多线程的LRU缓存
在之前的这篇LRU缓存Java实现中介绍了LRU缓存的简单实现。今天尝试来继续深入点。
首先我们抽象接口,我的文件结构如下:
为了面向非单一的固定类型,这里使用泛型来定义:
public interface Cache<K, V> {V get(K key);void set(K key, V value);int size();
}
1. 单线程LUR缓存
在单线程LUR缓存的设计中,保持和上篇的一致,即还是使用HashMap+双向链表来实现。另外为了测试比较方便在这个类中添加一个获取所有的key的方法。如下:
public class SingleThreadLRUCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V>{private static class Node<K, V>{K key;V val;Node<K, V> next;Node<K, V> pre;public Node(K key, V val){this.key = key;this.val = val;this.next = this.pre = null;}}private static class DoubleList<K, V>{Node<K, V> head, tail;public DoubleList(){this.head = new Node<>(null, null);this.tail = new Node<>(null, null);this.head.next = tail;this.tail.pre = head;}/*** 头插*/public void insert(Node<K, V> node){node.next = head.next;head.next.pre = node;head.next = node;node.pre = head;}/*** 删除当前node*/public Node<K, V> delete(Node<K, V> node){node.pre.next = node.next;node.next.pre = node.pre;return node;}/*** 删除尾部*/public Node<K, V> deleteLast(){if(head.next != tail){return this.delete(tail.pre);}return null;}}private final int capacity;private HashMap<K, Node<K, V>> map;private DoubleList<K, V> list;public SingleThreadLRUCache(int capacity){this.capacity = capacity;this.map = new HashMap<>();this.list = new DoubleList<>();}@Overridepublic V get(K key) {if(this.map.containsKey(key)){Node<K, V> node = this.map.get(key);this.set(key, node.val);return node.val;}return null;}@Overridepublic void set(K key, V value) {Node<K, V> curNode = new Node<>(key, value);if(this.map.containsKey(key)){Node<K, V> oldNode = this.map.get(key);this.list.delete(oldNode);this.map.put(key, curNode);this.list.insert(curNode);}else{if(this.map.size() >= this.capacity){Node<K, V> last = this.list.deleteLast();this.map.remove(last.key);}this.map.put(key, curNode);this.list.insert(curNode);}}public Set<K> keySet() {return this.map.keySet();}@Overridepublic int size() {return this.map.size();}
}
测试:
public class TestC {private static SingleThreadLRUCache<Integer, String> lruCache = new SingleThreadLRUCache<>(5);public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {lruCache.set(i, "val#"+(i + 1));}printDatas();lruCache.set(3, "val#"+(3 + 1));printDatas();}private static void printDatas() {Set<Integer> keys = lruCache.keySet();for (Integer key : keys) {System.out.print(key+"\t");}System.out.println();}
}
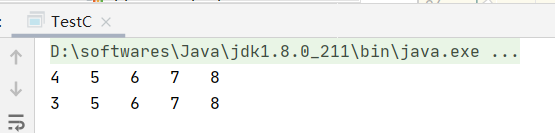
从上面可以看出,最终的结果符合我们的预期。测试的时候设置容量为5,在一次性添加9个的时候,会导致前面的几个失效被移除,最终我添加3,它淘汰了4。符合预期。注意到这里因为使用的是HashMap,故而上面打印的顺序没有实际意义(除非自己去遍历双向链表,然后返回,但是这样开销大),因为存放是无序的,不要将上面的输出顺序当做它的淘汰匹配顺序。
2. 多线程LRU缓存
为了满足多线程, 我们需要多数据的操作加锁,对共享的数据区域加volatile关键字。
public class MultithreadedLRUCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V>{private static class Node<K, V>{K key;V val;Node<K, V> next;Node<K, V> pre;public Node(K key, V val){this.key = key;this.val = val;this.next = this.pre = null;}}private static class DoubleList<K, V>{Node<K, V> head, tail;public DoubleList(){this.head = new Node<>(null, null);this.tail = new Node<>(null, null);this.head.next = tail;this.tail.pre = head;}/*** 头插*/public void insert(Node<K, V> node){node.next = head.next;head.next.pre = node;head.next = node;node.pre = head;}/*** 删除当前node*/public Node<K, V> delete(Node<K, V> node){node.pre.next = node.next;node.next.pre = node.pre;return node;}/*** 删除尾部*/public Node<K, V> deleteLast(){if(head.next != tail){return this.delete(tail.pre);}return null;}}private final int capacity;private volatile HashMap<K, Node<K, V>> map;private DoubleList<K, V> list;public MultithreadedLRUCache(int capacity){this.capacity = capacity;this.map = new HashMap<>();this.list = new DoubleList<>();}@Overridepublic V get(K key) {if(this.map.containsKey(key)){Node<K, V> node = this.map.get(key);this.set(key, node.val);return node.val;}return null;}@Overridepublic synchronized void set(K key, V value) {Node<K, V> curNode = new Node<>(key, value);if(this.map.containsKey(key)){Node<K, V> oldNode = this.map.get(key);this.list.delete(oldNode);this.map.put(key, curNode);this.list.insert(curNode);}else{if(this.map.size() >= this.capacity){Node<K, V> last = this.list.deleteLast();this.map.remove(last.key);}this.map.put(key, curNode);this.list.insert(curNode);}}public Set<K> keySet() {return this.map.keySet();}@Overridepublic int size() {return this.map.size();}}
测试的时候注意到一个问题,也就是在Map对象的KeySet的类中,在遍历的时候如果有另一个线程修改,就会导致ConcurrentModificationException。故而这里我们在处理遍历的时候,需要额外加一把锁。
测试类:
public class TestC {private static MultithreadedLRUCache<Integer, String> lruCache = new MultithreadedLRUCache<>(5);private static Object object = new Object();static class ThreadFactory{private static AtomicInteger tag = new AtomicInteger(1);public static Thread getThread(Runnable r){return new Thread(r, "Thread #" + tag.getAndIncrement());}}public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadFactory.getThread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {int i = 0;while(i < 10){try {synchronized (object){lruCache.set(i, ""+(i+1));printDatas(i);}i++;Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}).start();ThreadFactory.getThread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {int i = 10;while(i < 20){try {synchronized (object){lruCache.set(i, ""+(i+1));printDatas(i);} i++;Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}).start();}private static synchronized void printDatas(int k) {System.out.print("【"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"】 set " + k +"\t:");Set<Integer> keys = lruCache.keySet();for (Integer key : keys) {System.out.print(key+"\t");}System.out.println();}
}
结果:
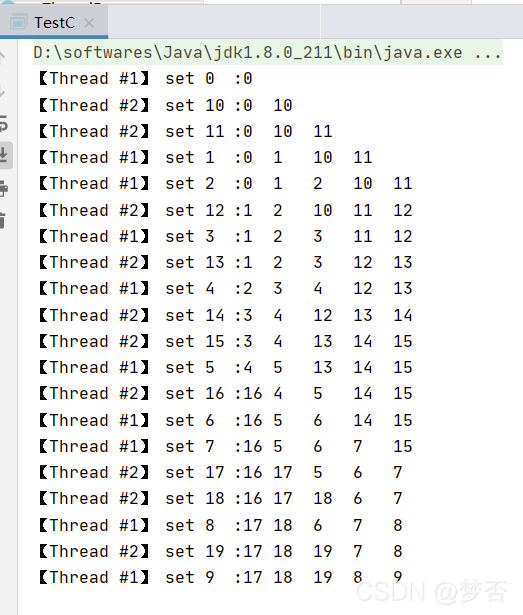
为了方便,我就直接在操作和打印的时候,加了一把对象锁,让线程的set和打印操作为一个”原子“操作。但这样一来,感觉在多线程LRU中加入的synchronized就没多大意义了。
应该借鉴ConcurrentHashMap的设计思想,之后再考虑继续探索。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!