在jupyter中引用import jupyter的.ipynb文件的四种方法
在jupyter中导入.ipynb文件
- 直接引用问题
- 四种解决的方法
- 被引用functionDataset.ipynb文件定义
- 方法1.用%run命令
- 方法2.用import_ipynb模块导入
- 方法3.加入另外语句
- 方法3-引用文件importFile.ipynb定义
- 方法4.将被引用文件导出.py文件
直接引用问题
用jupyter时,保存的文件后缀是.ipynb。直接import是不能使用的。直接导入会报错为:没有该模块。
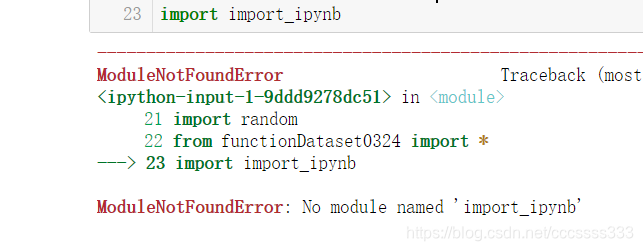
四种解决的方法
1.用%run命令,最简单,但被引用文件最好只有类和函数
2.用import_ipynb模块导入.ipynb文件,简单,但无法读取最新修改的被引用文件
3.加入另外语句,比较麻烦
4.将.ipynb文件转化为.py文件。但是在后期的使用时会造成一定的不便。因为习惯使用.ipynb进行编程,每次修改之后都必须重新进行文件的转化,特别是引用文件比较多时,对文件的管理以及后续的编程带来很大的不便。
被引用functionDataset.ipynb文件定义
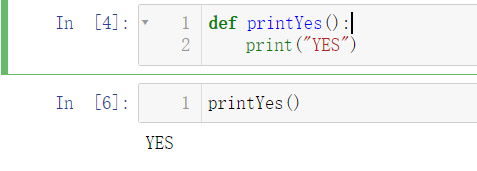
假定现在有一个jupyter文件为functionDataset.ipynb。里面有内置函数printYes,定义和运行结果如下所示:
def printYes():print("YES")
方法1.用%run命令
%run functionDataset.ipynb
printYes()
这个方法的好处就是,修改了被引用文件functionDataset.ipynb之后,保存,无需运行。
在引用它的文件里面再运行一次%run命令,就可以读取新的functionDataset.ipynb了。
方法2.用import_ipynb模块导入
// 用之前需要先下载该模块
import import_ipynb
from functionDataset import *
printYes()
即可运行,非常简单。但是无法读取修改后的文件。笔者能找到的方法只有退出jupyter再打开才能读取新的被引用文件。非常麻烦
方法3.加入另外语句
方法3-引用文件importFile.ipynb定义
现在在其他的jupyter文件中引用该.ipynb文件,定义为importFile.ipynb
// 导入相关模块
import io, os, sys, types
from IPython import get_ipython
from nbformat import read
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
def find_notebook(fullname, path=None):"""find a notebook, given its fully qualified name and an optional pathThis turns "foo.bar" into "foo/bar.ipynb"and tries turning "Foo_Bar" into "Foo Bar" if Foo_Bardoes not exist."""name = fullname.rsplit('.', 1)[-1]if not path:path = ['']for d in path:nb_path = os.path.join(d, name + ".ipynb")if os.path.isfile(nb_path):return nb_path# let import Notebook_Name find "Notebook Name.ipynb"nb_path = nb_path.replace("_", " ")if os.path.isfile(nb_path):return nb_path
class NotebookLoader(object):"""Module Loader for Jupyter Notebooks"""def __init__(self, path=None):self.shell = InteractiveShell.instance()self.path = pathdef load_module(self, fullname):"""import a notebook as a module"""path = find_notebook(fullname, self.path)print ("importing Jupyter notebook from %s" % path)# load the notebook objectwith io.open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:nb = read(f, 4)# create the module and add it to sys.modules# if name in sys.modules:# return sys.modules[name]mod = types.ModuleType(fullname)mod.__file__ = pathmod.__loader__ = selfmod.__dict__['get_ipython'] = get_ipythonsys.modules[fullname] = mod# extra work to ensure that magics that would affect the user_ns# actually affect the notebook module's nssave_user_ns = self.shell.user_nsself.shell.user_ns = mod.__dict__try:for cell in nb.cells:if cell.cell_type == 'code':# transform the input to executable Pythoncode = self.shell.input_transformer_manager.transform_cell(cell.source)# run the code in themoduleexec(code, mod.__dict__)finally:self.shell.user_ns = save_user_nsreturn mod
class NotebookFinder(object):"""Module finder that locates Jupyter Notebooks"""def __init__(self):self.loaders = {}def find_module(self, fullname, path=None):nb_path = find_notebook(fullname, path)if not nb_path:returnkey = pathif path:# lists aren't hashablekey = os.path.sep.join(path)if key not in self.loaders:self.loaders[key] = NotebookLoader(path)return self.loaders[key]
sys.meta_path.append(NotebookFinder())
最后导入.ipynb文件即可,导入后就可以使用其内置函数,使用方法和.py的一样
from functionDataset import *
printYes()
显示运行结果为
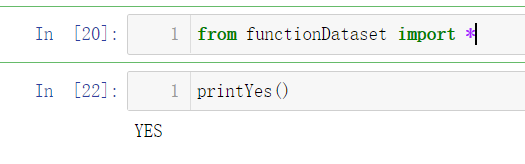
即运行成功。
方法4.将被引用文件导出.py文件
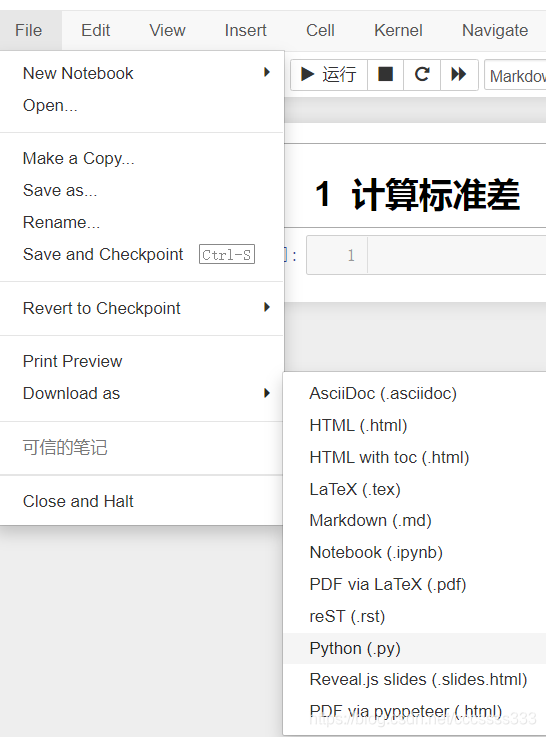
在jupyter界面工具栏依次选择file-download as - python(.py)即可导出。
具体可以看参考的nbviewer的教程链接。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!