力扣LeetBook<二叉树>学习笔记
二叉树
文章目录
- 一、概述
- 二、树的遍历
- 1.二叉树的前序遍历
- 2.二叉树的中序遍历
- 3.二叉树的后序遍历
- 4.二叉树的层序遍历
- 三、运用递归解决问题
- 1.二叉树的最大深度
- 2.对称二叉树
- 3.路径总和
- 四、总结
- 1.从中序和后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 2.从前序和中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 3.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 4.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针Ⅱ
- 5.二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 6.二叉树的序列化和反序列化
- 五、闲话
一、概述
从图的观点:树是一个拥有N个结点和N-1条边的有向无环图。
二叉树:每个节点最多有两个子树。

二、树的遍历
前序:根-左-右
中序:左-根-右(对于二叉搜索树,我们可以通过中序遍历得到一个递增的有序序列。)
后序:左-右-根(删除树中的节点)
层序:逐层遍历树结构(BFS:从一个根节点开始,首先访问节点本身。 然后遍历它的相邻节点,其次遍历它的二级邻节点、三级邻节点,以此类推)
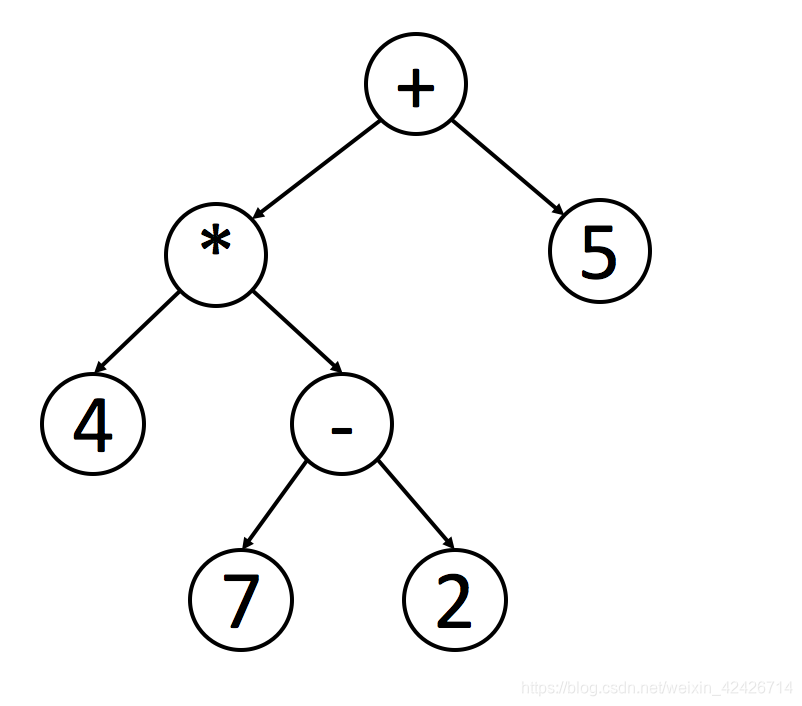
如图,使用中序遍历找出原始表达式,但程序不好处理这个表达式,因为必须检查优先级。
如果想后序遍历,使用栈来处理这个表达式会更容易。每遇到一个操作符,就从栈中弹出栈顶的两个元素,计算并将结果返回栈中。

1.二叉树的前序遍历
144.二叉树的前序遍历
法1:递归
发现递归有三点注意,落实好就行。针对这道题而言,
- 终止条件:当越过叶节点,即(root == null)则直接返回
- 递推工作:当list添加元素后,开启递归左子结点,无返回值;再开启递归右子结点,无返回值
- 返回值:这里不需要返回值
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();preorderTraversal(root, list);return list;}private void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}list.add(root.val);preorderTraversal(root.left, list);preorderTraversal(root.right, list);
// if (root != null) {
// list.add(root.val);
// preorderTraversal(root.left, list);
// preorderTraversal(root.right, list);
// }}
注释掉的内容是可以代替上面部分的。
法2:迭代
递归法是隐式调用了系统栈,迭代法则是创建了一个显式内置栈来模拟系统栈。通常比递归麻烦,因为是我们自己来操纵栈的一举一动了。
// 前序:根左右public List<Integer> preorderTraversal1(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// if (root == null) {
// return res;
// }Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();TreeNode node = root;while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {while (node != null) {res.add(node.val);stack.push(node);node = node.left;}node = stack.pop();node = node.right;}return res;}
2.二叉树的中序遍历
法1:递归
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();inorderTraversal(root, list);return list;}private void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}inorderTraversal(root.left, list);list.add(root.val);inorderTraversal(root.right, list);}
法2:迭代
// 中序:左根右public List<Integer> inorderTraversal1(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
// if (root == null) {
// return res;
// }Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();TreeNode node = root;while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {while (node != null) {stack.push(node);node = node.left;}node = stack.pop();res.add(node.val);node = node.right;}return res;}
3.二叉树的后序遍历
法1:递归
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {// 递归List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();postorderTraversal(root, list);return list;}private void postorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}postorderTraversal(root.left, list);postorderTraversal(root.right, list);list.add(root.val);}
法2:迭代
// 后序:左右根public List<Integer> postorderTraversal1(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();TreeNode prev = null;while (!stack.isEmpty() || root != null) {while (root != null) {stack.push(root);root = root.left;}root = stack.pop();if (root.right == null || root.right == prev) {res.add(root.val);prev = root;root = null;} else {stack.push(root);root = root.right;}}return res;}
4.二叉树的层序遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
// 层序public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) {return res;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);// 起点:rootwhile (!queue.isEmpty()) {List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();int sz = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();level.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);}}res.add(level);}return res;}
三、运用递归解决问题
1.二叉树的最大深度
104.二叉树的最大深度
法1:递归
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {return root == null ? 0 : Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;}
当然我不喜欢写成这样,虽然极简,但我更喜欢看到有秩序的递归:
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int depth = Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;return depth;}
甚至可以再详细点,让人一目了然的那种。
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left) + 1;int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right) + 1;int maxDepth = Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth);return maxDepth;
这样可读性就提高了啦~
法2:BFS
public int maxDepth1(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int sz = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
// if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {
// continue;
// }if (cur.left != null) {queue.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null) {queue.offer(cur.right);}}depth++;}return depth;}
可以对比一下最小深度:
111. 二叉树的最小深度
法1:递归
public int minDepth1(TreeNode root) {//1.根为空(已经越过叶子节点)if (root == null)return 0;//2.左右子树都为空(叶子节点)if (root.left == null && root.right == null)return 1;//3.左子树右子树有一个为空,取不是空的方向。//4.左右子树都不为空,就取两个子树深度较小的,最后加1.int depth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;if (root.left != null)depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.left), depth);if (root.right != null)depth = Math.min(minDepth(root.right), depth);return depth + 1;}
法2:BFS
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 1;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int sz = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {TreeNode cur = queue.poll();if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {return depth;}if (cur.left != null) {queue.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null) {queue.offer(cur.right);}}depth++;}return depth;}
2.对称二叉树
101.对称二叉树
- 递归结束条件:
- 都为null返回true
- 只有一个为null返回false
- 递归过程
- 两个节点值是否相等
- n1的左子树和n2的右子树是否对称
- n1的右子树和n2的左子树是否对称
法1:
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {return isMirror(root, root);}public boolean isMirror(TreeNode n1, TreeNode n2) {if (n1 == null && n2 == null) {return true;}if (n1 == null || n2 == null) {return false;}return n1.val == n2.val && isMirror(n1.left, n2.right) && isMirror(n1.right, n2.left);}
法2:
public boolean isSymmetric1(TreeNode root) {return isMirror(root, root);}public boolean isMirror(TreeNode n1, TreeNode n2) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(n1);queue.offer(n2);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {n1 = queue.poll();n2 = queue.poll();if (n1 == null && n2 == null)continue;if (n1 == null || n2 == null || n1.val != n2.val)return false;queue.offer(n1.left);queue.offer(n2.right);queue.offer(n1.right);queue.offer(n2.left);}return true;}
3.路径总和
112.路径总和
法1:
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {if (root == null) {return false;}if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {return sum == root.val;}return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);}
法2:
public boolean hasPathSum1(TreeNode root, int sum) {if (root == null) {return false;}Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();Queue<Integer> valQueue = new LinkedList<>();nodeQueue.offer(root);valQueue.offer(root.val);while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode cur = nodeQueue.poll();int temp = valQueue.poll();if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null) {if (sum == temp) {return true;}continue;}if (cur.left != null) {nodeQueue.offer(cur.left);valQueue.offer(cur.left.val + temp);}if (cur.right != null) {nodeQueue.offer(cur.right);valQueue.offer(cur.right.val + temp);}}return false;}
四、总结
1.从中序和后序遍历序列构造二叉树
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
搞清楚遍历数组/序列的性质:
后序遍历数组的最后一个元素代表根节点root,以此信息找到中序遍历数组的root下标值,就可以把中序数组分成左右子树部分。针对每个部分可以这样递归下去构造二叉树。
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {int len = inorder.length;if (len == 0)return null;int left = 0;while (inorder[left] != postorder[len - 1])left++;TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[len - 1]);root.left = buildTree(Arrays.copyOf(inorder, left), Arrays.copyOf(postorder, left));root.right = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, left + 1, len), Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, left, len - 1));return root;}
2.从前序和中序遍历序列构造二叉树
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
前序遍历数组的第一个元素代表根节点root,以此信息找到中序遍历数组的root下标值,就可以把中序数组分成左右子树部分。针对每个部分可以这样递归下去构造二叉树。
public BinaryTree.TreeNode buildTree1(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {int len = preorder.length;if (len == 0)return null;int index = 0;while (preorder[0] != inorder[index])index++;BinaryTree.TreeNode root = new BinaryTree.TreeNode(preorder[0]);root.left = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, 1, index + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0, index));root.right = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, index + 1, len), Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, index + 1, len));return root;}
还有一种迭代法,以后有空再实现吧。
3.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
法1:BFS+链表
首先,我第一次尝试写得是被注释掉的代码,可以看到代码很冗余,频繁使用hashmap,虽然很容易想到但是很麻烦。主要是我一开始没有注意到next这一个属性的内涵。暗示着什么?——链表。所以我第二次就用了链表的思维来做这一道题,但要注意每一层遍历前加个null给每层最后一个元素的next,如果不给的话,它会指向下一层的第一个元素。
public Node connect(Node root) {if (root == null)return null;Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int sz = queue.size();queue.offer(null);Node cur = queue.poll();while (cur != null) {cur.next = queue.poll();if (cur.left != null) {queue.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null) {queue.offer(cur.right);}cur = cur.next;//熟悉的链表操作。}
// Map level = new HashMap<>();
// int sz = queue.size();
// for (int i = 0; i <= sz; i++) {
// level.put(i, queue.poll());
// }
// for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
// level.get(i).next = level.get(i + 1);
// if (level.get(i).left != null) {
// queue.offer(level.get(i).left);
// queue.offer(level.get(i).right);
// }
// }}return root;}
法2:BFS
我感觉大部分人都是想到这个,不用考虑链表指针指这指那的问题。这个方法也很值得学习,主要是要熟悉peek()方法的妙用。而且这种方法不用考虑每层最后一个元素的next了,默认为null。
public Node connect1(Node root) {if (root == null)return null;Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int sz = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {//取出队首Node cur = queue.poll();//进行连接if (i < sz - 1) {cur.next = queue.peek();}if (cur.left != null) {queue.add(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null) {queue.add(cur.right);}}}return root;}
4.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针Ⅱ
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针Ⅱ
代码和上一道题一样。
5.二叉树的最近公共祖先
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
本质就是搜索,搜索到两个目标节点后判断他们所处的位置来确定最近公共祖先。(注释掉的代码也能实现,只是会污染原二叉树。只是找个祖先而已,别把孩子弄没了啊)
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null || root == p || root == q)return root;
// root.left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
// root.right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
// if (root.left == null)
// return root.right;
// if (root.right == null)
// return root.left;
// return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left == null)return right;if (right == null)return left;return root;}
6.二叉树的序列化和反序列化
297.二叉树的序列化与反序列化
值得记录,这是我在leetcode上做的第一道困难题,但这道题其实不难想,只是细节有点多。
class Codec {// Encodes a tree to a single string.public String serialize(TreeNode root) {if (root == null)return "[]";StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode cur = queue.poll();if (cur == null) {sb.append("null,");continue;}sb.append(cur.val + ",");queue.offer(cur.left);queue.offer(cur.right);}return "[" + sb.toString().substring(0, sb.length() - 1) + "]";}// Decodes your encoded data to tree.public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {data = data.trim().substring(1, data.length() - 1);if (data.length() == 0) {return null;}String[] parts = data.split(",");String item = parts[0];TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(item));Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();nodeQueue.add(root);int index = 1;while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = nodeQueue.remove();if (index == parts.length) {break;}item = parts[index++];item = item.trim();if (!item.equals("null")) {int leftNumber = Integer.parseInt(item);node.left = new TreeNode(leftNumber);nodeQueue.add(node.left);}if (index == parts.length) {break;}item = parts[index++];item = item.trim();if (!item.equals("null")) {int rightNumber = Integer.parseInt(item);node.right = new TreeNode(rightNumber);nodeQueue.add(node.right);}}return root;}}
幸好在学二叉树之前学了队列&栈,这里做来做去都是BFS和DFS。
快要写完这篇文章的时候,居然收到了面试通知,这是我第一次收到啊……JVM、计算机网络、操作系统方面的知识几乎接近空白,框架也没复习,这该怎么搞呢,就当去取点经验把。现在还是先好好把数据结构与算法搞好。
next target:哈希表
五、闲话
最近压力有点大,也听了几天的梅特纳,突然会想换换音乐的口味。于是又回到了Danny Chan的歌声里,陈百强的歌声在我心里意味着美好、高贵、纯真与永恒,我一直都这么爱他。他是唯一一位在我什么心情都乐意聆听的歌者,在低落时刻则更需要他了。接下来分享的是两首很励志的歌,分别是《Greatest Love Of All》和《未唱的歌》。

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!