gRPC 高级特性之 重试机制
GRPC 重试机制
重试机制
超时与重试机制在集群环境中像是一个一卵同胞的双胞胎,像是天平两端的砝码,即相互区别又相互联系。集群环境中设置重试是为了保证系统容错,在单节点出错的情况下,将RPC调用平滑的迁移到其他节点上,保证系统整体可用。一般情况下,查询接口可以设置重试机制,不建议将数据修改接口设置重试,理由是系统必须保证每一个数据修改接口的幂等性,在集群环境下如何实现高效的分布式锁机制来保证接口幂等性是一个很难的问题。
gRPC支持两种重试策略,每一个RPC调用在同一个时间点只能使用其中一种策略:
- Retry policy - 重试策略。重试策略包含以下几点功能
- 最大重试次数
- 重试状态码 状态码定义请参考 Grpc 高级特性之 重试机制 &状态码定义
- Exponential Backoff - 重试时间点
- Hedging policy - 限流策略 限制时间范围内的并发次数. 该策略包含以下功能
- 最大限制次数
- Delay between hedged requests - 限制延迟
- Set of non-fatal status codes - 设置状态码
此外,当接口调用失败/成功比率阈值时,gRPC提供一种机制限制重试。请看 限制重试。
Retry Policy - 重试策略
关于重试机制的示意图如下
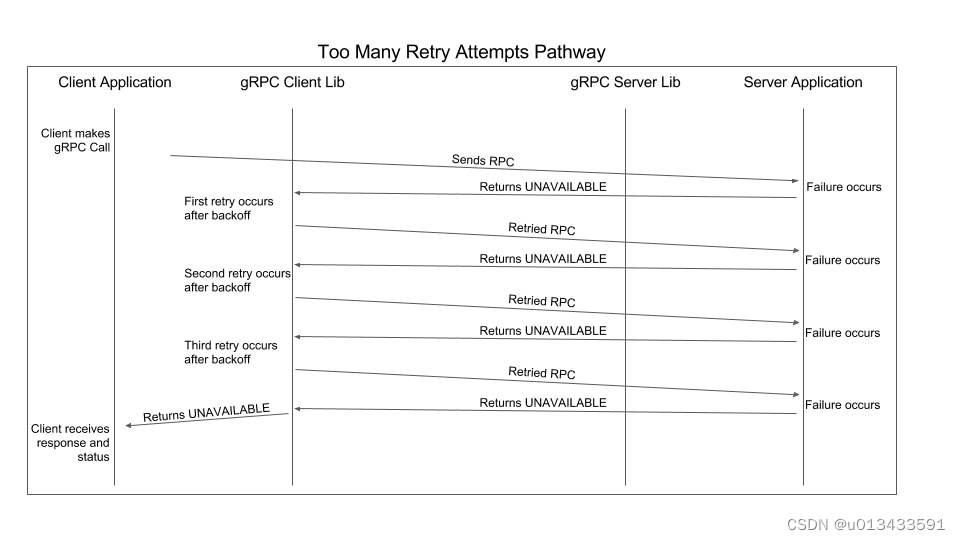
请看一下配置
"retryPolicy": {"maxAttempts": 4,"initialBackoff": "0.1s","maxBackoff": "1s","backoffMultiplier": 2,"retryableStatusCodes": ["UNAVAILABLE"]
}
最大重试次数
指定重试策略执行的次数,包含最开始的第一次调用。
需要注意的是,当grpc调用期限 跟重试次数同时存在时,以调用期限位置。例如,如果RPC的指定截止日期为7月23日,即PDT晚上9:00:00,则无论配置或尝试了多少次尝试,该操作都将在该时间之后失败。
Exponential Backoff
个人把他翻译成重试时机,即在客户端发生重试时,在什么时间点触发重试。initialBackoff, maxBackoff, backoffMultiplier 这三个参数确定了重试操作前随机延迟。即重试机制发生的时间点并不固定,而是利用这三个参数通过算法随机产生。
重试机制发生的时间点包含以下两种算法:
- random(0, initialBackoff)
- random(0, min(initialBackoff*backoffMultiplier**(n-1), maxBackoff))
重试状态码
当gRPC客户端收到服务端返回的异常状态时,并不是所有的非正常状态码都会触发重试,而是通过 retryableStatusCodes 参数指定对应的状态码,从而重发重试操作。
重试参数验证:
maxAttempts必须大于1,当数值大于5时系统系统默认为5(不会报错),潜规则就是: gRPC最大重试次数为5.- initialBackoff 、 maxBackoff 这两个参数必须指定,且值大于0.
- backoffMultiplier 必须指定, 且值大于0
- retryableStatusCodes 必须指定,可以同时指定多个状态码。不区分大小写 [“UNAVAILABLE”] or [“unavailable”],都正确。
Hedging Policy - 并行重试策略
gRPC允许在指定时间内未等到响应的情况下,发送多个请求副本(集群环境下的其他节点)。因此一个rpc请求可能会被执行多次,系统需要确保执行多次的情况下不会产生任何不利的影响,如数据幂等性等。
请看以下配置
"hedgingPolicy": {"maxAttempts": 4,"hedgingDelay": "0.5s","nonFatalStatusCodes": ["UNAVAILABLE","INTERNAL","ABORTED"]
}
参数说明:
- 最大重试次数为4 包含第一次调用
- 并发延迟时间 0.5S 即500毫秒
- 遇到 “UNAVAILABLE”, “INTERNAL”, “ABORTED” 状态码时触发
配置说明
以上面的配置为例,假设在1ms的时候触发第一次rpc调用 并没有得到正常返回
- 第二次调用在501ms触发
- 第三次调用在1001ms触发
- 第四次调用在1501ms触发
直到所有重试次数用完。当任一一次请求获取到服务端返回的正常状态时,则取消其他调用,其调用架构图如下

Validation of hedgingPolicy
maxAttempts必须大于1,当数值大于5时系统系统默认为5(不会报错),潜规则就是: gRPC最大重试次数为5.- hedgingDelay 可选参数,数值必须满足 proto3 Duration 类型.
- nonFatalStatusCodes必须指定,可以同时指定多个状态码。不区分大小写 [“UNAVAILABLE”] or [“unavailable”],都正确。
Throttling Retry - 限制重试
gGPC通过客户端失败/成功的比率跟设置阈值进行比较来禁用重试操作,目的是为了保护服务端系统过载。该配置是针对每一个服务,不能细化到method级别
Throttling Configuration
"retryThrottling": {"maxTokens": 10,"tokenRatio": 0.1
}
对每个服务名,gRPC客户端都维护一个token_count变量,该变量最初设置maxToken,范围在 0 - maxToken之间,token_count的计算规则如下:
- RPC调用失败 token_count - 1
- RPC调用成功 token_count 按照 tokenRatio 递增
如果token_count小于或等于阈值,定义为(maxTokens/2),则在token_count超过阈值之前,不会重试RPC。
该策略同样适用于 Hedging Policy, 在Hedging 策略中 第一次RPC请求无论如何都会触发,但是后续的RPC请求只有token_count大于阈值才会被发送。
参数验证
- maxTokens 必须指定 且数值范围在 (0,1000]
- tokenRatio 必须指定 数值大于0,保留3位小数,超过三位小数自动截取 (eg. 0.5466 当成 0.546.)
重试逻辑之状态码汇总
存在5种服务端返回类型,不同的策略(Retry、Hedging)对不不同的返回类型有不同的表现:
-
OK
- Retry policy : 成功返回给客户端
- Hedging policy :成功返回 取消之前、队列中的请求
-
Fatal Status Code
- Retry policy : 不触发重试 返回失败信息给客户端
- Hedging policy :取消之前、队列中的请求
-
Retryable/Non-Fatal Status Code without Server Pushback
- Retry policy : 根据策略触发重试
- Hedging policy :立即发送下一个请求,并根据延迟时间唤醒后续请求(如有必要)
-
Pushback: Don’t Retry
- Retry policy : 不触发重试 返回失败信息给客户端
- Hedging policy :不会发送任何hedging 请求
-
Pushback: Retry in n ms
-
Retry policy : N毫秒后重试,如果重试也失败,则根据延迟时间、次数继续进行重试操作
-
Hedging policy :N毫秒内,发送下一个hedged 请求,后续的请求在 n + hedgingDelay 唤起
-
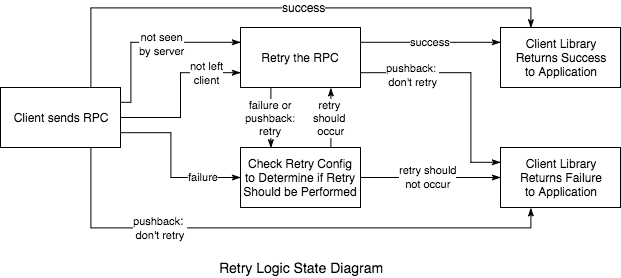
重试原理
重试策略发生在channel通道与负载均衡策略之间,因此每次重试利用负载均衡机制使用不同的通道去调用不同的服务端。示意图如下:
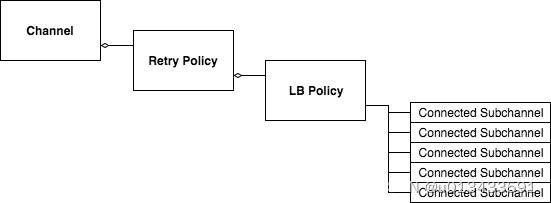
配置模板
{"loadBalancingPolicy": string,"methodConfig": [{"name": [{"service": string,"method": string,}],// Only one of retryPolicy or hedgingPolicy may be set. If neither is set,// RPCs will not be retried or hedged."retryPolicy": {// The maximum number of RPC attempts, including the original RPC.//// This field is required and must be two or greater."maxAttempts": number,// Exponential backoff parameters. The initial retry attempt will occur at// random(0, initialBackoff). In general, the nth attempt since the last// server pushback response (if any), will occur at random(0,// min(initialBackoff*backoffMultiplier**(n-1), maxBackoff)).// The following two fields take their form from:// https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto3#json// They are representations of the proto3 Duration type. Note that the// numeric portion of the string must be a valid JSON number.// They both must be greater than zero."initialBackoff": string, // Required. Long decimal with "s" appended"maxBackoff": string, // Required. Long decimal with "s" appended"backoffMultiplier": number // Required. Must be greater than zero.// The set of status codes which may be retried.//// Status codes are specified in the integer form or the case-insensitive// string form (eg. [14], ["UNAVAILABLE"] or ["unavailable"])//// This field is required and must be non-empty."retryableStatusCodes": []}"hedgingPolicy": {// The hedging policy will send up to maxAttempts RPCs.// This number represents the all RPC attempts, including the// original and all the hedged RPCs.//// This field is required and must be two or greater."maxAttempts": number,// The original RPC will be sent immediately, but the maxAttempts-1// subsequent hedged RPCs will be sent at intervals of every hedgingDelay.// Set this to "0s", or leave unset, to immediately send all maxAttempts RPCs.// hedgingDelay takes its form from:// https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto3#json// It is a representation of the proto3 Duration type. Note that the// numeric portion of the string must be a valid JSON number."hedgingDelay": string,// The set of status codes which indicate other hedged RPCs may still// succeed. If a non-fatal status code is returned by the server, hedged// RPCs will continue. Otherwise, outstanding requests will be canceled and// the error returned to the client application layer.//// Status codes are specified in the integer form or the case-insensitive// string form (eg. [14], ["UNAVAILABLE"] or ["unavailable"])//// This field is optional."nonFatalStatusCodes": []}"waitForReady": bool,"timeout": string,"maxRequestMessageBytes": number,"maxResponseMessageBytes": number}]// If a RetryThrottlingPolicy is provided, gRPC will automatically throttle// retry attempts and hedged RPCs when the client’s ratio of failures to// successes exceeds a threshold.//// For each server name, the gRPC client will maintain a token_count which is// initially set to maxTokens, and can take values between 0 and maxTokens.//// Every outgoing RPC (regardless of service or method invoked) will change// token_count as follows://// - Every failed RPC will decrement the token_count by 1.// - Every successful RPC will increment the token_count by tokenRatio.//// If token_count is less than or equal to maxTokens / 2, then RPCs will not// be retried and hedged RPCs will not be sent."retryThrottling": {// The number of tokens starts at maxTokens. The token_count will always be// between 0 and maxTokens.//// This field is required and must be in the range (0, 1000]. Up to 3// decimal places are supported"maxTokens": number,// The amount of tokens to add on each successful RPC. Typically this will// be some number between 0 and 1, e.g., 0.1.//// This field is required and must be greater than zero. Up to 3 decimal// places are supported."tokenRatio": number}
}
测试代码
服务端-核心代码
// 结构体定义
type failingServer struct {pb.UnimplementedEchoServermu sync.Mutex// 请求计数器 累加reqCounter uint// 指定请求成功需要调用的次数reqModulo uint
}// this method will fail reqModulo - 1 times RPCs and return status code Unavailable,
// and succeeded RPC on reqModulo times.
func (s *failingServer) maybeFailRequest() error {s.mu.Lock()defer s.mu.Unlock()s.reqCounter++if (s.reqModulo > 0) && (s.reqCounter%s.reqModulo == 0) {return nil}// 系统自动报错,抛出异常状态码,供客户端进行重试return status.Errorf(codes.Unavailable, "maybeFailRequest: failing it")
}func (s *failingServer) UnaryEcho(ctx context.Context, req *pb.EchoRequest) (*pb.EchoResponse, error) {//执行业务逻辑之前根据请求次数、进行判断 模拟服务器内部异常if err := s.maybeFailRequest(); err != nil {log.Println("request failed count:", s.reqCounter)return nil, err}log.Println("request succeeded count:", s.reqCounter)return &pb.EchoResponse{Message: req.Message}, nil
}func main() {flag.Parse()address := fmt.Sprintf(":%v", *port)lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", address)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)}fmt.Println("listen on address", address)s := grpc.NewServer()// 初始化请求次数、rpc调用成功次数failingservice := &failingServer{reqCounter: 0,reqModulo: 4,}pb.RegisterEchoServer(s, failingservice)if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)}
}
客户端-核心代码
var (// 定义端口占用addr = flag.String("addr", "localhost:50052", "the address to connect to")// 定义重试策略retryPolicy = `{"methodConfig": [{"name": [{"service": "grpc.examples.echo.Echo"}],"waitForReady": true,"retryPolicy": {"MaxAttempts": 4,"InitialBackoff": ".01s","MaxBackoff": ".01s","BackoffMultiplier": 1.0,"RetryableStatusCodes": [ "UNAVAILABLE" ]}}]}`
)// 根据配置文件初始化重试策略
func retryDial() (*grpc.ClientConn, error) {return grpc.Dial(*addr, grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()), grpc.WithDefaultServiceConfig(retryPolicy))
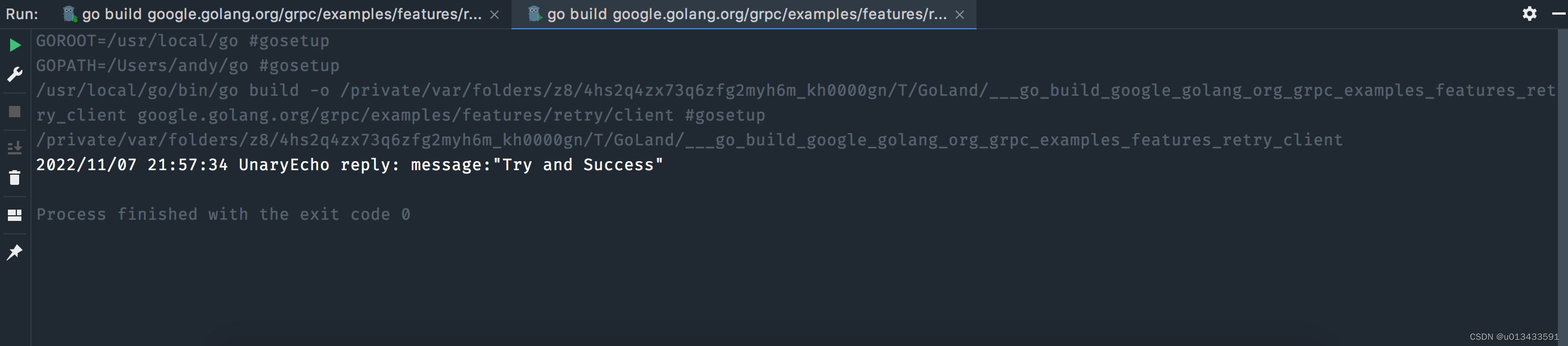
}func main() {flag.Parse()// 连接服务器 (同时 初始化重试配置)conn, err := retryDial()if err != nil {log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)}defer func() {if e := conn.Close(); e != nil {log.Printf("failed to close connection: %s", e)}}()c := pb.NewEchoClient(conn)ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 1*time.Second)defer cancel()reply, err := c.UnaryEcho(ctx, &pb.EchoRequest{Message: "Try and Success"})if err != nil {log.Fatalf("UnaryEcho error: %v", err)}log.Printf("UnaryEcho reply: %v", reply)
}
完整代码
// 1. 拉取代码
git clone https://github.com/grpc/grpc-go.git // 2. 进入代码模块
cd grpc-go/examples/features/retry
测试截图
- 先启动服务器
- 在启动客户端
服务器截图如下:
客户端截图如下:
HTTP Header 之重试协议
目前为止,已经通过代码测试了gRPC重试机制,更为复杂的一些特性就不一一展示了,现在来通过抓包工具来分析下,重试机制是如何通过协议进行客户端、服务器之间的数据传输。
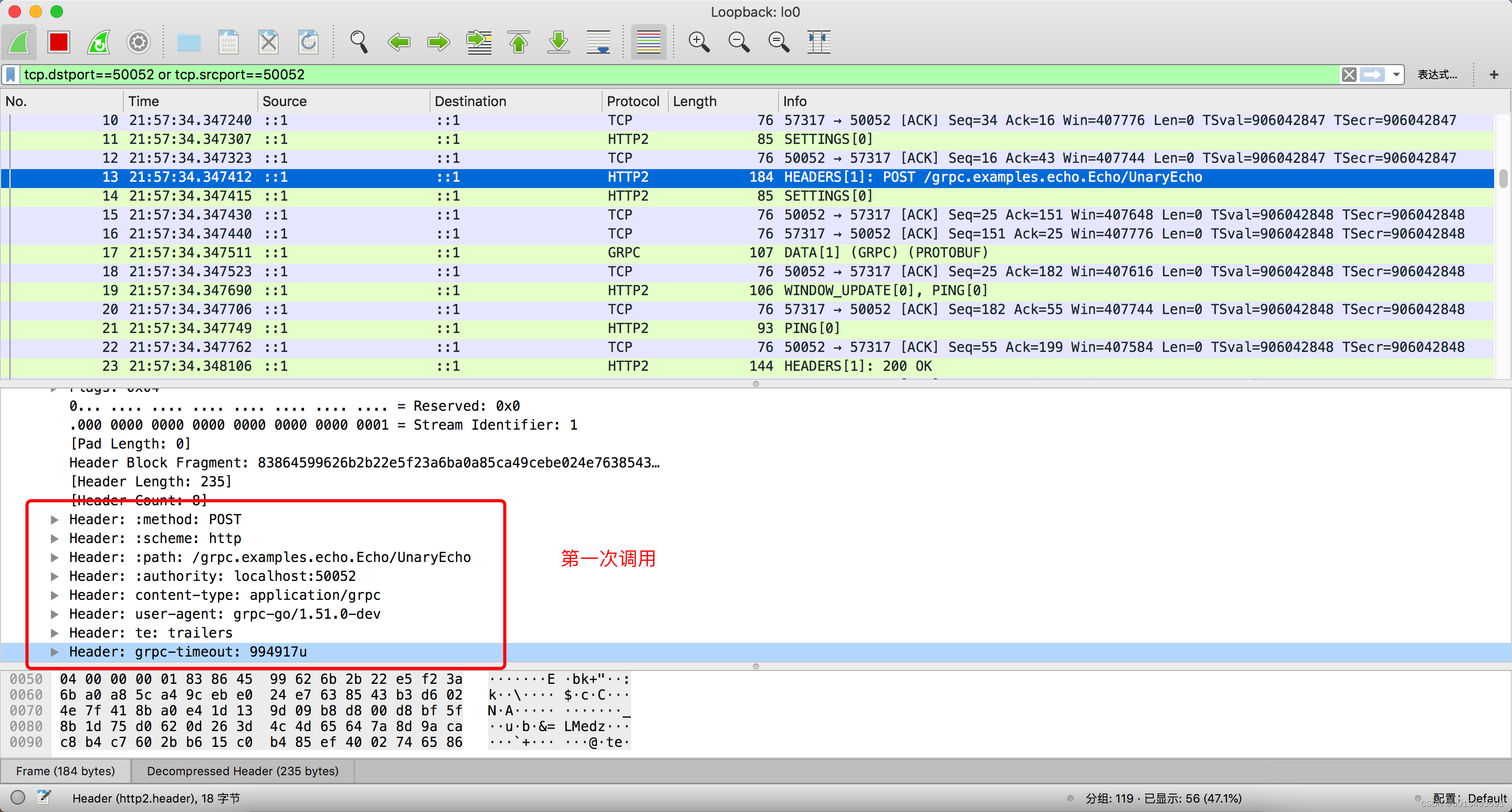
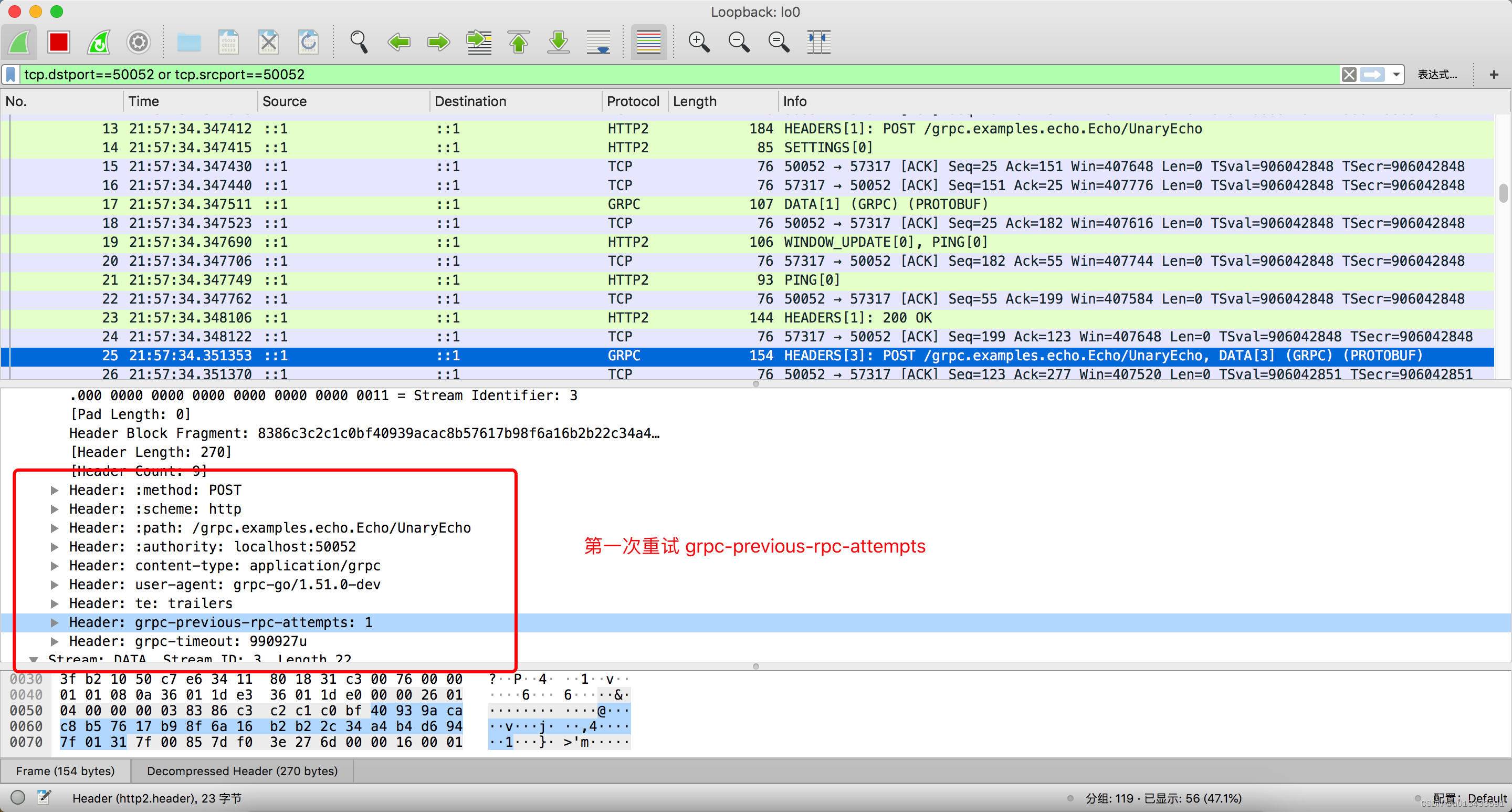
如上图所示:
- 正常第一次调用 HTTP header 里面不携带任何跟重试相关信息
- 第一次重试,使用 grpc-previous-rpc-attempts 消息头携带重试次数 发送到服务端
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!