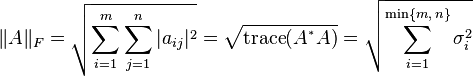Frobenius范数
Frobenius norm
Main article: Hilbert–Schmidt operatorFor p = 2, this is called the Frobenius norm or the Hilbert–Schmidt norm, though the latter term is often reserved for operators on Hilbert space. This norm can be defined in various ways:
where A* denotes the conjugate transpose of A, σi are the singular values of A, and the trace function is used. The Frobenius norm is very similar to the Euclidean norm on Kn and comes from the Frobenius inner product on the space of all matrices.
The Frobenius norm is sub-multiplicative and is very useful for numerical linear algebra. This norm is often easier to compute than induced norms and has the useful property of being invariant under rotations. This property follows easily from the trace definition restricted to real matrices,
-
 ,
,
where we have used the orthogonal nature of P,  and the cyclic nature of the trace,
and the cyclic nature of the trace, 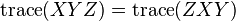 . More generally the norm is invariant under a unitary transformation for complex matrices.
. More generally the norm is invariant under a unitary transformation for complex matrices.
Max norm
The max norm is the elementwise norm with p = ∞:
This norm is not sub-multiplicative.
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!