NLP07:基于潜在隐语义索引的文本相似度计算
1.潜在隐语义索引(LSI)概述
潜在语义索引(Latent Semantic Indexing,以下简称LSI),有的文章也叫Latent Semantic Analysis(LSA)。其实是一个东西,后面我们统称LSI,它是一种简单实用的主题模型。LSI是基于奇异值分解(SVD)的方法来得到文本的主题的。
这里我们简要回顾下SVD:对于一个 m × n m \times n m×n的矩阵 A A A,可以分解为下面三个矩阵:
A m × n = U m × m Σ m × n V n × n T A_{m \times n} = U_{m \times m}\Sigma_{m \times n} V^T_{n \times n} Am×n=Um×mΣm×nVn×nT
有时为了降低矩阵的维度到k,SVD的分解可以近似的写为:
A m × n ≈ U m × k Σ k × k V k × n T A_{m \times n} \approx U_{m \times k}\Sigma_{k \times k} V^T_{k \times n} Am×n≈Um×kΣk×kVk×nT
如果把上式用到我们的主题模型,则SVD可以这样解释:我们输入的有m个文本,每个文本有n个词。而 A i j A_{ij} Aij则对应第 i i i个文本的第 j j j个词的特征值,这里最常用的是基于预处理后的标准化TF-IDF值。k是我们假设的主题数,一般要比文本数少。SVD分解后, U i l U_{il} Uil对应第 i i i个文本和第 l l l个主题的相关度。 V j m V_{jm} Vjm对应第 j j j个词和第 m m m个词义的相关度。 Σ l m Σ_{lm} Σlm对应第 l l l个主题和第 m m m个词义的相关度。
也可以反过来解释:我们输入的有 m m m个词,对应 n n n个文本。而 A i j A_{ij} Aij则对应第 i i i个词档的第 j j j个文本的特征值,这里最常用的是基于预处理后的标准化TF-IDF值。k是我们假设的主题数,一般要比文本数少。SVD分解后, U i l U_{il} Uil对应第 i i i个词和第 l l l个词义的相关度。 V j m V_{jm} Vjm对应第 j j j个文本和第 m m m个主题的相关度。 Σ l m Σ_{lm} Σlm对应第 l l l个词义和第 m m m个主题的相关度。
这样我们通过一次SVD,就可以得到文档和主题的相关度,词和词义的相关度以及词义和主题的相关度。
2. 相似度计算
通过LSI得到的文本主题矩阵可以用于文本相似度计算。而计算方法一般是通过余弦相似度。
from gensim.test.utils import common_dictionary, common_corpus
from gensim.models import LsiModel
from gensim import similaritiesif __name__ == '__main__':for k, v in common_dictionary.items():print(k, v)print(len(common_dictionary)) # 12个词汇print(len(common_corpus)) # 9个文档model = LsiModel(common_corpus, num_topics=3, id2word=common_dictionary) # 3个主题vectorized_corpus = model[common_corpus] # 右奇异向量,文档-主题 (9,3)# for x in vectorized_corpus:# print(x)#print(model.projection.u.shape) # 左奇异向量主题-单词,shape为(12,3)print(model.projection.s.shape) # 奇异值 (3,)for x in vectorized_corpus:print(x)index = similarities.MatrixSimilarity(vectorized_corpus)print("==" * 30)print(vectorized_corpus[0])print(list(enumerate(index[vectorized_corpus[0]]))) # 计算各个文本与第一个文本的相似度3.实战
import re
from collections import defaultdict
import jieba.posseg
import numpy as np
import codecs
import os
import pickle
from gensim import corpora,models,similarities
def tokenizer(filename, stop_words):"""读取文件内容,并进行分词:param filename:文件名称:param stop_words:list,停用词:return:[[word1,word2]]"""texts = []with open(filename, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:for line in f.readlines():texts.append([token for token, _ in jieba.posseg.cut(line.rstrip()) if token not in stop_words])# 去除仅出现一次的单词frequency = defaultdict(int)for text in texts:for token in text:frequency[token] += 1texts = [[token for token in text if frequency[token] > 1] for text in texts]return texts
stop_words_filepath = "/content/drive/My Drive/data/qa/data/stop_words.txt"
knowledge_texts_filepath = "/content/drive/My Drive/data/qa/data/knowledge.txt"
stop_words = codecs.open(stop_words_filepath, "r", encoding="utf-8").readlines()
stop_words = [w.strip() for w in stop_words]
texts = tokenizer(knowledge_texts_filepath, stop_words)
def topk_sim_ix(texts,stops,k):""":param file_name: 分词后的训练样本:param stop_words:停用词:param k:与每个文本top k相似度的文本:return:list"""dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(texts) #构建词典corpus=[dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in texts] #bow# 构建LSI模型lsi = models.LsiModel(corpus, id2word=dictionary, num_topics=10) # 潜在语义索引(分析),主题数量为10index = similarities.MatrixSimilarity(lsi[corpus],num_best=k) # 计算相似度vec_lsi=lsi[corpus]return index[vec_lsi]index=topk_sim_ix(texts,stop_words,5)
总共11740个文档,每个文档选择5个最相似的文档
len(index),len(texts),len(index[0])

第一个文档,除了文档本身外,最相似的就是第123、39、3985、11176个文档
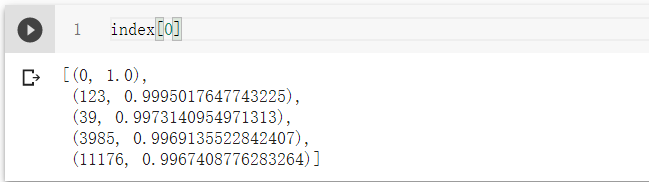
for index_text in index[0]:print(texts[index_text[0]],index_text[1])

参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6805861.html
代码:https://github.com/chongzicbo/nlp-ml-dl-notes/blob/master/code/nlp_tutorial/NLP07%EF%BC%9A%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8ELSI%E7%9A%84%E6%96%87%E6%9C%AC%E7%9B%B8%E4%BC%BC%E5%BA%A6%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97.ipynb
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!