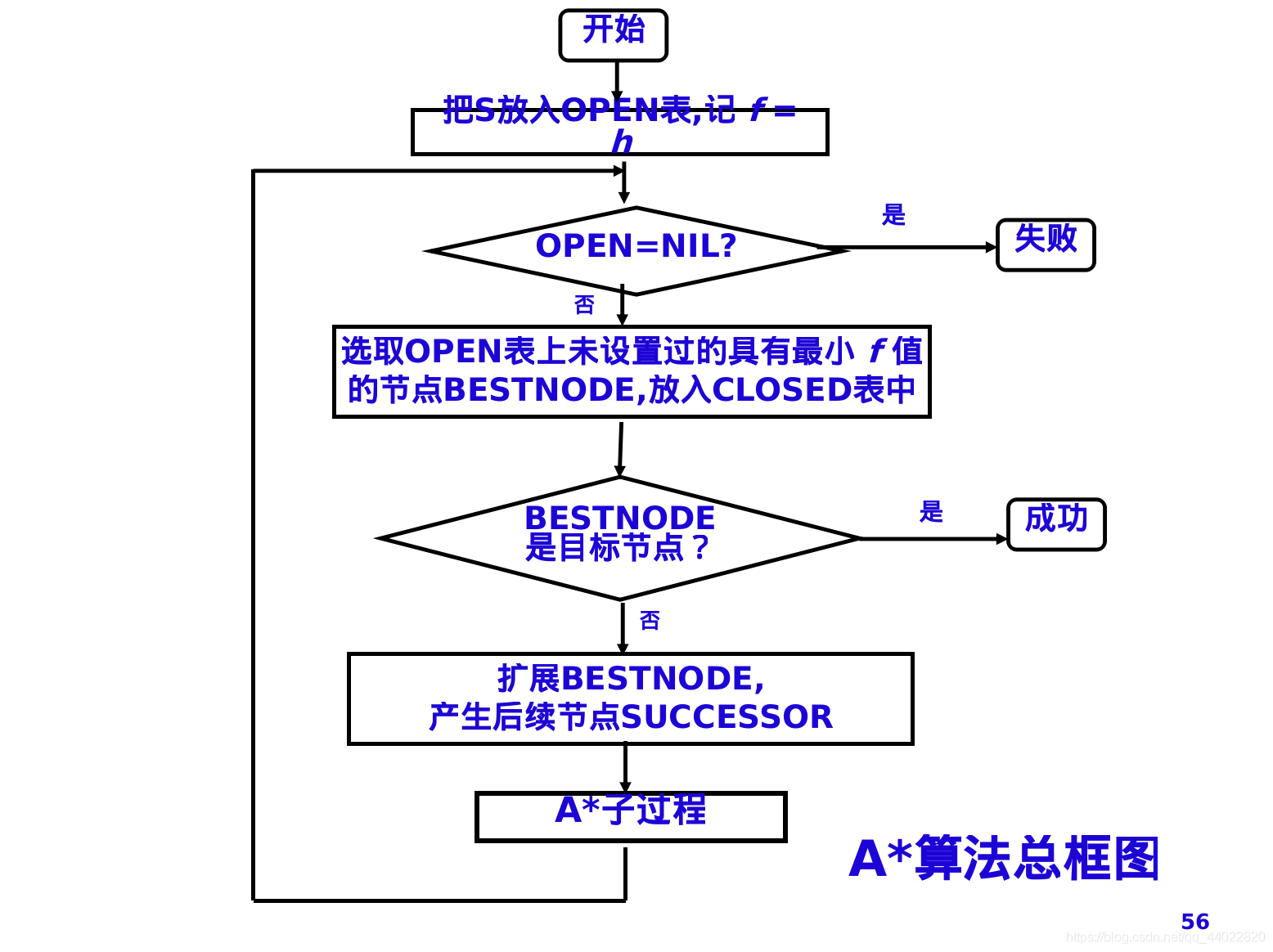
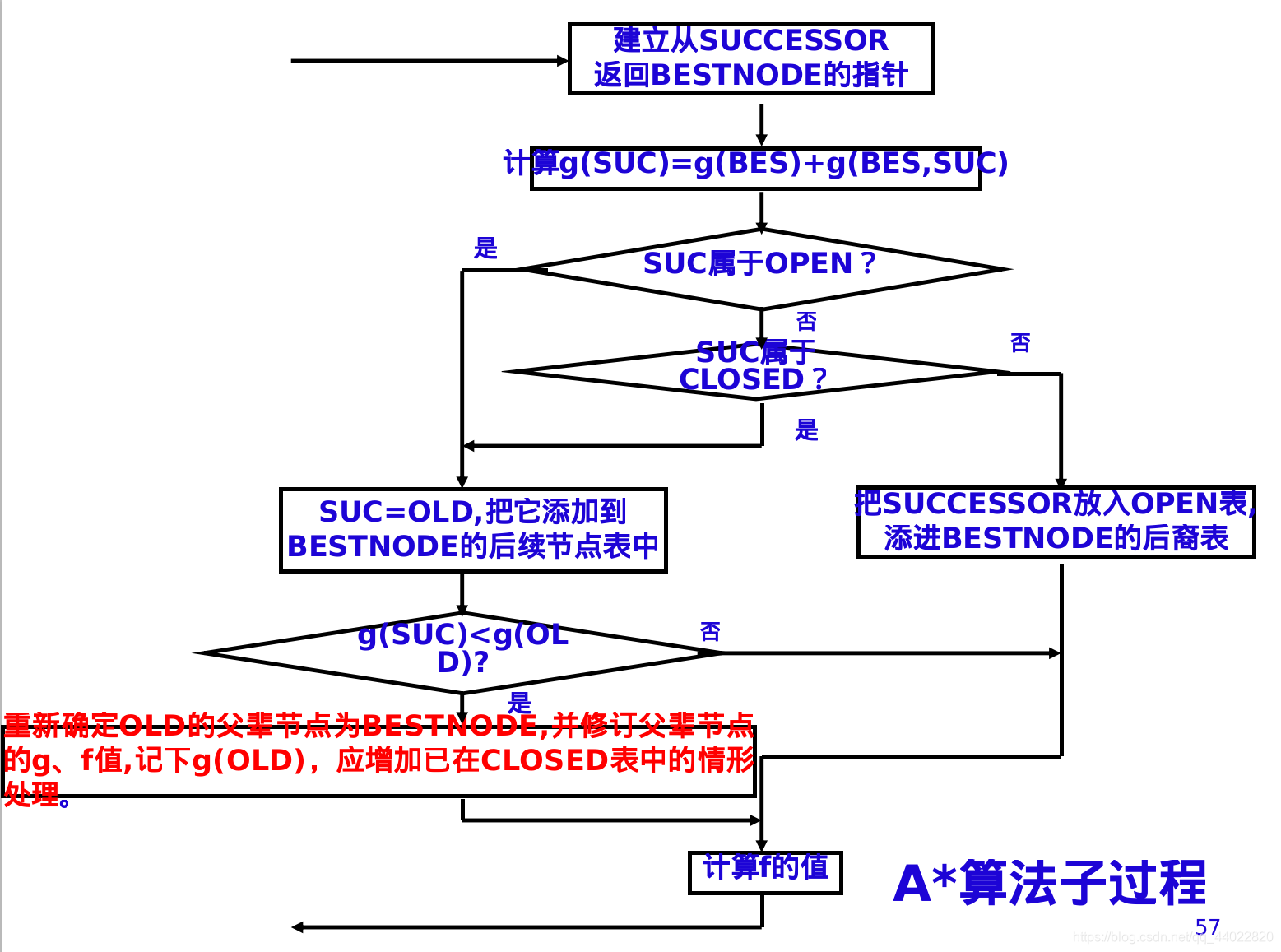
-
算法实现
#include -
简单说明:
- 函数的编译命令为:
gcc test.c -o test -lm,由于使用了math头文件,因此需要-lm参数去链接头文件 - 函数
in_open_list在插入节点n时,会根据估价函数进行排序操作,这也是Astar算法的核心 - 回收资源时要格外注意:
- 重复节点,在函数
insert_node中判断完估价函数大小后,较差的节点会从表中移除,并释放内存 - 在找到目标节点或无访问路径时,未释放的内存包括open表,close表,des节点(loc节点在开始时已加入open表中,可跟随open表一同释放内存)。open表和close表可使用recycle函数释放内存。
- 重复节点,在函数
- 按照提示,先后输入地图大小,初始位置,目标位置,各参量用空白符号隔开。没有做专门的输入判断。
- 函数的编译命令为:
-
在写程序时遇到的一些问题
在处理链表时,新创建的节点一定要使用
malloc函数申请内存,而不要直接使用struct结构创建
接下来进行详细说明#include#include typedef struct Node{int y;int x;int step; // g(x)int distance; // h(x)struct Node *next;struct Node *last; }node;int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++)ma();printf("---------------\n");ba(); } 函数
ma()和ba()的不同定义,以及相应结果如下:-
ma()函数:- 直接构造struct结构
void ma(){node n = {.x = 1, .y = 1};printf("%p\n", &n); }main函数中的ma函数输出结果为:0x7fffffffdd50 0x7fffffffdd50 0x7fffffffdd50几次调用ma()函数创建的node结构的地址相同
- 使用malloc函数构造,不使用free函数释放内存
void ma(){node *m = (node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));printf("%p\n", m); }main函数中的ma函数输出结果为:0x5555555592a0 0x5555555596e0 0x555555559710几次调用ma()函数创将的node结构地址不同
- 使用malloc函数构造,使用free函数释放内存
void ma(){node *m = (node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));printf("%p\n", m);free(m); }main函数中的ma函数输出结果为:0x5555555592a0 0x5555555592a0 0x5555555592a0几次调用ma()函数创建的node结构的地址相同
-
ba()函数- 直接构造struct结构
void ba(){for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++){node n;printf("%p\n", &n);} }main函数中的ba函数输出结果为:0x7fffffffdd50 0x7fffffffdd50 0x7fffffffdd50-
使用malloc函数构造,不使用free函数释放内存
void ba(){for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++){node *m = (node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));printf("%p\n", m);} }main函数中的ba函数输出结果为:0x5555555592a00x5555555596e00x555555559710几次调用ba()函数创将的node结构地址不同
- 使用malloc函数构造,使用free函数释放内存
void ba(){for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++){node *m = (node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));printf("%p\n", m);free(m);} }main函数中的ba函数输出结果为:0x5555555592a0 0x5555555592a0 0x5555555592a0几次调用ba()函数创建的node结构的地址相同
-
块变量作为auto变量,在块外一般被回收,重新调用函数时分配的内存依旧是同一块内存,这就带来了问题
使用struct构造变量,节点插入链表后退出函数。重新调用函数,申请的依旧是同一块内存,本次创建的节点地址和上一次完全相同,处理的依旧是同一个节点。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!