FabricV2.2_X.509:为什么需要X.509证书?
FabricV2.2_X.509:为什么需要X.509证书?
先抛出结论哈!
- FabricV2.2 X.509证书是直接调用go standard lib crypto/x509包实现的
- X.509证书是解决:在基础的数字签名模型过程中可能会出现公钥被替换的问题
首先了解一下为什么要X.509证书?
模型:
-
背景:在基础的数字签名模型下A向B发送消息的过程
-
A用自己的私钥签名生成数字签名(R,S)然后向B发送(Msg,(R,S)),其中Msg为消息
-
B方接受到(Msg,(R,S))时,用A方的公钥验证签名来判断Msg是否是由A方发送的
数字签名的过程
-
-
问题:当B方上拥有的A的公钥被恶意者攻击且替换成恶意者的公钥,那么B方就会误认为恶意者发送的消息就是A方发送的消息
-
解决方案:
该问题的核心是A的公钥可信度
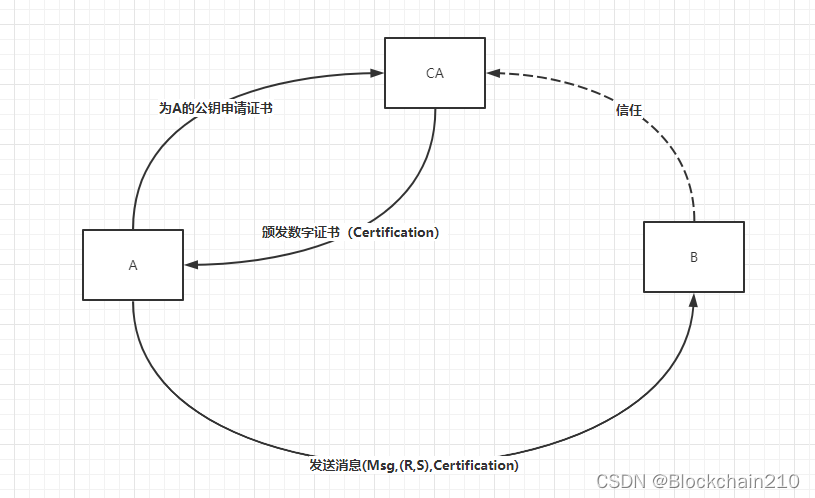
因此找到一个受到全体都信任的第三方机构CA对A的公钥做认证
-
具体方法:
-
A请求证书中心CA为自己的公钥做认证,那么A方获得数字证书Certification
具体过程:CA用自己的私钥为A的公钥做“加密”生成数字证书Certification**(此处的加密也是签名的过程)**
-
A向B发送消息时不仅会附上数字签名也会附上数字证书(Msg,(R,S),Certification)
-
B收到(Msg,(R,S),Certification),则用CA的公钥“解密”Certification获得A的真实公钥(此处的解密其实是验签的过程),然后用A的真实公钥去验证签名,判断消息的有效性
解释:当CA的公钥被假冒情况下如何解决呢?
大家可以在评论区发表自己的想法哦!
-
CA的类型
CA的类型可以分为中间CA和RootCA
那么User向中间CA申请自己的公钥证书是什么样的呢?即信任链

CA颁发数字证书的类型可以是X.509证书
此处先给出Go标准库X.509证书的结构体组成(具体介绍下一篇Blog哦哈哈):
// A Certificate represents an X.509 certificate.
type Certificate struct {Raw []byte // Complete ASN.1 DER content (certificate, signature algorithm and signature).RawTBSCertificate []byte // Certificate part of raw ASN.1 DER content.RawSubjectPublicKeyInfo []byte // DER encoded SubjectPublicKeyInfo.RawSubject []byte // DER encoded SubjectRawIssuer []byte // DER encoded IssuerSignature []byteSignatureAlgorithm SignatureAlgorithmPublicKeyAlgorithm PublicKeyAlgorithmPublicKey interface{}Version intSerialNumber *big.IntIssuer pkix.NameSubject pkix.NameNotBefore, NotAfter time.Time // Validity bounds.KeyUsage KeyUsage// Extensions contains raw X.509 extensions. When parsing certificates,// this can be used to extract non-critical extensions that are not// parsed by this package. When marshaling certificates, the Extensions// field is ignored, see ExtraExtensions.Extensions []pkix.Extension// ExtraExtensions contains extensions to be copied, raw, into any// marshaled certificates. Values override any extensions that would// otherwise be produced based on the other fields. The ExtraExtensions// field is not populated when parsing certificates, see Extensions.ExtraExtensions []pkix.Extension// UnhandledCriticalExtensions contains a list of extension IDs that// were not (fully) processed when parsing. Verify will fail if this// slice is non-empty, unless verification is delegated to an OS// library which understands all the critical extensions.//// Users can access these extensions using Extensions and can remove// elements from this slice if they believe that they have been// handled.UnhandledCriticalExtensions []asn1.ObjectIdentifierExtKeyUsage []ExtKeyUsage // Sequence of extended key usages.UnknownExtKeyUsage []asn1.ObjectIdentifier // Encountered extended key usages unknown to this package.// BasicConstraintsValid indicates whether IsCA, MaxPathLen,// and MaxPathLenZero are valid.BasicConstraintsValid boolIsCA bool// MaxPathLen and MaxPathLenZero indicate the presence and// value of the BasicConstraints' "pathLenConstraint".//// When parsing a certificate, a positive non-zero MaxPathLen// means that the field was specified, -1 means it was unset,// and MaxPathLenZero being true mean that the field was// explicitly set to zero. The case of MaxPathLen==0 with MaxPathLenZero==false// should be treated equivalent to -1 (unset).//// When generating a certificate, an unset pathLenConstraint// can be requested with either MaxPathLen == -1 or using the// zero value for both MaxPathLen and MaxPathLenZero.MaxPathLen int// MaxPathLenZero indicates that BasicConstraintsValid==true// and MaxPathLen==0 should be interpreted as an actual// maximum path length of zero. Otherwise, that combination is// interpreted as MaxPathLen not being set.MaxPathLenZero boolSubjectKeyId []byteAuthorityKeyId []byte// RFC 5280, 4.2.2.1 (Authority Information Access)OCSPServer []stringIssuingCertificateURL []string// Subject Alternate Name values. (Note that these values may not be valid// if invalid values were contained within a parsed certificate. For// example, an element of DNSNames may not be a valid DNS domain name.)DNSNames []stringEmailAddresses []stringIPAddresses []net.IPURIs []*url.URL// Name constraintsPermittedDNSDomainsCritical bool // if true then the name constraints are marked critical.PermittedDNSDomains []stringExcludedDNSDomains []stringPermittedIPRanges []*net.IPNetExcludedIPRanges []*net.IPNetPermittedEmailAddresses []stringExcludedEmailAddresses []stringPermittedURIDomains []stringExcludedURIDomains []string// CRL Distribution PointsCRLDistributionPoints []stringPolicyIdentifiers []asn1.ObjectIdentifier
}
总结
-
在基础的数字签名模型过程中可能会出现公钥被替换的问题
-
CA本质是用CA的私钥为需要做认证的公钥做加密过程生成数字证书,此时数字证书可以是X.509或者其他证书标准
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!