JS常用的几种设计模式
文章目录
- 1. 工厂模式
- 2.单例模式
- 3.原型模式
- 4.代理模式
- 5.迭代器模式
- 6.状态模式
1. 工厂模式
// 汽车构造函数
function SuzukiCar(color) {this.color = color;this.brand = 'Suzuki';
}// 汽车构造函数
function HondaCar(color) {this.color = color;this.brand = 'Honda';
}// 汽车构造函数
function BMWCar(color) {this.color = color;this.brand = 'BMW';
}// 汽车品牌枚举
const BRANDS = {suzuki: 1,honda: 2,bmw: 3
}/*** 汽车工厂*/
function CarFactory() {this.create = (brand, color)=> {switch (brand) {case BRANDS.suzuki:return new SuzukiCar(color);case BRANDS.honda:return new HondaCar(color);case BRANDS.bmw:return new BMWCar(color);default:break;}}
}
const carFactory = new CarFactory();
const cars = [];cars.push(carFactory.create(BRANDS.suzuki, 'brown'));
cars.push(carFactory.create(BRANDS.honda, 'grey'));
cars.push(carFactory.create(BRANDS.bmw, 'red'));function sayHello() {console.log(`Hello, I am a ${this.color} ${this.brand} car`);
}for (const car of cars) {sayHello.call(car);
}
Hello, I am a brown Suzuki car
Hello, I am a grey Honda car
Hello, I am a red BMW car
2.单例模式
const Person = (function(){let instance = null;return class{constructor(){if(!instance){//第一次创建实例,那么需要把实例保存instance = this;}else{return instance;}}}
})()
let p3 = new Person();
let p4 = new Person();
console.log(p3===p4) //true
3.原型模式
最简单的原型模式的实现就是通过Object.create()。Object.create(),会使用现有的对象来提供新创建的对象的__proto__。例如下方代码:
let person = {name:'hello',age:24
}let anotherPerson = Object.create(person);
console.log(anotherPerson.__proto__) //{name: "hello", age: 24}anotherPerson.name = 'world'; //可以修改属性
anotherPerson.job = 'teacher';
原型继承
function F(){}F.prototype.g = function(){}//G类继承F类function G(){F.call(this);
}//原型继承
function Fn(){};
Fn.prototype = F.prototype;
G.prototype = new Fn();G.prototype.constructor = G;
4.代理模式
/*** pre:代理模式* 小明追求A,B是A的好朋友,小明比不知道A什么时候心情好,不好意思直接将花交给A,* 于是小明将花交给B,再由B交给A.*/// 花的类
class Flower{constructor(name){this.name = name }
}// 小明拥有sendFlower的方法
let Xioaming = {sendFlower(target){var flower = new Flower("玫瑰花")target.receive(flower)}
}
// B对象中拥有接受花的方法,同时接收到花之后,监听A的心情,并且传入A心情好的时候函数
let B = {receive(flower){this.flower =flowerA.listenMood(()=>{A.receive(this.flower)})}}
// A接收到花之后输出花的名字
let A = {receive(flower){console.log(`A收到了${flower.name} `)// A收到了玫瑰花 },listenMood(func){setTimeout(func,1000)}
}
Xioaming.sendFlower(B)
ES6 Proxy
let star={name : "张XX",age:25,phone : "1300001111"
}
let agent = new Proxy(star,{get:function(target,key){if(key === "phone"){return "18839552597"}else if(key === "name"){return "张XX"}else if(key === "price"){return "12W"}else if(key === "customPrice"){return target.customPrice}},set:function(target,key,value){if(key === "customPrice"){if(value < "10"){console.log("太低了!!!")return false}else{target[key] = valuereturn true}}}}
)console.log(agent.name)
console.log(agent.price)
console.log(agent.phone)
console.log(agent.age)
agent.customPrice = "12"
console.log(agent)
console.log(agent.customPrice)
5.迭代器模式
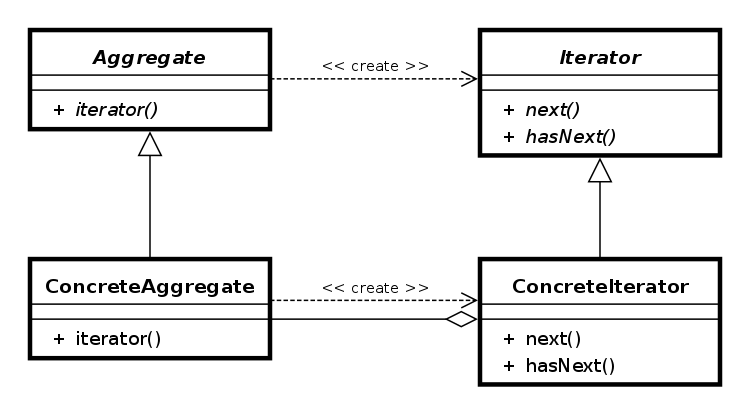
const item = [1, 'red', false, 3.14];function Iterator(items) {this.items = items;this.index = 0;
}Iterator.prototype = {hasNext: function () {return this.index < this.items.length;},next: function () {return this.items[this.index++];}
}
const iterator = new Iterator(item);while(iterator.hasNext()){console.log(iterator.next());
}
1, red, false, 3.14
6.状态模式
状态模式:一个对象有状态变化,每次状态变化都会触发一个逻辑。
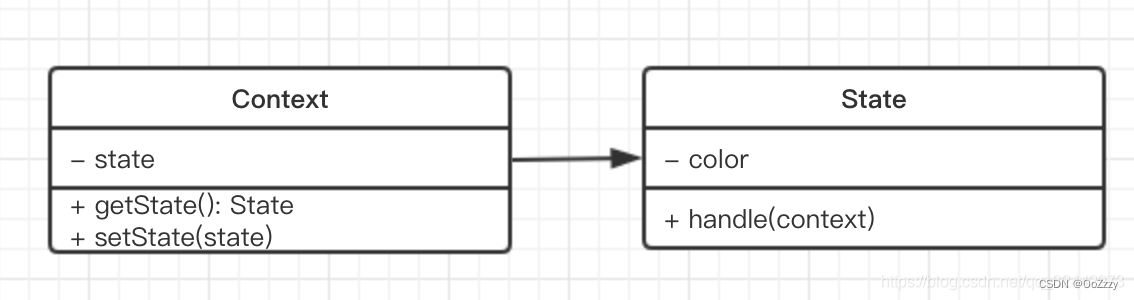
// 状态(红灯,绿灯 黄灯)
class State {constructor(color) {this.color = color;}// 设置状态handle(context) {console.log(`turn to ${this.color} light`);context.setState(this)}
}// 主体
class Context {constructor() {this.state = null;}// 获取状态getState() {return this.state;}setState(state) {this.state = state;}
}// 测试
let context = new Context();
let green = new State('green');
let yellow = new State('yellow');
let red = new State('red');// 绿灯亮了
green.handle(context);
console.log(context.getState())// 黄灯亮了
yellow.handle(context);
console.log(context.getState())// 红灯亮了
red.handle(context);
console.log(context.getState())
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!