数据结构——单链表(C语言实现)
单链表(C语言实现)
- 单链表
- 1.单链表的概念
- 2.单链表的结构体设计
- 3.单链表的基本操作
- 3.1 初始化
- 3.2 头插
- 3.3 尾插
- 3.4 按位置插
- 3.5 头删
- 3.6 尾删
- 3.7 按位置删
- 3.8 按值删
- 3.9 查找
- 3.10 获取有效值个数
- 3.11 判空
- 3.12 销毁
- 3.13 打印
- 4.主函数
- 5.总结
单链表
1.单链表的概念
- 单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素(数据元素的映象) + 指针(指示后继元素存储位置),元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。以“结点的序列”表示的线性表称作线性链表(单链表),单链表是链式存取的结构。
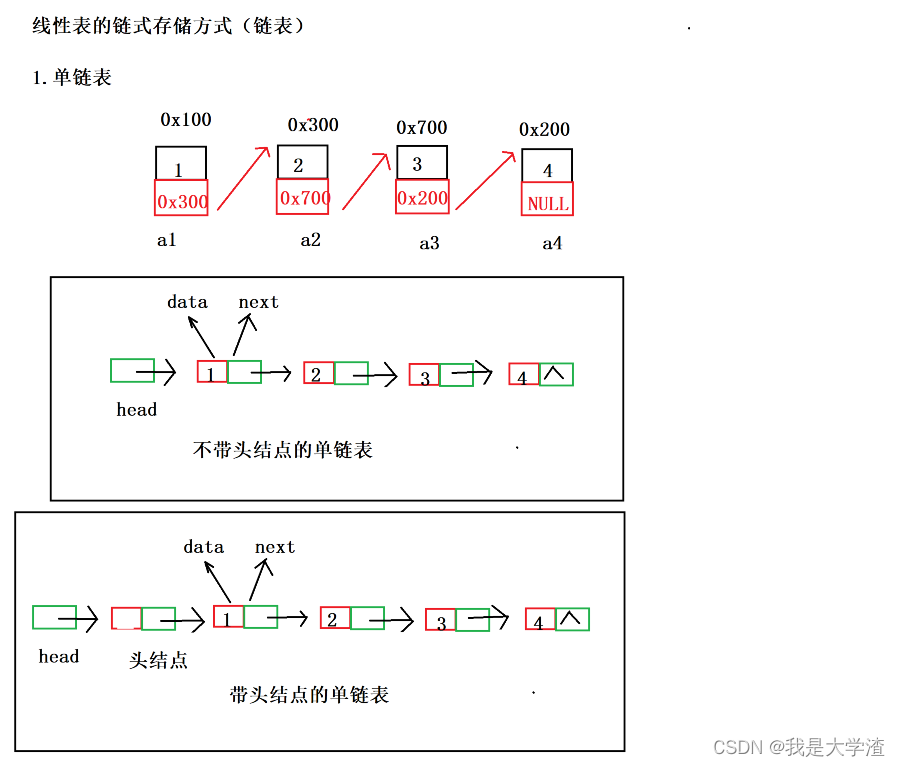
2.单链表的结构体设计
- 结构体中有个数据类型,一个保存有效值,另一个保存下一个有效节点的地址
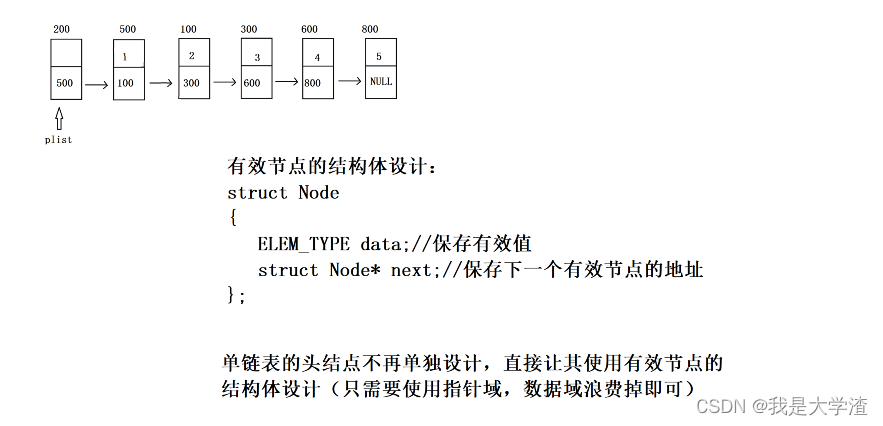
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;
//带头结点的单链表
//有效节点的结构体设计
typedef struct Node
{ELEM_TYPE data; //数据域 //保存节点有效值struct Node *next; //指针域 //保存下一个有效节点的地址
}Node, *PNode;
//typedef struct Node Node;
//typedef struct Node* PNode;
3.单链表的基本操作
单链表的基本操作有 初始化,头插,尾插,按位置插,头删,尾删,按位置删,查找,按值删,获取有效值个数,判空,清空,销毁,打印
函数
//初始化
void Init_list(PNode plist);//头插
bool Insert_Head(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val);//尾插
bool Insert_Tail(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val);//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(struct Node *plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val);//头删
bool Del_head(struct Node* plist);//尾删
bool Del_tail(struct Node *plist);//按位置删
bool Del_pos(struct Node *plist, int pos);//按值删
bool Del_val(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val);//查找节点
struct Node* Search(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val);//获取有效值个数
int Get_Length(struct Node *plist);//判空
bool IsEmpty(struct Node *plist);//清空
void Clear(struct Node *plist);
//20:10
//销毁
void Destroy(struct Node *plist);//打印
void Show(struct Node *plist);3.1 初始化
- 初始化,将头节点的指针域置为空,数据域不使用
void Init_list(PNode plist)
{//assert plistplist->next = NULL;//plist->data; 头结点的数据域不使用
}
3.2 头插
- 申请一个新结点,将数据放入到新结点之中,然后将新结点插入到头节点之后即可。
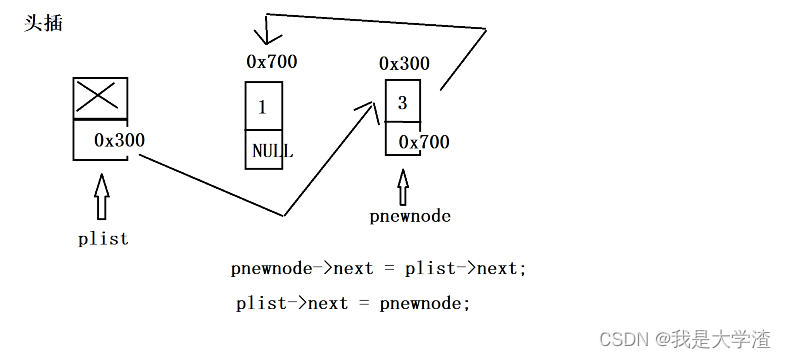
//头插
bool Insert_Head(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{//1.assert plistassert(plist != NULL);//2.购买新节点(购买好节点之后,记得将val值赋值进去)struct Node *pnewnode = (struct Node *)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Node));assert(pnewnode != NULL);pnewnode->data = val;//3.找到合适的插入位置//因为是头插函数 所以不需要特意的去合适的位置 直接向plist后面插即可//4.插入pnewnode->next = plist->next;plist->next = pnewnode;return true;
}
3.3 尾插
- 将新结点插入到当前单链表的表尾
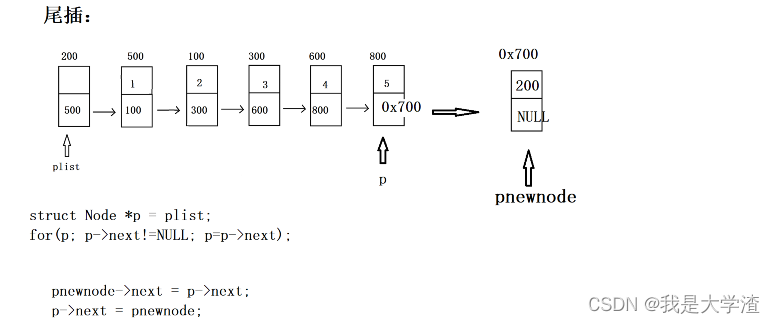
//尾插
bool Insert_Tail(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{//1.assert plistassert(plist != NULL);//2.购买新节点(购买好节点之后,记得将val值赋值进去)struct Node *pnewnode = (struct Node *)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Node));assert(pnewnode != NULL);pnewnode->data = val;//3.找到合适的插入位置struct Node *p = plist;for(p; p->next!=NULL; p=p->next);//此时 p就指向尾结点//4.插入pnewnode->next = p->next;p->next = pnewnode;return true;
}
3.4 按位置插
- 首先要判断 pos是否合法,要插入的位置必须大于零小于等于链表总长度
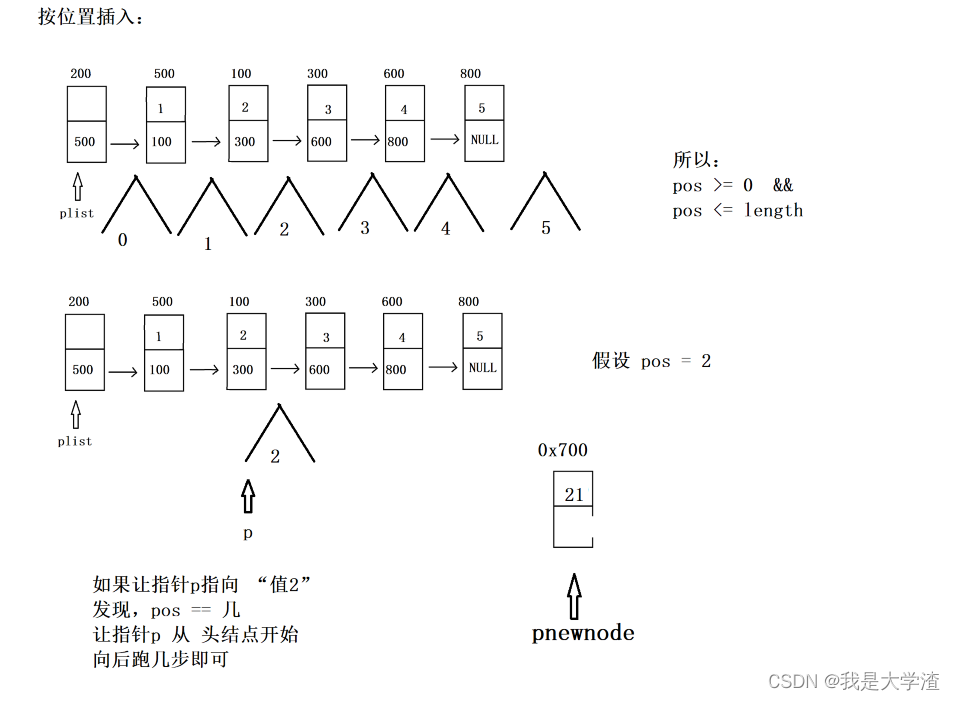
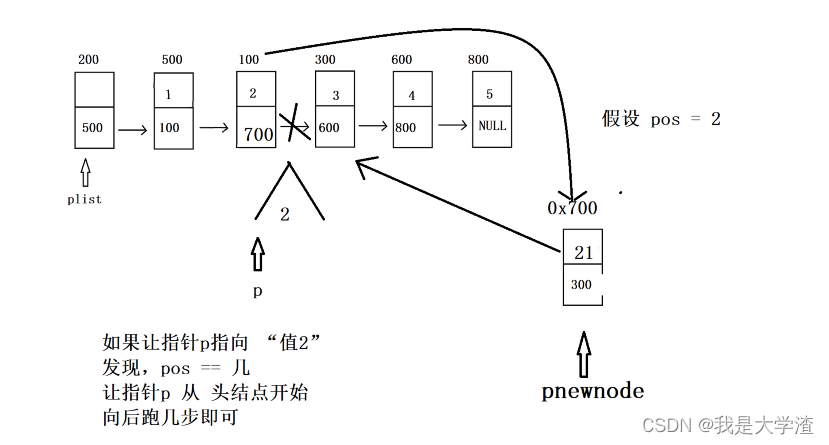
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(struct Node *plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val)
{//assert assert(plist != NULL);assert(pos>=0 && pos<=Get_Length(plist));//1.购买新节点(购买好节点之后,记得将val值赋值进去)struct Node *pnewnode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));assert(pnewnode != NULL);pnewnode->data = val;//2.找到合适的插入位置(让指针p指向合适的节点)struct Node *p = plist;for(int i=0; i<pos; i++){p=p->next;}//3.插入pnewnode->next = p->next;p->next = pnewnode;return true;
}
3.5 头删
- 和头插类似,只不过一个是插入一个是删除,删除需要判空空链表不能删除
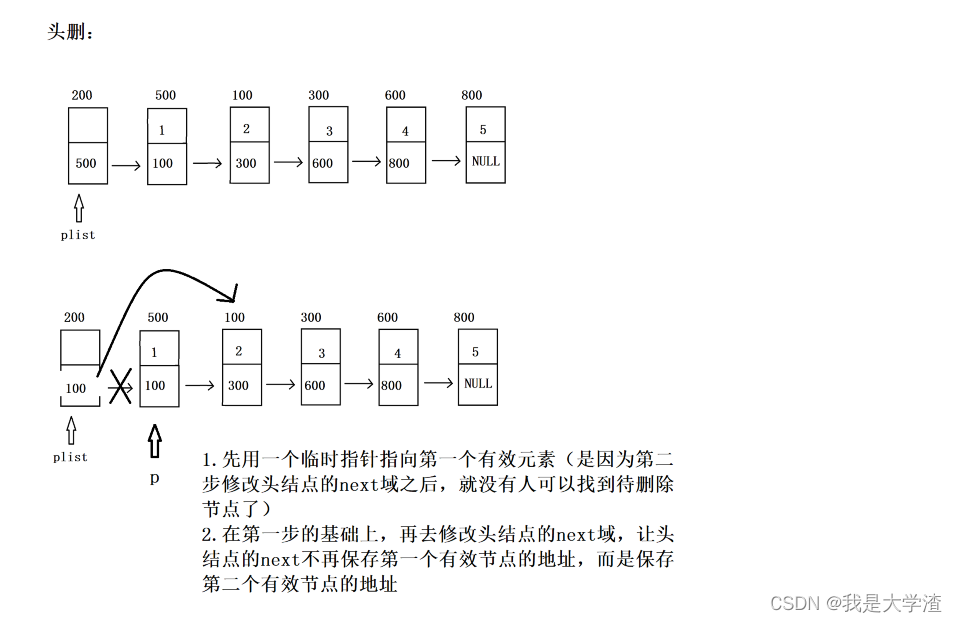
//头删
bool Del_head(struct Node* plist)
{//1.对plist 断言assert(plist != NULL);//2.删除需要判空if(IsEmpty(plist)){return false;}//3.先申请一个临时指针p,指向第一个有效节点的地址struct Node *p = plist->next;//4.头结点的next域跨越指向(不再指向第一个有效节点,而是指向第二个)plist->next = p->next;//plist->next = plist->next->next;free(p);return true;
}
3.6 尾删
- 删除链表中最后一个结点
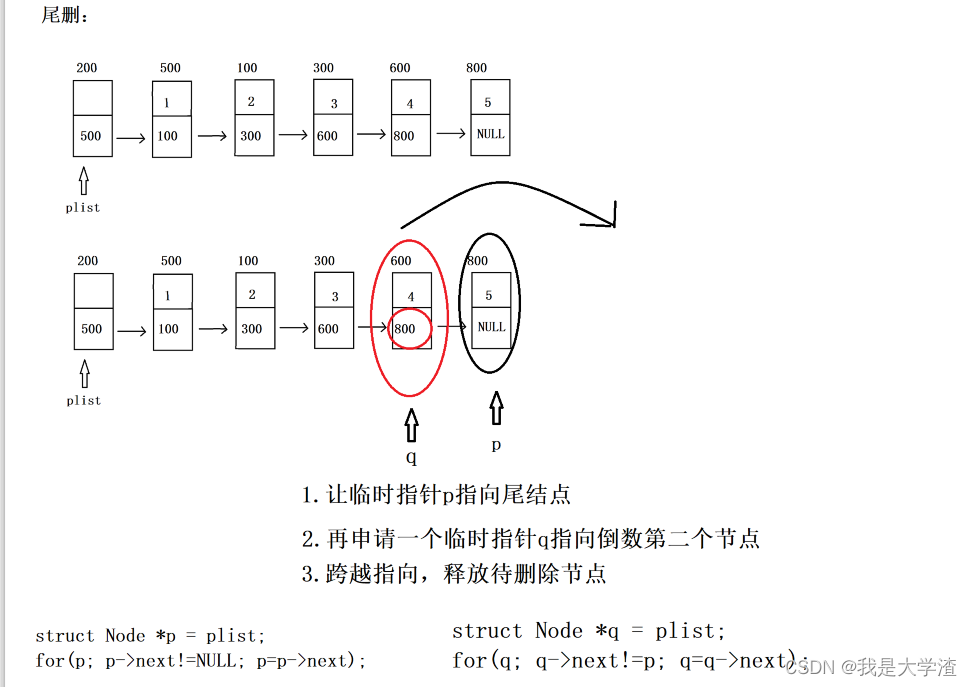
//尾删
bool Del_tail(struct Node *plist)
{//1.对plist 断言assert(plist != NULL);//2.删除需要判空(判空链表)if(IsEmpty(plist)){return false;}//3.让临时指针p指向待删除节点(尾结点)struct Node *p = plist;for(; p->next!=NULL; p=p->next);//4.再让临时指针q指向倒数的第二个节点struct Node *q = plist;for(; q->next!=p; q=q->next);//5.跨越指向,并释放待删除节点q->next = p->next;//q->next = NULL;free(p);return true;
}
3.7 按位置删
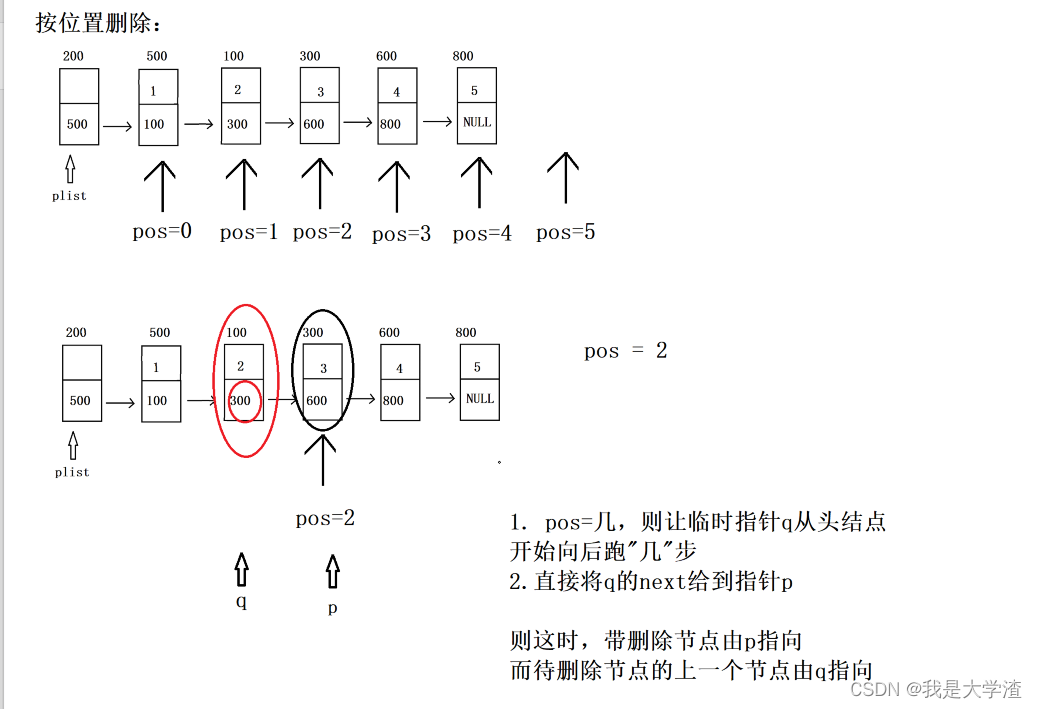
- 根据位置删除结点,需要判断结点的合法性,这次的pos需要小于链表长度
//按位置删
bool Del_pos(struct Node *plist, int pos)
{//1.对plist 断言 pos做合法性判断assert(plist != NULL);assert(pos >=0 && pos < Get_Length(plist));//2.删除需要判空(判空链表)if(IsEmpty(plist)){return false;}//3.pos="几",则让指针q从头结点开始向后跑"几"步(此时,q指向待删除节点的上一个节点)struct Node *q = plist;for(int i=0; i<pos; i++)//此时,for循环结束,指针q指向待删除节点的上一个节点{q=q->next;}//4.直接让q的next域给到指针p(此时,指针p指向待删除节点)struct Node *p = q->next;//此时,指针p指向待删除节点//5.跨越指向,释放待删除节点q->next = p->next;free(p);return true;
}
3.8 按值删
- 按值删需要先找到数据域是该值的结点,然后将其删除
//按值删
bool Del_val(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{//assert plist//删除需要判空(判空链表)if(IsEmpty(plist)){return false;}//用指针p去接收Search函数的返回值struct Node *p = Search(plist, val);if(p == NULL)//如果p==NULL 代表val不存在{return false;}//执行这一行时,代表val值节点存在,且此时用p指向//让指着q停留在指针p的上一个节点位置struct Node *q = plist;for(; q->next!=p; q=q->next);//此时p和q分别已经指向了待删除节点和待删除节点的上一个节点//,则此时直接跨越指向,并且释放待删除节点q->next = p->next;free(p);return true;
}3.9 查找
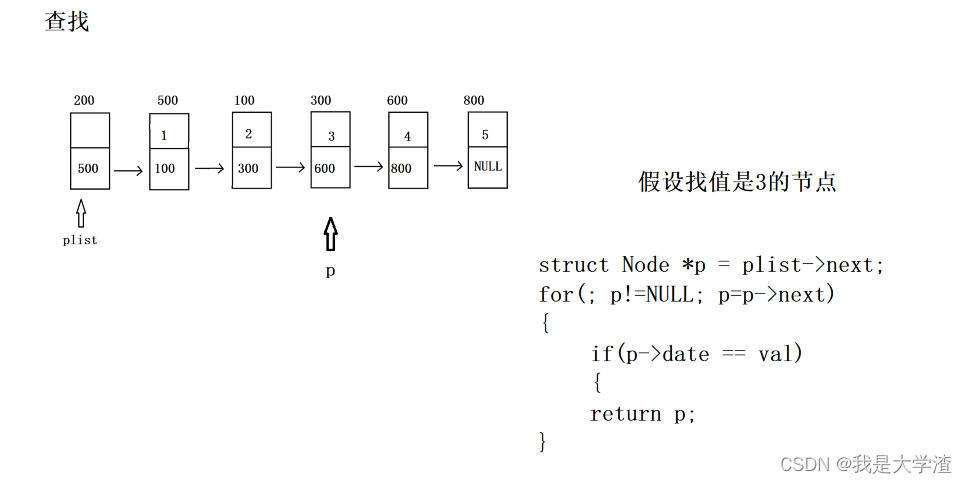
- 按值查找,返回该值的结点
//查找节点
struct Node* Search(struct Node *plist, ELEM_TYPE val)
{//assert pliststruct Node *p = plist->next;for(; p!=NULL; p=p->next){if(p->data == val){return p;}}return NULL;
}
3.10 获取有效值个数
- 计算出有效节点的个数
int Get_Length(struct Node *plist)
{//assertint count = 0;struct Node *p = plist->next;for(; p!=NULL; p=p->next){count++;}return count;
}
3.11 判空
- 在删除时需要进行判空
//判空
bool IsEmpty(struct Node *plist)
{assert(plist != NULL);//如果头结点的next域为NULL,则代表没有有效节点,为空链表return plist->next == NULL;
}
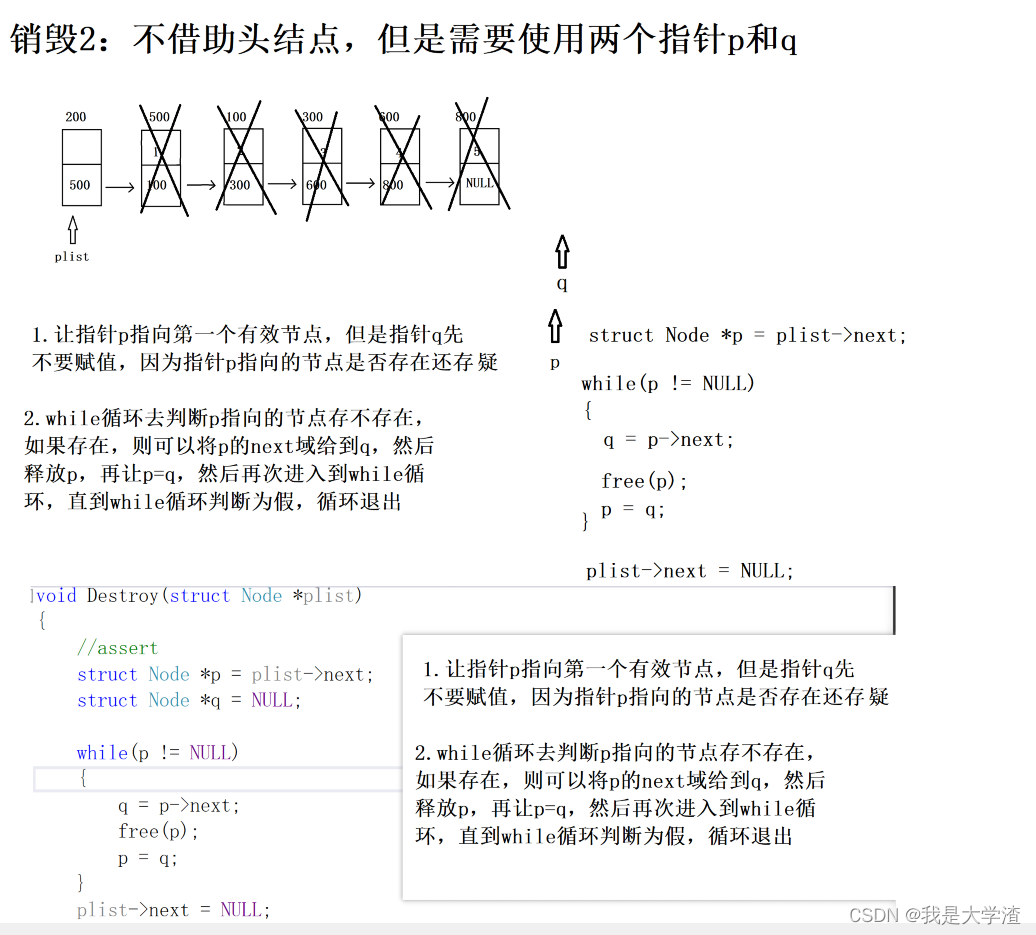
3.12 销毁
-
有两种销毁方式
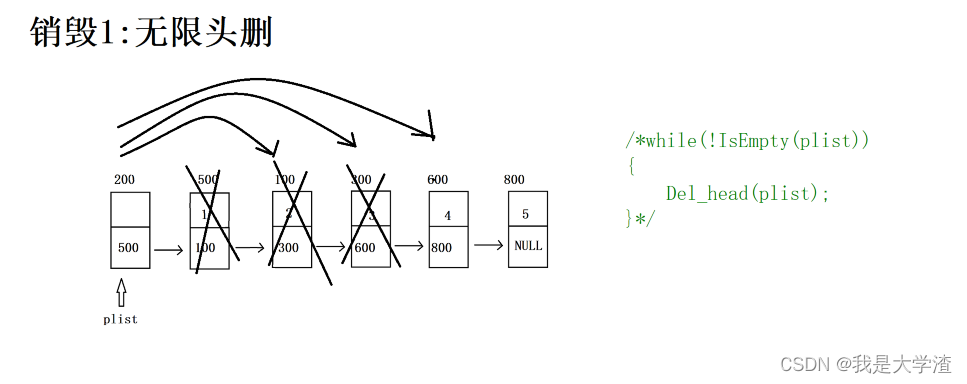
无限头删
双指针
//销毁1(无限头删)
void Destroy1(struct Node *plist)
{/*while(!IsEmpty(plist)){Del_head(plist);}*/while(plist->next != NULL){struct Node *p = plist->next;plist->next = p->next;free(p);}
}//销毁2(不借助头结点, 需要两个指针)
void Destroy(struct Node *plist)
{//assertstruct Node *p = plist->next;struct Node *q = NULL;while(p != NULL){q = p->next;free(p);p = q;}plist->next = NULL;
}
3.13 打印
//打印
void Show(struct Node *plist)
{struct Node *p = plist->next;for(; p!=NULL; p=p->next){printf("%d ", p->data);}printf("\n");
}
4.主函数
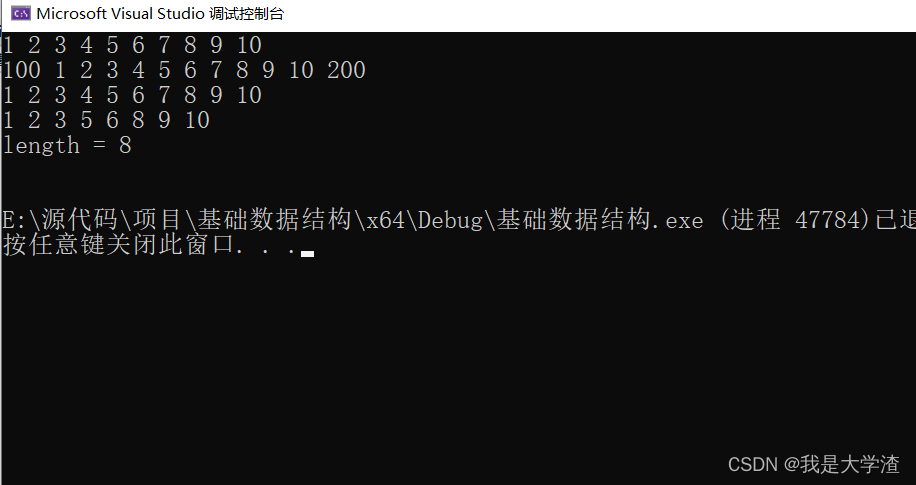
//单链表测试用例
int main()
{struct Node head;Init_list(&head);for(int i=0; i<10; i++){Insert_pos(&head, i, i+1);}Show(&head);Insert_Head(&head, 100);Insert_Tail(&head, 200);Show(&head);Del_head(&head);Del_tail(&head);Show(&head);Del_pos(&head, 3);//1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10Del_val(&head, 7);//1 2 3 5 6 8 9 10Show(&head);printf("length = %d\n", Get_Length(&head));Destroy(&head);Show(&head);return 0;
}结果如下:
5.总结

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!