双向带头循环链表C语言版
文章目录
- 0.前言
- 1. List.h
- 2. List.c
- 2.1 开辟一个新节点
- 2.2 初始化链表
- 2.3 摧毁链表
- 2.4 尾插
- 2.5 和之前不带哨兵位的单链表传参的区别
- 2.6 尾删
- 2.7 打印链表
- 2.8 头插
- 2.9 头删
- 2.10 查找
- 2.11 在pos之前插入
- 2.12 删除pos位置的节点
- 2.13 10min实现双向循环链表
- 2.14 List.c完整代码
- 3.Test.c
- 4. 运行结果
- 5. 顺序表和链表的区别
0.前言
带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了,同样我们也采用分文件的方式实现。
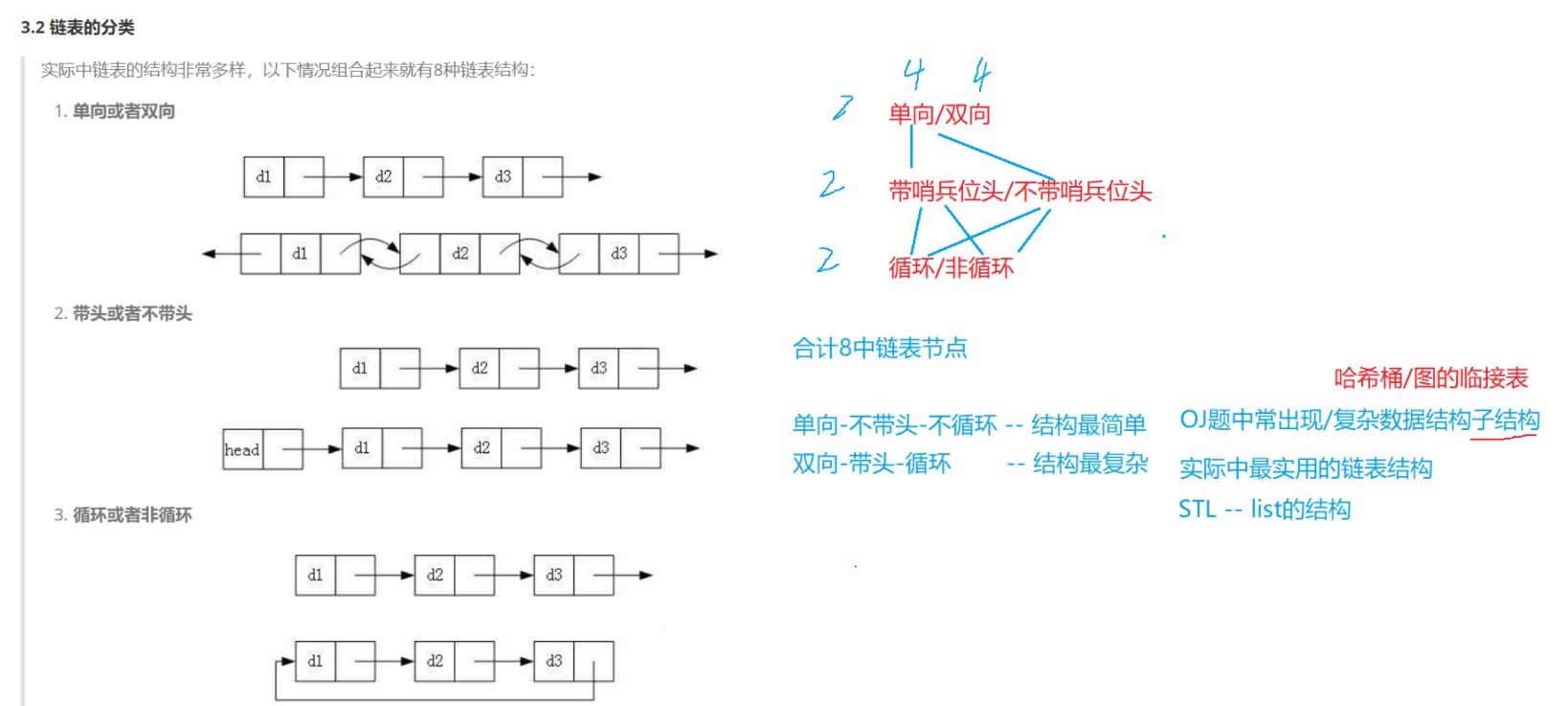
1. List.h
#pragma once#include 2. List.c
2.1 开辟一个新节点
LTNode* BuyLTNode(LTDataType x)
{LTNode *newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if(newnode == NULL){printf("malloc fail\n");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->prev = NULL;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}
2.2 初始化链表
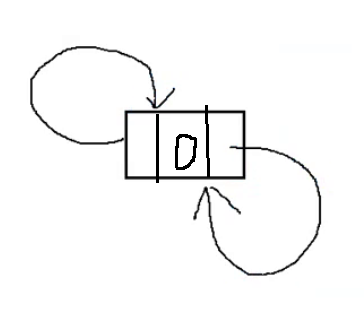
LTNode* ListInit()
{LTNode* phead = BuyLTNode(0);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}
2.3 摧毁链表
void ListDestroy(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){LTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL;
}
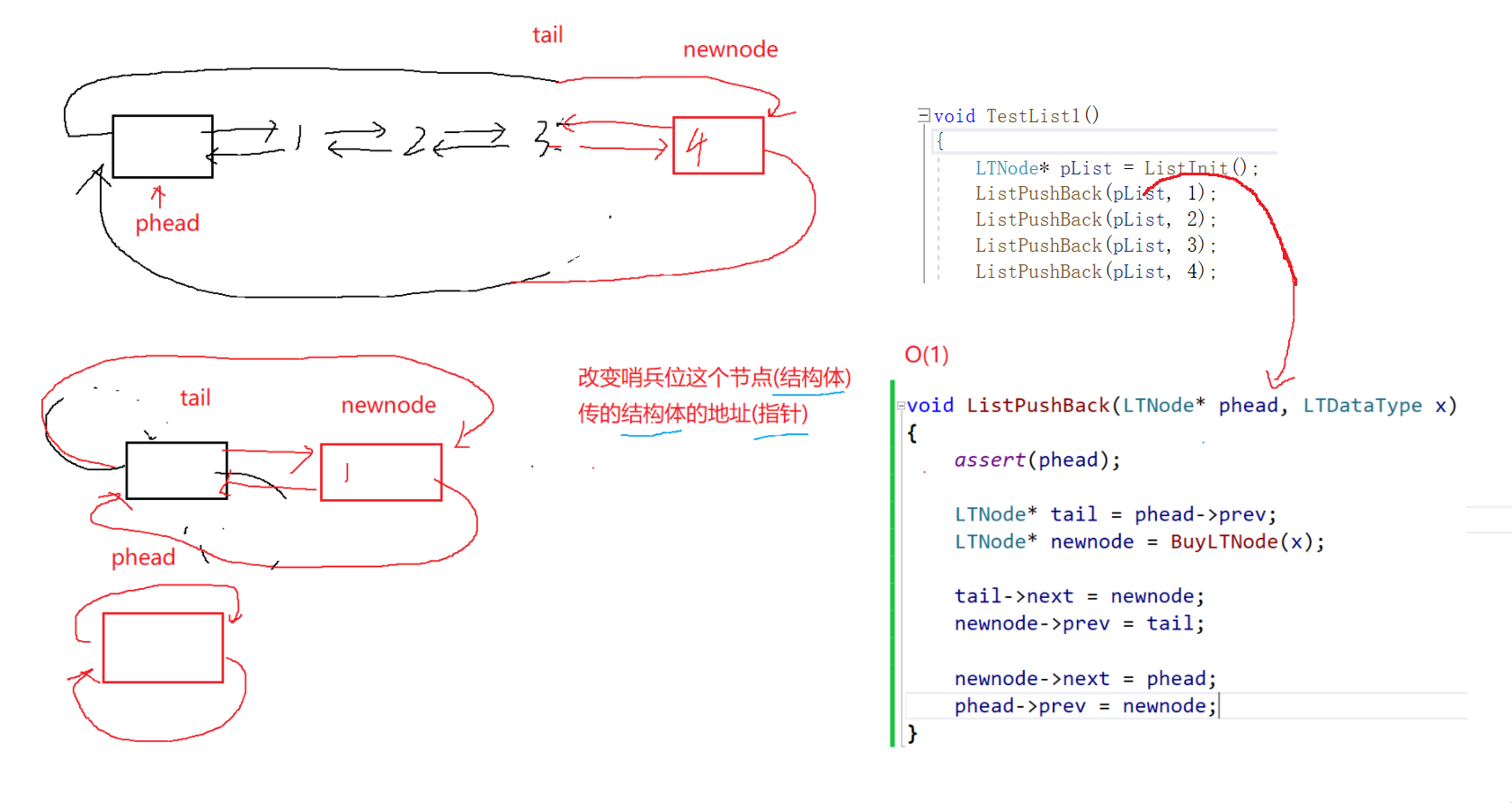
2.4 尾插
多个节点的情况:

这种方法也能解决空链表的情况

代码实现:
void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode *tail = phead->prev;LTNode *newnode = BuyLTNode(X);tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;
}
2.5 和之前不带哨兵位的单链表传参的区别
带哨兵位的双向循环链表:
不带哨兵位的单链表:

2.6 尾删
多个节点:

这种方法也能解决一个节点的情况:
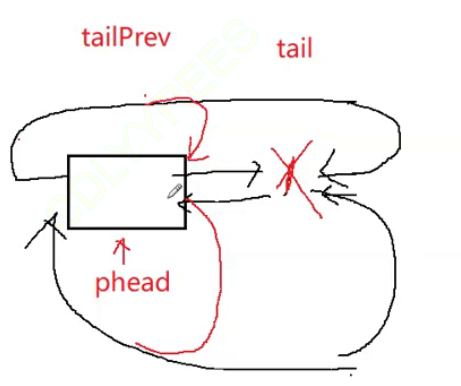
void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);//链表为空assert(phead !=phead->next);LTNode* tail = phead->prev;LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;free(tail);tail = NULL;tailPrev->next = phead;phead->prev = tailPrev;
}
2.7 打印链表
 我们发现
我们发现cur指针再次回到phead为结束条件。
void ListPrint(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){printf("%d ",cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n\n");
}
2.8 头插
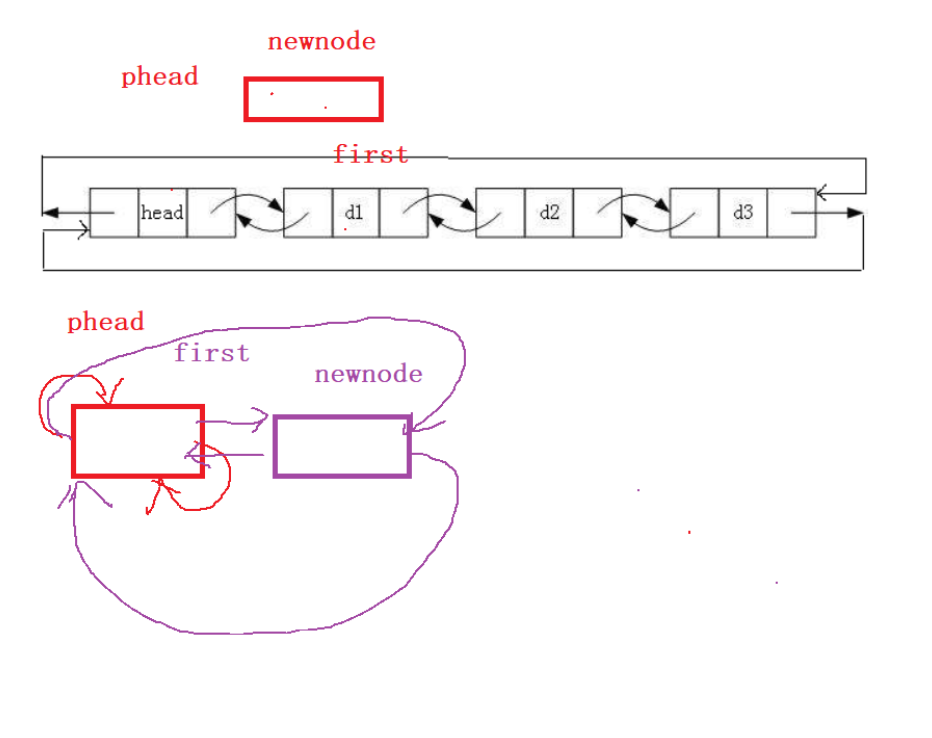
void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* first = phead->next;LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode;
}
2.9 头删
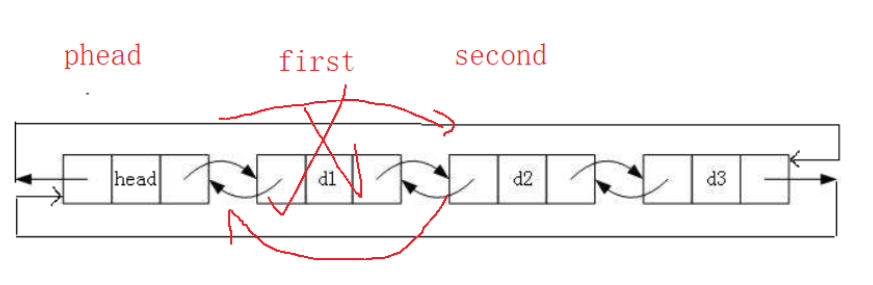
void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);LTNode* first = phead->next;LTNode* second = first->next;free(first);phead->next = second;second->prev = phead;
}
2.10 查找
LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}
2.11 在pos之前插入
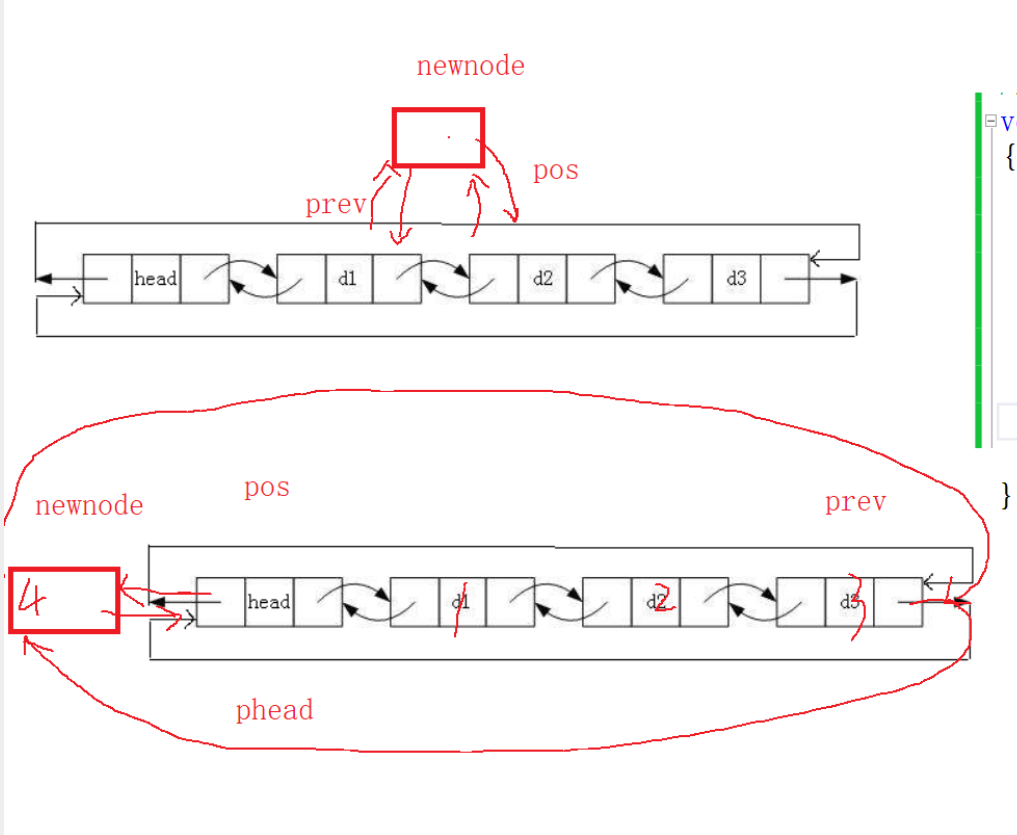
void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{assert(pos);LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;posPrev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = posPrev;
}
2.12 删除pos位置的节点
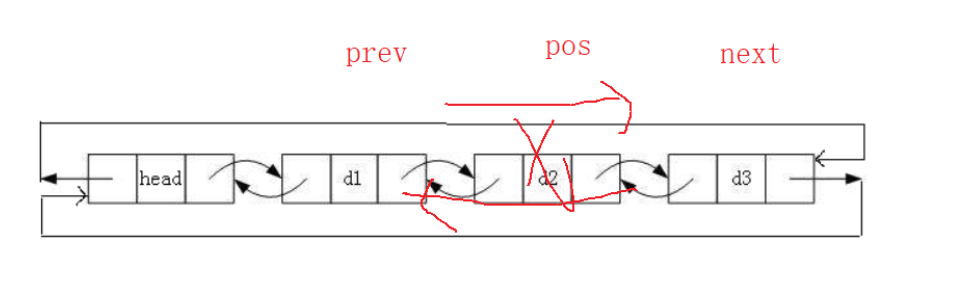
void ListErase(LTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);LTNode* prev = pos->prev;LTNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);
}
2.13 10min实现双向循环链表
//尾插
void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListInsert(phead,x);
}
//尾删
void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListErase(phead->prev);
}
//头插
void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListInsert(phead,x);
}
//头删
void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListErase(phead->next);
}
2.14 List.c完整代码
#include"List.h"LTNode* BuyLTNode(LTDataType x)
{LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (newnode == NULL){printf("malloc fail\n");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;
}void ListPrint(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n\n");
}void ListDestroy(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){LTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL;
}LTNode* ListInit()
{LTNode* phead = BuyLTNode(0);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{//assert(phead);//LTNode* tail = phead->prev;//LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);//tail->next = newnode;//newnode->prev = tail;//newnode->next = phead;//phead->prev = newnode;ListInsert(phead, x);
}void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);// Ϊassert(phead->next != phead);LTNode* tail = phead->prev;LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;free(tail);tail = NULL;tailPrev->next = phead;phead->prev = tailPrev;}void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDateType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* first = phead->next;LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode;
}void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);LTNode* first = phead->next;LTNode* second = first->next;free(first);phead->next = second;second->prev = phead;
}LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{assert(pos);/*LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);pos->prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = pos->prev;pos->prev = newnode;newnode->next = pos;*/LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;posPrev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = posPrev;
}void ListErase(LTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);LTNode* prev = pos->prev;LTNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);
}
3.Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "List.h"void TestList1()
{LTNode* pList = ListInit();ListPushBack(pList, 1);ListPushBack(pList, 2);ListPushBack(pList, 3);ListPushBack(pList, 4);ListPushBack(pList, 5);ListPushBack(pList, 6);ListPrint(pList);ListPopBack(pList);ListPopBack(pList);ListPopBack(pList);ListPopBack(pList);ListPopBack(pList);ListPopBack(pList);//ListPopBack(pList);ListPrint(pList);ListDestroy(plist);
}void TestList2()
{//LTNode* pList = NULL;//ListInit(&pList);LTNode* pList = ListInit();ListPushBack(pList, 1);ListPushBack(pList, 2);ListPushBack(pList, 3);ListPushBack(pList, 4);ListPrint(pList);ListPushFront(pList, 0);ListPushFront(pList, -1);ListPrint(pList);LTNode* pos = ListFind(pList, 3);if (pos){ListInsert(pos, 30);}ListPrint(pList);}int main()
{TestList1();return 0;
}
4. 运行结果
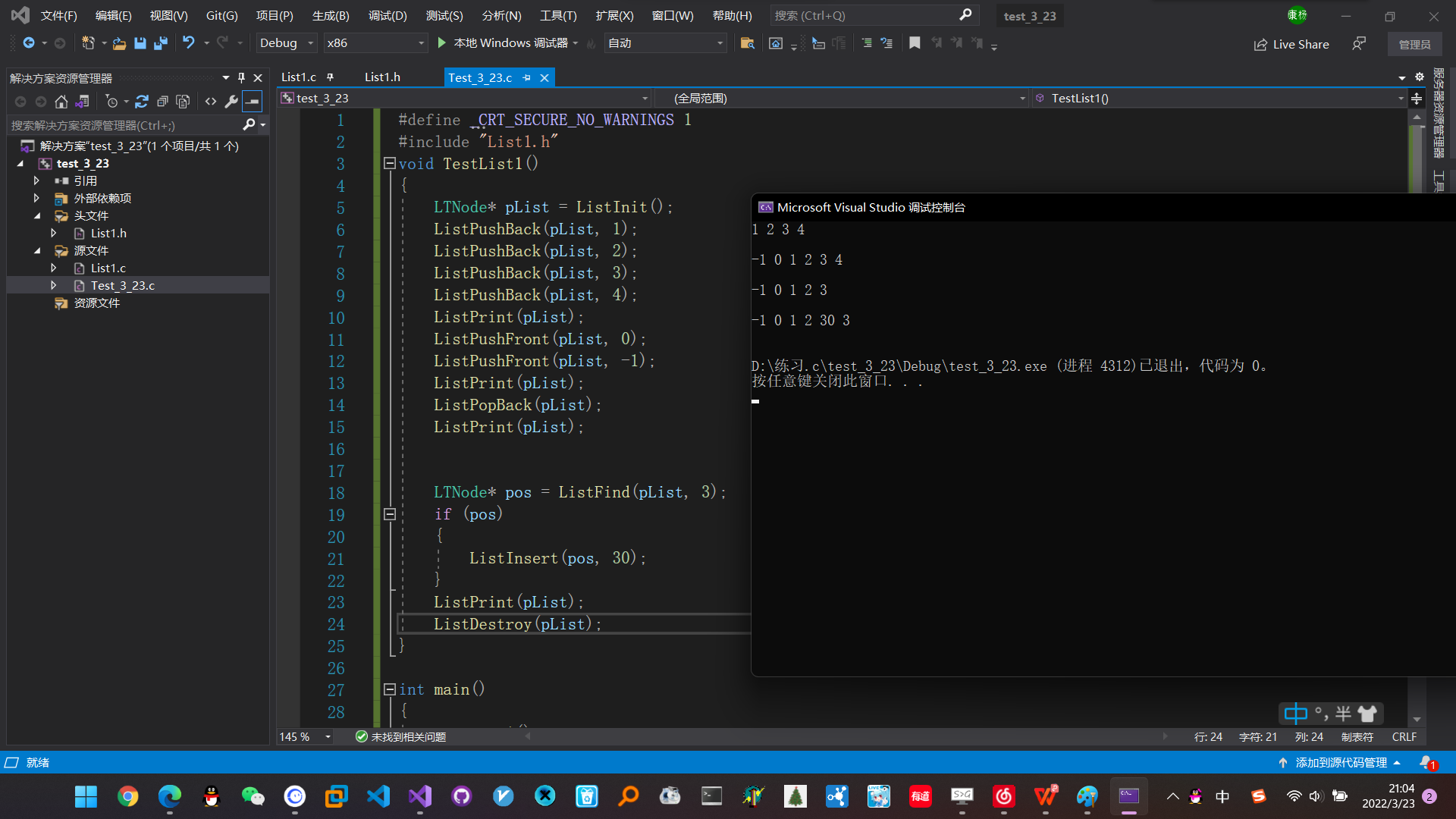
5. 顺序表和链表的区别
| 不同点 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1) | 不支持:O(N) |
| 任意位置插入或者删除元素 | 可能需要搬移元素,效率低O(N) | 只需修改指针指向 |
| 插入 | 动态顺序表,空间不够时需要扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储+频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |
| 缓存利用率 | 高 | 低 |
备注:缓存利用率参考存储体系结构以及局部原理性。
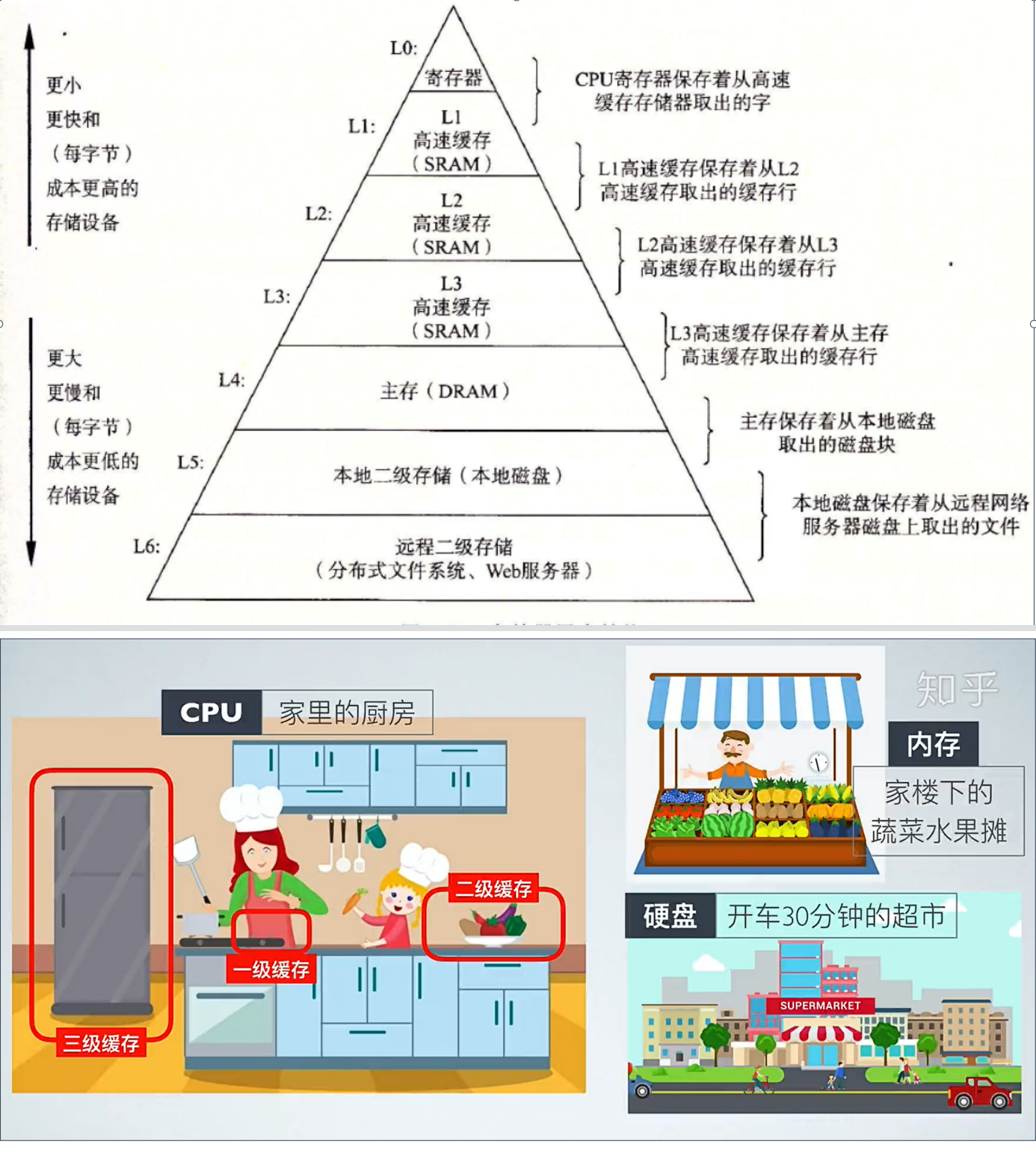
与程序员相关的cpu缓存知识
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!