Mysql(基础篇)
目录
一、MYSQL
二、SQL
1.可以单行或多行书写,以分号结尾
2.Mysql数据库的SQL语句不区分大小写,关键字建议使用大写
3.注释:-- 或# 或/**/
4.分类
5.函数
6.约束(MySql不支持检查约束)
7.数据库设计
8.事务

性别的时候定char(1) 存储的是男或者女 ——>
Java中的char和c中的不同,不是ASCII,而是UNICODE码,占两个字节
char a = ’a’ 占两个字节,只能存放一个字母或数字,或一个汉字
一、MYSQL
1.下载
2.添加配置环境MYSQL_HOME,编辑一下Path
3.新建配置文件my.ini
4.初始化MySQL,在管理员的cmd中运行
mysqld –initialize-insecure,没有出现报错信息则说明data目录初始化没有问题,此时查看Mysql目录下就有data目录生成
5.注册MySQL服务,说明计算机上安装好了MySQL服务器了
mysqld –install
6.启动MySQL服务
启动:net start mysql ,停止:net stop mysql
7.修改默认账户密码
mysqladmin –u root password root
8.登录Mysql,这里的mysql指mysql.exe
mysql –uroot –proot
9.退出mysql exit,quit
10.登录参数(连接别人的数据库,需要指定别人的ip和端口)
mysql –u用户名 –p密码 –h要连接的 mysql服务器的ip地址(默认127.0.0.1) –p端口号(默认3306)
11.卸载MySQL
1)管理员运行cmd
2)输入net stop mysql
3)输入mysqld –remove mysql
4)最后删除MySQL目录及相关的环境变量
二、SQL
(结构化查询语言,是一种操作关系型数据库的编程语言,定义了一套操作关系型数据库统一标准)
1.可以单行或多行书写,以分号结尾
2.Mysql数据库的SQL语句不区分大小写,关键字建议使用大写
3.注释:-- 或# 或/**/
4.分类
DDL, 数据定义语言,用来定义数据库对象:数据库,表,列等
DML, 数据库操作语言,用来对数据库中表进行增删改
DQL, 数据查询语言,用来查询数据库中表的记录(数据)
DCL, 数据控制语言,用来定义数据库访问权限和安全级别,及创建用户
DML是数据操作语言增删改查数据,
DDL是数据定义语言增删改查表或者数据库
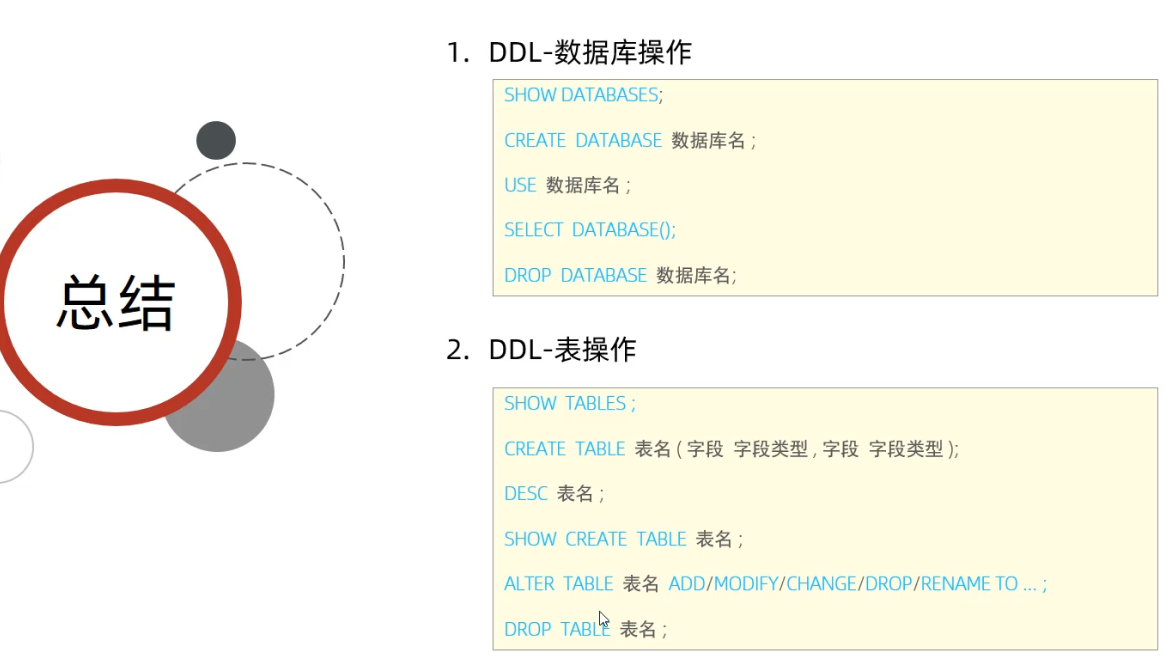
1)DDL数据库操作
1]show databases就能看的mysql安装好之后自带的数据库,
information_schema :mysql中有哪些库、表(存储的是视图,视图是一种逻辑表,并不存在物理的文件,在安装好的data目录里面并不存在对应的文件夹来存数据库)
mysql:存储的最为主要的一些信息(eg:权限,安全)
performance_schema:存储的是mysql中与性能相关的信息
sys:系统相关的信息
2]create database (if not exists) 数据库名;
3]drop database (if exists) 数据库名;
4]使用数据库use 数据库名;
5]查看当前数据库select database();
2)DDL表操作
1]创建Create
create 表名 ( 字段名 数据类型, …, …);最后一个不能加逗号
score double(5,2)说明总长度为5,小数点后保留两位
2]查询Retrieve
查询当前数据库下所有表名称show tables,查询表结构 desc表名
查询指定表的建表语句 show create table 表名;
3]修改Update
alter table 表名 rename to 新表名;
alter table 表名 add 列名 数据类型(长度) [comment 注释] [约束];
alter table 表名 modify列名 数据类型;
alter table 表名 change列名 新列名 新数据类型 [comment 注释] [约束];
alter table 表名 drop列名;
alter table 表名 RENAME TO 新表名;
4]删除Delete
drop table (if exists)表名
3)DML
1]添加insert
insert into 表名(列名1,列名2,…) [添加全部列时不用写列名] values(值1,值2,…), (值1,值2,…),…[添加一组数据时,只需要写需要添加的数据 ]
2]修改update
update 表名 set 列名=值1, 列名=值2,…[where 条件]
注:修改语句如果不加条件,所有数据都会被修改
3]删除delete
delete from 表名 [where 条件]
注:删除语句如果不加条件,所有数据都会被删除
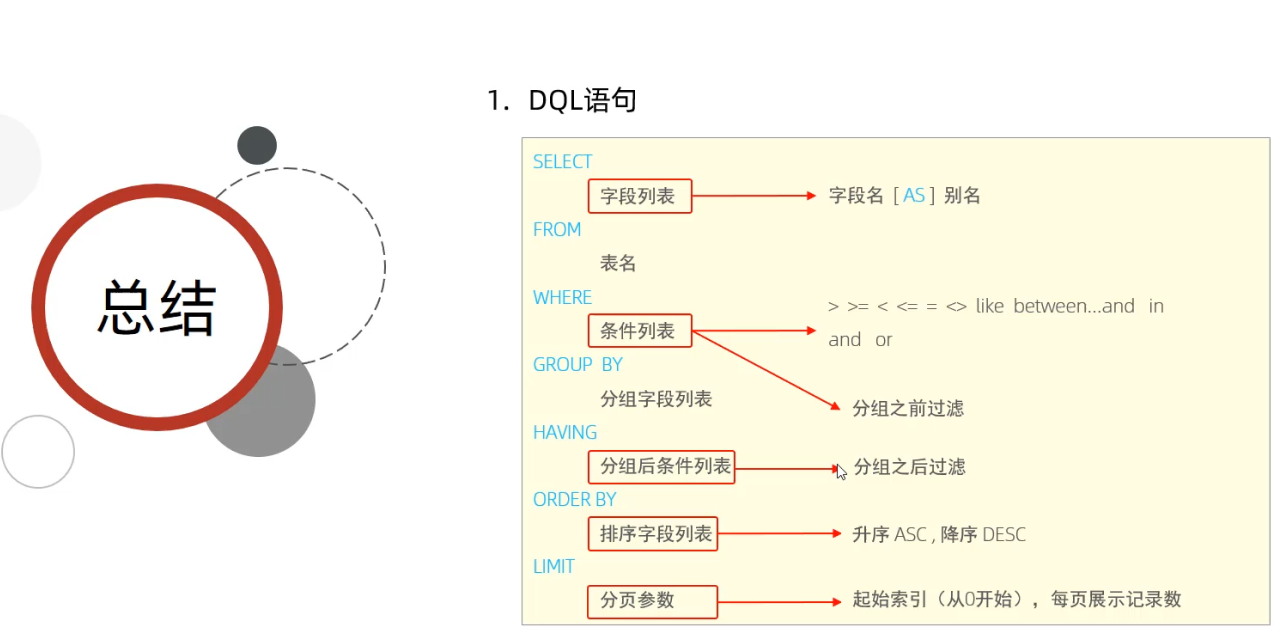
4)DQL
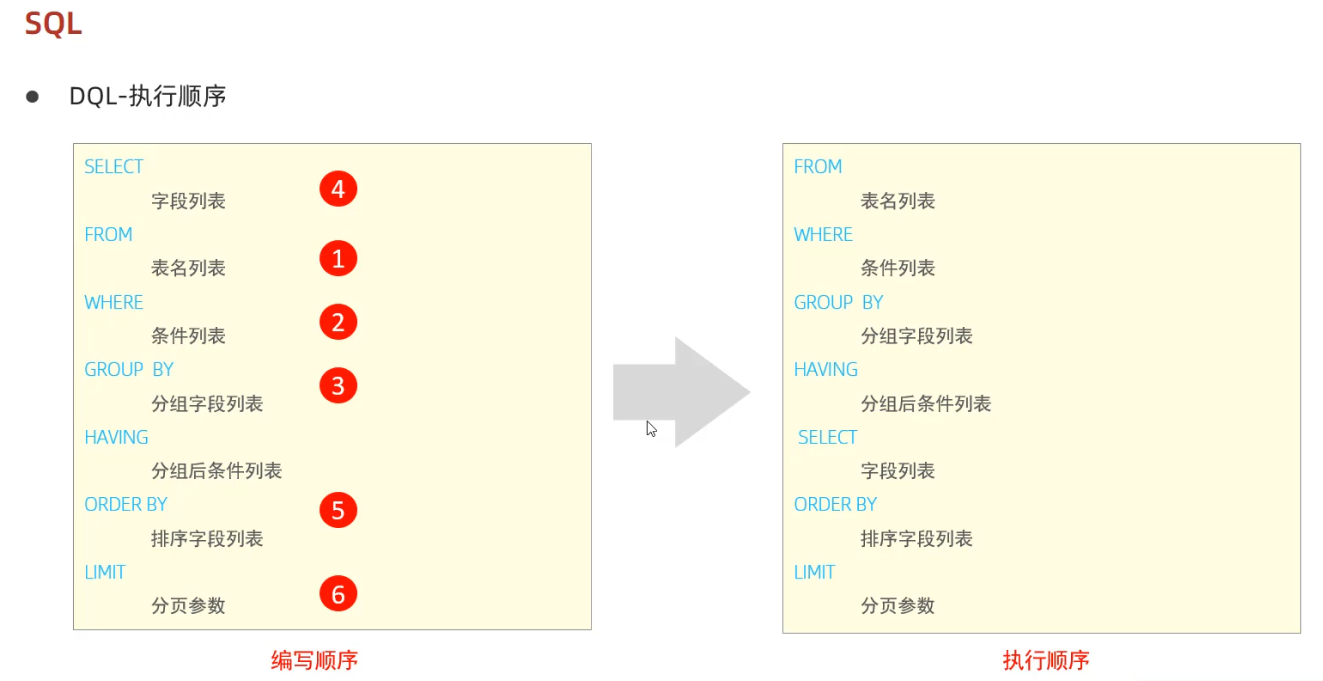
select (distinct[去重复记录]) 字段列表 (as xxx[ as可省略])
from 表名列表
where 条件列表 (注意null值得比较需要用 is /is not这种方式)
group by 分组列表
having 分组后的条件
order by 排序字段 (asc升序[默认]/desc降序)
如果有多个排序条件,当前边的条件值一样时才会根据第二个条件进行排序
limit 分页限定 起始索引[从0开始],查询条目数;
计算公式:起始索引 = (当前页码-1)*每页显示的条数
Tips:MYSQL数据库中分页查询使用limit
Oracle分页查询使用rownumber
SQL Server 分页查询使用top
分组操作,需要用到聚合函数,将一列作为一个整体计算
select 聚合函数名(列表) from 表 注意:null值不参与所有聚合函数运算
分组之后,查询的字段为聚合函数和分组字段,查询其他字段无意义
where和having区别
执行时机不一样:where是分组之前进行限定,不满足where条件,则不参与分组,而having是分组之后对结果进行过滤
可判断条件不一样:where不能对聚合函数进行判断,having可以
执行顺序:where > 聚合函数 > having
使用单引号来环绕文本值(大部分也接受双引号),如果是数值,就不要使用引号
between…and…的使用一般是左闭右开的
无法比较 NULL 和 0;它们是不等价的,必须使用 IS NULL 和 IS NOT NULL 操作符来判断
inner join 关键字在表中存在至少一个匹配时返回行
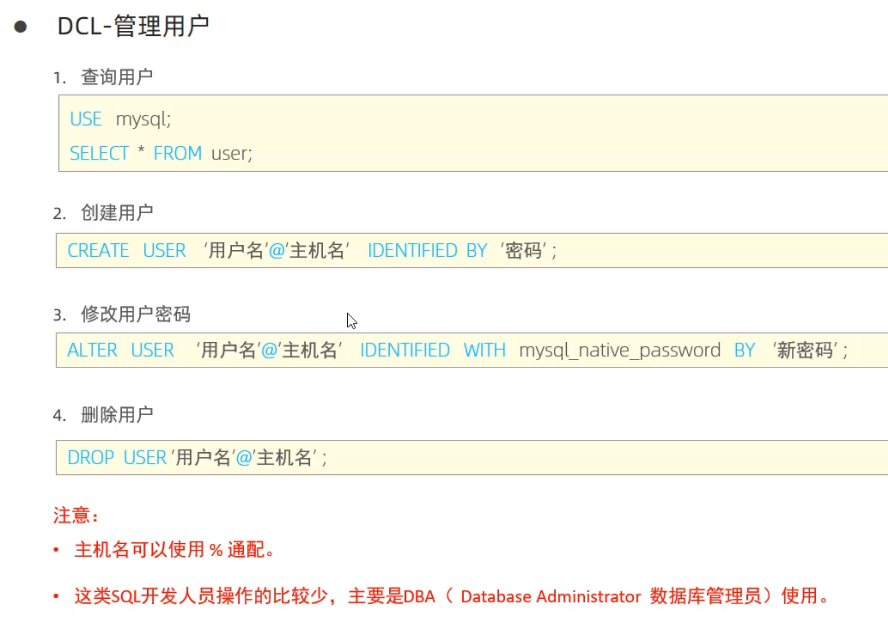
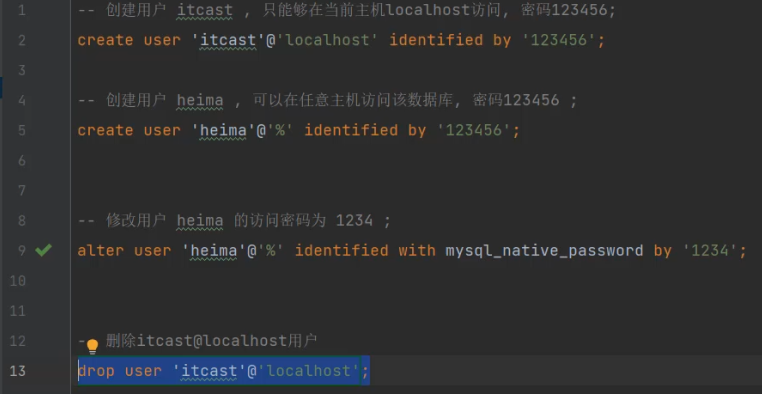

-- 创建用户 itcast , 只能够在当前主机localhost访问, 密码123456;
create user 'itcast'@'localhost' identified by '123456';-- 创建用户 heima , 可以在任意主机访问该数据库, 密码123456 ;
create user 'heima'@'%' identified by '123456';-- 修改用户 heima 的访问密码为 1234 ;
alter user 'heima'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by '1234';-- 删除itcast@localhost用户
drop user 'itcast'@'localhost';-- 查询权限
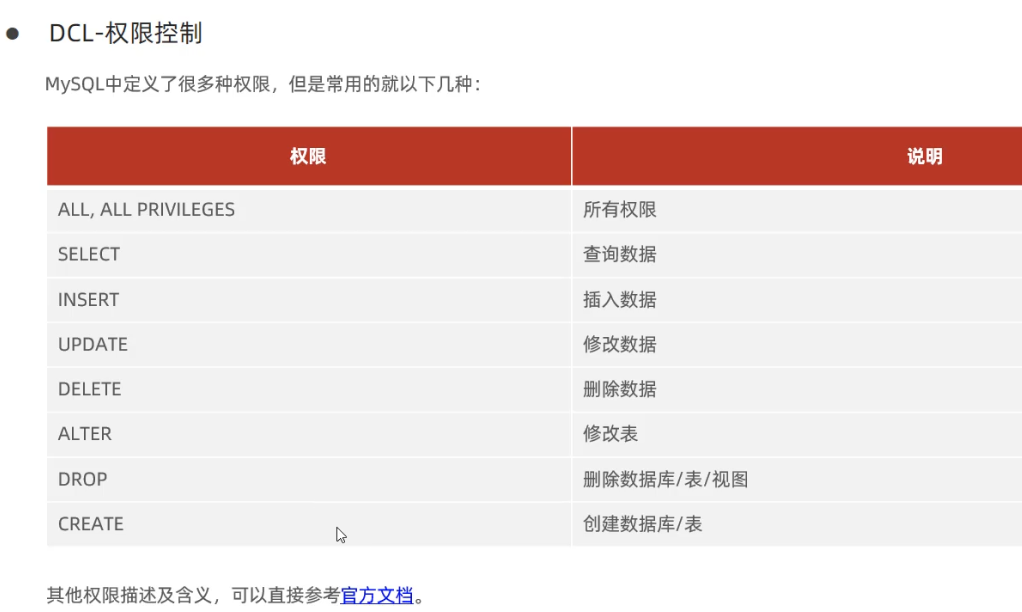
show grants for 'heima'@'%';-- 授予权限
grant all on itcast.* to 'heima'@'%';-- 撤销权限
revoke all on itcast.* from 'heima'@'%';5.函数
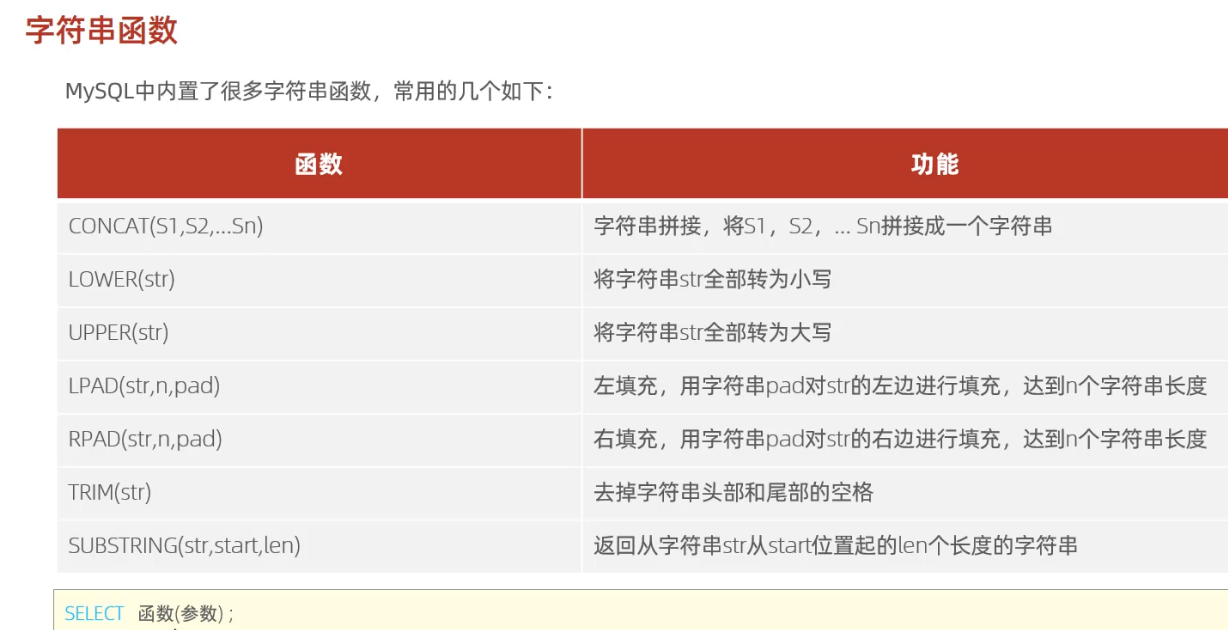
-- 字符串函数
-- concat
select concat('Hello' , ' MySQL');-- lower
select lower('Hello');-- upper
select upper('Hello');-- lpad
select lpad('01', 5, '-');-- rpad
select rpad('01', 5, '-');-- trim
select trim(' Hello MySQL ');-- substring
select substring('Hello MySQL',1,5);-- 案例: 由于业务需求变更,企业员工的工号,统一为5位数,目前不足5位数的全部在前面补0。比如: 1号员工的工号应该为00001。
update emp set workno = lpad(workno, 5, '0');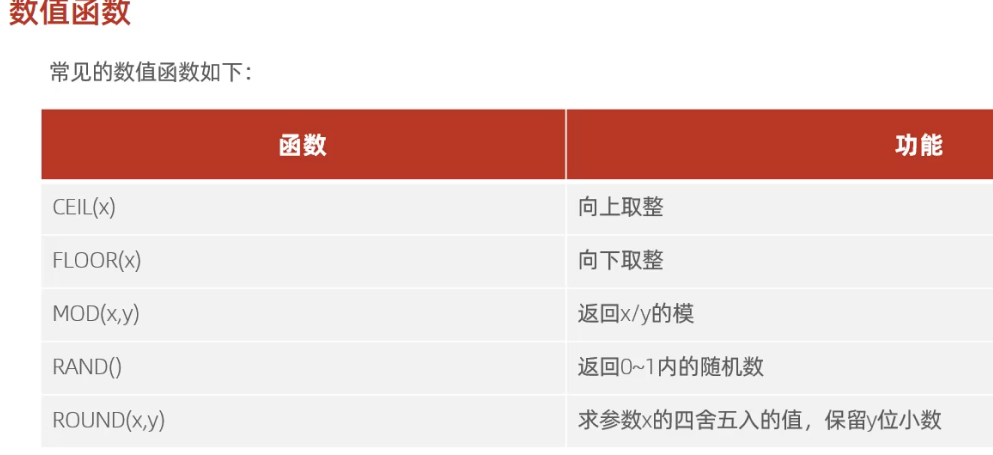
-- 数值函数
-- ceil
select ceil(1.1);-- floor
select floor(1.9);-- mod
select mod(7,4);-- rand
select rand();-- round
select round(2.344,2);-- 案例: 通过数据库的函数,生成一个六位数的随机验证码。
select lpad(round(rand()*1000000 , 0), 6, '0');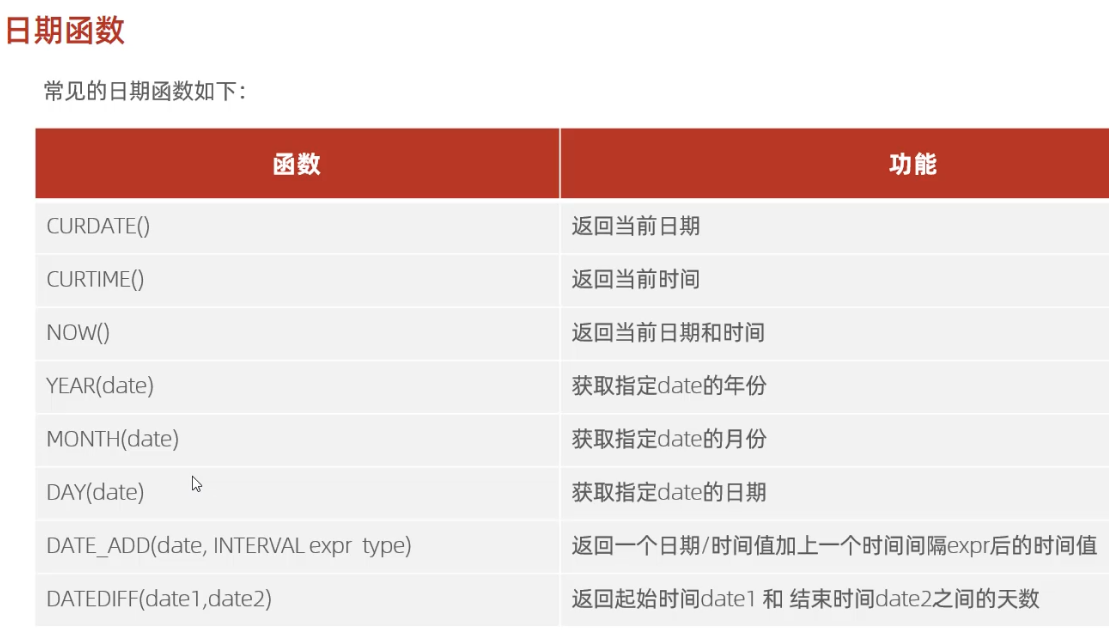
-- 日期函数
-- curdate()
select curdate();-- curtime()
select curtime();-- now()
select now();-- YEAR , MONTH , DAY
select YEAR(now());select MONTH(now());select DAY(now());-- date_add
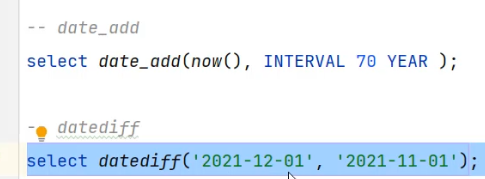
select date_add(now(), INTERVAL 70 YEAR );-- datediff
select datediff('2021-10-01', '2021-12-01');-- 案例: 查询所有员工的入职天数,并根据入职天数倒序排序。
select name, datediff(curdate(), entrydate) as 'entrydays' from emp order by entrydays desc;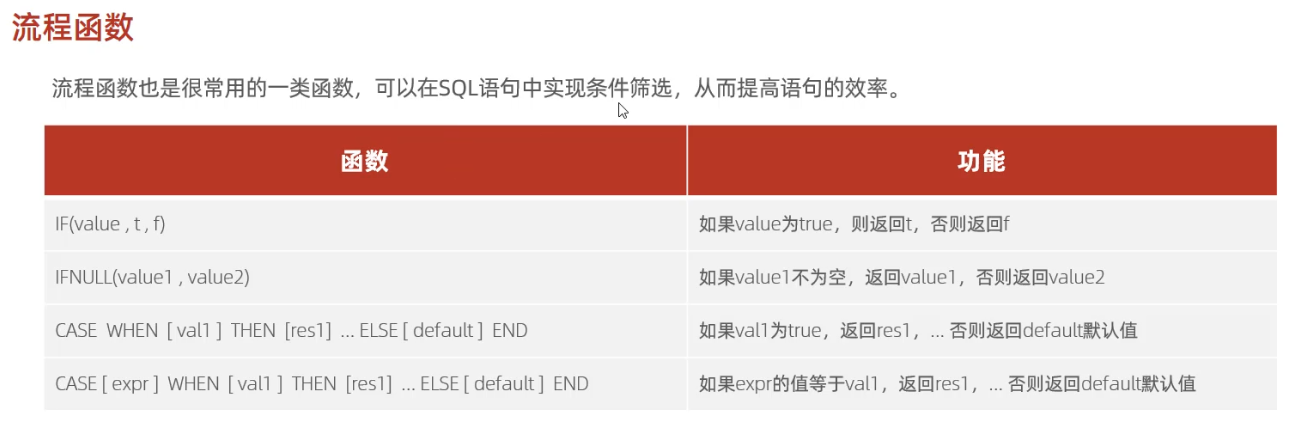

-- 流程控制函数
-- if
select if(false, 'Ok', 'Error');-- ifnull
select ifnull('Ok','Default');select ifnull('','Default');select ifnull(null,'Default');-- case when then else end
-- 需求: 查询emp表的员工姓名和工作地址 (北京/上海 ----> 一线城市 , 其他 ----> 二线城市)
selectname,( case workaddress when '北京' then '一线城市' when '上海' then '一线城市' else '二线城市' end ) as '工作地址'
from emp;-- 案例: 统计班级各个学员的成绩,展示的规则如下:
-- >= 85,展示优秀
-- >= 60,展示及格
-- 否则,展示不及格create table score(id int comment 'ID',name varchar(20) comment '姓名',math int comment '数学',english int comment '英语',chinese int comment '语文'
) comment '学员成绩表';
insert into score(id, name, math, english, chinese) VALUES (1, 'Tom', 67, 88, 95 ), (2, 'Rose' , 23, 66, 90),(3, 'Jack', 56, 98, 76);--
selectid,name,(case when math >= 85 then '优秀' when math >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end ) '数学',(case when english >= 85 then '优秀' when english >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end ) '英语',(case when chinese >= 85 then '优秀' when chinese >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end ) '语文'
from score;
6.约束(MySql不支持检查约束)
(约束是作用于表中字段上的,可以在创建表/修改表的时候添加约束)
作用于表中列上的规则,用于限制加入表的数据,保证了数据库中数据的正确性有效性和完整性,
包括NOT NULL,UNIQUE,PRIMARY KEY,CHECK,DEFAULT,FOREIGN KEY
自动增长:auto_increment 当列时数字类型并且唯一约束
修改删除约束也可以实现(不常用),例如:
非空
修改:alter table 表名modify字段名 数据类型 not null;
删除:alter table 表名modify字段名 数据类型;
唯一
修改:alter table 表名modify字段名 数据类型 unique;
删除:alter table 表名drop index字段名;
主键
修改:alter table 表名add primary key(字段名);
删除:alter table 表名drop primary key;
默认
修改:alter table 表名alter 列名set default 默认值;
删除:alter table 表名alter 列名drop default;
外键约束
添加
创建表的添加
Create table 表名(
列名 数据类型,
…
[constraint] [外键名称] foreign key(外键列名) references 主表(主表列名)
)
建完表后添加
alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段名) references 主表名称(主表列名称);
删除alter table 表名drop foreign key 外键名称;
create table user(id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键',name varchar(10) not null unique comment '姓名',age int check ( age > 0 && age <= 120 ) comment '年龄',status char(1) default '1' comment '状态',gender char(1) comment '性别'
) comment '用户表';-- 插入数据
insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values ('Tom1',19,'1','男'),('Tom2',25,'0','男');
insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values ('Tom3',19,'1','男');insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values (null,19,'1','男');
insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values ('Tom3',19,'1','男');insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values ('Tom4',80,'1','男');
insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values ('Tom5',-1,'1','男');
insert into user(name,age,status,gender) values ('Tom5',121,'1','男');insert into user(name,age,gender) values ('Tom5',120,'男');

-- --------------------------------------------- 约束 (外键) -------------------------------------
-- 准备数据
create table dept(id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,name varchar(50) not null comment '部门名称'
)comment '部门表';
INSERT INTO dept (id, name) VALUES (1, '研发部'), (2, '市场部'),(3, '财务部'), (4, '销售部'), (5, '总经办');create table emp(id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名',age int comment '年龄',job varchar(20) comment '职位',salary int comment '薪资',entrydate date comment '入职时间',managerid int comment '直属领导ID',dept_id int comment '部门ID'
)comment '员工表';INSERT INTO emp (id, name, age, job,salary, entrydate, managerid, dept_id) VALUES(1, '金庸', 66, '总裁',20000, '2000-01-01', null,5),(2, '张无忌', 20, '项目经理',12500, '2005-12-05', 1,1),(3, '杨逍', 33, '开发', 8400,'2000-11-03', 2,1),(4, '韦一笑', 48, '开发',11000, '2002-02-05', 2,1),(5, '常遇春', 43, '开发',10500, '2004-09-07', 3,1),(6, '小昭', 19, '程序员鼓励师',6600, '2004-10-12', 2,1);-- 添加外键
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);-- 删除外键
alter table emp drop foreign key fk_emp_dept_id;-- 外键的删除和更新行为
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id) on update cascade on delete cascade ;alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id) on update set null on delete set null ;7.数据库设计
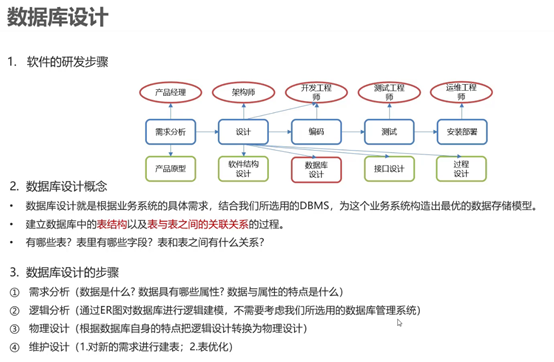
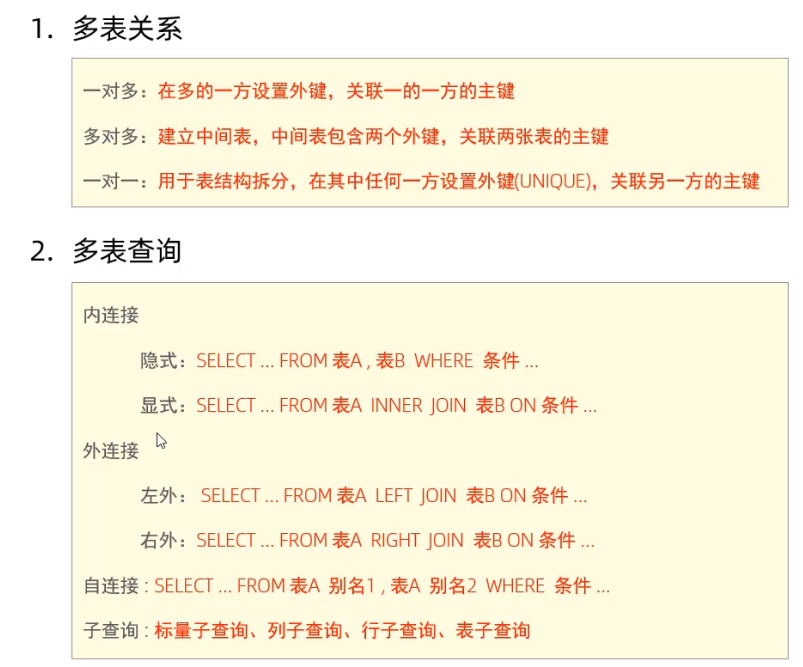
表关系
一对一 多用于表拆分,将实体经常使用的字段放在一张表里,不经常使用的字段放另一张表里,用于提升查询性能
在任意一方加入外键,关联另一方的主键,并设置外键为UNIQUE(唯一)
一对多 在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
多对多 建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
-- -------------------------------- 多表关系 演示 ----------------------------------------------- 多对多 ----------------
create table student(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '姓名',no varchar(10) comment '学号'
) comment '学生表';
insert into student values (null, '黛绮丝', '2000100101'),(null, '谢逊', '2000100102'),(null, '殷天正', '2000100103'),(null, '韦一笑', '2000100104');create table course(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '课程名称'
) comment '课程表';
insert into course values (null, 'Java'), (null, 'PHP'), (null , 'MySQL') , (null, 'Hadoop');create table student_course(id int auto_increment comment '主键' primary key,studentid int not null comment '学生ID',courseid int not null comment '课程ID',constraint fk_courseid foreign key (courseid) references course (id),constraint fk_studentid foreign key (studentid) references student (id)
)comment '学生课程中间表';insert into student_course values (null,1,1),(null,1,2),(null,1,3),(null,2,2),(null,2,3),(null,3,4);-- --------------------------------- 一对一 ---------------------------
create table tb_user(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '姓名',age int comment '年龄',gender char(1) comment '1: 男 , 2: 女',phone char(11) comment '手机号'
) comment '用户基本信息表';create table tb_user_edu(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',degree varchar(20) comment '学历',major varchar(50) comment '专业',primaryschool varchar(50) comment '小学',middleschool varchar(50) comment '中学',university varchar(50) comment '大学',userid int unique comment '用户ID',constraint fk_userid foreign key (userid) references tb_user(id)
) comment '用户教育信息表';insert into tb_user(id, name, age, gender, phone) values(null,'黄渤',45,'1','18800001111'),(null,'冰冰',35,'2','18800002222'),(null,'码云',55,'1','18800008888'),(null,'李彦宏',50,'1','18800009999');insert into tb_user_edu(id, degree, major, primaryschool, middleschool, university, userid) values(null,'本科','舞蹈','静安区第一小学','静安区第一中学','北京舞蹈学院',1),(null,'硕士','表演','朝阳区第一小学','朝阳区第一中学','北京电影学院',2),(null,'本科','英语','杭州市第一小学','杭州市第一中学','杭州师范大学',3),(null,'本科','应用数学','阳泉第一小学','阳泉区第一中学','清华大学',4);多表查询
笛卡尔积:取AB集合所有组合情况
连接查询
内连接 查询AB交集数据
隐式 select 字段列表 from 表1, 表2,… where 条件
显式 select 字段列表 from 表1 [inner] join表2 on 条件
外连接 左外:相当于查询A表所有数据和交集部分数据
右外:相当于查询B表所有数据和交集部分数据
select 字段列表 from 表1 LEFT/RIGHT [outer] join表2 on 条件
select 字段列表 from 表1 LEFT [outer] join表2 on 条件
自连接
当前表与自身连接查询,自连接必须使用表别名
select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表B 别名B on 条件
自连接查询可以是内连接查询,也可以是外连接查询
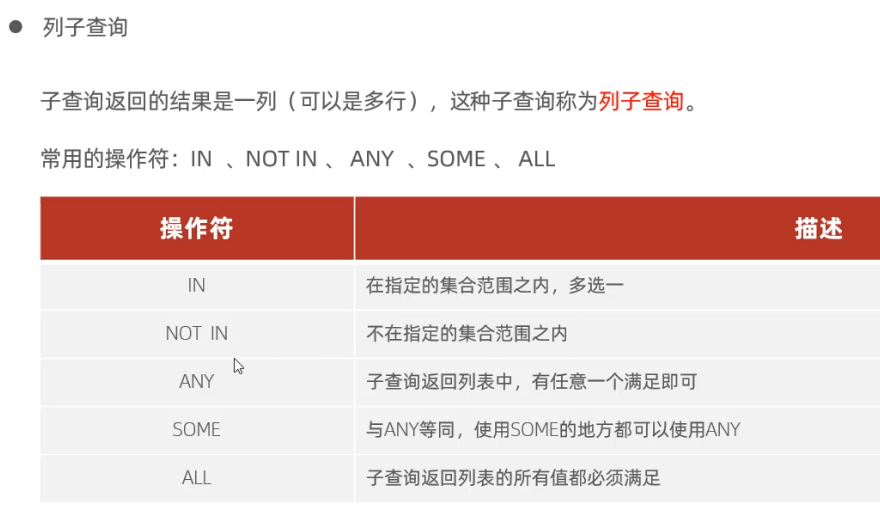
子查询 嵌套查询
子查询外部的语句可以是insert/update/delete/select的任何一个
根据子查询的结果不同可以分为标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值),列子查询(子查询结果为一列),行子查询(子查询结果为一行)和表子查询(多行多列)
标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值[数字,字符串,日期],最简单的形式
列子查询(子查询结果为一列)
行子查询(子查询结果为一行)
表子查询(多行多列)
根据查询结果不同,作用不同
单行单列:作为条件值,使用 = != < >进行条件判断
select 字段列表 from 表where 字段名 = (子查询);
多行单列:作为条件值,使用in等关键字进行条件判断
select 字段列表 from 表where 字段名 in (子查询);
多行多列:作为虚拟表
select 字段列表 from (子查询) where 条件;
-- ------------------------------------> 多表查询 <--------------------------------------------
-- 准备数据
create table dept(id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,name varchar(50) not null comment '部门名称'
)comment '部门表';create table emp(id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名',age int comment '年龄',job varchar(20) comment '职位',salary int comment '薪资',entrydate date comment '入职时间',managerid int comment '直属领导ID',dept_id int comment '部门ID'
)comment '员工表';-- 添加外键
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);INSERT INTO dept (id, name) VALUES (1, '研发部'), (2, '市场部'),(3, '财务部'), (4, '销售部'), (5, '总经办'), (6, '人事部');
INSERT INTO emp (id, name, age, job,salary, entrydate, managerid, dept_id) VALUES(1, '金庸', 66, '总裁',20000, '2000-01-01', null,5),(2, '张无忌', 20, '项目经理',12500, '2005-12-05', 1,1),(3, '杨逍', 33, '开发', 8400,'2000-11-03', 2,1),(4, '韦一笑', 48, '开发',11000, '2002-02-05', 2,1),(5, '常遇春', 43, '开发',10500, '2004-09-07', 3,1),(6, '小昭', 19, '程序员鼓励师',6600, '2004-10-12', 2,1),(7, '灭绝', 60, '财务总监',8500, '2002-09-12', 1,3),(8, '周芷若', 19, '会计',48000, '2006-06-02', 7,3),(9, '丁敏君', 23, '出纳',5250, '2009-05-13', 7,3),(10, '赵敏', 20, '市场部总监',12500, '2004-10-12', 1,2),(11, '鹿杖客', 56, '职员',3750, '2006-10-03', 10,2),(12, '鹤笔翁', 19, '职员',3750, '2007-05-09', 10,2),(13, '方东白', 19, '职员',5500, '2009-02-12', 10,2),(14, '张三丰', 88, '销售总监',14000, '2004-10-12', 1,4),(15, '俞莲舟', 38, '销售',4600, '2004-10-12', 14,4),(16, '宋远桥', 40, '销售',4600, '2004-10-12', 14,4),(17, '陈友谅', 42, null,2000, '2011-10-12', 1,null);-- 多表查询 -- 笛卡尔积
select * from emp , dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id;-- 内连接演示
-- 1. 查询每一个员工的姓名 , 及关联的部门的名称 (隐式内连接实现)
-- 表结构: emp , dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.id
select emp.name , dept.name from emp , dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id ;select e.name,d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;-- 2. 查询每一个员工的姓名 , 及关联的部门的名称 (显式内连接实现) --- INNER JOIN ... ON ...
-- 表结构: emp , dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.idselect e.name, d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;select e.name, d.name from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;-- 外连接演示
-- 1. 查询emp表的所有数据, 和对应的部门信息(左外连接)
-- 表结构: emp, dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.idselect e.*, d.name from emp e left outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;-- 2. 查询dept表的所有数据, 和对应的员工信息(右外连接)select d.*, e.* from emp e right outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;select d.*, e.* from dept d left outer join emp e on e.dept_id = d.id;-- 自连接
-- 1. 查询员工 及其 所属领导的名字
-- 表结构: empselect a.name , b.name from emp a , emp b where a.managerid = b.id;-- 2. 查询所有员工 emp 及其领导的名字 emp , 如果员工没有领导, 也需要查询出来
-- 表结构: emp a , emp bselect a.name '员工', b.name '领导' from emp a left join emp b on a.managerid = b.id;-- union all , union
-- 1. 将薪资低于 5000 的员工 , 和 年龄大于 50 岁的员工全部查询出来.select * from emp where salary < 5000
union all
select * from emp where age > 50;select * from emp where salary < 5000
union
select * from emp where age > 50;
-- -------------------------------------- 子查询 -------------------------- 标量子查询
-- 1. 查询 "销售部" 的所有员工信息
-- a. 查询 "销售部" 部门ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部';-- b. 根据销售部部门ID, 查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');-- 2. 查询在 "方东白" 入职之后的员工信息
-- a. 查询 方东白 的入职日期
select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白';-- b. 查询指定入职日期之后入职的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白');-- 列子查询
-- 1. 查询 "销售部" 和 "市场部" 的所有员工信息
-- a. 查询 "销售部" 和 "市场部" 的部门ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部';-- b. 根据部门ID, 查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部');-- 2. 查询比 财务部 所有人工资都高的员工信息
-- a. 查询所有 财务部 人员工资
select id from dept where name = '财务部';select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部');-- b. 比 财务部 所有人工资都高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > all ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '财务部') );-- 3. 查询比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
-- a. 查询研发部所有人工资
select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部');-- b. 比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > some ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部') );-- 行子查询
-- 1. 查询与 "张无忌" 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息 ;
-- a. 查询 "张无忌" 的薪资及直属领导
select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌';-- b. 查询与 "张无忌" 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息 ;
select * from emp where (salary,managerid) = (select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌');-- 表子查询
-- 1. 查询与 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
-- a. 查询 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资
select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥';-- b. 查询与 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (job,salary) in ( select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥' );-- 2. 查询入职日期是 "2006-01-01" 之后的员工信息 , 及其部门信息
-- a. 入职日期是 "2006-01-01" 之后的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01';-- b. 查询这部分员工, 对应的部门信息;
select e.*, d.* from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id ;-- ---------------------------------------> 多表查询案例 <----------------------------------
create table salgrade(grade int,losal int,hisal int
) comment '薪资等级表';insert into salgrade values (1,0,3000);
insert into salgrade values (2,3001,5000);
insert into salgrade values (3,5001,8000);
insert into salgrade values (4,8001,10000);
insert into salgrade values (5,10001,15000);
insert into salgrade values (6,15001,20000);
insert into salgrade values (7,20001,25000);
insert into salgrade values (8,25001,30000);-- 1. 查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息 (隐式内连接)
-- 表: emp , dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.idselect e.name , e.age , e.job , d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;-- 2. 查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
-- 表: emp , dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.idselect e.name , e.age , e.job , d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age < 30;-- 3. 查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称
-- 表: emp , dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.idselect distinct d.id , d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;-- 4. 查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工, 及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门, 也需要展示出来
-- 表: emp , dept
-- 连接条件: emp.dept_id = dept.id
-- 外连接select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age > 40 ;-- 5. 查询所有员工的工资等级
-- 表: emp , salgrade
-- 连接条件 : emp.salary >= salgrade.losal and emp.salary <= salgrade.hisalselect e.* , s.grade , s.losal, s.hisal from emp e , salgrade s where e.salary >= s.losal and e.salary <= s.hisal;select e.* , s.grade , s.losal, s.hisal from emp e , salgrade s where e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;-- 6. 查询 "研发部" 所有员工的信息及 工资等级
-- 表: emp , salgrade , dept
-- 连接条件 : emp.salary between salgrade.losal and salgrade.hisal , emp.dept_id = dept.id
-- 查询条件 : dept.name = '研发部'select e.* , s.grade from emp e , dept d , salgrade s where e.dept_id = d.id and ( e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal ) and d.name = '研发部';-- 7. 查询 "研发部" 员工的平均工资
-- 表: emp , dept
-- 连接条件 : emp.dept_id = dept.idselect avg(e.salary) from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id and d.name = '研发部';-- 8. 查询工资比 "灭绝" 高的员工信息。
-- a. 查询 "灭绝" 的薪资
select salary from emp where name = '灭绝';-- b. 查询比她工资高的员工数据
select * from emp where salary > ( select salary from emp where name = '灭绝' );-- 9. 查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
-- a. 查询员工的平均薪资
select avg(salary) from emp;-- b. 查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > ( select avg(salary) from emp );-- 10. 查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息-- a. 查询指定部门平均薪资 1
select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = 1;
select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = 2;-- b. 查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
select * from emp e2 where e2.salary < ( select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = e2.dept_id );-- 11. 查询所有的部门信息, 并统计部门的员工人数
select d.id, d.name , ( select count(*) from emp e where e.dept_id = d.id ) '人数' from dept d;select count(*) from emp where dept_id = 1;-- 12. 查询所有学生的选课情况, 展示出学生名称, 学号, 课程名称
-- 表: student , course , student_course
-- 连接条件: student.id = student_course.studentid , course.id = student_course.courseidselect s.name , s.no , c.name from student s , student_course sc , course c where s.id = sc.studentid and sc.courseid = c.id ;
8.事务
是一组操作的集合,是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务会把所有的操作作为一个整体,一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,这些操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
默认MYSQL的事务是自动提交的当执行一条DML语句,mysql会立即隐式的提交事务。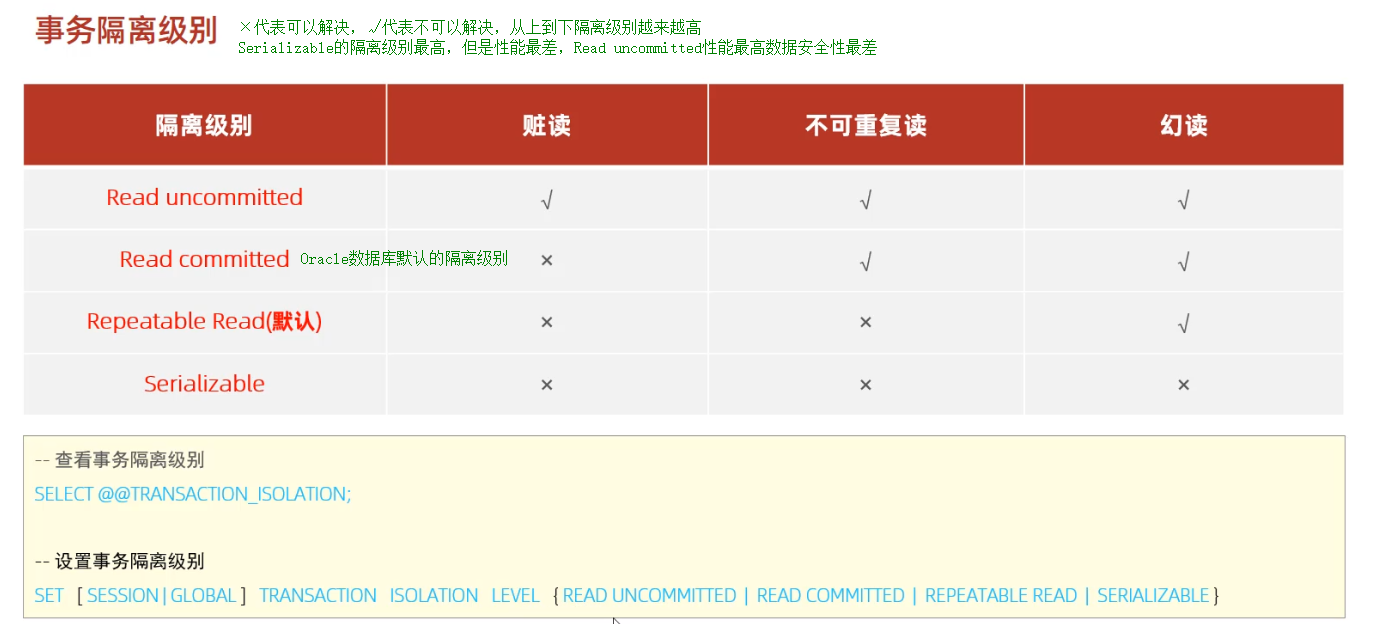
-- 查看事务隔离级别
select @@transaction_isolation;-- 设置事务隔离级别
set session transaction isolation level read uncommitted ;set session transaction isolation level repeatable read ;×代表可以解决,√代表不可以解决,从上到下隔离级别越来越高,Serializable的隔离级别最高,但是性能最差,Read uncommitted性能最高数据安全性最差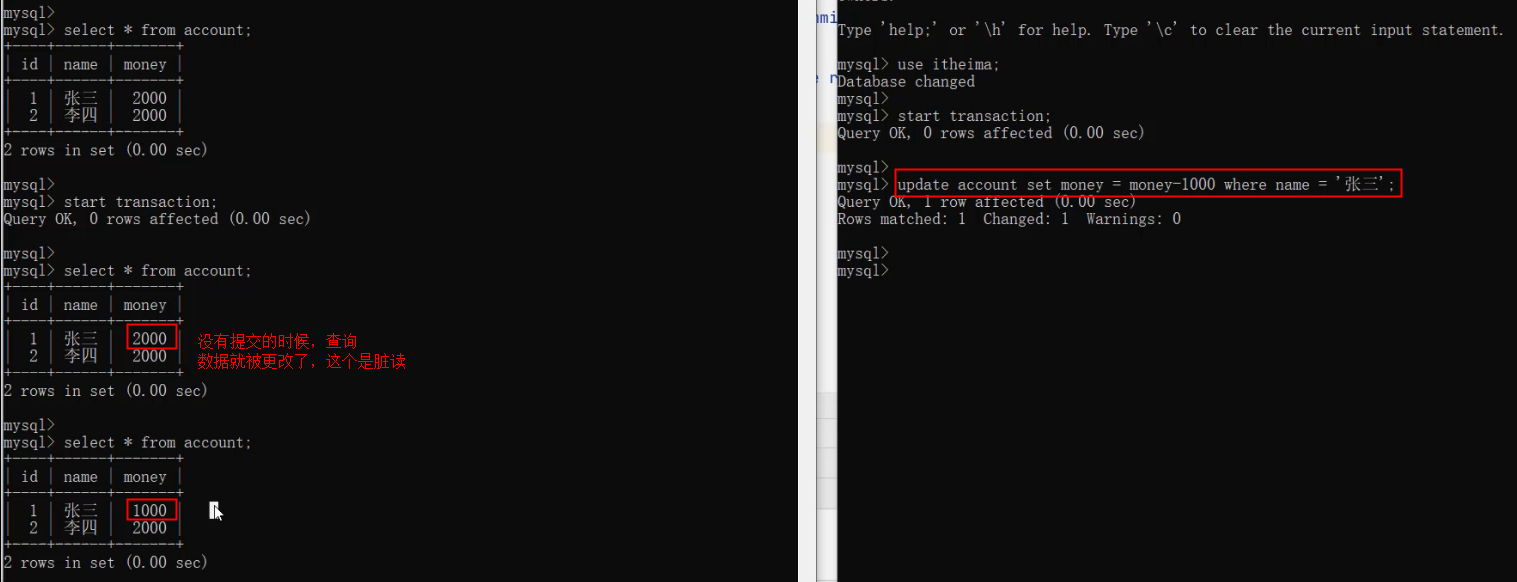
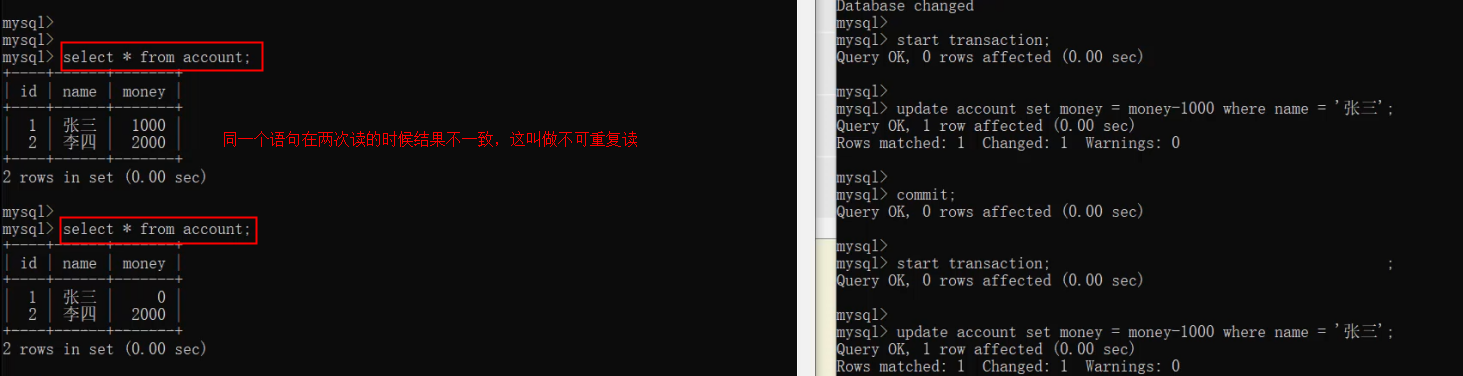
 1)数据库中的事务,包含了一组数据库操作命令
1)数据库中的事务,包含了一组数据库操作命令
2)事务把所有的命令作为一个整体一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,即这一组数据库命令要不同时成功,要不同时失败
3)事务是一个不可分割的工作逻辑单元
4)事务的三个命令
开启事务Start transaction; 或者begin;
提交事务commit;
回滚事务Rollback;
5)事务的四大特征ACID
Atomicity 原子性(事务是不可分割的最小操作单位,要么同时成功,要么同时失败)
Consistency一致性(事务完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致的状态)
Isolation 隔离性(多个事务之间,操作的可见性)
Durability 持久性(事务一旦提交或者回滚,它对数据库中的数据的改变就是永久的)
6)mysql事务默认自动提交
查看事务的默认的提交方式
Select @@autocommit;可以查看到事务的默认提交方式是1自动提交
Set @@autocommit=0; 修改事务提交方式为0
Oracle的事务默认是自动提交的
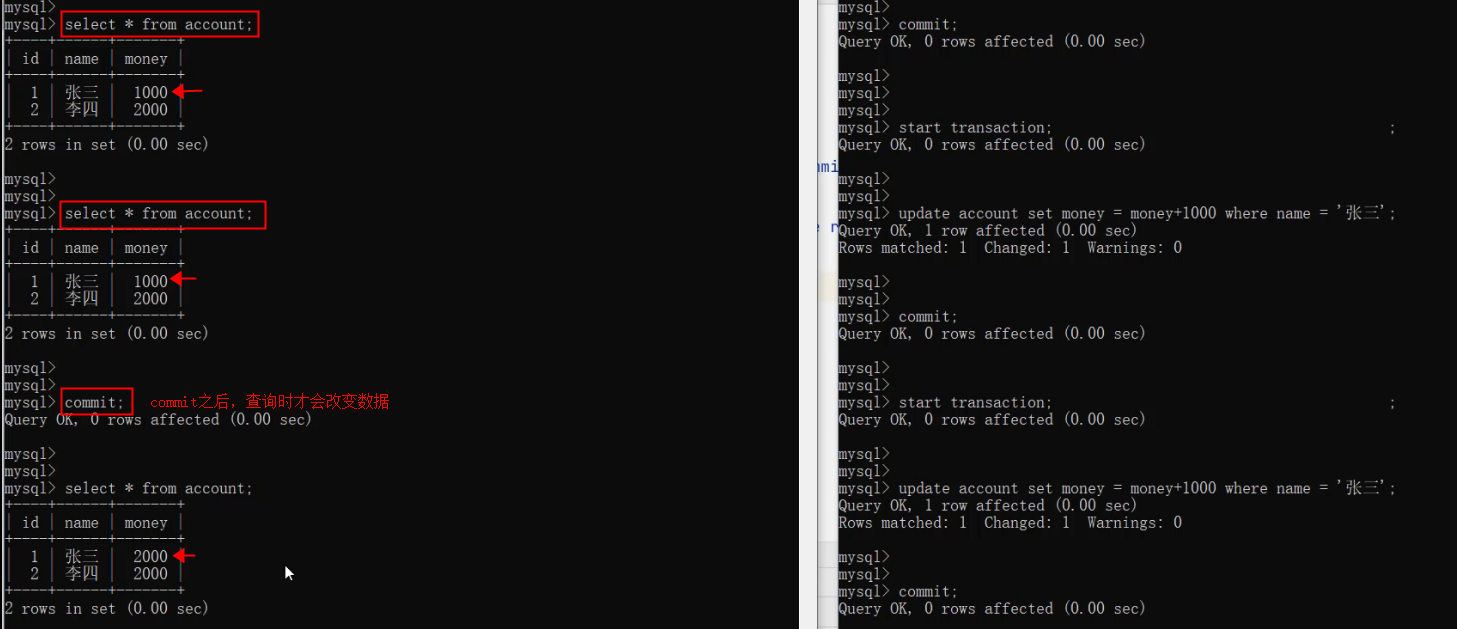
-- ---------------------------- 事务操作 ----------------------------
-- 数据准备
create table account(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '姓名',money int comment '余额'
) comment '账户表';
insert into account(id, name, money) VALUES (null,'张三',2000),(null,'李四',2000);-- 恢复数据
update account set money = 2000 where name = '张三' or name = '李四';select @@autocommit;set @@autocommit = 0; -- 设置为手动提交-- 转账操作 (张三给李四转账1000)
-- 1. 查询张三账户余额
select * from account where name = '张三';-- 2. 将张三账户余额-1000
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = '张三';程序执行报错 ...-- 3. 将李四账户余额+1000
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';-- 提交事务
commit;-- 回滚事务
rollback ;-- 方式二
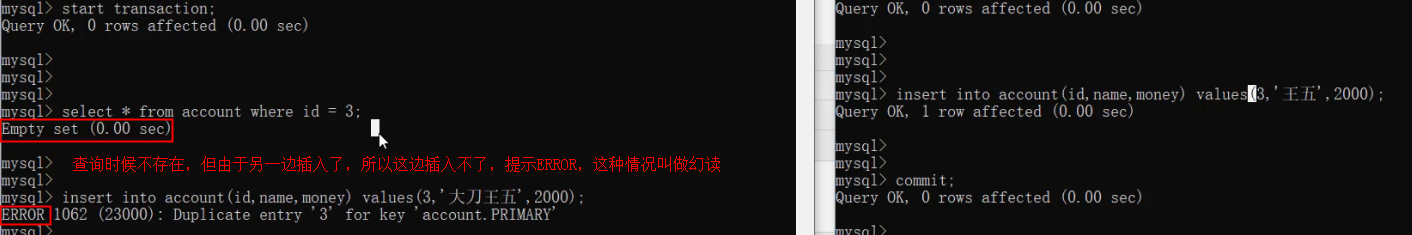
-- 转账操作 (张三给李四转账1000)
start transaction ;-- 1. 查询张三账户余额
select * from account where name = '张三';-- 2. 将张三账户余额-1000
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = '张三';程序执行报错 ...-- 3. 将李四账户余额+1000
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';-- 提交事务
commit;-- 回滚事务
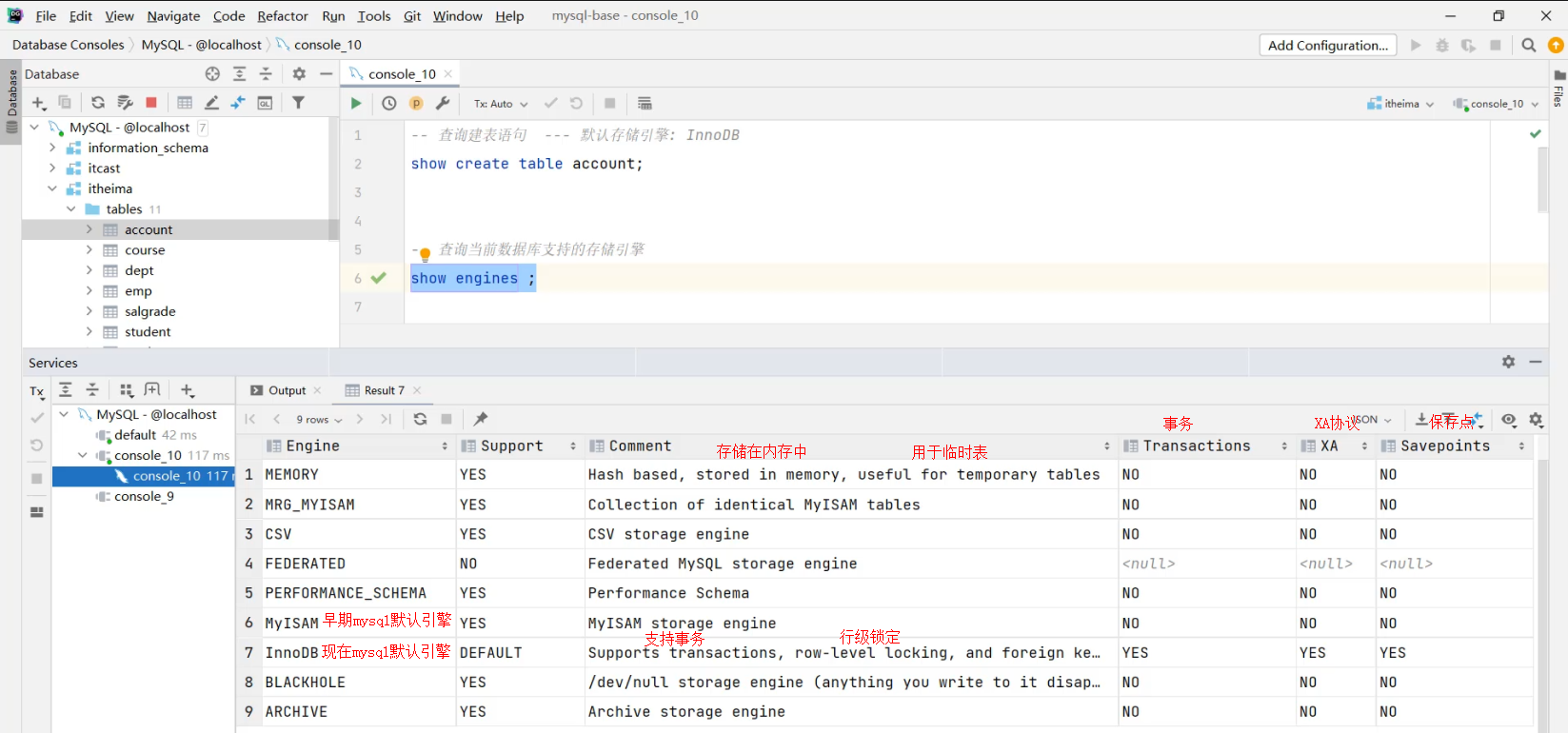
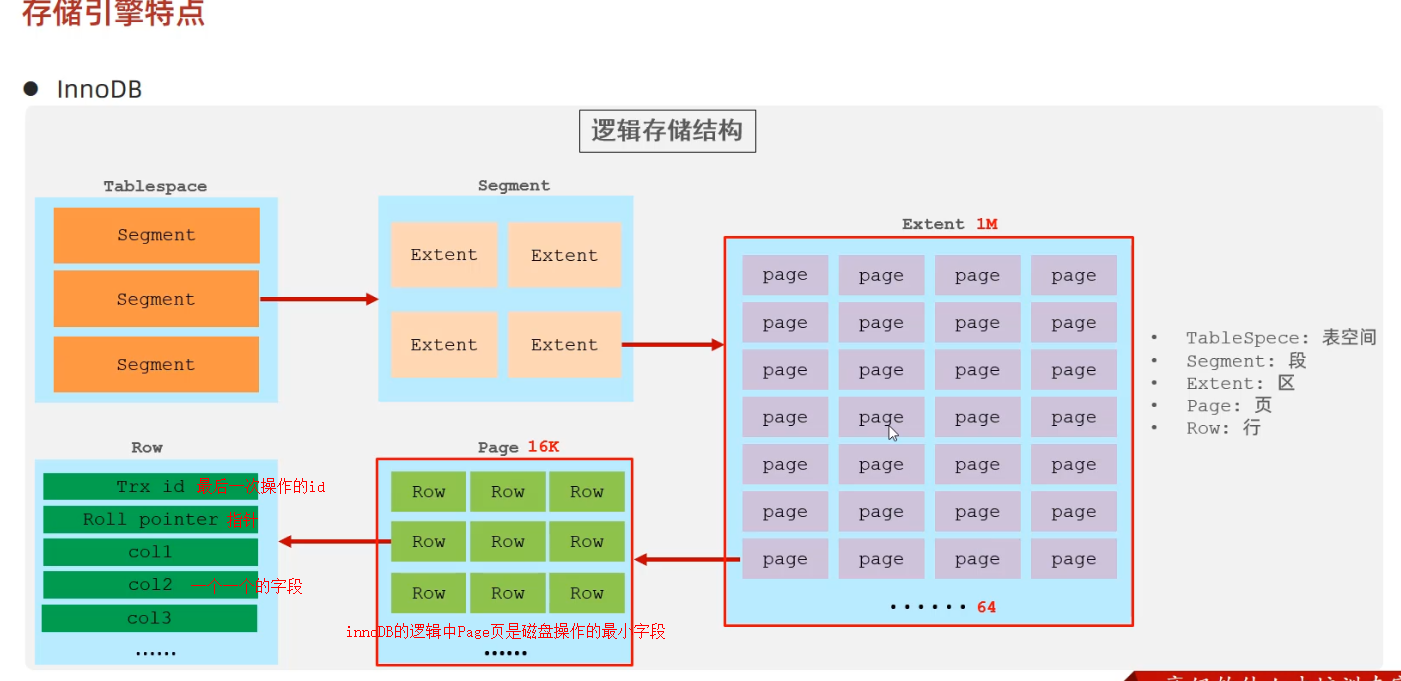
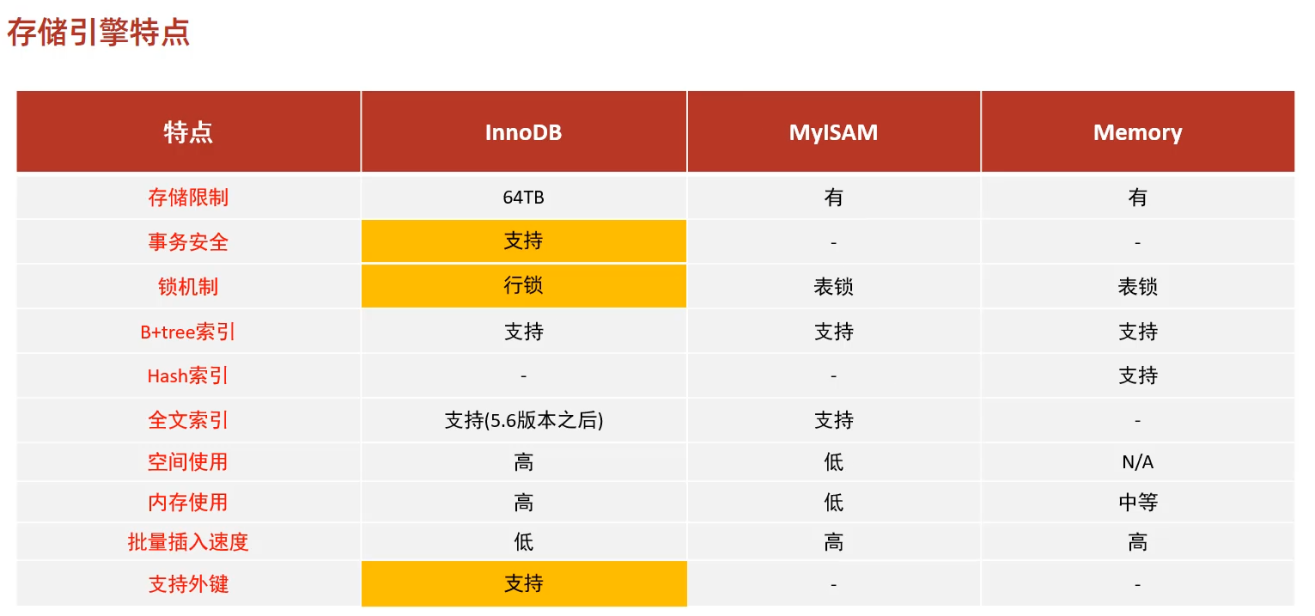
rollback;存储引擎就是存储数据,建立索引,更新/查询数据等技术的实现方式,存储引擎是基于表的,而不是基于库的,所以存储引擎也可被称为表类型
innoDB 存储结构
Tablespace表空间
Segment段
Extent区
Page页
Row行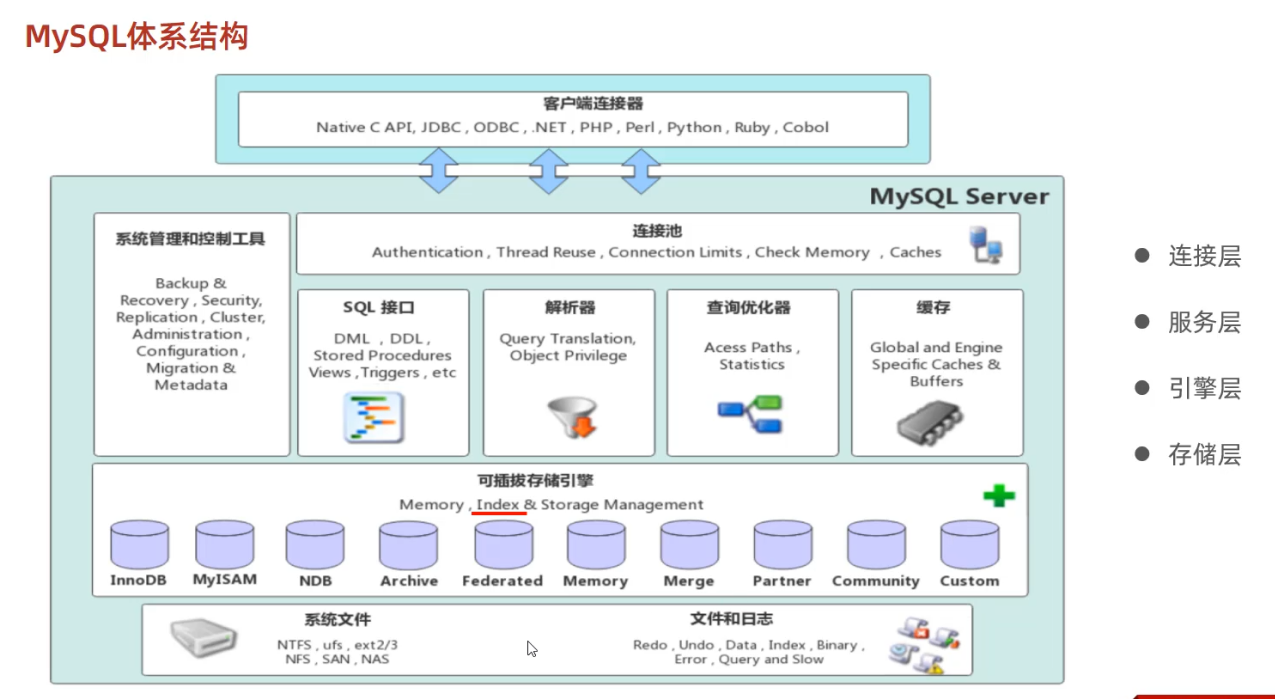





 索引是帮助Mysql高效获取数据的数据结构(有序)。在数据之外,数据库系统还维护着满足特定查找算法的数据结构,这些数据结构以某种方式引用(指向)数据,这样就可以在这些数据结构上实现高级查找算法,这种数据结构就是索引。
索引是帮助Mysql高效获取数据的数据结构(有序)。在数据之外,数据库系统还维护着满足特定查找算法的数据结构,这些数据结构以某种方式引用(指向)数据,这样就可以在这些数据结构上实现高级查找算法,这种数据结构就是索引。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!