vue面试中常见的面试题
1.谈一下你对MVVM原理的理解
- 传统的
MVC指的是,用户操作会请求服务端路由,路由会调用对应的控制器来处理,控制器会获取数据。将结果返回给前端,页面重新渲染 MVVM:传统的前端会将数据手动渲染到页面上,MVVM模式不需要用户收到操作dom元素,将数据绑定到viewModel层上,会自动将数据渲染到页面中,视图变化会通知viewModel层更新数据。ViewModel就是我们MVVM模式中的桥梁.
2.请说一下响应式数据的原理?
- 1.核心点:
Object.defineProperty - 2.默认
Vue在初始化数据时,会给data中的属性使用Object.defineProperty重新定义所有属性,当页面取到对应属性时。会进行依赖收集(收集当前组件的watcher) 如果属性发生变化会通知相关依赖进行更新操作。
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {enumerable: true,configurable: true,get: function reactiveGetter () {const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : valif (Dep.target) {dep.depend() // ** 收集依赖 ** /if (childOb) {childOb.dep.depend()if (Array.isArray(value)) {dependArray(value)}}}return value},set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : valif (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {return}if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {customSetter()}val = newValchildOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)dep.notify() /**通知相关依赖进行更新**/}})
3.Vue中是如何检测数组变化?
- 使用函数劫持的方式,重写了数组的方法
Vue将data中的数组,进行了原型链重写。指向了自己定义的数组原型方法,这样当调用数组api时,可以通知依赖更新.如果数组中包含着引用类型。会对数组中的引用类型再次进行监控。
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)
const methodsToPatch = ['push','pop','shift','unshift','splice','sort','reverse'
]
methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) { // 重写原型方法const original = arrayProto[method] // 调用原数组的方法def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) {const result = original.apply(this, args)const ob = this.__ob__let insertedswitch (method) {case 'push':case 'unshift':inserted = argsbreakcase 'splice':inserted = args.slice(2)break}if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)// notify changeob.dep.notify() // 当调用数组方法后,手动通知视图更新return result})
})this.observeArray(value) // 进行深度监控
4.为何Vue采用异步渲染?
因为如果不采用异步更新,那么每次更新数据都会对当前组件进行重新渲染.所以为了性能考虑。Vue会在本轮数据更新后,再去异步更新视图!
update () {/* istanbul ignore else */if (this.lazy) {this.dirty = true} else if (this.sync) {this.run()} else {queueWatcher(this); // 当数据发生变化时会将watcher放到一个队列中批量更新}
}
export function queueWatcher (watcher: Watcher) {const id = watcher.id // 会对相同的watcher进行过滤if (has[id] == null) {has[id] = trueif (!flushing) {queue.push(watcher)} else {let i = queue.length - 1while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {i--}queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)}// queue the flushif (!waiting) {waiting = trueif (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {flushSchedulerQueue()return}nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue) // 调用nextTick方法 批量的进行更新}}
}
5.nextTick实现原理
nextTick方法主要是使用了宏任务和微任务,定义了一个异步方法.多次调用nextTick 会将方法存入队列中,通过这个异步方法清空当前队列。 所以这个nextTick方法就是异步方法
let timerFunc // 会定义一个异步方法
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) { // promiseconst p = Promise.resolve()timerFunc = () => {p.then(flushCallbacks)if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)}isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && ( // MutationObserverisNative(MutationObserver) ||MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]'
)) {let counter = 1const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks)const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter))observer.observe(textNode, {characterData: true})timerFunc = () => {counter = (counter + 1) % 2textNode.data = String(counter)}isUsingMicroTask = true
} else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' ) { // setImmediatetimerFunc = () => {setImmediate(flushCallbacks)}
} else {timerFunc = () => { // setTimeoutsetTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)}
}
// nextTick实现
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {let _resolvecallbacks.push(() => {if (cb) {try {cb.call(ctx)} catch (e) {handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')}} else if (_resolve) {_resolve(ctx)}})if (!pending) {pending = truetimerFunc()}
}6.Vue中Computed的特点
- 默认
computed也是一个watcher是具备缓存的,只要当依赖的属性发生变化时才会更新视图
function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) {const watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)const isSSR = isServerRendering()for (const key in computed) {const userDef = computed[key]const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.getif (!isSSR) {// create internal watcher for the computed property.watchers[key] = new Watcher(vm,getter || noop,noop,computedWatcherOptions)}// component-defined computed properties are already defined on the// component prototype. We only need to define computed properties defined// at instantiation here.if (!(key in vm)) {defineComputed(vm, key, userDef)} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {if (key in vm.$data) {warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined in data.`, vm)} else if (vm.$options.props && key in vm.$options.props) {warn(`The computed property "${key}" is already defined as a prop.`, vm)}}}
}
function createComputedGetter (key) {return function computedGetter () {const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]if (watcher) {if (watcher.dirty) { // 如果依赖的值没发生变化,就不会重新求值watcher.evaluate()}if (Dep.target) {watcher.depend()}return watcher.value}}
}
7.Watch中的deep:true 是如何实现的
- 当用户指定了
watch中的deep属性为true时,如果当前监控的值是数组类型。会对对象中的每一项进行求值,此时会将当前watcher存入到对应属性的依赖中,这样数组中对象发生变化时也会通知数据更新
get () {pushTarget(this) // 先将当前依赖放到 Dep.target上let valueconst vm = this.vmtry {value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)} catch (e) {if (this.user) {handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)} else {throw e}} finally {if (this.deep) { // 如果需要深度监控traverse(value) // 会对对象中的每一项取值,取值时会执行对应的get方法}popTarget()}return value
}
function _traverse (val: any, seen: SimpleSet) {let i, keysconst isA = Array.isArray(val)if ((!isA && !isObject(val)) || Object.isFrozen(val) || val instanceof VNode) {return}if (val.__ob__) {const depId = val.__ob__.dep.idif (seen.has(depId)) {return}seen.add(depId)}if (isA) {i = val.lengthwhile (i--) _traverse(val[i], seen)} else {keys = Object.keys(val)i = keys.lengthwhile (i--) _traverse(val[keys[i]], seen)}
}8.Vue组件的生命周期
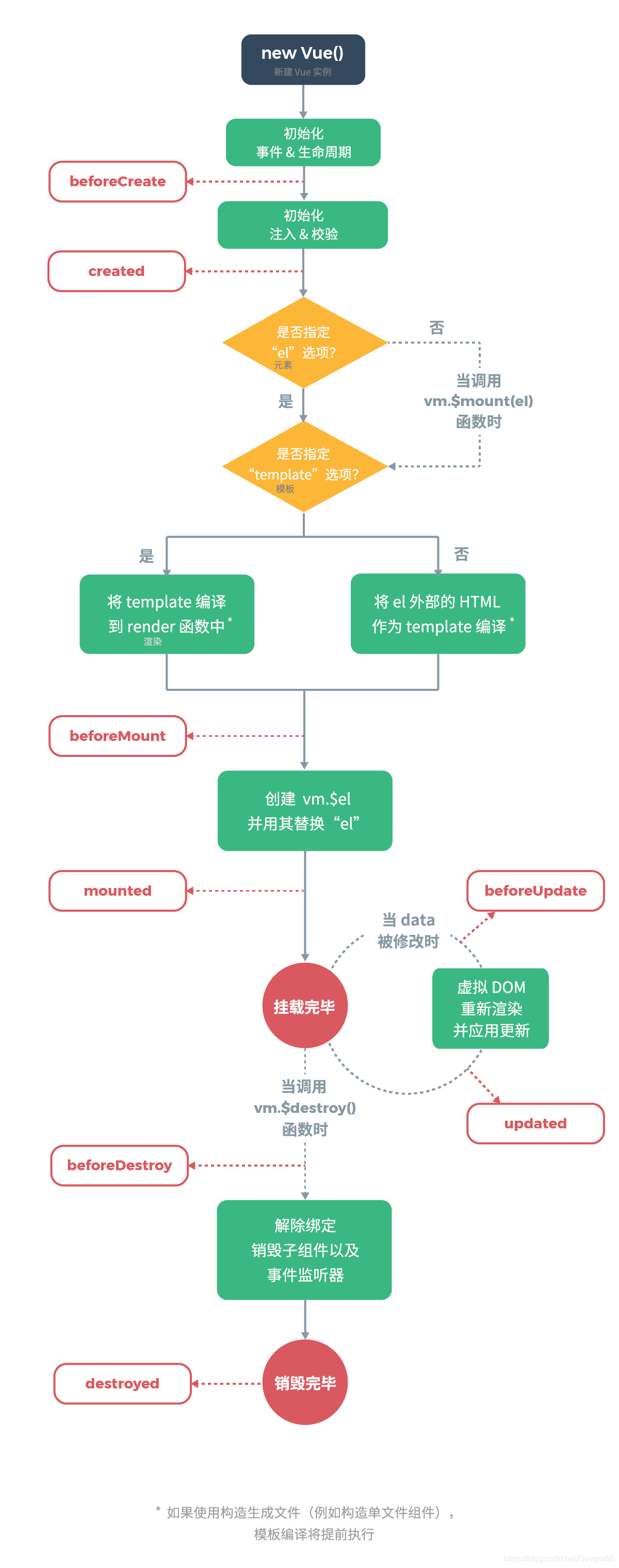
要掌握每个生命周期什么时候被调用
beforeCreate在实例初始化之后,数据观测(data observer) 之前被调用。created实例已经创建完成之后被调用。在这一步,实例已完成以下的配置:数据观测(data observer),属性和方法的运算, watch/event 事件回调。这里没有$elbeforeMount在挂载开始之前被调用:相关的 render 函数首次被调用。mountedel 被新创建的vm.$el替换,并挂载到实例上去之后调用该钩子。beforeUpdate数据更新时调用,发生在虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁之前。updated由于数据更改导致的虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁,在这之后会调用该钩子。beforeDestroy实例销毁之前调用。在这一步,实例仍然完全可用。destroyedVue实例销毁后调用。调用后,Vue实例指示的所有东西都会解绑定,所有的事件监听器会被移除,所有的子实例也会被销毁。 该钩子在服务器端渲染期间不被调用。
要掌握每个生命周期内部可以做什么事
created实例已经创建完成,因为它是最早触发的原因可以进行一些数据,资源的请求。mounted实例已经挂载完成,可以进行一些DOM操作beforeUpdate可以在这个钩子中进一步地更改状态,这不会触发附加的重渲染过程。updated可以执行依赖于 DOM 的操作。然而在大多数情况下,你应该避免在此期间更改状态,因为这可能会导致更新无限循环。 该钩子在服务器端渲染期间不被调用。destroyed可以执行一些优化操作,清空定时器,解除绑定事件
9.ajax请求放在哪个生命周期中
- 在created的时候,视图中的
dom并没有渲染出来,所以此时如果直接去操dom节点,无法找到相关的元素 - 在mounted中,由于此时
dom已经渲染出来了,所以可以直接操作dom节点
一般情况下都放到mounted中,保证逻辑的统一性,因为生命周期是同步执行的,ajax是异步执行的
服务端渲染不支持mounted方法,所以在服务端渲染的情况下统一放到created中
10.何时需要使用beforeDestroy
- 可能在当前页面中使用了
$on方法,那需要在组件销毁前解绑。 - 清除自己定义的定时器
- 解除事件的绑定
scroll mousemove ....
11.Vue中模板编译原理
- 将
template转化成render函数
function baseCompile (template: string,options: CompilerOptions
) {const ast = parse(template.trim(), options) // 1.将模板转化成ast语法树if (options.optimize !== false) { // 2.优化树optimize(ast, options)}const code = generate(ast, options) // 3.生成树return {ast,render: code.render,staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns}
})
const ncname = `[a-zA-Z_][\\-\\.0-9_a-zA-Z]*`;
const qnameCapture = `((?:${ncname}\\:)?${ncname})`;
const startTagOpen = new RegExp(`^<${qnameCapture}`); // 标签开头的正则 捕获的内容是标签名
const endTag = new RegExp(`^<\\/${qnameCapture}[^>]*>`); // 匹配标签结尾的
const attribute = /^\s*([^\s"'<>\/=]+)(?:\s*(=)\s*(?:"([^"]*)"+|'([^']*)'+|([^\s"'=<>`]+)))?/; // 匹配属性的
const startTagClose = /^\s*(\/?)>/; // 匹配标签结束的 >
let root;
let currentParent;
let stack = []
function createASTElement(tagName,attrs){return {tag:tagName,type:1,children:[],attrs,parent:null}
}
function start(tagName,attrs){let element = createASTElement(tagName,attrs);if(!root){root = element;}currentParent = element;stack.push(element);
}
function chars(text){currentParent.children.push({type:3,text})
}
function end(tagName){const element = stack[stack.length-1];stack.length --; currentParent = stack[stack.length-1];if(currentParent){element.parent = currentParent;currentParent.children.push(element)}
}
function parseHTML(html){while(html){let textEnd = html.indexOf('<');if(textEnd == 0){const startTagMatch = parseStartTag();if(startTagMatch){start(startTagMatch.tagName,startTagMatch.attrs);continue;}const endTagMatch = html.match(endTag);if(endTagMatch){advance(endTagMatch[0].length);end(endTagMatch[1])}}let text;if(textEnd >=0 ){text = html.substring(0,textEnd)}if(text){advance(text.length);chars(text);}}function advance(n) {html = html.substring(n);}function parseStartTag(){const start = html.match(startTagOpen);if(start){const match = {tagName:start[1],attrs:[]}advance(start[0].length);let attr,endwhile(!(end = html.match(startTagClose)) && (attr=html.match(attribute))){advance(attr[0].length);match.attrs.push({name:attr[1],value:attr[3]})}if(end){advance(end[0].length);return match}}}
}
// 生成语法树
parseHTML(`hellozf
`);
function gen(node){if(node.type == 1){return generate(node);}else{return `_v(${JSON.stringify(node.text)})`}
}
function genChildren(el){const children = el.children;if(el.children){return `[${children.map(c=>gen(c)).join(',')}]`}else{return false;}
}
function genProps(attrs){let str = '';for(let i = 0; i < attrs.length;i++){let attr = attrs[i];str+= `${attr.name}:${attr.value},`;}return `{attrs:{${str.slice(0,-1)}}}`
}
function generate(el){let children = genChildren(el);let code = `_c('${el.tag}'${el.attrs.length? `,${genProps(el.attrs)}`:''}${children? `,${children}`:''})`;return code;
}
// 根据语法树生成新的代码
let code = generate(root);
let render = `with(this){return ${code}}`;// 包装成函数
let renderFn = new Function(render);
console.log(renderFn.toString());
12.Vue中v-if和v-show的区别
v-if如果条件不成立不会渲染当前指令所在节点的dom元素v-show只是切换当前dom的显示或者隐藏
const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let r1 = VueTemplateCompiler.compile(`hello`);
/**
with(this) {return (true) ? _c('div', _l((3), function (i) {return _c('span', [_v("hello")])}), 0) : _e()
}
*/
const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let r2 = VueTemplateCompiler.compile(``);
/**
with(this) {return _c('div', {directives: [{name: "show",rawName: "v-show",value: (true),expression: "true"}]})
}*/// v-show 操作的是样式 定义在platforms/web/runtime/directives/show.js
bind (el: any, { value }: VNodeDirective, vnode: VNodeWithData) {vnode = locateNode(vnode)const transition = vnode.data && vnode.data.transitionconst originalDisplay = el.__vOriginalDisplay =el.style.display === 'none' ? '' : el.style.displayif (value && transition) {vnode.data.show = trueenter(vnode, () => {el.style.display = originalDisplay})} else {el.style.display = value ? originalDisplay : 'none'}
}
13.为什么V-for和v-if不能连用
- 当 v-if 与 v-for 一起使用时,v-for 具有比 v-if 更高的优先级,这意味着 v-if 将分别重复运行于每个 v-for 循环中。所以,不推荐v-if和v-for同时使用。
如果v-if和v-for一起用的话,vue中的的会自动提示v-if应该放到外层去。
const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let r1 = VueTemplateCompiler.compile(`hello`);
/**
with(this) {return _l((3), function (i) {return (false) ? _c('div', [_v("hello")]) : _e()})
}
*/
console.log(r1.render);
v-for会比v-if的优先级高一些,如果连用的话会把v-if给每个元素都添加一下,会造成性能问题
14.用vnode来描述一个DOM结构
- 虚拟节点就是用一个对象来描述真实的
dom元素
function $createElement(tag,data,...children){let key = data.key;delete data.key;children = children.map(child=>{if(typeof child === 'object'){return child}else{return vnode(undefined,undefined,undefined,undefined,child)}})return vnode(tag,props,key,children);
}
export function vnode(tag,data,key,children,text){return {tag, // 表示的是当前的标签名data, // 表示的是当前标签上的属性key, // 唯一表示用户可能传递children,text}
}
15.diff算法的时间复杂度
两个树的完全的diff算法是一个时间复杂度为 O(n3),Vue进行了优化·O(n3) 复杂度的问题转换成 O(n) 复杂度的问题(只比较同级不考虑跨级问题) 在前端当中, 你很少会跨越层级地移动Dom元素。 所以 Virtual Dom只会对同一个层级的元素进行对比。
16.简述Vue中diff算法原理
- 1.先同级比较,在比较子节点
- 2.先判断一方有儿子一方没儿子的情况
- 3.比较都有儿子的情况
- 4.递归比较子节点
const oldCh = oldVnode.children // 老的儿子
const ch = vnode.children // 新的儿子
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {// 比较孩子if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)} else if (isDef(ch)) { // 新的儿子有 老的没有if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)} else if (isDef(oldCh)) { // 如果老的有新的没有 就删除removeVnodes(oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) { // 老的有文本 新的没文本nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '') // 将老的清空}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) { // 文本不相同替换nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {let oldStartIdx = 0let newStartIdx = 0let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1let newStartVnode = newCh[0]let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm// removeOnly is a special flag used only by 17.v-for中为什么要用key
- 要使用key来给每个节点做一个唯一标识,Diff算法就可以正确的识别此节点。
作用主要是为了高效的更新虚拟DOM。
18.描述组件渲染和更新过程
- 渲染组件时,会通过
Vue.extend方法构建子组件的构造函数,并进行实例化。最终手动调用$mount()进行挂载。更新组件时会进行patchVnode流程.核心就是diff算法
19.组件中的 data为什么是一个函数?
同一个组件被复用多次,会创建多个实例。这些实例用的是同一个构造函数,如果data是一个对象的话。那么所有组件都共享了同一个对象。为了保证组件的数据独立性要求每个组件必须通过data函数返回一个对象作为组件的状态。
Sub.options = mergeOptions(Super.options,extendOptions
)
function mergeOptions(){function mergeField (key) {const strat = strats[key] || defaultStratoptions[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key)}
}
strats.data = function ( parentVal: any,childVal: any,vm?: Component
): ?Function {if (!vm) { // 合并是会判断子类的data必须是一个函数if (childVal && typeof childVal !== 'function') {process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn('The "data" option should be a function ' +'that returns a per-instance value in component ' +'definitions.',vm)return parentVal}return mergeDataOrFn(parentVal, childVal)}return mergeDataOrFn(parentVal, childVal, vm)
}
- 一个组件被使用多次,用的都是同一个构造函数。为了保证组件的不同的实例data不冲突,要求data必须是一个函数,这样组件间不会相互影响
20.Vue中事件绑定的原理
- 1.原生
dom事件的绑定,采用的是addEventListener实现 - 2.组件绑定事件采用的是
$on方法 - 事件的编译:
let compiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let r1 = compiler.compile('');
let r2 = compiler.compile('[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2PlBh54m-1582383865261)(note.assets/事件初始化.png)]
1.原生dom的绑定
Vue在创建真是dom时会调用createElm,默认会调用invokeCreateHooks- 会遍历当前平台下相对的属性处理代码,其中就有
updateDOMListeners方法,内部会传入add方法
function updateDOMListeners (oldVnode: VNodeWithData, vnode: VNodeWithData) {if (isUndef(oldVnode.data.on) && isUndef(vnode.data.on)) {return}const on = vnode.data.on || {}const oldOn = oldVnode.data.on || {}target = vnode.elmnormalizeEvents(on)updateListeners(on, oldOn, add, remove, createOnceHandler, vnode.context)target = undefined
}function add (name: string,handler: Function,capture: boolean,passive: boolean
) {target.addEventListener( // 给当前的dom添加事件name,handler,supportsPassive? { capture, passive }: capture)
}
vue中绑定事件是直接绑定给真实dom元素的
- 2.组件中绑定事件
export function updateComponentListeners (vm: Component,listeners: Object,oldListeners: ?Object
) {target = vmupdateListeners(listeners, oldListeners || {}, add, remove, createOnceHandler, vm)target = undefined
}
function add (event, fn) {target.$on(event, fn)
}组件绑定事件是通过
vue中自定义的$on方法来实现的
21.v-model中的实现原理及如何自定义v-model
组件的v-model是value+input方法的语法糖
<el-checkbox :value="" @input="">el-checkbox>
<el-checkbox v-model="check">el-checkbox>
可以自己重新定义v-model的含义
Vue.component('el-checkbox',{template:``,model:{prop:'check', // 更改默认的value的名字event:'change' // 更改默认的方法名},props: {check: Boolean},
})
原理:
- 会将组件的
v-model默认转化成value+input
const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
const ele = VueTemplateCompiler.compile('
core/vdom/create-component.js line:155
function transformModel (options, data: any) {const prop = (options.model && options.model.prop) || 'value'const event = (options.model && options.model.event) || 'input';(data.attrs || (data.attrs = {}))[prop] = data.model.valueconst on = data.on || (data.on = {})const existing = on[event]const callback = data.model.callbackif (isDef(existing)) {if (Array.isArray(existing)? existing.indexOf(callback) === -1: existing !== callback) {on[event] = [callback].concat(existing)}} else {on[event] = callback}
}
- 原生的
v-model,会根据标签的不同生成不同的事件和属性
const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
const ele = VueTemplateCompiler.compile('');
/**
with(this) {return _c('input', {directives: [{name: "model",rawName: "v-model",value: (value),expression: "value"}],domProps: {"value": (value)},on: {"input": function ($event) {if ($event.target.composing) return;value = $event.target.value}}})
}
*/编译时:不同的标签解析出的内容不一样
platforms/web/compiler/directives/model.js
if (el.component) {genComponentModel(el, value, modifiers)// component v-model doesn't need extra runtimereturn false} else if (tag === 'select') {genSelect(el, value, modifiers)} else if (tag === 'input' && type === 'checkbox') {genCheckboxModel(el, value, modifiers)} else if (tag === 'input' && type === 'radio') {genRadioModel(el, value, modifiers)} else if (tag === 'input' || tag === 'textarea') {genDefaultModel(el, value, modifiers)} else if (!config.isReservedTag(tag)) {genComponentModel(el, value, modifiers)// component v-model doesn't need extra runtimereturn false}
运行时:会对元素处理一些关于输入法的问题
platforms/web/runtime/directives/model.js
inserted (el, binding, vnode, oldVnode) {if (vnode.tag === 'select') {// #6903if (oldVnode.elm && !oldVnode.elm._vOptions) {mergeVNodeHook(vnode, 'postpatch', () => {directive.componentUpdated(el, binding, vnode)})} else {setSelected(el, binding, vnode.context)}el._vOptions = [].map.call(el.options, getValue)} else if (vnode.tag === 'textarea' || isTextInputType(el.type)) {el._vModifiers = binding.modifiersif (!binding.modifiers.lazy) {el.addEventListener('compositionstart', onCompositionStart)el.addEventListener('compositionend', onCompositionEnd)// Safari < 10.2 & UIWebView doesn't fire compositionend when// switching focus before confirming composition choice// this also fixes the issue where some browsers e.g. iOS Chrome// fires "change" instead of "input" on autocomplete.el.addEventListener('change', onCompositionEnd)/* istanbul ignore if */if (isIE9) {el.vmodel = true}}}}
22.Vue中v-html会导致哪些问题?
- 可能会导致
xss攻击 v-html会替换掉标签内部的子元素
let template = require('vue-template-compiler');
let r = template.compile(`hello'">`)
// with(this){return _c('div',{domProps:{"innerHTML":_s('hello')}})}
console.log(r.render);// _c 定义在core/instance/render.js
// _s 定义在core/instance/render-helpers/index,jsif (key === 'textContent' || key === 'innerHTML') {if (vnode.children) vnode.children.length = 0if (cur === oldProps[key]) continue// #6601 work around Chrome version <= 55 bug where single textNode// replaced by innerHTML/textContent retains its parentNode propertyif (elm.childNodes.length === 1) {elm.removeChild(elm.childNodes[0])}
}
23. Vue父子组件生命周期调用顺序
组件的调用顺序都是先父后子,渲染完成的顺序肯定是先子后父
组件的销毁操作是先父后子,销毁完成的顺序是先子后父
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {if (isUndef(vnode)) {if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)return}let isInitialPatch = falseconst insertedVnodeQueue = [] // 定义收集所有组件的insert hook方法的数组// somthing ...createElm(vnode,insertedVnodeQueue,oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm))// somthing...// 最终会依次调用收集的insert hookinvokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch);return vnode.elm
}
function createElm (vnode,insertedVnodeQueue,parentElm,refElm,nested,ownerArray,index) {// createChildren会递归创建儿子组件createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue) // something...}// 将组件的vnode插入到数组中
function invokeCreateHooks (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {cbs.create[i](emptyNode, vnode)}i = vnode.data.hook // Reuse variableif (isDef(i)) {if (isDef(i.create)) i.create(emptyNode, vnode)if (isDef(i.insert)) insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)}}
// insert方法中会依次调用mounted方法
insert (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {const { context, componentInstance } = vnodeif (!componentInstance._isMounted) {componentInstance._isMounted = truecallHook(componentInstance, 'mounted')}
}function invokeInsertHook (vnode, queue, initial) {// delay insert hooks for component root nodes, invoke them after the// element is really insertedif (isTrue(initial) && isDef(vnode.parent)) {vnode.parent.data.pendingInsert = queue} else {for (let i = 0; i < queue.length; ++i) {queue[i].data.hook.insert(queue[i]); // 调用insert方法}}
}
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy') // // invoke destroy hooks on current rendered treevm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null) // 先销毁儿子 // fire destroyed hookcallHook(vm, 'destroyed')
}
24.Vue组件如何通信?
- 父子间通信 父->子通过
props、子-> 父$on、$emit - 获取父子组件实例的方式
$parent、$children - 在父组件中提供数据子组件进行消费
Provide、inject Ref获取实例的方式调用组件的属性或者方法Event Bus实现跨组件通信Vuex状态管理实现通信
25.Vue中相同逻辑如何抽离?
Vue.mixin用法 给组件每个生命周期,函数等都混入一些公共逻辑
Vue.mixin = function (mixin: Object) {this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, mixin); // 将当前定义的属性合并到每个组件中return this
}
export function mergeOptions (parent: Object,child: Object,vm?: Component
): Object {if (!child._base) {if (child.extends) { // 递归合并extendsparent = mergeOptions(parent, child.extends, vm)}if (child.mixins) { // 递归合并mixinfor (let i = 0, l = child.mixins.length; i < l; i++) {parent = mergeOptions(parent, child.mixins[i], vm)}}}const options = {} // 属性及生命周期的合并let keyfor (key in parent) {mergeField(key)}for (key in child) {if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) {mergeField(key)}}function mergeField (key) {const strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat// 调用不同属性合并策略进行合并options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key)}return options
}
26.为什么要使用异步组件?
理解:
-
如果组件功能多打包出的结果会变大,我可以采用异步的方式来加载组件。主要依赖
import()这个语法,可以实现文件的分割加载。components:{AddCustomerSchedule(resolve) {require(["../components/AddCustomer"], resolve);} }
原理:
export function createComponent (Ctor: Class<Component> | Function | Object | void,data: ?VNodeData,context: Component,children: ?Array<VNode>,tag?: string
): VNode | Array<VNode> | void {// async componentlet asyncFactoryif (isUndef(Ctor.cid)) {asyncFactory = CtorCtor = resolveAsyncComponent(asyncFactory, baseCtor) // 默认调用此函数时返回undefiend// 第二次渲染时Ctor不为undefinedif (Ctor === undefined) {return createAsyncPlaceholder( // 渲染占位符 空虚拟节点asyncFactory,data,context,children,tag)}}
}
function resolveAsyncComponent (factory: Function,baseCtor: Class<Component>
): Class<Component> | void {if (isDef(factory.resolved)) { // 3.在次渲染时可以拿到获取的最新组件return factory.resolved}const resolve = once((res: Object | Class<Component>) => {factory.resolved = ensureCtor(res, baseCtor)if (!sync) {forceRender(true) //2. 强制更新视图重新渲染} else {owners.length = 0}})const reject = once(reason => {if (isDef(factory.errorComp)) {factory.error = trueforceRender(true)}})const res = factory(resolve, reject)// 1.将resolve方法和reject方法传入,用户调用resolve方法后sync = falsereturn factory.resolved
}
27.什么是作用域插槽?
1.插槽:
- 创建组件虚拟节点时,会将组件的儿子的虚拟节点保存起来。当初始化组件时,通过插槽属性将儿子进行分类
{a:[vnode],b[vnode]} - 渲染组件时会拿对应的slot属性的节点进行替换操作。(插槽的作用域为父组件)
2.作用域插槽:
- 作用域插槽在解析的时候,不会作为组件的孩子节点。会解析成函数,当子组件渲染时,会调用此函数进行渲染。(插槽的作用域为子组件)
const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let ele = VueTemplateCompiler.compile(`nodereactvue
`)const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');
let ele = VueTemplateCompiler.compile(`作用域插槽:
let ele = VueTemplateCompiler.compile(`{{msg.a}}
`);const VueTemplateCompiler = require('vue-template-compiler');VueTemplateCompiler.compile(`28.谈谈你对 keep-alive 的了解?
keep-alive可以实现组件的缓存,当组件切换时不会对当前组件进行卸载,常用的2个属性include/exclude,2个生命周期activated,deactivated
core/components/keep-alive.js
export default {name: 'keep-alive',abstract: true, // 抽象组件props: {include: patternTypes,exclude: patternTypes,max: [String, Number]},created () {this.cache = Object.create(null) // 创建缓存列表this.keys = [] // 创建缓存组件的key列表},destroyed () { // keep-alive销毁时 会清空所有的缓存和keyfor (const key in this.cache) { // 循环销毁pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, key, this.keys)}},mounted () { // 会监控include 和 include属性 进行组件的缓存处理this.$watch('include', val => {pruneCache(this, name => matches(val, name))})this.$watch('exclude', val => {pruneCache(this, name => !matches(val, name))})},render () {const slot = this.$slots.default // 会默认拿插槽const vnode: VNode = getFirstComponentChild(slot) // 只缓存第一个组件const componentOptions: ?VNodeComponentOptions = vnode && vnode.componentOptionsif (componentOptions) {// check patternconst name: ?string = getComponentName(componentOptions) // 取出组件的名字const { include, exclude } = thisif ( // 判断是否缓存// not included(include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||// excluded(exclude && name && matches(exclude, name))) {return vnode}const { cache, keys } = thisconst key: ?string = vnode.key == null// same constructor may get registered as different local components// so cid alone is not enough (#3269)? componentOptions.Ctor.cid + (componentOptions.tag ? `::${componentOptions.tag}` : ''): vnode.key // 如果组件没key 就自己通过 组件的标签和key和cid 拼接一个keyif (cache[key]) {vnode.componentInstance = cache[key].componentInstance // 直接拿到组件实例// make current key freshestremove(keys, key) // 删除当前的 [b,c,d,e,a] // LRU 最近最久未使用法keys.push(key) // 并将key放到后面[b,a]} else {cache[key] = vnode // 缓存vnodekeys.push(key) // 将key 存入// prune oldest entryif (this.max && keys.length > parseInt(this.max)) { // 缓存的太多超过了max 就需要删除掉pruneCacheEntry(cache, keys[0], keys, this._vnode) // 要删除第0个 但是现在渲染的就是第0个}}vnode.data.keepAlive = true // 并且标准keep-alive下的组件是一个缓存组件}return vnode || (slot && slot[0]) // 返回当前的虚拟节点}
}
29.Vue中常见性能优化
1.编码优化:
-
1.不要将所有的数据都放在data中,data中的数据都会增加getter和setter,会收集对应的watcher
-
2.
vue在 v-for 时给每项元素绑定事件需要用事件代理 -
3.
SPA页面采用keep-alive缓存组件 -
4.拆分组件( 提高复用性、增加代码的可维护性,减少不必要的渲染 )
-
5.
v-if当值为false时内部指令不会执行,具有阻断功能,很多情况下使用v-if替代v-show -
6.
key保证唯一性 ( 默认vue会采用就地复用策略 ) -
7.
Object.freeze冻结数据 -
8.合理使用路由懒加载、异步组件
-
9.尽量采用runtime运行时版本
-
10.数据持久化的问题 (防抖、节流)
2.Vue加载性能优化:
-
第三方模块按需导入 (
babel-plugin-component) -
滚动到可视区域动态加载 ( https://tangbc.github.io/vue-virtual-scroll-list )
-
图片懒加载 (https://github.com/hilongjw/vue-lazyload.git)
3.用户体验:
app-skeleton骨架屏app-shellapp壳pwa
4.SEO优化:
- 预渲染插件
prerender-spa-plugin - 服务端渲染
ssr
5.打包优化:
- 使用
cdn的方式加载第三方模块 - 多线程打包
happypack splitChunks抽离公共文件sourceMap生成
6.缓存,压缩
- 客户端缓存、服务端缓存
- 服务端
gzip压缩
30.Vue3.0你知道有哪些改进?
Vue3采用了TS来编写- 支持
Composition API Vue3中响应式数据原理改成proxyvdom的对比算法更新,只更新vdom的绑定了动态数据的部分
31.实现hash路由和history路由
onhashchangehistory.pushState
32.Vue-Router中导航守卫有哪些?
- 导航被触发。
- 在失活的组件里调用离开守卫。
- 调用全局的
beforeEach守卫。 - 在重用的组件里调用
beforeRouteUpdate守卫 (2.2+)。 - 在路由配置里调用
beforeEnter。 - 解析异步路由组件。
- 在被激活的组件里调用
beforeRouteEnter。 - 调用全局的
beforeResolve守卫 (2.5+)。 - 导航被确认。
- 调用全局的
afterEach钩子。 - 触发 DOM 更新。
- 用创建好的实例调用
beforeRouteEnter守卫中传给next的回调函数。
33.action 和 mutation区别
mutation是同步更新数据(内部会进行是否为异步方式更新数据的检测)action异步操作,可以获取数据后调佣mutation提交最终数据
34.简述Vuex工作原理
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!